Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gear & Gear Ratio
Uploaded by
Souvik GhatakCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gear & Gear Ratio
Uploaded by
Souvik GhatakCopyright:
Available Formats
Gear & Gear Ratio
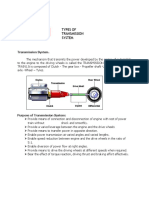
Introduction: Transmission is the mechanism by which the power transfers from the crankshaft to the
wheel. A gear transmission system is often used in cars. In transmission system a set of gears is attached
to the crank shaft called as Main Shaft Gears and other set of gears are attached to the Counter Shaft
Gears. The gears are usually directly attached with each other and sometimes idle gears are used between
the Main Shaft Gears and Counter Shaft Gears. The rotational energy transmitted to the counter shaft
gears is the power in which the wheel moves. To transfer the energy from the counter shaft to the wheels
three mechanism is used-
1. Shaft drive (about 25% loss)
2. Chain sprocket drive (3-5% loss)
3. Belt drive (6-9% loss)
In the transmission system Gear Ratio plays an important role.
The crankshaft rotates in a high rpm after starting the engine. But initially its more important to generate
torque in the wheels and keep the speed low. And gradually speed is increased. For a same amount of
energy and power gear ratio provides different velocity to the counter shaft and to the wheel. So we have
to Understand the Gear Ratio and how to modify it at its best.
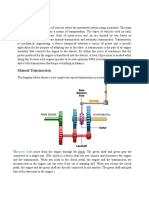
Gears:
Gears are toothed wheels which interlock to form simple machines.
Gear teeth are designed to ensure the pitch circles of engaging gears roll on each other without slipping,
providing a smooth transmission of rotation from one gear to the next.
Outcome of using gears:
• To reverse the direction of rotation.
• To increase or decrease the speed of rotation.
• To move rotational motion to a different axis.
• To keep the rotation of two axes synchronized.
Gear Ratio:
A gear ratio is the ratio between the driver gear (the one being powered) and the driven gear (the one
connected to the driver).
– Gear Ratios are expressed as fractions and can be written a number of ways.
• 1 to 3
• 1/3
• 1:3 most commonly used
– The driven gear will turn in the opposite direction of the driver gear
Calculation of Gear Ratio:
𝒏𝒐.𝒐𝒇 𝒕𝒆𝒆𝒕𝒉 𝒐𝒏 𝒕𝒉𝒆 𝒅𝒓𝒊𝒗𝒊𝒏𝒈 𝒈𝒆𝒂𝒓
Gear Ratio= 𝒏𝒐.𝒐𝒇 𝒕𝒆𝒆𝒕𝒉 𝒐𝒏 𝒕𝒉𝒆 𝒅𝒓𝒊𝒗𝒆𝒏 𝒈𝒆𝒂𝒓
Effects of Gear Ratio:
• Gear ratio as a multiplier on speed and a divider on torque.
• We can calculate the gear ratio by using the number of teeth of the “driving gear" (a.k.a. the input gear)
divided by the number of teeth of the “driven gear” (a.k.a. the output gear).
• We gear up when we increase velocity and decrease torque.
Ratio: 3:1
• We gear down when we increase torque and reduce velocity.
Ratio: 1:3
Gear Ratio and change of RPM:
We can calculate the change of rpm through following equations:
So we can say that, the bigger the ratio from driving gear to driven gear the more angular speed will be
seen to the wheels and the vehicle will run at a higher velocity.
For better top speed we can do some change on our transmissions regarding the given chart:
This charts shows an experiment on Hero Honda Karizma 225 Engine.
This engine provides 17 hp with a top speed of 125 kmph.
After the modification it gave an output of 170 kmph with the changed gear ratios.
You might also like
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiNo ratings yet
- Deutz D-TD 2011 Workshop Manual 03123326 PDFDocument590 pagesDeutz D-TD 2011 Workshop Manual 03123326 PDFDavy Gonzalez100% (10)
- Purpose of GearsDocument9 pagesPurpose of GearsM Jobayer AzadNo ratings yet
- GearboxesDocument70 pagesGearboxesanand007krishnan0% (1)
- Manual Transmission Chapter: Gears, Ratios and OperationDocument56 pagesManual Transmission Chapter: Gears, Ratios and Operationfaris iqbalNo ratings yet
- VOLVO G730B MOTOR GRADER Service Repair Manual PDFDocument14 pagesVOLVO G730B MOTOR GRADER Service Repair Manual PDFsekfsekmdddeNo ratings yet
- Automatic TransmissionDocument20 pagesAutomatic TransmissionAravindSaju100% (3)
- Hustler 54 ManualDocument120 pagesHustler 54 ManualTony Tankard100% (1)
- Engineering How Things Work How Manual Transmissions WorkDocument15 pagesEngineering How Things Work How Manual Transmissions WorkAkshay SinghNo ratings yet
- CBR1000RR 2010Document110 pagesCBR1000RR 2010LEONARDO100% (3)
- EoT Study MaterialsDocument24 pagesEoT Study Materialsishika SHANDILYANo ratings yet
- Spare Parts Catalogue: AXLE 26.27M REF: 635601 ECO: 27957Document11 pagesSpare Parts Catalogue: AXLE 26.27M REF: 635601 ECO: 27957xeraklii929No ratings yet
- DDC DieselDocument2 pagesDDC Dieseldolphingroup100% (1)
- Info For 0B5 GearboxesDocument2 pagesInfo For 0B5 GearboxesCatalin Belea100% (2)
- Gear Trains Simple PDFDocument43 pagesGear Trains Simple PDFYuvaraj GNo ratings yet
- 912 Engine SpecsDocument6 pages912 Engine SpecsAbdul ShukurNo ratings yet
- D 600 AP - enDocument253 pagesD 600 AP - enDedvirtualAutopeçasOnLineNo ratings yet
- Comparison For 500 KVA (PERKINS)Document3 pagesComparison For 500 KVA (PERKINS)amit singh0% (1)
- Chapter 2 - Manual Transmission P2Document36 pagesChapter 2 - Manual Transmission P2ahmad kamalNo ratings yet
- Robotics and Automation - Unit-2 (Part 2)Document33 pagesRobotics and Automation - Unit-2 (Part 2)jaiganeshNo ratings yet
- GeartrainsDocument19 pagesGeartrainsJnanesh K SNo ratings yet
- GeartrainsDocument19 pagesGeartrainsGgogpl YyoggshNo ratings yet
- Geartrains: Materials Taken From Several Sources Including: Building Robots With LEGODocument19 pagesGeartrains: Materials Taken From Several Sources Including: Building Robots With LEGOdhilip_sacetNo ratings yet
- Geartrains: Materials Taken From Several Sources Including: Building Robots With LEGODocument19 pagesGeartrains: Materials Taken From Several Sources Including: Building Robots With LEGOVinod KumarNo ratings yet
- Geartrains: Materials Taken From Several Sources Including: Building Robots With LEGODocument19 pagesGeartrains: Materials Taken From Several Sources Including: Building Robots With LEGOparas3775No ratings yet
- Module 3 - Lesson 1 - MEEC 101A PDFDocument8 pagesModule 3 - Lesson 1 - MEEC 101A PDFErica May MundinaNo ratings yet
- Automotive Driveline Overview ExplainedDocument8 pagesAutomotive Driveline Overview ExplainedKarniNo ratings yet
- Design Progress 123Document24 pagesDesign Progress 123a61812344No ratings yet
- Gear RatiosDocument1 pageGear RatiosMurali JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Automatic Transmission BasicsDocument20 pagesAutomatic Transmission BasicsDwy Bagus NNo ratings yet
- Understanding Manual TransmissionsDocument60 pagesUnderstanding Manual TransmissionsSesatthiri SesatNo ratings yet
- PowerDocument25 pagesPowervishnuNo ratings yet
- Clutches Transmissions and Drive 10Document53 pagesClutches Transmissions and Drive 10Napau AdelinNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Compound Gear TrainDocument22 pagesProject Report On Compound Gear Trainsourabh singh tomer71% (7)
- Engineering Mechanics (LAB) : Gear Train MechanismDocument13 pagesEngineering Mechanics (LAB) : Gear Train MechanismmalikNo ratings yet
- Geartrains: Materials Taken From Several Sources Including: Building Robots With LEGODocument19 pagesGeartrains: Materials Taken From Several Sources Including: Building Robots With LEGOHariansyahHariNo ratings yet
- GearsDocument34 pagesGearsJeba ChristoNo ratings yet
- Null 8Document27 pagesNull 8ali awadNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Power TransmissionsDocument22 pagesMechanical Power TransmissionsrodrigoperezsimoneNo ratings yet
- Gearboxes ClassDocument35 pagesGearboxes ClassNaveen Vachipalli100% (1)
- 2.2.2.A MechanismsDocument30 pages2.2.2.A MechanismscslourencoNo ratings yet
- Transmission SystemDocument64 pagesTransmission SystemABHISHEK VAISHYANo ratings yet
- MoM ManualDocument79 pagesMoM ManualHamid CheemaNo ratings yet
- Engine & TransmissionDocument32 pagesEngine & Transmission05 namrata pawarNo ratings yet
- Title: Automotive Powertrain Date: Objective: To Understand The Power Train Components of Automobiles Both Observation/TheoryDocument17 pagesTitle: Automotive Powertrain Date: Objective: To Understand The Power Train Components of Automobiles Both Observation/TheorybroNo ratings yet
- Referncce Material 1Document51 pagesReferncce Material 1LohithaNo ratings yet
- Title: Automotive Powertrain Date: Objective: To Understand The Power Train Components of Automobiles BothDocument6 pagesTitle: Automotive Powertrain Date: Objective: To Understand The Power Train Components of Automobiles BothbroNo ratings yet
- Final ReportDocument37 pagesFinal ReportAliNo ratings yet
- Unit IV-evhv Drive TrainDocument33 pagesUnit IV-evhv Drive TrainRajesh BhaskarlaNo ratings yet
- Projek Design Part 1Document19 pagesProjek Design Part 1Muluken TemesgenNo ratings yet
- Internship ReportDocument15 pagesInternship ReportEshwar Krishna50% (2)
- Sliding Mesh Miki FinalDocument93 pagesSliding Mesh Miki FinalalebiegashityNo ratings yet
- Gears and NomenclatureDocument27 pagesGears and NomenclatureJJNo ratings yet
- HaftaDocument5 pagesHaftaffra542No ratings yet
- Four Cylinder Engine: Figure 1-Slider Crank Mechanism in An EngineDocument6 pagesFour Cylinder Engine: Figure 1-Slider Crank Mechanism in An EngineRamsey MejiNo ratings yet
- Geartrains: Materials Taken From Several Sources Including: Building Robots With LEGODocument19 pagesGeartrains: Materials Taken From Several Sources Including: Building Robots With LEGOajaymechengineerNo ratings yet
- Gear Ratio: Navigation Search Gear TrainDocument53 pagesGear Ratio: Navigation Search Gear Trainjai karanNo ratings yet
- Auto TransmissionDocument14 pagesAuto TransmissionRinu SathyanNo ratings yet
- Calculating Gear RatiosDocument3 pagesCalculating Gear RatioslokeshNo ratings yet
- Activity Report Making The Gears Use The Frais Machine Pt. Minanga OganDocument8 pagesActivity Report Making The Gears Use The Frais Machine Pt. Minanga OganFirdaAtikaNo ratings yet
- Transmission PDFDocument21 pagesTransmission PDFMohanish ShahNo ratings yet
- Machine Element 2Document5 pagesMachine Element 2Muhammad Hazim FesaNo ratings yet
- Auto Transmission System ExplainedDocument5 pagesAuto Transmission System ExplainedSelvakumar JayarajNo ratings yet
- What Is A Gearbox? (Transmission) - Types, Parts, Function & DiagramDocument14 pagesWhat Is A Gearbox? (Transmission) - Types, Parts, Function & DiagramTisha GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Manual Transmission Automation Market SegmentsDocument52 pagesManual Transmission Automation Market SegmentsPranav EkhandeNo ratings yet
- Automotive Transmission System - Slide 01-63Document89 pagesAutomotive Transmission System - Slide 01-63Arifur Rahman MSquareNo ratings yet
- Clutches, Transmissions, and Drives: Study UnitDocument60 pagesClutches, Transmissions, and Drives: Study UnitPete MoonNo ratings yet
- Gear RatioDocument9 pagesGear RatioLekha SejpalNo ratings yet
- 6 TransmissionDocument38 pages6 TransmissionKamal Jit DhimanNo ratings yet
- 55: Brakes Handbrake, Brake Shoes, Replacing: 55: Brakes V70 (00-08), 2004, B5244S2, M56, L.H.D 25/5/2020Document5 pages55: Brakes Handbrake, Brake Shoes, Replacing: 55: Brakes V70 (00-08), 2004, B5244S2, M56, L.H.D 25/5/2020E MakinenNo ratings yet
- User Manual 2010: Suspension ForksDocument46 pagesUser Manual 2010: Suspension ForksAdrianAndrewsNo ratings yet
- Cat Remanufactured On-Highway Truck EnginesDocument4 pagesCat Remanufactured On-Highway Truck EnginesSergey SlomchinskiyNo ratings yet
- 2015-2016 Compatibility v010 enDocument28 pages2015-2016 Compatibility v010 enAlexander RamosNo ratings yet
- Stick Cylinder - EspecificationsDocument4 pagesStick Cylinder - EspecificationsFredy Alvarez CespedesNo ratings yet
- Catalogo de Partes Ak 3w180 2009-2014Document50 pagesCatalogo de Partes Ak 3w180 2009-2014juan pablo alvarez ardilaNo ratings yet
- Despiece IDB 1250Document2 pagesDespiece IDB 1250MarcosNo ratings yet
- Sp329a PRIMAAX EX For Mack HDT PDFDocument6 pagesSp329a PRIMAAX EX For Mack HDT PDFJonathan Smith Vargas torresNo ratings yet
- Kode Fault Dragon Yc6L E3Document333 pagesKode Fault Dragon Yc6L E3mecNo ratings yet
- Kepb032804 D61ex-15e0Document654 pagesKepb032804 D61ex-15e0Matheus FraguasNo ratings yet
- Motorcycle Operator Manual: With Supplementary Information For Three-Wheel MotorcyclesDocument60 pagesMotorcycle Operator Manual: With Supplementary Information For Three-Wheel MotorcyclesSeptimiu BotaNo ratings yet
- 2021 TOYOTA TUNDRA 5.7L V8 6x6 1Document10 pages2021 TOYOTA TUNDRA 5.7L V8 6x6 1Advenser GroupNo ratings yet
- Lovol Diesel Engine 1006tag CatalogDocument2 pagesLovol Diesel Engine 1006tag CatalogHendy AchmadNo ratings yet
- Project IEEE FormatDocument3 pagesProject IEEE FormatRAHULNo ratings yet
- Amalie OilsDocument2 pagesAmalie OilsJuan ArcosNo ratings yet
- A Series 1.3 - 2.0t 3-Pivot Electric Forklift Service Manual (CE) 2019.08Document92 pagesA Series 1.3 - 2.0t 3-Pivot Electric Forklift Service Manual (CE) 2019.08roberto_robledo_6No ratings yet
- Specifications: 4 Cylinders in Line - Diesel CycleDocument2 pagesSpecifications: 4 Cylinders in Line - Diesel CycleBahtiyar BelligüçükNo ratings yet
- C7.1 Generator Valve Guide InspectionDocument2 pagesC7.1 Generator Valve Guide InspectionbejoythomasNo ratings yet
- 2009 Auto Bulb GuideDocument228 pages2009 Auto Bulb GuideEverardo Pineda ParraNo ratings yet
- Format-of-Module (1) WK 1,2 SCSDocument17 pagesFormat-of-Module (1) WK 1,2 SCSRussell Sale100% (1)