Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IOT: The Future of Connectivity: International Journal of Emerging Trends & Technology in Computer Science (IJETTCS)
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IOT: The Future of Connectivity: International Journal of Emerging Trends & Technology in Computer Science (IJETTCS)
Copyright:
Available Formats
International Journal of Emerging Trends & Technology in Computer Science (IJETTCS)
Web Site: www.ijettcs.org Email: editor@ijettcs.org, editorijettcs@gmail.com
Volume 7, Issue 3, May - June 2018 ISSN 2278-6856
IOT: The Future of Connectivity
Mr. ALSTYNE VICTOR. KURATY
Lecturer, Dept of Computer Science, K.L.E’s J.G. College Of Commerce
Vidyanagar, Hubballi
ABSTRACT: Internet of things , in basic terms is layer
Connectivity of different devices through wireless Gateway and the
means.Today many tasks are based on IOT. Devices are network layer
becoming smarter these days , Cities for instance are Application Layer
becoming intelligent by implementing IOT. Smart cities
incorporate obstacle tracking, Object sensing,Network
sensing and control , tracking people around them , 1. APPLICATION LAYER:
monitoring lights etc. The main objective of IOT in cities is • Lowest Abstraction Layer With sensors we are creating
to keep the cities clean using various methods such as digital nervous system.
Garbage management systems and the second objective is • Measure physical quantities.
making people more responsible. Keeping this in ming • It Interconnects the physical with digital world.
“IOT based Intelligent Garbage Bin for Smart cities” has • It Collects and process the information in real time.
been developed . Garbage management is one major
application of IOT. We use sensors ,that are connected to
2. GATEWAY AND THE NETWORK LAYER:
the bins at different locations. These sense the garbage • Has a robust and high performance network infrastructure.
levels when full, Notifies with a message via GSM to the • Supports all the communication requirements for latency,
concerned admin to clean the bins. bandwidth or security
etc.
DEFINITION OF INTERNET OF THINGS (IOT) : • Allows several multiple organisations to share and use the
“Today computers and the Internet are totally dependent on same network independently whenever needed
humans for information. Roughly 50 petabyte of data
available on the Internet were first 3. MANAGEMENT LAYER:
captured and created by humans by typing, pressing a • It captures periodic sensory data.
record button, taking a digital picture, or scanning a bar • Data Analytics (Extracting relevant information from
code etc. Conventional diagrams in the Internet massive amount of raw
leaves out most numerous and important routers - people. data).
The problem is that people have less time, attention and • Streaming Analytics (It Process the real time data)
accuracy all of which means they are not very good at • Maintains security and privacy of data.
capturing data about things in the real world.Today's
information technology is totally dependent on data 4.SENSOR LAYER:
originated by people that our computers know more about • Provides user interface for using IoT.
ideas . If computer could learn from the generated data and • Different applications for various sectors like
gathered information, would help us immensely ,we would Transportation, Healthcare, Supply
be able to track and count everything, and greatly reduce chains, Agriculture, Automotive sectors,Retail
waste and cost. We would know, when things ,Government etc.
need to be replaced, repaired or recalling,. The Internet of
Things has a huge potential to change the world. ENABLING TECHNOLOGIES:
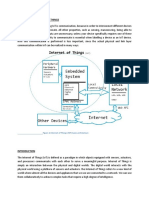
ARCHITECTURE OF INTERNET OF THINGS
Architecture of internet Of Things contains basically 4 Energy:
layers: This concern about low-power chipset having new and
1. Application Layer efficient and compact battery cells like fuel cells, polymer
2. Gateway and the network layer batteries which can help in case of IoT.
3. Management Service layer
4. Sensor layer Intelligence:
The devices should have capabilities of context awareness
fig.1:Architecture of IOT and inter-machine communication.
Sensor layer Communication:
Management Service
Volume 7, Issue 3, May – June 2018 Page 24
International Journal of Emerging Trends & Technology in Computer Science (IJETTCS)
Web Site: www.ijettcs.org Email: editor@ijettcs.org, editorijettcs@gmail.com
Volume 7, Issue 3, May - June 2018 ISSN 2278-6856
The devices with smart multi-frequency band antennas, they refer mainly to M2M communication to cover the OSI
integrated on-chip made of new materials that will enable stack's lower layers. For instance, the network layer could
the devices to communicate effectively . be implemented by IPv6, whereas network and transport
could be based on UDP (User Datagram Protocol) and
Integration: CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol). The lightweight
Integration of smart devices into packaging, or better, into protocol MQTT could be used on top of TCP/IP instead of
the products themselves will allow a significant cost saving HTTP if it is
and increase the eco-friendliness of the alternatively realised.
products.
The third perspective is things orientation, which focus on
Interoperability: assets such as sensors, actuators, and tags that are vital in
It means communication of different protocols by using both the IoT-A and IIRA. This is the classic approach for
some protocol stack. Two devices might not be the automation industry, which tries to define bottom-up a
interoperable even if they belong to same standards. reference around tangible objects and their individual data
sources and information needs.Both architectures have
Available Architectures: management and security mechanisms across all layers.
The architecture proposals help define and explain
Two major architectures available are: the IoT-A and IIRA.
Proposals of both the architectures have been prepared fig.2: Available Architectures
attentively but the IoT-A has been escribed
completely and expanded. It has been going hand in hand Perspective Application
with the Io'T community and incorporates multiple views Semantic oriented Service protocols such as
since its launch in 2012. In contrast, the IIRA still aims for OSA A,UPnP,DPWS
feedback and further detailing. and EXI
Comparison of these architectures are now done regarding Internet oriented Inter connectivity and
their capabilities and layers according to three perspectives. protocol conversion based
on UDP vs TCP with
The first perspective is semantic orientation-data and HTTP Support for IPV4
information are interpreted to create knowledge for and IPV6
business cases. The IoT-A focuses on the generic aspects of Things oriented A physical layer and data
informatics instead of specific application facets of link layer conversion with
semantics. In contrast, the IIRA focuses on the low communication
functionality of the industry domain, such as business, protocols suitable for easy
operations(prognostics, monitoring, optimisation, and so installation and
on), information (analytics and data), and application (UIs, maintenance
APIs, logic, and rules).
RAMI 4.0 is domain specific and it extends the view of the Perspective Application
IIRA toward the life cycle and value streams of Semantic oriented Service protocols such as OSA
manufacturing applications.In particular, it intensifies UA,UPnP,DPWS and EXI Internet oriented Inter
the functional-layer structure by two dimensions-the life connectivity and protocol conversion based on UDP vs
cycle and value stream TCP with HTTP Support for IPV4 and IPV6
and also by hierarchy levels (for further details, see Things oriented A physical layer and data link layer
International Electrotechnical Commission [IEC] standards conversion with low communication protocols suitable for
62890, 62264, and 61512). easy installation and maintenance
The second perspective is Internet orientation. It has two Proposed Methodology
aspects. The first is middleware for service support and
data management in the cloud and servers. In an abstract Sensors like weight sensors, IR sensors can be used for
manner, the IoT-A extensively covers the modelling and garbage detection. The information about the weight of
structuring of IoT business process management, virtual garbage is given by weight sensor, but it is not efficient
entities, IoT services, and cross-service organisation from because it fails to identify the level of waste in the bin.
the functional, information, and domain viewpoints. The Hence Infrared sensor (IR sensor) is used to detect the level
serverside of garbage. IR sensor is a
architecture and its management are defined by the multipurpose sensor which emits the light , invisible to
implementation. The same applies to agents and code on naked eye but the electronic components can detect it. It
domain-specific devices. The IIRA focuses consists of IR transmitter and IR receiver. IR sensor
mainly on business and use cases apart from other aspects. produces both analog and digital output.
This sensor produces the output as logic „1‟ at the digital
The second aspect is networking, transport, and data links. output when an object is sensed and a logic „0‟ if no object
These things are considered by both the architectures but is sensed. Sensor produces the analog output voltage
Volume 7, Issue 3, May – June 2018 Page 25
International Journal of Emerging Trends & Technology in Computer Science (IJETTCS)
Web Site: www.ijettcs.org Email: editor@ijettcs.org, editorijettcs@gmail.com
Volume 7, Issue 3, May - June 2018 ISSN 2278-6856
between 0 and 5V based on the distance between sensor safety and quality of life. Also, Will never run out of
and the object. anything when you need it at the last moment.
An LED present on the IR sensor board is used to indicate 3. Time: The amount of time saved in monitoring and the
the presence of an object. IR sensors are highly sensitive to number of trips done otherwise would be tremendous.
surrounding lights and therefore these are covered properly.
Potentiometer is used to calibrate the sensor. The output of 4. Money: The financial aspect is the best advantage. IOT
IR sensor is acquired by The National Instruments myRIO- technology could replace humans who are involved in
1900. It is an input-output device which is portable and monitoring and maintaining supplies.
reconfigurable. This can be used in the design of robotics,
controls and many other designs. The NI myRIO-1900 has Disadvantages :
a ZYNQ chip.This ZYNQ chip is a combination of 1. Compatibility: As of now, there is no standard for
processor (ARM Dual core) and FPGA (Xilinx).The NI tagging and monitoring with sensors. A uniform concept
myRIO-1900 consists of analog input, digital input, analog like the USB or Bluetooth is required which
output, digital output, power output, non-volatile memory should not be that difficult to do.
and audio input and output in an embedded device. USB
acts as a connector between the NI myRIO-1900 and host 2. Complexity: There are several opportunities for failure
computer. It has connectors A and B that act as an with complex systems. For example, you or one of ur
expansion port and a connector C that act as a mini-system registered family members may receive messages that the
port that carry signals and these signals are milk is over and both of you may end up buying the same.
differentiated by connector names. Here the mostly used which leaves you with double the quantity required Or a
connector is mini-system port connector C. This device can software bug causing the printer to order ink multiple times
even create wireless network by connecting to the wireless when it only requires a single cartridge.
network. It can be connected to Wi-Fi which is an inbuilt
option available. 3. Privacy/Security: Privacy is a big issue in IoT. All the
data must be securely encrypted so that various data like
APPLICATIONS : financial status or how much milk you consume isn’t
There are several application domains which will be common knowledge at the work place or known with your
impacted by the emerging IOT. The applications can be friends.
classified based on the network availability, coverage,
scale, heterogeneity, repeatability, user involvement and 4. Safety: There is a chance that the software can be hacked
impact. and your personal information misused. The possibilities
are endless. Your prescription being changed or your
We categorise the applications into four application account details being hacked could put you at risk. Hence,
domains: all the safety risks become the consumer’s responsibility.
(1) Personal and Home
(2) Enterprise CONCLUSION:
(3) Utilities The rapid increase of devices with communicating–
(4) Mobile. actuating capabilities is bringing closer the actual vision of
There is a huge crossover between applications and the use IOT, where the actuation and sensing functions seamlessly
of data between these domains. For instance, the Personal blend into the background and new capabilities are also
and Home IOT produces electricity usage data of the house made possible through access of rich and new information
and makes it available to the electricity company, which sources. The evolution of the next generation of mobile
can in turn optimise the power supply and demand. The system and devices will depend on the creativity of the
internet enables sharing of information between different users in designing these new applications and products .IoT
service providers seamlessly also creating multiple is an emerging technology, influencing this domain by
business opportunities. providing new changing data and the required
computational resources for creating the revolutionary apps
and software.
Advantages : References:
1. Data: The more the information, the easier it is to make 1. R. Howells, "The Business Case for IoT", June
the right decision. Knowing what to get from the grocery 2015,[online]Available:
while you are out, without having to check on your own, http://scn.sap.com/community/business-
not only saves time but is convenient as well. ends/blog/2015/06/18/thebusiness- case-for-iot.
2. D. Evans, "The Internet of Things: How the Next
2. Tracking: The computers keep track of both quality and Evolution of the Internet Is Changing Everything", Apr.
the viability of things at home. Knowing the expiration date 2011, [online] Available: www.cisco.com/web/
of products/items before one consumes them , increases about/ac79/docs/innov/IoT_IBSG_0411FINAL.pdf.
Show Context
Volume 7, Issue 3, May – June 2018 Page 26
International Journal of Emerging Trends & Technology in Computer Science (IJETTCS)
Web Site: www.ijettcs.org Email: editor@ijettcs.org, editorijettcs@gmail.com
Volume 7, Issue 3, May - June 2018 ISSN 2278-6856
3.L. Atzori, A. Iera, G. Morabito, "The Internet of Things:
A Survey", Computer Networks, vol. 54, no. 15, pp.
2787-2805, 2010, [online] Available:
www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S138912861000
1568.
4. Status Report: Reference Architecture Model Industrie
4.0 (RAMI4.0), VDI/ VDE Society Measurement and
Automatic Control, July 2015, [online]
www.vdi.de/fileadmin/vdi_de/redakteur_dateien/gma_d
ateien/
5305Publikation_GMA_Status_Report_ZVEI_Reference_
Architecture_Mod.pdf.
5.Santucci, G. From internet to data to internet of things. In
Proceedings of the International Conference on Future
Trends of the Internet , 2009.
6. Atzori, L., Lera, A., & Morabito, G. The internet of
things: A survey. Computer Networks, 54(15), 2787–
2805, 2010.
7. Sakamura, K. Challenges in the age of ubiquitous
computing: A case study of T-Engine—an open
development platform for embedded systems.
In:Proceedings of ICSE’06 . Shanghai, China 2006. Co-
operation with the working group RFID of the ETP
EPOSS, Internet of Things in 2020, roadmap for the
future, Version 1.1, May27 . 2008
8. Hui, J., Culler, D., & Chakrabarti, S. 6LoWPAN:
Incorporating IEEE 802.15.4into IP architecture–
internet protocol for smart objects (IPSO) Alliance,
WhitePaper # 3.http://www.ispo-alliance.org2009.
9. Katasonov, A., Kaykova, O., Khriyenko, O., Nikitin, S.,
& Terziyan, V. Smartsemantic middleware for the
internet of things. In: Proceedings of the 5th
International Conference on Informaticsin Control,
Automation and Robotics.Funchal, Mederia, Portugal
2008
Volume 7, Issue 3, May – June 2018 Page 27
You might also like
- The Five Layer Network ModelDocument32 pagesThe Five Layer Network ModelDaksh AilawadiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - RGPV IOT CS6005Document11 pagesUnit 1 - RGPV IOT CS6005Aaditya TamrakarNo ratings yet
- Zero TierDocument24 pagesZero TierijbasuraNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id3168575Document5 pagesSSRN Id3168575User-kaNo ratings yet
- Network Protocols, Schemes, and Mechanisms For Internet of Things (IoT) Features, Open Challenges, and TrendsDocument25 pagesNetwork Protocols, Schemes, and Mechanisms For Internet of Things (IoT) Features, Open Challenges, and TrendsThomas LagkasNo ratings yet
- Internet of Things (Iot) /cloud Computing: Prameet P. PatilDocument6 pagesInternet of Things (Iot) /cloud Computing: Prameet P. PatilPrameet P PatilNo ratings yet
- Internet of ThingsDocument25 pagesInternet of ThingssofimukhtarNo ratings yet
- Internet of Things 1Document95 pagesInternet of Things 1ENG20DS0040 SukruthaGNo ratings yet
- Gioia 2016Document5 pagesGioia 2016Thường Nguyễn VănNo ratings yet
- POV-Internet of Things Nirmal Nag: Design Authority, SAP Enterprise ApplicationDocument20 pagesPOV-Internet of Things Nirmal Nag: Design Authority, SAP Enterprise ApplicationNirmal NagNo ratings yet
- IOT Future in Edge ComputingDocument7 pagesIOT Future in Edge ComputingIJAERS JOURNALNo ratings yet
- ) Module - 1: Iot First Internals Question Bank (AnswersDocument15 pages) Module - 1: Iot First Internals Question Bank (AnswersAryan ShahNo ratings yet
- PESIT Bangalore South Campus: Internal Assessment Test 1Document16 pagesPESIT Bangalore South Campus: Internal Assessment Test 1jkqwertyNo ratings yet
- Survey On Recent Advances in IoT Application Layer Protocols PDFDocument18 pagesSurvey On Recent Advances in IoT Application Layer Protocols PDFnaseemNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Internet of Things - FinalDocument22 pagesModule 2 - Internet of Things - Finalelsa galgaoNo ratings yet
- A Home Automation Architecture Based On LoRa TechnDocument12 pagesA Home Automation Architecture Based On LoRa TechnDannyNo ratings yet
- ISI: Integrate Sensor Networks To Internet With ICNDocument9 pagesISI: Integrate Sensor Networks To Internet With ICNdan_intel6735No ratings yet
- With Neat Diagram, Explain Wireless Temperature Monitoring System Using Rasp BDocument6 pagesWith Neat Diagram, Explain Wireless Temperature Monitoring System Using Rasp BMEHRAN KAPRANo ratings yet
- (Soutik Dey Iot)Document7 pages(Soutik Dey Iot)Soutik DeyNo ratings yet
- 2011 - Research On The Key Technologies of IOT Applied On Smart GridsDocument4 pages2011 - Research On The Key Technologies of IOT Applied On Smart GridsAnkit SoniNo ratings yet
- A Survey On IoT Communication and Computation FrameworksDocument6 pagesA Survey On IoT Communication and Computation Frameworksociel felipe gomezNo ratings yet
- Fog Computing PDFDocument5 pagesFog Computing PDFRAHUL SINGHNo ratings yet
- IoT NotesDocument91 pagesIoT NotesVishu JaiswalNo ratings yet
- alahari 2017 ijca 912973 هذا PDFDocument5 pagesalahari 2017 ijca 912973 هذا PDFكن صديقيNo ratings yet
- Power Control Application in Smart Grid Using IOTDocument45 pagesPower Control Application in Smart Grid Using IOTPalakshVismayNo ratings yet
- Internet of ThingsDocument11 pagesInternet of ThingsASHOKA KUMARNo ratings yet
- 11 IoT July 2021 Solution Key To Final ExamDocument20 pages11 IoT July 2021 Solution Key To Final ExamManjot KaurNo ratings yet
- Sesi 1 - IoT Ecosystem - AamirDocument49 pagesSesi 1 - IoT Ecosystem - AamirfilzaNo ratings yet
- Smart Home Automation Based On Iot Using Arduino Mega: Abstract-In The Advancement of TechnologiesDocument4 pagesSmart Home Automation Based On Iot Using Arduino Mega: Abstract-In The Advancement of TechnologiesUdupiSri groupNo ratings yet
- Granjal 2015Document19 pagesGranjal 2015Hannan SatopayNo ratings yet
- A Study of Link Layer Protocols in IOT: Mani Pareek Sushil BuriyaDocument5 pagesA Study of Link Layer Protocols in IOT: Mani Pareek Sushil BuriyaRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- A Survey On IoT Architectures, Protocols, Applications, Security, Privacy, Real-World Implementation and Future TrendsDocument6 pagesA Survey On IoT Architectures, Protocols, Applications, Security, Privacy, Real-World Implementation and Future TrendsirvanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 NotesDocument99 pagesUnit 2 NotesKaushalNo ratings yet
- Setting Up A Multi-Purpose Internet of Things SystemDocument4 pagesSetting Up A Multi-Purpose Internet of Things SystemtHe lOsErNo ratings yet
- Scalable Methodology For Data Stream Analytics in Real-Time Internet of Things (IoT) ApplicationsDocument6 pagesScalable Methodology For Data Stream Analytics in Real-Time Internet of Things (IoT) Applicationsjava webNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - IoTDocument31 pagesChapter 4 - IoTeyobNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: Internet of Things (Iot)Document31 pagesChapter Four: Internet of Things (Iot)Ērmias ÁlemayehuNo ratings yet
- Synopsis IOTDocument6 pagesSynopsis IOThemantNo ratings yet
- IOT NotesDocument12 pagesIOT NotesMalay NiravNo ratings yet
- Conducted by NIELIT Jorhat EC Venue: Nielit Jorhat Ec Isbt 1 Floor, Tarajan, JorhatDocument26 pagesConducted by NIELIT Jorhat EC Venue: Nielit Jorhat Ec Isbt 1 Floor, Tarajan, JorhatTanushree KalitaNo ratings yet
- Narrow Band Internet of Things Implementations and ApplicationsDocument6 pagesNarrow Band Internet of Things Implementations and ApplicationsnadaNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence Approaches For IoT Security: State of ArtDocument12 pagesArtificial Intelligence Approaches For IoT Security: State of ArtIJAERS JOURNALNo ratings yet
- IoT StandardsDocument79 pagesIoT StandardsTheo NtwaliNo ratings yet
- Iot Architecture, Onem2M Model, Reference Model: L-T-P - (C) 4-0-0Document25 pagesIot Architecture, Onem2M Model, Reference Model: L-T-P - (C) 4-0-0deva dattaNo ratings yet
- IOT-Module 1 PDFDocument73 pagesIOT-Module 1 PDFM.A rajaNo ratings yet
- Integrating The Iot With Cloud: International Journal of Emerging Trends & Technology in Computer Science (Ijettcs)Document3 pagesIntegrating The Iot With Cloud: International Journal of Emerging Trends & Technology in Computer Science (Ijettcs)International Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Internet of Things: 18 MCA 5 4 EDocument44 pagesInternet of Things: 18 MCA 5 4 ESarita Kumar100% (1)
- Analysis of IoT Data Transfer Messaging Protocols On Application LayerDocument10 pagesAnalysis of IoT Data Transfer Messaging Protocols On Application LayerIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- IOT NotesDocument40 pagesIOT NotesIshan Pradhan100% (1)
- School of Engineering Fundamentals of Industrial Internet of Things Worksheet For Lesson Package 1: Introduction To Internet of Things (Iot)Document14 pagesSchool of Engineering Fundamentals of Industrial Internet of Things Worksheet For Lesson Package 1: Introduction To Internet of Things (Iot)Makhmudul FikriNo ratings yet
- Cyberi 2018 8337550Document6 pagesCyberi 2018 8337550Nguyễn Văn AnhNo ratings yet
- Internet of Things A Survey On Enabling PDFDocument30 pagesInternet of Things A Survey On Enabling PDFKarim HashemNo ratings yet
- Figure 1:internet of Things (IOT) Basic ArchitectureDocument7 pagesFigure 1:internet of Things (IOT) Basic Architecturekavita thakranNo ratings yet
- Preface 2016 Internet of ThingsDocument2 pagesPreface 2016 Internet of ThingsSeac IngenieríaNo ratings yet
- Io TresearchpaperDocument5 pagesIo TresearchpaperWarrior SoulNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document99 pagesUnit 2nagamalleswari2010No ratings yet
- Adc PaperDocument34 pagesAdc Papersharmasiddhant2063No ratings yet
- Politecnico Di Torino Repository ISTITUZIONALEDocument7 pagesPolitecnico Di Torino Repository ISTITUZIONALEMiguelChoqueLandivarNo ratings yet
- Building the Internet of Things with IPv6 and MIPv6: The Evolving World of M2M CommunicationsFrom EverandBuilding the Internet of Things with IPv6 and MIPv6: The Evolving World of M2M CommunicationsNo ratings yet
- The Internet of Things: Living in a connected worldFrom EverandThe Internet of Things: Living in a connected worldBCS, The Chartered Institute for ITNo ratings yet
- Detection of Malicious Web Contents Using Machine and Deep Learning ApproachesDocument6 pagesDetection of Malicious Web Contents Using Machine and Deep Learning ApproachesInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Study of Customer Experience and Uses of Uber Cab Services in MumbaiDocument12 pagesStudy of Customer Experience and Uses of Uber Cab Services in MumbaiInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Product Reliability Using Failure Mode Effect Critical Analysis (FMECA) - Case StudyDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Product Reliability Using Failure Mode Effect Critical Analysis (FMECA) - Case StudyInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- THE TOPOLOGICAL INDICES AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF n-HEPTANE ISOMERSDocument7 pagesTHE TOPOLOGICAL INDICES AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF n-HEPTANE ISOMERSInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Soil Stabilization of Road by Using Spent WashDocument7 pagesSoil Stabilization of Road by Using Spent WashInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- The Mexican Innovation System: A System's Dynamics PerspectiveDocument12 pagesThe Mexican Innovation System: A System's Dynamics PerspectiveInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- An Importance and Advancement of QSAR Parameters in Modern Drug Design: A ReviewDocument9 pagesAn Importance and Advancement of QSAR Parameters in Modern Drug Design: A ReviewInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Performance of Short Transmission Line Using Mathematical MethodDocument8 pagesPerformance of Short Transmission Line Using Mathematical MethodInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Staycation As A Marketing Tool For Survival Post Covid-19 in Five Star Hotels in Pune CityDocument10 pagesStaycation As A Marketing Tool For Survival Post Covid-19 in Five Star Hotels in Pune CityInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Analysis of Two Biggest Upi Paymentapps: Bhim and Google Pay (Tez)Document10 pagesA Comparative Analysis of Two Biggest Upi Paymentapps: Bhim and Google Pay (Tez)International Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Ijaiem 2021 01 28 6Document9 pagesIjaiem 2021 01 28 6International Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Design and Detection of Fruits and Vegetable Spoiled Detetction SystemDocument8 pagesDesign and Detection of Fruits and Vegetable Spoiled Detetction SystemInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Datasets For Myocardial Infarction Based On Actual DatasetsDocument9 pagesSynthetic Datasets For Myocardial Infarction Based On Actual DatasetsInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Impact of Covid-19 On Employment Opportunities For Fresh Graduates in Hospitality &tourism IndustryDocument8 pagesImpact of Covid-19 On Employment Opportunities For Fresh Graduates in Hospitality &tourism IndustryInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- A Deep Learning Based Assistant For The Visually ImpairedDocument11 pagesA Deep Learning Based Assistant For The Visually ImpairedInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Swot Analysis of Backwater Tourism With Special Reference To Alappuzha DistrictDocument5 pagesSwot Analysis of Backwater Tourism With Special Reference To Alappuzha DistrictInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Design and Manufacturing of 6V 120ah Battery Container Mould For Train Lighting ApplicationDocument13 pagesDesign and Manufacturing of 6V 120ah Battery Container Mould For Train Lighting ApplicationInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Anchoring of Inflation Expectations and Monetary Policy Transparency in IndiaDocument9 pagesAnchoring of Inflation Expectations and Monetary Policy Transparency in IndiaInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Work Involvement and Work Stress On Employee Performance: A Case Study of Forged Wheel Plant, IndiaDocument5 pagesThe Effect of Work Involvement and Work Stress On Employee Performance: A Case Study of Forged Wheel Plant, IndiaInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- CCNA 200-125: Eng Ayman Saeed 01005080910-01120440064 Whatspp 01005080910Document26 pagesCCNA 200-125: Eng Ayman Saeed 01005080910-01120440064 Whatspp 01005080910Ayman SaeedNo ratings yet
- Socket Programming Project 2Document20 pagesSocket Programming Project 2Preksha BansalNo ratings yet
- Network Simulator2 (NS2) Basic CommandsDocument4 pagesNetwork Simulator2 (NS2) Basic Commandshariharanpotter100% (7)
- CS2307 - Network Lab ManualDocument66 pagesCS2307 - Network Lab ManualAkshay Kumar Chandran67% (6)
- The Quality Management InterfaceDocument9 pagesThe Quality Management InterfaceandrefkatoNo ratings yet
- TCP Client AlgorithmDocument10 pagesTCP Client AlgorithmAlok GuptaNo ratings yet
- Automator 3.6.x ConfigurationGuide allOS en PDFDocument70 pagesAutomator 3.6.x ConfigurationGuide allOS en PDFAyman AniKedNo ratings yet
- Assessing Network Parameters by Web Real-Time CommunicationsDocument4 pagesAssessing Network Parameters by Web Real-Time CommunicationsVadivelan NNo ratings yet
- Sip - LogDocument639 pagesSip - LogsashaNo ratings yet
- Why NFS SucksDocument16 pagesWhy NFS SucksDesi BorisovaNo ratings yet
- Cisco ReviewerDocument7 pagesCisco ReviewerGray FullbusterNo ratings yet
- AX88179 Datasheet v131Document41 pagesAX88179 Datasheet v131Anonymous sNIiDlegYNo ratings yet
- Linux TCPDocument39 pagesLinux TCPdeath914No ratings yet
- Understanding TCP IPDocument16 pagesUnderstanding TCP IPJoseph DialloNo ratings yet
- Brocade FESX424Document12 pagesBrocade FESX424sati747No ratings yet
- CCNA 1 v60 Study Material Chapter 9 Transport LayerDocument9 pagesCCNA 1 v60 Study Material Chapter 9 Transport LayerRazaqNo ratings yet
- Flow of Traffic in ASADocument3 pagesFlow of Traffic in ASAAsifNo ratings yet
- Selected Exercises ETSF10/ETSF05 Internet Protocols: Exercise Group Internet RoutingDocument2 pagesSelected Exercises ETSF10/ETSF05 Internet Protocols: Exercise Group Internet Routingteerthesh1No ratings yet
- Citrix HDX For Dummies 2.3Document77 pagesCitrix HDX For Dummies 2.3MIRELA100% (1)
- UDP Socket Programming in PHP - How To Code Client and Server - BinaryTidesDocument7 pagesUDP Socket Programming in PHP - How To Code Client and Server - BinaryTidesSup' Tan'No ratings yet
- Cisco 200-301 v2020-11-17 q75Document31 pagesCisco 200-301 v2020-11-17 q75Joel Guede100% (1)
- QOS Openvswitch - enDocument27 pagesQOS Openvswitch - enSteve NguyenNo ratings yet
- FMG FAZ Ports and ProtocolsDocument12 pagesFMG FAZ Ports and Protocolsewan koNo ratings yet
- Development of Earthquake Early Warning System Using ADXL335 AccelerometerDocument6 pagesDevelopment of Earthquake Early Warning System Using ADXL335 Accelerometerebank ekalayaNo ratings yet
- Lista de Puertos CompletaDocument286 pagesLista de Puertos CompletaJCesar Cusi AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- DS Af50h en V12 1020Document6 pagesDS Af50h en V12 1020kyawoo.sgNo ratings yet
- BCS-052 J16 CompressedDocument3 pagesBCS-052 J16 CompressedAmanNo ratings yet
- MindCert Wireshark MindMap PDFDocument1 pageMindCert Wireshark MindMap PDFAldevino FerreiraNo ratings yet