Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Indian Ancient History Timeline Chart
Uploaded by
Gopal Kumhar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
425 views4 pagesok
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentok
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
425 views4 pagesIndian Ancient History Timeline Chart
Uploaded by
Gopal Kumharok
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
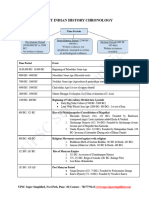
Indian History timeline chart
Ancient India
Period: Prehistoric to AD 700
There were activities of Homo erectus in the Indian subcontinent 20
lakh years ago and of Homo sapiens since 70,000 BC.
The first inhabitants of Indian subcontinent might have been tribal
like:
o Nagas in North-East
o Santhals in East-India
o Bhils in Central India
o Gonds in Central India
o Todas in South India
These people speak Austric, pre-Dravidian languages like Munda
and Gondvi.
Aryans and Dravidians are supposed to be immigrants who came
later to the sub-continent.
Paleolithic Period (2 million BC – 10,000 BC)
Important Palaeolithic sites are Kaladgi Basin, Bhimbetka, Hunsgi,
Kurnool Caves, and Narmada Valley,
Tools made up of lime stone
Fire was discovered
Mesolithic Period (10,000 BC – 8,000 BC)
Microliths was found at Brahmagiri, Narmada, and Gujarat
Domestication of animals and Cattle rearing were started in this
period
Significant climatic change happened
Neolithic Period (8000 BC – 4,000 BC)
Wheel discovered and agriculture was started in this period
Inamgaon is an early Neolithic village
The major megalithic Sites are Brahmagiri and Adichanallur
Important Neolithic Sites:
o Hallur(Andhra Pradesh)
o Mahagara(Uttar Pradesh)
o Maski
o Paiyampalli(Andhra Pradesh)
o Sangana Kaller
o Utnur
o Burzahom (Kashmir)
o Chirand (Bihar)
o Daojali Hading(Tripura and Assam)
o Gufkral (Kashmir)
o Kodekal
o Koldihwa(Uttar Pradesh)
o Mehrgarh (Pakistan)
o Takkala Kota
Indus Valley Civilization (BC 2700 – BC 1900)
Chalcolithic Period (4000 BC – 1,500 BC)
It is also known as Copper Age and considered part of Bronze Age.
Iron Age (BC 1500 – BC 200)
Vedic Period and Arrival of Aryans
Basic books of Hinduism, Vedas were composed in this period.
Rise of Jainism and Buddhism
Mahajanapadas
Magadha empire- Bimbisara of Haryanka Kula
Sisunga dynasty – Kalasoka (Kakavarnin)
Nanda empire – Mahapadma-Nanda, Dhana-Nanda
Persians – Greek arrival: Alexander 327 BC
Mauryan Empire (321-185 BC)
322–298 BCE- Chandragupta
298–272 BCE- Bindusara
268–232 BCE – Ashoka
Maurya Empire
(322 BCE–180 BCE)
Chandragupta (322–297 BCE)
Bindusara (297–272/268 BCE)
Ashoka (272/268–232 BCE)
Dasharatha (232–224 BCE)
Samprati (224–215 BCE)
Shalishuka (215–202 BCE)
Devavarman (202–195 BCE)
Shatadhanvan (195–187 BCE)
Brihadratha (187–180 BCE)
Mauryan Kingdoms was succeeded by
o Sunga (181-71 BC)
o Kanva (71-27BC)
o Satavahanas (235-100BC)
o Indo-Greeks, Parthians (19-45AD)
o Sakas (90BC-150AD)
o Kushanas(78AD)
o Cholas
o Pandyas
o Cheras
Gupta Kingdom (300AD – 800AD)
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire
Samudra Gupta of Gupta kingdom is known as Indian Napoleon
Gupta Empire
320 CE–550 CE
Sri Gupta (240 – 280)
Ghatotkacha (280 – 319)
Chandragupta I (320 – 335)
Kachagupta (335)
Samudragupta (335 – 380)
Ramagupta
Chandragupta II (380 – 413/415)
Kumaragupta I (415 – 455)
Skandagupta (455 - 467)
Purugupta (467 – 473)
Kumaragupta II (473 - 476)
Budhagupta (476 – 495)
Narasimhagupta (495 – ?)
(Bhanugupta) (circa 510)
Vainyagupta (circa 507)
Kumaragupta III (circa 530)
Vishnugupta (540 – 550)
Post-Gupta or Contemporary Gupta
The deterioration of Imperial Guptas, Magadha and its capital,
Pataliputra
After the fall of the Guptas, five major centers of power immersed in
north India
o Vakataka
o Mukharis
o Harshvardana
o Chalukyas
o Pallavas
o Sena
o Deva
o Hoysala
o Kakatiya
o Kalachuri
Also, Hunas, Maitrakas, Pushyabhutis, Gaudas, Rajputs, Senas and
Chauhans succeeded later.
You might also like
- Mcqs Indian History Chronology Economy Constitution GeographyDocument11 pagesMcqs Indian History Chronology Economy Constitution GeographyMuhammad TahirNo ratings yet
- Medieval and Modern HistoryDocument50 pagesMedieval and Modern HistoryPrince SharmaNo ratings yet
- General AwarenessDocument116 pagesGeneral AwarenessUma ShankarNo ratings yet
- GK BookDocument13 pagesGK BookJatin VatsNo ratings yet
- Mnemonics For UPSCDocument12 pagesMnemonics For UPSCSahil GautamNo ratings yet
- General Studies-II: (Governance, Constitution, Polity, Social Justice and International Relations)Document8 pagesGeneral Studies-II: (Governance, Constitution, Polity, Social Justice and International Relations)Xylo MartyNo ratings yet
- Assam GK Rapid Revision - Study - InsightDocument22 pagesAssam GK Rapid Revision - Study - InsightBishalDey100% (1)
- History of AssamDocument15 pagesHistory of AssamKhagemba MeiteiNo ratings yet
- Complete Geography Notes by Dr. ShivinDocument444 pagesComplete Geography Notes by Dr. ShivinAJAYNo ratings yet
- Modern Indian HistoryDocument40 pagesModern Indian HistoryDivansh SinghNo ratings yet
- English Medium Reasoning Sbvq6aDocument160 pagesEnglish Medium Reasoning Sbvq6asandhya sriNo ratings yet
- Nuclear & Thermal Power Plants (Top MCQ)Document27 pagesNuclear & Thermal Power Plants (Top MCQ)mat kumarNo ratings yet
- Ancient India by RS AgarwalDocument3 pagesAncient India by RS Agarwalsid011No ratings yet
- The MauryasDocument10 pagesThe MauryasM TejaNo ratings yet
- Famous SloganDocument17 pagesFamous SloganVanshika ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Awards and Honours 2023Document44 pagesAwards and Honours 2023Atul AnandNo ratings yet
- 10th Social Bit BankDocument52 pages10th Social Bit BankSubramanyam K.V.R100% (1)
- Rivers of IndiaDocument12 pagesRivers of IndiaChetan s.k KattimaniNo ratings yet
- Kalyan Sir Indian History 2Document135 pagesKalyan Sir Indian History 2GayatriramanaNo ratings yet
- Indian Dynasties and Their Founders and Their Capitals PDFDocument4 pagesIndian Dynasties and Their Founders and Their Capitals PDFChaithra BhatNo ratings yet
- Indian Geography (2) .UnlockedDocument74 pagesIndian Geography (2) .UnlockedSai Swaroop Attada0% (1)
- Monthly Current Affairs March 2024 EnglishDocument77 pagesMonthly Current Affairs March 2024 EnglishMuhammad ImranNo ratings yet
- Short Notes IAS PQRN Indian History Puaird - 4787 - 1681447014Document101 pagesShort Notes IAS PQRN Indian History Puaird - 4787 - 1681447014Harish MeenaNo ratings yet
- 040 REXODAS History Ancient History English Printable BY REXODASDocument110 pages040 REXODAS History Ancient History English Printable BY REXODASMehdiNo ratings yet
- Indus River SystemDocument23 pagesIndus River SystemShivani MishraNo ratings yet
- Ancient & Medieval Indian HISTORY - QRM - CompressedDocument52 pagesAncient & Medieval Indian HISTORY - QRM - CompressedAbhishek GuptaNo ratings yet
- Static GK NotesDocument99 pagesStatic GK NotesTarique HassanNo ratings yet
- Indian Economy (Shortcut)Document3 pagesIndian Economy (Shortcut)Gurpreet SidhuNo ratings yet
- Buddhism & JainismDocument38 pagesBuddhism & JainismWHO AM INo ratings yet
- G K Short TricksDocument2 pagesG K Short Tricksuzumakhinaruto100% (3)
- Assam History GK PDFDocument2 pagesAssam History GK PDFBaha Dur BasumataryNo ratings yet
- Buddhism-Delhi UPSC SecretsDocument14 pagesBuddhism-Delhi UPSC SecretsTransporter 007No ratings yet
- Last Minute Series 1Document6 pagesLast Minute Series 1Aseena NiyasNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity HandWritten - NotesDocument135 pagesIndian Polity HandWritten - NotesAjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Geography AppscDocument378 pagesGeography AppscKiran B100% (1)
- Tricks of GeographyDocument2 pagesTricks of GeographyRUTHERSON SNo ratings yet
- History Capsule SSC 2014Document20 pagesHistory Capsule SSC 2014mkiriti0% (1)
- Fairs and FestivalsDocument43 pagesFairs and FestivalsM TejaNo ratings yet
- G.S. 26000 - One Liner Book (English Medium) FinalDocument360 pagesG.S. 26000 - One Liner Book (English Medium) FinalgovernmentpleaderofficeganjamNo ratings yet
- Poverty and Un EmploymentDocument22 pagesPoverty and Un Employmentramana3339No ratings yet
- List of ART Centres For Web PDFDocument23 pagesList of ART Centres For Web PDFsharma rsNo ratings yet
- World Map PointsDocument183 pagesWorld Map Pointssriramdeep8771No ratings yet
- Ancient Medieval Modern History PDFDocument342 pagesAncient Medieval Modern History PDFRajani JPNo ratings yet
- Nidhanpur Copper Plate InscriptionDocument6 pagesNidhanpur Copper Plate InscriptionRatna Pritam BarmanNo ratings yet
- General Studies HistoryDocument102 pagesGeneral Studies Historysrikanthmic100% (1)
- Iasbaba'S Prelims Exclusive PROGRAM (PEP) 2022: Medieval History HandoutsDocument11 pagesIasbaba'S Prelims Exclusive PROGRAM (PEP) 2022: Medieval History HandoutsGagandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Notes From Lucent HDocument16 pagesNotes From Lucent Hravirsn100% (1)
- History Handout 10Document49 pagesHistory Handout 10Gagandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Economics Handwritten Class Notes. by MyNotesAddaDocument32 pagesEconomics Handwritten Class Notes. by MyNotesAddaRudra Pratap RathourNo ratings yet
- Basic History TricksDocument7 pagesBasic History TricksAmit Shukla100% (1)
- GS-1 1Document151 pagesGS-1 1Martha SharathNo ratings yet
- HistoryDocument11 pagesHistoryMuthulakshmi JehanNo ratings yet
- Indian Geography Handwritten Notes PDF in Hindi (For More Book - WWW - GktriDocument45 pagesIndian Geography Handwritten Notes PDF in Hindi (For More Book - WWW - GktriAjit RaikwarNo ratings yet
- Dristi Gs 1 SampleDocument16 pagesDristi Gs 1 Samplelegal accNo ratings yet
- Ancient Indian History Chronology Os0dyuDocument2 pagesAncient Indian History Chronology Os0dyuvikash150919No ratings yet
- Chronology of Important Events in Indian HistoryDocument9 pagesChronology of Important Events in Indian HistoryRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chronology of Ancient To Modern History of India: Indian History Timeline ChartDocument3 pagesChronology of Ancient To Modern History of India: Indian History Timeline Chart11111111111-675818100% (1)
- Demo 50 One Liner Approach General Knowledge - Kiran PDFDocument50 pagesDemo 50 One Liner Approach General Knowledge - Kiran PDFthe Guru100% (2)
- AoB I ADocument125 pagesAoB I Atanzin tanhaNo ratings yet
- One Liner Approach General Knowledge - KiranDocument614 pagesOne Liner Approach General Knowledge - Kirankumar Raushan Ratnesh67% (3)
- Mac 2e Complete SSGDocument246 pagesMac 2e Complete SSGGopal KumharNo ratings yet
- Economics Paper IDocument5 pagesEconomics Paper IGopal KumharNo ratings yet
- Chamberlin's Group Equilibrium: Concept and TheoryDocument4 pagesChamberlin's Group Equilibrium: Concept and TheoryGopal KumharNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between A SWIFT ACK and SWIFT NACKDocument2 pagesThe Difference Between A SWIFT ACK and SWIFT NACKGopal Kumhar67% (3)
- IAS Baba Test 12 QDocument45 pagesIAS Baba Test 12 QGopal KumharNo ratings yet
- Purging Workflow TablesDocument10 pagesPurging Workflow TablesGopal KumharNo ratings yet
- Mock Test 17 EconomyDocument2 pagesMock Test 17 EconomyGopal KumharNo ratings yet
- Geography-8: Physiography of India-1Document1 pageGeography-8: Physiography of India-1Gopal KumharNo ratings yet
- Ancient Indian History McqsDocument12 pagesAncient Indian History McqsSaidulu RamanaNo ratings yet
- ADR DissertationDocument140 pagesADR Dissertationiram mirNo ratings yet
- GS RRB Eng Railway Exam PDFDocument75 pagesGS RRB Eng Railway Exam PDFPrabhatNo ratings yet
- CL 6, History, WK 27 28Document9 pagesCL 6, History, WK 27 28Aman JunejaNo ratings yet
- BAsyllabus PDFDocument31 pagesBAsyllabus PDFAjay VermaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University, Lucknow.: Topic: Decline of The Mauryan EmpireDocument11 pagesDr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University, Lucknow.: Topic: Decline of The Mauryan EmpiredivyavishalNo ratings yet
- 2 Kings, Farmers and TownsDocument30 pages2 Kings, Farmers and TownsAnushka MishraNo ratings yet
- History SyallabusDocument39 pagesHistory Syallabuswondertiger2No ratings yet
- Wa0003Document27 pagesWa0003PRINT WHEELSNo ratings yet
- Buddhist Art in AsiaDocument30 pagesBuddhist Art in AsiaAustin Macauley Publishers Ltd.100% (3)
- Adda Ace Geneeral-Awareness - NewDocument710 pagesAdda Ace Geneeral-Awareness - NewSisir PradhanNo ratings yet
- Sample Ancient History One LinerDocument10 pagesSample Ancient History One Linerroopanath245100% (1)
- Class 12 History Book 1 Short NotesDocument54 pagesClass 12 History Book 1 Short Noteslokanshu pandey0% (1)
- The Mauryan Empire - SchoolDocument11 pagesThe Mauryan Empire - SchoolTryambakNo ratings yet
- ITC Maurya SynopsisDocument3 pagesITC Maurya SynopsisShubhan RathourNo ratings yet
- ANCIENT CIVILIZATIONS Active Reading and Note-Taking Guide G6Document214 pagesANCIENT CIVILIZATIONS Active Reading and Note-Taking Guide G6Roxana Soledad Marin Parra100% (8)
- ProspectusDocument17 pagesProspectusTanveer IqbalNo ratings yet
- MCQ 25 Years PyqDocument31 pagesMCQ 25 Years PyqM.D. DANCENo ratings yet
- 11th History Vol 1 EM @upsc - PDF - 1Document102 pages11th History Vol 1 EM @upsc - PDF - 1Saatvika Maulihar BA p 1stNo ratings yet
- QP - WB - CB - VI - Hist - Reconstructing HistoryDocument5 pagesQP - WB - CB - VI - Hist - Reconstructing HistoryAhaan DoshiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Ancient IndiaDocument44 pagesChapter 5 Ancient Indiaapi-234908816100% (2)
- Hydrology and Water Resources Management in Ancient IndiaDocument21 pagesHydrology and Water Resources Management in Ancient IndiaAbburi KarthikNo ratings yet
- History - Notes - EnglishDocument188 pagesHistory - Notes - EnglishAnimated TamashaNo ratings yet
- Buddhism in AfghanistanDocument25 pagesBuddhism in AfghanistanSalma Faiz UsmaniNo ratings yet
- 10304Document70 pages10304hk_scribdNo ratings yet
- Foreign Travelers & Envoys in Indian History - UPSC IASDocument13 pagesForeign Travelers & Envoys in Indian History - UPSC IASShraddha PatilNo ratings yet
- The Rise and Decline of Brahmanism in IndiaDocument40 pagesThe Rise and Decline of Brahmanism in IndiaNikhilUdinurNo ratings yet
- Indian Traditions, Cultural and Society QuantumDocument143 pagesIndian Traditions, Cultural and Society QuantumSwapnil Tiwari (SWA)No ratings yet
- Ashoka The Emperor Who Gave Up WarDocument2 pagesAshoka The Emperor Who Gave Up WarPriyanshi AnejaNo ratings yet
- Mauryan EmpireDocument3 pagesMauryan EmpireSameer NameNo ratings yet
- Gnosticism: The History and Legacy of the Mysterious Ancient ReligionFrom EverandGnosticism: The History and Legacy of the Mysterious Ancient ReligionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (132)
- Byzantium: The Surprising Life of a Medieval EmpireFrom EverandByzantium: The Surprising Life of a Medieval EmpireRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (138)
- 1177 B.C.: The Year Civilization Collapsed: Revised and UpdatedFrom Everand1177 B.C.: The Year Civilization Collapsed: Revised and UpdatedRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (111)
- The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire - Volume IFrom EverandThe Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire - Volume IRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (78)
- Twelve Caesars: Images of Power from the Ancient World to the ModernFrom EverandTwelve Caesars: Images of Power from the Ancient World to the ModernRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (9)
- The Riddle of the Labyrinth: The Quest to Crack an Ancient CodeFrom EverandThe Riddle of the Labyrinth: The Quest to Crack an Ancient CodeNo ratings yet
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyFrom EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNo ratings yet
- Ur: The History and Legacy of the Ancient Sumerian CapitalFrom EverandUr: The History and Legacy of the Ancient Sumerian CapitalRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (75)
- Strange Religion: How the First Christians Were Weird, Dangerous, and CompellingFrom EverandStrange Religion: How the First Christians Were Weird, Dangerous, and CompellingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- The book of Thoth: A Short Essay on the Tarot of the EgyptiansFrom EverandThe book of Thoth: A Short Essay on the Tarot of the EgyptiansRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Roman History 101: From Republic to EmpireFrom EverandRoman History 101: From Republic to EmpireRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (59)
- The Emperor's Handbook: A New Translation of The MeditationsFrom EverandThe Emperor's Handbook: A New Translation of The MeditationsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Past Mistakes: How We Misinterpret History and Why it MattersFrom EverandPast Mistakes: How We Misinterpret History and Why it MattersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Nineveh: The History and Legacy of the Ancient Assyrian CapitalFrom EverandNineveh: The History and Legacy of the Ancient Assyrian CapitalRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- The Scythian Empire: Central Eurasia and the Birth of the Classical Age from Persia to ChinaFrom EverandThe Scythian Empire: Central Eurasia and the Birth of the Classical Age from Persia to ChinaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Strange Religion: How the First Christians Were Weird, Dangerous, and CompellingFrom EverandStrange Religion: How the First Christians Were Weird, Dangerous, and CompellingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Early Christianity and the First ChristiansFrom EverandEarly Christianity and the First ChristiansRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (19)
- Gods and Robots: Myths, Machines, and Ancient Dreams of TechnologyFrom EverandGods and Robots: Myths, Machines, and Ancient Dreams of TechnologyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (42)
- Ten Caesars: Roman Emperors from Augustus to ConstantineFrom EverandTen Caesars: Roman Emperors from Augustus to ConstantineRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (114)
- The Book of the Dead: The History and Legacy of Ancient Egypt’s Famous Funerary TextsFrom EverandThe Book of the Dead: The History and Legacy of Ancient Egypt’s Famous Funerary TextsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (49)
- Caligula: The Mad Emperor of RomeFrom EverandCaligula: The Mad Emperor of RomeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (16)
- Pandora's Jar: Women in the Greek MythsFrom EverandPandora's Jar: Women in the Greek MythsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (256)