Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Latitude Deg SI US /G: Table 2: Engineering Constants A) Acceleration of Gravity
Uploaded by
ASIM KUMAR SRIVASTAVAOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Latitude Deg SI US /G: Table 2: Engineering Constants A) Acceleration of Gravity
Uploaded by
ASIM KUMAR SRIVASTAVACopyright:
Available Formats
Table 2: ENGINEERING CONSTANTS
a) Acceleration of Gravity
Latitude
Deg SI US g/g0
0 9.780 32.088 0.9973
10 9.782 32.093 0.9975
20 9.786 32.108 0.9979
30 9.793 32.130 0.9986
40 9.802 32.158 0.9995
45* 9.80665 32.1740 1
50 9.811 32.187 1.0004
60 9.819 32.215 1.0013
70 9.826 32.238 1.0020
80 9.831 32.253 1.0024
90 9.832 32.258 1.0026
*standard acceleration due to gravity
b) Gravitational Constant
G = 6.673 (10-11) m3/kg-s2 = 3.44 (10-8) ft-4-lb-1-s-4.
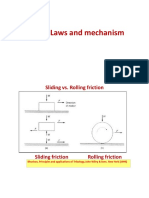
c) Coefficients of Static and Kinetic Friction
Coefficients of Static Friction
Aluminum 1.35 Brass 0.3
Copper 2.5 Iron 1.0
Magnesium 0.6 Nickel 0.7
Platinum 1.2 Steel 0.8
Zinc 0.6 Diamond 0.1
Graphite 0.1 Nylon 0.2
Teflon 0.04 Tungsten carbide 0.12
Glass 0.95 Plexi-glass 0.8
Brick 0.65 Wood 0.35
Coefficients of Kinetic Friction
Aluminum – steel 0.47 Automotive brake pad – cast iron 0.35
Brick – brick 0.65 Copper – steel 0.36
Glass – glass 0.4 Ice – ice 0.03
Metal – metal 0.05 Rubber – concrete 0.8
Steel – steel 0.3 Teflon – Teflon 0.04
Wood – wood 0.4
Coefficients of Kinetic Friction used in Construction
Concrete – soil 0.3 Concrete – steel 0.45
Steel – Teflon 0.1 Brick – moist clay 0.33
Brick – dry clay 0.5 Brick – masonry on sand 0.4
Brick – masonry on gravel 0.6 Granite – granite 0.6
Limestone – limestone 0.75 Cement block – cement block 0.65
Cement concrete – dry clay 0.4 Cement concrete – wet clay 0.2
Cement concrete – dry sand 0.5 Cement concrete – wet sand 0.4
Cement concrete – dry gravel 0.5 Cement concrete – dry rock 0.6
Cement concrete – wet rock 0.5
COEFFICIENT OF FRICTION
The following friction coefficients shall be considered in calculating the sliding
friction forces :
Concrete to Soil / Rock 0.30
Concrete to Steel 0.45
Steel to Steel 0.30
Steel to Teflon Plate 0.10
Brick Masonry on moist clay 0.33
Brick Masonry on dry clay 0.50
Brick Masonry on sand 0.40
Brick Masonry on gravel 0.60
Brick Masonry to Brick 0.70
Brick Masonry on rock 0.75
Granite on Granite 0.60
Limestone on Limestone 0.75
Cement Blocks on Cement Blocks 0.65
Cement concrete on dry clay 0.40
Cement concrete on wet clay 0.20
Cement concrete on wet sand 0.40
Cement concrete on dry sand 0.50 - 0.60
Cement concrete on dry gravel 0.50 - 0.60
Cement concrete on dry rock 0.60 - 0.70
Cement concrete on wet rock 0.50
Brick on Brick 0.65
Wood on Wood 0.48
Note: Friction is more on dry surfaces of the same material
compared to wet surface.
d) Strength of Materials
Metal Tensile Strength* [klb/in2] Yield Strength [klb/in2]
Cast Iron 18 – 60 8 – 40
Wrought Iron 45 – 55 25 – 35
Pure Iron, annealed 42 19
Hot rolled 48 30
Cold rolled 100 95
Structural steel 50 – 65 30 – 40
Low alloy 65 – 90 40 – 80
Steel
(SAE1300, annealed) 70 40
Quenched: 1300○F 100 80
Quenched: 1000○F 130 110
Quenched: 700○F 200 180
Quenched: 400○F 240 210
Steel
(SAE 4340, annealed) 80 45
Quenched: 1300○F 130 110
Quenched: 1000○F 190 170
Quenched: 700○F 240 215
Quenched: 400○F 290 260
Steel, cold rolled
(SAE 1112) 84 76
Steel, stainless
(18 – S) 85 – 95 30 – 35
Aluminum, pure rolled 13 – 24 5 – 21
Aluminum-copper alloys, cast 19 – 23 12 – 16
Wrought, heat treated 30 – 60 10 – 50
Aluminum, die castings 30
Aluminum, alloy 17ST 56 34
Aluminum, alloy 51ST 48 40
Copper, annealed 32 5
Copper, hard-drawn 68 60
Silver, cast, annealed 18 8
Titanium, 6 – 4 alloy
Annealed 130 120
*compressive yield strength = tensile yield strength except in cold-rolled metals
e) Mass Densities
Metal mass density averages
[gr/cm3] [lb/ft3] [kg/m3]
Aluminum 2.55 – 2.80 165 2640
Copper , cast rolled 8.8 – 8.95 556 8910
Iron, cast, pig 7.2 450 7207
Iron, slag 2.5 – 3.0 172 2760
Platinum, cast 21.5 1330 21300
Steel, cold drawn 7.83 489 7830
Steel, machine 7.80 487 7800
Steel, tool 7.70 – 7.73 481 7700
Tungsten 19.22 1200 18800
Zinc, cast – rolled 6.9 – 7.2 440 7050
Timber mass density averages
[gr/cm3] [lb/ft3] [kg/m3]
Ash 0.55 34 545
Birch 0.71 – 0.72 44 705
Cedar 0.35 22 352
Cherry 0.43 27 433
Cypress 0.45 – 0.48 29 465
Fir, Douglas 0.48 – 0.55 32 513
Hickory 0.74 – 0.8 48 769
Mahogany 0.56 – 0.85 44 705
Oak, chestnut 0.74 46 737
Oak, red, black 0.64 – 0.71 42 673
Oak, white 0.77 48 770
Pine, Oregon 0.51 32 513
Pine, southern 0.61 – 0.67 40 641
Poplar 0.43 27 433
Redwood, California 0.42 26 417
Spruce 0.45 28 449
Teak, African 0.99 62 994
Teak, Indian 0.66 – 0.88 48 769
Walnut 0.59 37 593
Liquids mass density averages
[gr/cm3] [lb/ft3] [kg/m3]
Alcohol (100% ethyl) 0.789 49 802
Alcohol (100% methyl) 0.796 50 809
Oils, vegetable 0.91 – 0.94 58 930
Oils, mineral, lubricants 0.88 – 0.94 57 914
Water (4○C) 1.0 62.4 1000
Water (100○C) 0.958 59.8 958.1
Water (ice) 0.88 – 0.92 56 897
Water (snow) 0.125 8 128
Water (sea) 1.02 – 1.03 64 1025
Masonry mass density averages
[gr/cm3] [lb/ft3] [kg/m3]
Ashlar
Granite 2.4 – 2.7 159 2550
Limestone 2.1 – 2.8 153 2450
Marble 2.4 – 2.8 162 2600
Sandstone 2.0 – 2.6 143 2290
Rubble
Granite 2.3 – 2.6 153 2450
Limestone 2.0 – 2.7 147 2360
Marble 2.3 – 2.7 156 2500
Sandstone 1.9 – 2.5 137 2190
Brick
Hard 1.8 – 2.3 128 2050
Medium 1.6 – 2.0 112 1790
Soft 1.4 – 1.9 103 1650
Concrete
Cement, stone, sand 2.2 – 2.4 144 2310
Cement, slag, etc. 1.9 – 2.3 130 2080
Cement, cinder, etc. 1.5 – 1.7 100 1600
Earth mass density averages
[gr/cm3] [lb/ft3] [kg/m3]
Clay, dry 1.0 63 1010
Earth, dry, loose 1.2 76 1220
Earth, dry packed 1.5 95 1520
Earth, moist, loose 1.3 78 1250
Earth, moist, packed 1.6 96 1540
Earth, mud 1.7 108 1730
You might also like
- Emissivity Table of Various Surfaces For Infrared ThermometryDocument19 pagesEmissivity Table of Various Surfaces For Infrared Thermometryntiiac201No ratings yet
- Liter Tank DetailDocument281 pagesLiter Tank DetailrkpragadeeshNo ratings yet
- AISI 1040 Carbon Steel (UNS G10400)Document4 pagesAISI 1040 Carbon Steel (UNS G10400)عابد زاهدNo ratings yet
- Embodied Energy - TilesDocument13 pagesEmbodied Energy - TilesfakemasterkgpNo ratings yet
- Thermal Expansion Practice ProblemsDocument1 pageThermal Expansion Practice Problemsadimegha100% (1)
- Elastic Constants and Theri RelationshipsDocument4 pagesElastic Constants and Theri RelationshipsrchallahaliNo ratings yet
- Carbon Steels: Hot-Rolled Steel StripDocument7 pagesCarbon Steels: Hot-Rolled Steel Stripwulfgang66No ratings yet
- Astm A449Document1 pageAstm A449Vitor Rigueira de GodoyNo ratings yet
- F = Μ N (1) where F = frictional force (N, lb) μ = static (μ) or kinetic (μ) frictional coefficient N = normal force (N, lb)Document7 pagesF = Μ N (1) where F = frictional force (N, lb) μ = static (μ) or kinetic (μ) frictional coefficient N = normal force (N, lb)bhavesh shuklaNo ratings yet
- Tabla de MaterialesDocument2 pagesTabla de MaterialesAlan Mauricio InsaustiNo ratings yet
- New 4340 Alloy SteelDocument3 pagesNew 4340 Alloy Steeljimmy julian pava vargasNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Emissivity TableDocument7 pagesUltimate Emissivity TableAnil KattnaNo ratings yet
- S.O.R FOR BUILDING AHMEDABAD DISTRICT 2015-16-Edited PDFDocument695 pagesS.O.R FOR BUILDING AHMEDABAD DISTRICT 2015-16-Edited PDFDixit JariwalaNo ratings yet
- S.O.R FOR BUILDING AHMEDABAD DISTRICT 2015-16-Edited PDFDocument695 pagesS.O.R FOR BUILDING AHMEDABAD DISTRICT 2015-16-Edited PDFDixit JariwalaNo ratings yet
- First Schedule Tariff ChangesDocument38 pagesFirst Schedule Tariff ChangesSamiNo ratings yet
- Rate AnalysisDocument38 pagesRate AnalysisSarin0% (1)
- Material Yield Stress COMPARITIVE DATADocument4 pagesMaterial Yield Stress COMPARITIVE DATAshNo ratings yet
- Rate-Analysis GHFDocument64 pagesRate-Analysis GHFSandeep VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Kriteria Kegagalan Material Berdasarkan ATCDocument3 pagesKriteria Kegagalan Material Berdasarkan ATCAlAzzam CostaNo ratings yet
- ASME BPVC - II.A-2017 SA-182/SA-182M: Table 2Document1 pageASME BPVC - II.A-2017 SA-182/SA-182M: Table 2rajeshNo ratings yet
- PHYS 235 Formula BookDocument8 pagesPHYS 235 Formula BookSimranjitNo ratings yet
- C Staehle Kalt Datenblatt EN 1511Document7 pagesC Staehle Kalt Datenblatt EN 1511pierocarnelociNo ratings yet
- جدول ضرايب اصطكاك موادDocument25 pagesجدول ضرايب اصطكاك موادOmid7686No ratings yet
- Stainless Steel GradesDocument8 pagesStainless Steel Gradesnathan1979No ratings yet
- Properties of Engineering Material - Waleed NassefDocument1 pageProperties of Engineering Material - Waleed NassefWaleed NassefNo ratings yet
- Aisi 1030 Steel - PPTX Resistencia de MaterialesDocument11 pagesAisi 1030 Steel - PPTX Resistencia de MaterialesAlexCastroBallesterosNo ratings yet
- Properties of Nonmetals.: Temperature 10 Substance C W/M C KG/M KJ/KG C M /s Structural and Heat-Resistant MaterialsDocument3 pagesProperties of Nonmetals.: Temperature 10 Substance C W/M C KG/M KJ/KG C M /s Structural and Heat-Resistant MaterialsMalik Mohammad AsifNo ratings yet
- Thermo-Optical Property DataDocument2 pagesThermo-Optical Property DataMariela BaigorriaNo ratings yet
- Die Casting AlloysDocument6 pagesDie Casting AlloyskeeblerkhanNo ratings yet
- 8-Lecture 8Document45 pages8-Lecture 8mustafNo ratings yet
- Milling Speeds and FeedsDocument1 pageMilling Speeds and FeedsirinaNo ratings yet
- SWD Trench CalculationDocument8 pagesSWD Trench Calculationsalmaan mastanNo ratings yet
- Piping Materials Selection TrainingDocument60 pagesPiping Materials Selection TrainingKagira Drawing Soltuion100% (2)
- Vulcan Industrial Engineering Co. Pvt. LTDDocument3 pagesVulcan Industrial Engineering Co. Pvt. LTDk koradiaNo ratings yet
- SilcoTek Coatings For High Purity ApplicationsDocument30 pagesSilcoTek Coatings For High Purity ApplicationsKommu RohithNo ratings yet
- Thermal Conductivity TableDocument3 pagesThermal Conductivity TableFadi QassimNo ratings yet
- New 4140 Alloy SteelDocument3 pagesNew 4140 Alloy SteelShariq KhanNo ratings yet
- HSS & Cobalt Drill Speed - FeedDocument1 pageHSS & Cobalt Drill Speed - FeedPuneeth KumarNo ratings yet
- Duplex Stainless Steel 2205 PDFDocument1 pageDuplex Stainless Steel 2205 PDFSalmanNo ratings yet
- Coefficient of Friction Dry Greasy Static Sliding StaticDocument7 pagesCoefficient of Friction Dry Greasy Static Sliding StaticezhiljananiNo ratings yet
- Radit Supriyanto - Tabel Cutting SpeedDocument4 pagesRadit Supriyanto - Tabel Cutting SpeedNasserNo ratings yet
- Building GSR 2022Document44 pagesBuilding GSR 2022Neil AgshikarNo ratings yet
- Coefficient of Friction Equation and Table ChartDocument11 pagesCoefficient of Friction Equation and Table ChartBobNo ratings yet
- Core 321/4541: EN 1.4541, ASTM TYPE 321 / UNS S32100Document8 pagesCore 321/4541: EN 1.4541, ASTM TYPE 321 / UNS S32100Nguyen03No ratings yet
- New 4130 Alloy SteelDocument3 pagesNew 4130 Alloy SteelfsijestNo ratings yet
- 4 - Stainless Steels - Wrought and CastDocument24 pages4 - Stainless Steels - Wrought and CastdennykvgNo ratings yet
- Density TableDocument8 pagesDensity TableAhmed SakrNo ratings yet
- MetalDocument2 pagesMetalvibhorsoni123No ratings yet
- 2017-91 Heat Treatment of SteelDocument74 pages2017-91 Heat Treatment of SteelJen Megah Bremanda SembiringNo ratings yet
- Duplex Stainless Steel 2507 (UNS S32750) : Heanjia Super-Metals Co., LTD, Call-12068907337. WebDocument3 pagesDuplex Stainless Steel 2507 (UNS S32750) : Heanjia Super-Metals Co., LTD, Call-12068907337. Websudish mishraNo ratings yet
- Manual For CPWDDocument56 pagesManual For CPWDabhay9411No ratings yet
- Coefficient of Thermal ExpansionDocument1 pageCoefficient of Thermal ExpansionankitNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel 441 UNS S43940Document5 pagesStainless Steel 441 UNS S43940Enrique Ruiz HonoratoNo ratings yet
- FrictionDocument14 pagesFrictionManvendra YadavNo ratings yet
- C03physical Properties of MaterialsDocument5 pagesC03physical Properties of MaterialsEngr. Jeremiah BadanaNo ratings yet
- C Staehle Kalt Datenblatt en 1511Document7 pagesC Staehle Kalt Datenblatt en 1511Yokesh SamannanNo ratings yet
- The Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelFrom EverandThe Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelNo ratings yet
- Tertiary Treatment, Chemical Processes & Advance TreatmentDocument13 pagesTertiary Treatment, Chemical Processes & Advance Treatmentmon2x2No ratings yet
- A564A564M-13 Standard Specification For Hot-Rolled and Cold-Finished Age-Hardening Stainless Steel Bars and ShapesDocument8 pagesA564A564M-13 Standard Specification For Hot-Rolled and Cold-Finished Age-Hardening Stainless Steel Bars and Shapestjt4779No ratings yet
- Skema Jawapan Kimia p2Document12 pagesSkema Jawapan Kimia p2HenrySeow50% (8)
- Glass Coatings On Stainless Steels For High-Temperature Oxidation Protection MechanismDocument12 pagesGlass Coatings On Stainless Steels For High-Temperature Oxidation Protection MechanismJabbar AljanabyNo ratings yet
- Practical Aspects of Production Bright Annealing of Stainless SteelDocument2 pagesPractical Aspects of Production Bright Annealing of Stainless SteelAgniva DuttaNo ratings yet
- ATM145P Time Schedule 2023 - GEDocument6 pagesATM145P Time Schedule 2023 - GExOx LiT NNo ratings yet
- Project With Kmno4 NWDocument4 pagesProject With Kmno4 NWShandev IndoiNo ratings yet
- Enhancement in Biogas Production From Press MudDocument5 pagesEnhancement in Biogas Production From Press MudHarsha Vardhan ReddyNo ratings yet
- QCVN 01 2009 BYT - enDocument9 pagesQCVN 01 2009 BYT - enRoxyRoseNo ratings yet
- Di Benz Al AcetoneDocument3 pagesDi Benz Al AcetoneKristine Mae De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy - Question BankDocument12 pagesMetallurgy - Question BankSayantan Chatterjee100% (1)
- 2.2.1 Mixed Metal Oxide Tubular Anodes Rev 1Document2 pages2.2.1 Mixed Metal Oxide Tubular Anodes Rev 1Soltani AliNo ratings yet
- Bentone 34 TDSDocument2 pagesBentone 34 TDSAmir OsossNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument509 pagesSolutionssknoushad126No ratings yet
- AFCONA - Universal Pigment Concentrate ConceptDocument13 pagesAFCONA - Universal Pigment Concentrate ConceptAelya SanNo ratings yet
- 3 Painting and Coating Selection Schedules: 3.1 New Construction WorksDocument2 pages3 Painting and Coating Selection Schedules: 3.1 New Construction WorksmuthuvelaaNo ratings yet
- 2012 ReferenceWorkEntry PDFDocument886 pages2012 ReferenceWorkEntry PDFandr9s9centenoNo ratings yet
- Alternatives To Toluene & XyleneDocument2 pagesAlternatives To Toluene & Xyleneanant_z12No ratings yet
- Redox and Electrochemical I. PurposeDocument21 pagesRedox and Electrochemical I. PurposeClarissa Amalia PutriNo ratings yet
- Air Liquide HandBook Nov 2020Document106 pagesAir Liquide HandBook Nov 2020Shailesh ChettyNo ratings yet
- TOPIC WISE REVIEW CPP-IV-CK-FINAL - PMDDocument6 pagesTOPIC WISE REVIEW CPP-IV-CK-FINAL - PMDSaksham PanghalNo ratings yet
- Alloy Selection For Dilute and Medium Concentration Sulfuric Acid NACE CORROSION OnePetroDocument5 pagesAlloy Selection For Dilute and Medium Concentration Sulfuric Acid NACE CORROSION OnePetroYaroo YarooNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas ProcessingDocument4 pagesNatural Gas ProcessingChung WyNo ratings yet
- Fuels, Furnaces & Refractories 4Document6 pagesFuels, Furnaces & Refractories 4PRAKHAR SINGHNo ratings yet
- NMAT - Anal2017 PDFDocument88 pagesNMAT - Anal2017 PDFAthena Marielle PrudenteNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Biochemistry 7th Edition CampbellDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Biochemistry 7th Edition Campbellemulgemileagetpmau9100% (40)
- KRL ProductsDocument3 pagesKRL ProductsLokesh KNo ratings yet
- Rate of Decomposition of H2O2Document41 pagesRate of Decomposition of H2O2Beeta Moulik100% (1)
- Einstein Classes QualitativeDocument7 pagesEinstein Classes QualitativemadhavNo ratings yet
- Refining of Stainless SteelsDocument27 pagesRefining of Stainless SteelsirajfarjiNo ratings yet