Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Solution Manual For Introduction To Engineering Analysis 4th Edition by Hagen
Uploaded by
a729316280Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Solution Manual For Introduction To Engineering Analysis 4th Edition by Hagen
Uploaded by
a729316280Copyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 1
END-OF-CHAPTER PROBLEMS
Analysis and engineering design
1.1 Essay
1.2 A 1-m long cantilevered beam of rectangular cross section carries a uniform load of w = 15
kN/m. The design specification calls for a 5-mm maximum deflection of the end of the
beam. The beam is to be constructed of fir (E = 13 GPa). By analysis, determine at least five
combinations of beam height h and beam width b that meet the specification. Use the
equation
where,
ymax = deflection of end of beam (m)
w = uniform loading (N/m)
L = beam length (m)
E = modulus of elasticity of beam (N/m2)
I = bh3/12 = moment of inertia of beam cross section (m4)
Note: 1 Pa = 1 N/m2, 1 kN = 103 N and 1 GPa = 109 Pa.
What design conclusions can you draw about the influence of beam height and width on the
maximum deflection? Is the deflection more sensitive to h or b? If the beam were
constructed of a different material, how would the deflection change? See Figure P1.2 for
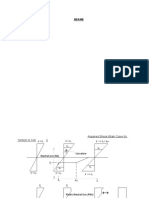
an illustration of the beam.
Figure P1.2
Full file at https://testbanku.eu/Solution-Manual-for-Introduction-to-Engineering-Analysis-4th-Edition-by-Hagen
Solution
Given information:
L = 1m w = 15 × 103 N/m ymax = 5 mm = 0.005 m
E = 13 × 109 Pa = 13 × 109 N/m2
The deflection of the beam, ymax, will be calculated for one combination of h and b, and the
rest can be done in the same manner.
By trial and error, we choose h = 200 mm and b = 100 mm. Thus, we have
ymax = wL4 = 12 wL4
8EI 8Ebh3
= 12(15 × 103 N/m)(1 m)4
8(13 × 109 Pa)(0.1 m)(0.2 m)3
= 0.00216 m = 2.16 mm < 5 mm
An alternative way of doing the calculation is to set ymax equal to or below its maximum
value, select an arbitrary value of h or b, and then find the other beam dimension.
The beam deflection is directly proportional to beam length, L, and inversely proportional
to beam height, h, and beam width, b. Beam deflection is more sensitive to beam height,
h, because this dimension is cubed. A beam can be made very stiff, i.e., the deflection can
be made very small for a given load, by increasing the beam height. For example, if the
beam height is doubled to 400 mm, the maximum deflection is only 0.270 mm.
If the beam were constructed of a different material, the modulus of elasticity, E, would be
different. The beam deflection is inversely proportional to E. Modulus of elasticity is a
mechanical property that denotes the stiffness of a material. A higher value of E means a
higher stiffness. It is clear that a higher value of E results in a lower beam deflection. For
example, if the beam were constructed of structural steel (E = 200 GPa) instead of fir, the
beam deflection is only 0.141 mm.
Analysis and engineering failure
1.3 Essay
1.4 Essay
Full file at https://testbanku.eu/Solution-Manual-for-Introduction-to-Engineering-Analysis-4th-Edition-by-Hagen
You might also like
- Mf7017 Materials Testing and Characterlation TechniquesDocument1 pageMf7017 Materials Testing and Characterlation TechniquesSudhir Chakravarthy KatragaddaNo ratings yet
- Unit 11Document20 pagesUnit 11Venkatesh Gangadhar100% (1)
- Engineering Fluid Mechanics SolutionsDocument30 pagesEngineering Fluid Mechanics SolutionsOmar Albakhit Bany SakherNo ratings yet
- ASM16-Torsion of Noncircular Shafts VI PDFDocument101 pagesASM16-Torsion of Noncircular Shafts VI PDFHusnain JabbarNo ratings yet
- Flow Around Submerged Bodies-Drag GATEDocument7 pagesFlow Around Submerged Bodies-Drag GATEhcsharma1967No ratings yet
- Q 7.12Document59 pagesQ 7.12Qil AznanNo ratings yet
- Axisymmetric ProblemsDocument41 pagesAxisymmetric ProblemsAVINASH CHAVANNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids IntroductionDocument51 pagesMechanics of Solids IntroductionSatish DhanyamrajuNo ratings yet
- Theory of Simple Bending - Full1Document62 pagesTheory of Simple Bending - Full1Rahul KasaudhanNo ratings yet
- Deflection of BeamsDocument28 pagesDeflection of BeamsishwaryaNo ratings yet
- EGF316 Rotating Discs - NotesDocument11 pagesEGF316 Rotating Discs - NotesJigneshNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems - Shear Strength (II)Document2 pagesPractice Problems - Shear Strength (II)Kok Soon ChongNo ratings yet
- Solve: 196.13 KG/CM 242.2 KG/CMDocument9 pagesSolve: 196.13 KG/CM 242.2 KG/CMAhmed ShakerNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 Torsion in Reinforced Concrete MembersDocument8 pagesChapter - 5 Torsion in Reinforced Concrete MembersHelen NegashNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra Question BankDocument1 pageLinear Algebra Question BankDanial SadiqNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Differential EquationsDocument34 pagesBasic Concepts of Differential EquationsJimson MasculinoNo ratings yet
- Applied Fluid Mechanics - 02 Viscosity of FluidsDocument19 pagesApplied Fluid Mechanics - 02 Viscosity of Fluidssourz18100% (1)
- Strain: Strength of MaterialsDocument5 pagesStrain: Strength of MaterialsDon MatiasNo ratings yet
- Moment of Inertia PDFDocument18 pagesMoment of Inertia PDFBernalyn ManaogNo ratings yet
- Fracture MechanicsDocument12 pagesFracture MechanicsSANTOSH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Indeterminate Beams Using Three Moment TheoremDocument16 pagesAnalyzing Indeterminate Beams Using Three Moment Theoremkalpanaadhi100% (1)
- Strength of Materials: Theory and ExamplesDocument314 pagesStrength of Materials: Theory and ExamplesNkrumah JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials (CH 3 and 4Document19 pagesMechanics of Materials (CH 3 and 4Praveen Kumar RNo ratings yet
- Torsion Design of Prestressed ConcreteDocument20 pagesTorsion Design of Prestressed ConcreteDr. M.V.Krishna RaoNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Through Insulation and Composite WallsDocument8 pagesHeat Transfer Through Insulation and Composite WallsRonard Pa–a0% (1)
- Torsion of Non Circular BeamsDocument24 pagesTorsion of Non Circular BeamsXavier WallerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Bending: Moments Forces Perpendicular To AxisDocument13 pagesChapter 6 Bending: Moments Forces Perpendicular To AxisSumaya MahmoodNo ratings yet
- ch16 Plane Frame Analysis Using The Stiffness Method (For Student) (Compatibility Mode)Document33 pagesch16 Plane Frame Analysis Using The Stiffness Method (For Student) (Compatibility Mode)Darkman EliteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 in Class Problems SolutionsDocument7 pagesChapter 3 in Class Problems Solutionsarnob vsd100% (2)
- Applied Mechanics For Engineers-A Text Book For Students 1909 PDFDocument408 pagesApplied Mechanics For Engineers-A Text Book For Students 1909 PDFChandresh M Sachdev100% (1)
- SolutionDocument3 pagesSolutionbahast faiqNo ratings yet
- Stresses in BeamDocument34 pagesStresses in BeamWijayanto BekasiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Truss ElementsDocument19 pagesChapter 3 Truss Elementsanoop asokanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8. Axisymmetrically Loaded Members: Figure P7.42Document43 pagesChapter 8. Axisymmetrically Loaded Members: Figure P7.42asifNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual 3rdrd Ed. Metal Forming - Mechanics and MetallurgyDocument11 pagesSolution Manual 3rdrd Ed. Metal Forming - Mechanics and MetallurgyJeevanantham KannanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Conduction by Prince KhanDocument8 pagesTutorial 1 Conduction by Prince KhanPrince KhanNo ratings yet
- Kinetics of A Particle-ExDocument20 pagesKinetics of A Particle-ExDerrick Maatla MoadiNo ratings yet
- Q.15. Derive Expression For Ratio of Tension On Tight Side and Slack SideDocument8 pagesQ.15. Derive Expression For Ratio of Tension On Tight Side and Slack SideVishal RajNo ratings yet
- MCQ Unit 1 Resolution and Composition of ForcesDocument10 pagesMCQ Unit 1 Resolution and Composition of ForcesAjit MoreNo ratings yet
- Callister Solutions of Ch07Document52 pagesCallister Solutions of Ch07Malika NavaratnaNo ratings yet
- Exam 3 Material Science MATS 2001 UMN Fall 2012Document7 pagesExam 3 Material Science MATS 2001 UMN Fall 2012Zaki Smn100% (1)
- Problems Phase FeDocument9 pagesProblems Phase FeAshutoshKumarNo ratings yet
- Advanced Solid Mechanics U SarvananDocument385 pagesAdvanced Solid Mechanics U Sarvananமாறன் செங்கேணிNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of MaterialDocument3 pagesMechanics of MaterialChhaya Sharma100% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics Cengel (Solutions Manual) Chap11-043Document20 pagesFluid Mechanics Cengel (Solutions Manual) Chap11-043NURUL SYUHADA BT ISMAIL HAJAR33% (3)
- Chapter 9. Beams On Elastic Foundations: Prob. 8.51 Fig. 8.4 Prob. 8.51Document20 pagesChapter 9. Beams On Elastic Foundations: Prob. 8.51 Fig. 8.4 Prob. 8.51Maria TnsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document38 pagesChapter 2radhika100% (1)
- Assignment 7 SolutionsDocument11 pagesAssignment 7 SolutionsIsaiah Qe LiewNo ratings yet
- Design of Plate GirderDocument9 pagesDesign of Plate GirdermunnaiitrNo ratings yet
- AEB650 Materials For Engineering Chapter 8 SolutionsDocument6 pagesAEB650 Materials For Engineering Chapter 8 SolutionsNina Fadzil50% (2)
- NCKU Advanced Mechanics Homework #1 Stress ProblemsDocument3 pagesNCKU Advanced Mechanics Homework #1 Stress ProblemsNaveen RajNo ratings yet
- Pre Stressed Concrete 18Cv641: Topic: Magnels MethodDocument14 pagesPre Stressed Concrete 18Cv641: Topic: Magnels MethodShobhaNo ratings yet
- Beam Deflections: Strength of MaterialsDocument21 pagesBeam Deflections: Strength of MaterialsNicole Ann PedriñaNo ratings yet
- Analysis For Deflection and Stress in A SimplyDocument4 pagesAnalysis For Deflection and Stress in A SimplyMirazul IslamNo ratings yet
- Peaci: Design of Flexural MembersDocument5 pagesPeaci: Design of Flexural MembersZeroseveen SeveenNo ratings yet
- EPTD W9 - (L1+L2) SagDocument26 pagesEPTD W9 - (L1+L2) SagJunied TazrianNo ratings yet
- Buckling Load Optimization of BeamsDocument10 pagesBuckling Load Optimization of BeamsAbrham Yair Aguilar RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 11.deflection in BeamsDocument88 pages11.deflection in Beamsajaikumar ShankarNo ratings yet
- Timoshenko beam theory shear deformationDocument3 pagesTimoshenko beam theory shear deformationtimsykiNo ratings yet
- Forces and design loads in suspension bridgesDocument8 pagesForces and design loads in suspension bridgesFirew TibebuNo ratings yet
- M30 Grade Concrete: Proportioning of Concrete MixDocument4 pagesM30 Grade Concrete: Proportioning of Concrete Mixgrkvani10No ratings yet
- Dimensionamento de Ligacoes Estruturais Betao-BetaoDocument93 pagesDimensionamento de Ligacoes Estruturais Betao-BetaoFilomena Branco SilvaNo ratings yet
- Compressible VS Incompressible FluidsDocument2 pagesCompressible VS Incompressible FluidsAbdulhamid DaudaNo ratings yet
- Fans Static Head Calculation SheetDocument1 pageFans Static Head Calculation SheetLeandro FelipeNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Course OverviewDocument2 pagesFluid Mechanics Course OverviewParamvir GuliaNo ratings yet
- Rigid PavementDocument55 pagesRigid PavementRamakrishna Ramakrishna100% (1)
- Amendments-IRC 112-2011 PDFDocument7 pagesAmendments-IRC 112-2011 PDFharnishtanna212100% (2)
- Design of Composite BridgeDocument80 pagesDesign of Composite BridgeHarold Jackson Mtyana100% (2)
- Revised Refuse Area DesignDocument1 pageRevised Refuse Area DesignanzaniNo ratings yet
- Vane Shear Test: Dr. B. Munwar BashaDocument17 pagesVane Shear Test: Dr. B. Munwar BashaArif AzizanNo ratings yet
- Deflection - Ontario Building CodeDocument2 pagesDeflection - Ontario Building CodechidsalazarNo ratings yet
- Nestle PaintDocument1 pageNestle PaintFirst ChoiceNo ratings yet
- Architectural exam questions and answers covering building design, construction materials, codes and regulationsDocument10 pagesArchitectural exam questions and answers covering building design, construction materials, codes and regulationsMarie Franz VillafuerteNo ratings yet
- 2015 IRC Revision History PDFDocument1,301 pages2015 IRC Revision History PDFviralisursNo ratings yet
- DARSHANA TRADING CO. BILL OF MATERIALSDocument16 pagesDARSHANA TRADING CO. BILL OF MATERIALSsamyak munotNo ratings yet
- Rapport Heli WinchDocument29 pagesRapport Heli WinchAkram FerchichiNo ratings yet
- Beams: Assumed Stress-Strain Curve (In Tension or Compression) ε ε ε >> ε > ε ε > ε ε = εDocument14 pagesBeams: Assumed Stress-Strain Curve (In Tension or Compression) ε ε ε >> ε > ε ε > ε ε = εEhsan WasimNo ratings yet
- PCI Survey SheetDocument5 pagesPCI Survey SheetHAZIQ RAHMANNo ratings yet
- 12 - WellTec - Gary TaitDocument18 pages12 - WellTec - Gary TaityangtzeuNo ratings yet
- Complete SpecificationsDocument36 pagesComplete SpecificationsMichica TalensNo ratings yet
- Crane TP 410Document128 pagesCrane TP 410Antonio Alonso Diaz ArriagaNo ratings yet
- Figure 4.1: Basic Concrete Materials: Water Fine AggregaDocument49 pagesFigure 4.1: Basic Concrete Materials: Water Fine AggregahanimNATHRAHNo ratings yet
- 1 Front ElevationsDocument1 page1 Front Elevationsasitha eranga kumarawanshaNo ratings yet
- Coagulation and Floculation - 062 - Part 2Document18 pagesCoagulation and Floculation - 062 - Part 2Joce8888100% (1)
- Scaff Wind CalcsDocument1 pageScaff Wind CalcsHari HaranNo ratings yet
- Marking Guideline: Building and Structural Construction N5Document8 pagesMarking Guideline: Building and Structural Construction N5SaneleNo ratings yet
- AASHTO - LRFD Bridge Construction Specifications 2017Document607 pagesAASHTO - LRFD Bridge Construction Specifications 2017Mark El Ramy71% (7)
- Eight Vehicle Lanes, Two Train Lines, A Footway and A CyclewayDocument9 pagesEight Vehicle Lanes, Two Train Lines, A Footway and A CyclewayAkshara AkileshwarNo ratings yet
- Designing A Bellmouth Intake PDFDocument44 pagesDesigning A Bellmouth Intake PDFSankalp BhanjaNo ratings yet
- The Friction and Lubrication of SolidsDocument3 pagesThe Friction and Lubrication of SolidsJuan Carlos Benjamin Luna Veronico0% (1)