Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Name: - Subject: Chemistry Grade/NISN: - / - Date: March 14, 2018
Uploaded by
Mahyuddin AlghowryOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: - Subject: Chemistry Grade/NISN: - / - Date: March 14, 2018
Uploaded by
Mahyuddin AlghowryCopyright:
Available Formats
FIFTH MONTHLY TEST, SECOND SEMESTER
SECONDARY YEAR – METRO SCHOOL
ACADEMIC YEAR 2017/2018
Name : ______________________ Subject : Chemistry
Grade/NISN : ___ / __________________ Date : March 14th, 2018
Duration Score Teacher Signature Parent Signature
40 minutes
Questions
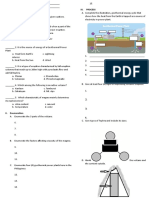
The diagram below shows a process of separating the petroleum into compounds based on their
boiling point. As you can see that compounds with less carbon atoms are at the top of the fraction.
You can use the information in the diagram to answer the questions.
1. The name of the separation process is
…….……………………………………………….............
2. One of the three major fossil fuel is petroleum or
sometimes called ........……………………………...……
3. Major fossil fuels that is come from fossil plant
material is ………………………………………………….
4. The result at the top of the fraction has boiling point
below 25oC means its phase in room temperature is….
5. In the fractional distillation of petroleum, where is
the hottest part of the fractionating column?
a. The top
b. The middle
c. The bottom
6. Which fraction leaves the tower at the very top?
a. Refinery gases
b. Petrol
c. Fuel oil
7. Which is a use for kerosene (paraffin)?
a. Airplane fuel
b. Fuel for cars
c. Tar for the roads
8. Where do the longest hydrocarbon molecules
condense?
a. At the top of the tower
b. At the bottom of the tower
c. They do not condense at all and remain a gas
9. Which fractions are the hardest to ignite? 12. What type of molecule is used as the
a. The ones at the top starting point in cracking?
b. The smallest molecules a. A large hydrocarbon molecule
c. The longest molecules b. A small hydrocarbon molecule
10. Which is the main compound in natural c. A large alcohol
gas? 13. What conditions are used for cracking?
a. Methane a. Low temperature, low pressure
b. Propane b. High temperature, catalyst
c. Butane c. High pressure, catalyst
11. What was coal originally formed from? 14. What are the typical products of
a. Remains of dead sea creatures cracking?
b. Sediment from ancient rocks a. Two short alkanes
c. Remains of ancient forests b. A short alkene and a short alkane
c. A variety of short alkenes
You might also like
- Instructional Design ProcessDocument1 pageInstructional Design ProcessMahyuddin Alghowry100% (3)
- 8Th Combustion and FlameDocument5 pages8Th Combustion and FlameKevaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Casting ProcessDocument34 pagesChapter 7 - Casting ProcessIjal HaizalNo ratings yet
- Grindability TestDocument8 pagesGrindability TestaghilifNo ratings yet
- Work Out Chemistry GCSE (PDFDrive)Document163 pagesWork Out Chemistry GCSE (PDFDrive)Rico ChanNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Protection of Steel Offshore Units and InstallationsDocument36 pagesCorrosion Protection of Steel Offshore Units and Installationsdamnamyte100% (1)
- Ten Cone 10 RecipesDocument7 pagesTen Cone 10 RecipesStefan Van Cleemput100% (1)
- Midyear Assessment General Chemistry 1Document7 pagesMidyear Assessment General Chemistry 1Jabeguero Marvelyn JessicaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Fluidized-Bed Chemical Processes: Butterworths Monographs in Chemical EngineeringFrom EverandFundamentals of Fluidized-Bed Chemical Processes: Butterworths Monographs in Chemical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Material Specification Sheet Saarstahl - 51Crv4 (50Crv4)Document3 pagesMaterial Specification Sheet Saarstahl - 51Crv4 (50Crv4)anilNo ratings yet
- Failure Analysis of Paints and Coatings: Revised EditionDocument15 pagesFailure Analysis of Paints and Coatings: Revised EditionDominika LisNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes Summative TestDocument2 pagesVolcanoes Summative Testjoan marie Pelias100% (3)
- Science 9 Second Quarter ExamDocument3 pagesScience 9 Second Quarter ExamMARY ROSE D. BORINAGANo ratings yet
- Summative Test On ChemistryDocument2 pagesSummative Test On ChemistryAngelyn P GultianoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Sma 2: FINAL EXAM SEM-2 2013/2014Document3 pagesChemistry Sma 2: FINAL EXAM SEM-2 2013/2014Arda RahmainiNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Petroleum Chemistry WS PDFDocument3 pagesIGCSE Petroleum Chemistry WS PDFNazarNo ratings yet
- High School 2 Worksheet Question Ans 09-22Document7 pagesHigh School 2 Worksheet Question Ans 09-22Jasmina DezmicNo ratings yet
- Cambridge School, Greater Noida: Class 8 Ch-Coal and Petroleum WorksheetDocument2 pagesCambridge School, Greater Noida: Class 8 Ch-Coal and Petroleum Worksheetrithvik evokeNo ratings yet
- First Sequence Chemistry Lss PrestigeDocument5 pagesFirst Sequence Chemistry Lss PrestigerichardNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledT20 world cup 2022No ratings yet
- Fire Protection and Investigation QADocument6 pagesFire Protection and Investigation QAMandanas GabrielNo ratings yet
- Indicate The Answer Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument19 pagesIndicate The Answer Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionRaabiah AzeezNo ratings yet
- Diamond Stone International School IGCSE Weekly Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesDiamond Stone International School IGCSE Weekly Lesson PlanjanithaNo ratings yet
- REVIEWDocument3 pagesREVIEWMikee MercadoNo ratings yet
- AteverwDocument2 pagesAteverw0divide1No ratings yet
- Long Quiz in Science 7Document2 pagesLong Quiz in Science 7janecil bonzaNo ratings yet
- Kumpulan Soal PTK Untuk Uas Surya Ayuati Ning Asih (1606905310)Document11 pagesKumpulan Soal PTK Untuk Uas Surya Ayuati Ning Asih (1606905310)Ranya JamalNo ratings yet
- MidtermDocument6 pagesMidtermJAnnisCatianNo ratings yet
- Universal Colleges of Paranaque, IncDocument3 pagesUniversal Colleges of Paranaque, IncInvincibleReineNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer (Chemistry)Document10 pagesScience Reviewer (Chemistry)CHRISTIAN NOE BONGALBALNo ratings yet
- Section 5 Fossil Fuels: CE: Section 5 MC P.1Document4 pagesSection 5 Fossil Fuels: CE: Section 5 MC P.1Kai Keung ChiuNo ratings yet
- RWS-4 TEE-Gr VIII - Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument2 pagesRWS-4 TEE-Gr VIII - Carbon and Its Compoundskinshuk.pradhanNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Geology Midsem AnswersDocument5 pagesPetroleum Geology Midsem AnswersSylvester TetteyNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 Crude Oil JCAFDocument12 pagesTopic 9 Crude Oil JCAFEllson LinNo ratings yet
- Combustion and Flame CPPDocument1 pageCombustion and Flame CPPNischal Reddy Sareddy100% (1)
- Instructions: Please Do Not Write Anything On The Questionnaires. The Correct Answer and Write in The Answer Sheet Provided. Multiple ChoicesDocument4 pagesInstructions: Please Do Not Write Anything On The Questionnaires. The Correct Answer and Write in The Answer Sheet Provided. Multiple ChoicesemeraldNo ratings yet
- Power Plant EngineeringDocument2 pagesPower Plant EngineeringMaydonuts C JaycoNo ratings yet
- Avionics General Equipment Uas 2022Document3 pagesAvionics General Equipment Uas 2022Dina HerdianaNo ratings yet
- 238 Exam SpringDocument18 pages238 Exam SpringNasyaNo ratings yet
- CE 112 Modular Quiz I. Multiple Choice:: (Type Here) Deadline at 11:59Pm TodayDocument3 pagesCE 112 Modular Quiz I. Multiple Choice:: (Type Here) Deadline at 11:59Pm TodayWild RiftNo ratings yet
- CE 112 Modular Quiz I. Multiple Choice:: (Type Here) Deadline at 11:59Pm TodayDocument3 pagesCE 112 Modular Quiz I. Multiple Choice:: (Type Here) Deadline at 11:59Pm TodayCzesarinePreciousJadeManibogNo ratings yet
- Midterm Examination Fire Protection and Arson InvestigationDocument2 pagesMidterm Examination Fire Protection and Arson InvestigationRodne Badua RufinoNo ratings yet
- Fire Technology and Arson InvestigatiionDocument4 pagesFire Technology and Arson InvestigatiionRico T. MusongNo ratings yet
- 3 of 3 Worksheet Class Viii Science L-6combustion and FlameDocument4 pages3 of 3 Worksheet Class Viii Science L-6combustion and FlameRekha kumariNo ratings yet
- Concept Review Chapt 17 Students 1Document5 pagesConcept Review Chapt 17 Students 1api-390763404No ratings yet
- 8 GS-UT1 L-2 & 6 Workheets 2023-24Document5 pages8 GS-UT1 L-2 & 6 Workheets 2023-24sathishprabhu10011984No ratings yet
- Admission Test-Fall 2017Document9 pagesAdmission Test-Fall 2017Ihsaan gulzarNo ratings yet
- Science JHS 1 - 1Document5 pagesScience JHS 1 - 1stanleyaklikaNo ratings yet
- Fossil Fuels Notes OutlineDocument8 pagesFossil Fuels Notes OutlineJoenetha Ann Aparici0% (1)
- Fire-tech-&-Arson TupeDocument15 pagesFire-tech-&-Arson TupeChristopher LlonorNo ratings yet
- Review Material Forn ChEDocument10 pagesReview Material Forn ChENobi PanisiganNo ratings yet
- Q4 - 3rd SummativeDocument2 pagesQ4 - 3rd SummativeRowenickNo ratings yet
- Quiz 9Document3 pagesQuiz 9James Rholdan PiedadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document3 pagesChapter 7Misbah Sajid ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- Che 520L Integrated Activity 1-Calculations 1 & 2 2 Sem 2018-19Document5 pagesChe 520L Integrated Activity 1-Calculations 1 & 2 2 Sem 2018-19Joice Bundang ManingoNo ratings yet
- MCQS Group B (Section-II) PDFDocument10 pagesMCQS Group B (Section-II) PDFCenter of KnowledgeNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Science Worksheet - Combustion and Flame Part BDocument2 pagesClass 8 Science Worksheet - Combustion and Flame Part Bsana100% (2)
- A. B. C. D.: Quiz 1 BWD 11103 (Organic Chemistry) Name: Matrix No.Document2 pagesA. B. C. D.: Quiz 1 BWD 11103 (Organic Chemistry) Name: Matrix No.Syazwan SamsudinNo ratings yet
- 1 Chemistry Jdjei Opek JeiDocument3 pages1 Chemistry Jdjei Opek JeiMahater SalicNo ratings yet
- FRI Entrance Exam: Sample QuestionsDocument25 pagesFRI Entrance Exam: Sample QuestionsDasSonamNo ratings yet
- Fire SafetyDocument4 pagesFire SafetyEunicia BascoNo ratings yet
- Chem f4 SX Y5Document45 pagesChem f4 SX Y5cazmi AndirahmanNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Materials Class Test 4Document2 pagesAircraft Materials Class Test 4SeanRiniFernandoNo ratings yet
- Green Chem PasscoDocument6 pagesGreen Chem PasscoAtanga EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Unit I. Chemistry and Us Factual KnowledgeDocument31 pagesChemistry: Unit I. Chemistry and Us Factual KnowledgeMARICEL MIRANDANo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Exam in Science 9 Q2Document3 pages2nd Quarter Exam in Science 9 Q2Arriane Joy ToledoNo ratings yet
- Formo ONE Term Exam - Doc 2019 Set 1-1Document8 pagesFormo ONE Term Exam - Doc 2019 Set 1-1Elkana PutinNo ratings yet
- Forester & Forest Guard 3 (GS) - WWW - Governmentexams.co - inDocument36 pagesForester & Forest Guard 3 (GS) - WWW - Governmentexams.co - inmagi20047No ratings yet
- Making Graph From The Experiment Results Making Graph From The Experiment ResultsDocument1 pageMaking Graph From The Experiment Results Making Graph From The Experiment ResultsMahyuddin AlghowryNo ratings yet
- Final Test Semester Ii Smas Metro School TAHUN PELAJARAN 2017/2018Document3 pagesFinal Test Semester Ii Smas Metro School TAHUN PELAJARAN 2017/2018Mahyuddin AlghowryNo ratings yet
- Name:: B. Make A Paragraph With Minimum 5 Paragraphs Using at Least 8 Words You Found in The CrosswordsDocument2 pagesName:: B. Make A Paragraph With Minimum 5 Paragraphs Using at Least 8 Words You Found in The CrosswordsMahyuddin AlghowryNo ratings yet
- 7HW Identifying MixturesDocument2 pages7HW Identifying MixturesMahyuddin AlghowryNo ratings yet
- Why Plastic Parts FailDocument4 pagesWhy Plastic Parts FailGowtham Kae KaeNo ratings yet
- Rtep1 Ipe2Document52 pagesRtep1 Ipe2Jyvan CaidocNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Water ChemistryDocument15 pagesUnit-2 Water ChemistryKunjal singhNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/52Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/52Megan AlbuquerqueNo ratings yet
- PBC® Battery OverviewDocument2 pagesPBC® Battery OverviewNikša StanojevićNo ratings yet
- Mass Relationships in Chemical ReactionsDocument28 pagesMass Relationships in Chemical ReactionsAries MalicdemNo ratings yet
- Filox RDocument6 pagesFilox RMahmudul HasanNo ratings yet
- XII Organic Reasoning QuestionsDocument7 pagesXII Organic Reasoning QuestionslakshvanthbalaNo ratings yet
- Assessment 6 (Concentration of Solution)Document2 pagesAssessment 6 (Concentration of Solution)shaneeeeNo ratings yet
- J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 15692Document4 pagesJ. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 15692CarlotaNo ratings yet
- Passivation: Corrosion ProtectionDocument51 pagesPassivation: Corrosion ProtectiondangminhNo ratings yet
- EHC 45 65 Sell Sheet 034 NewDocument2 pagesEHC 45 65 Sell Sheet 034 NewJahmia CoralieNo ratings yet
- 2013 Lect4c Epoxidation S of AlkenesDocument20 pages2013 Lect4c Epoxidation S of AlkenesBagusNo ratings yet
- Redox Review With ANSWERS - 4Document13 pagesRedox Review With ANSWERS - 4AYESHA NAAZNo ratings yet
- Biogas Generator PDFDocument5 pagesBiogas Generator PDFamerican_guy10No ratings yet
- SR No Industry Segment Sub Segment (Mining / Processing / Manufacturing)Document4 pagesSR No Industry Segment Sub Segment (Mining / Processing / Manufacturing)Vivek SengarNo ratings yet
- Test 2 - Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins and Nucleic AcidsDocument7 pagesTest 2 - Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins and Nucleic AcidsChrisNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 Alcohols & EthersDocument6 pagesUnit 11 Alcohols & EthersDeepesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Luanshya Akatiti DamDocument6 pagesLuanshya Akatiti DamRamoutar (Ken) SeecharranNo ratings yet
- Progress in Energy and Combustion ScienceDocument24 pagesProgress in Energy and Combustion ScienceIntenNo ratings yet
- Krantiaagrani G. D. Bapu Lad Mahavidyalay Kundal ,: "Study of Soap"Document14 pagesKrantiaagrani G. D. Bapu Lad Mahavidyalay Kundal ,: "Study of Soap"Sourabh KoliNo ratings yet
- Elements Project - CobaltDocument7 pagesElements Project - CobaltXoom JbNo ratings yet
- 2003 - Fukuoka - A Novel Non-Phosgene Polycarbonate Production Process Using By-Product CO2 As Starting MaterialDocument11 pages2003 - Fukuoka - A Novel Non-Phosgene Polycarbonate Production Process Using By-Product CO2 As Starting MaterialViraj EdirisingheNo ratings yet