Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Animal Tissues: Types, Structure and Functions
Uploaded by
L.C. GOYALOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Animal Tissues: Types, Structure and Functions
Uploaded by
L.C. GOYALCopyright:
Available Formats
AMITY INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL, NOIDA
CLASS-IX
BIOLOGY
HANDOUT
TOPIC-ANIMAL TISSUES
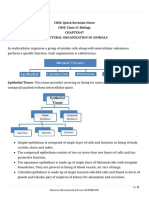
TYPES OF ANIMAL TISSUES:
1. Epithelial tissues- Protection ,secretion and absorption
2. Muscular Tissues- Movement and locomotion
3. Connective Tissue- Binding, support,protection,transport and circulation
4. Nervous Tissues- Conduction of nerve impulse, control and coordination of body.
EPITHELIAL TISSUE
S.No Type Structure Location Functions
1 Squamous Thin flattened cells From lining of Diffusion of
Epithelium with a centrally placed mouth, materials or
nucleus. oesophagus exchange of
Irregular-shaped cells, and lungs gases.
compactly arranged. Inner lining of Protection
blood vessels from
Cover the skin chemical and
surface mechanical
(stratified injury.
epithelium) Entry of
germs or
from drying.
2 Cuboidal Cube like cells with a Lining of kidney Secretion,
Epithelium central spherical tubules, lining of excretion and
nucleus salivary, absorption
pancreatic and
sweat ducts
3 Columanar Tall, pillar or column Lining of Secretion and
Epethelium like cells with nucleus stomach, intestine absorbtion
at the base and gall bladder
4 Ciliated Certain cuboidal and Oviducts, trachea, Movement of
Epethelium columner epithelium bronchioles and cilia direct the
have Cilia at their free in parts of flow of fluids in
ends. Cilia are thin, nephron in a particular one
hair like projections kidney. direction
that move to and fro.
5 Glandular Cuboidal and columner Salivary, gastric, Secretes
Epethelium epithelium are intestinal and seat enzymes,
modified into glands glands mucous or
hormones
CONNECTIVE TISSUE
A composite tissue, it has following three basic components –
1. Cells – Living part, loosely spaced, embedded in the matrix.
2. Fibres – Non-living part, several types, scattered in between the cells.
3. Matrix – Basic ground tissue, may be jelly like, fluid dense or rigid. Matrix
decides the nature and function of the connective tissue.
Functions
1. Binding and packaging tissue
2. Other function include storing fat, transporting substances depending on the
location of the tissue.
S No. Type of Matrix Type of Tissue Functions
1 Fluid Blood Helps in transport of various
substances.
Red blood cells carry oxygen since they
contain haemoglobin.
White blood cells provide immunity to
the body.
Platelets help in blood clotting
2 Solid Bone It is an important component of the
(Rich in skeletal framework
calcium & Provides strength & support to the
Phosphorus) body.
3 Solid Cartilage It is an important structural component
(Rich in of the body along with the bones.
proteins & Found in external or pinna and tip if the
Sugars) nose.
4 Solid Tendon Tendon connects a bone to a muscle
5 Solid Ligament Connects bone to another bone at the joints
6 Semi-solid Areolar Tissue It fills the cavities inside the organs
Provide support to the organs
Helps in repair of tissues
7 Semi-Solid Adipose Tissue Acts as an insulator
(Rich in Acts as a shock absorber
adipocytes)
Differences between Tendons and Ligament –
S No Tendon Ligaments
1 Tendons are very tough and non- Ligaments are very elastic
elastic
2 Connects skeletal muscles to the Connects a bone to another bone at the
bones joint
3 Made up of more amount of fibrous Made up of elastic fibres
tissue
4 Show great strength but limited Are very flexible
flexibility
MUSCULAR TISSUE
S No Striated Muscles Non-striated Muscle Cardiac Muscle
1 Also called as skeletal Also called as smooth or Also called as Heart
or voluntary muscles involuntary muscle. musce
2 Attached to the bones Present within the walls Present in the wall of the
of the body of the body organs like heart.
stomach, intestine,
bronchi etc. Also found
in blood vessels, irish of
eye
3 Elongated, cylindrical Spindle shaped and Elongated, cylindrical and
and unbranched tapering at the ends branched.
4 Light and dark bands No striations Faint regular striations
present
5 Multi-nucleate Uni-nucleate One or two nuclei
6 Voluntary Involuntary Involuntry
7 Undergo rapid Undergo slow and Undergo continous and
contraction, rhythmic contraction. Do rhythmic, contractions and
Get tired easily not get tired easily. relaxations without getting
fatigued
NERVOUS TISSUE
Nervous tissue is made up of millions of nerve cells calls neurons. Neurons are highly
specialized cells. Brain, spinal cord and nerves are all composed of neurons.
Structure –
A neuron consist of following parts –
1. Cell body or cyton – Has nucleus and cytoplasm. Cytoplasm has nissl’s granules.
2. Dendrites –
Fine branched fibres arising out of cell body.
Numerous in number.
Carry impulses towards the cell body
3. Axon –
Single elongated fibre also called nerve fibre
Generally unbranched.
Ends in many end fibres.
Conducts nerve impulses away from cell body
Functions of Nervous Tissue –
1. Specialized to receive and transmit messages in the body
2. Dendrites receives the impulse and axon take the impulse away from the cell body.
S No Dendrites Axon
1 Short, numerous and branched Long, generally unbranched – may be 1
or 2
2 Carry impulses towards the cell Carry impulses away from the cell body
body of the neuron of the neuron
You might also like
- Handout-Animal-Tissues-2023-2024Document4 pagesHandout-Animal-Tissues-2023-2024reece sayamNo ratings yet
- ANIMAL TISSUES AND ORGAN SYSTEMSDocument7 pagesANIMAL TISSUES AND ORGAN SYSTEMSKenneth Rodriguez HerminadoNo ratings yet
- Cell Types 1Document28 pagesCell Types 1IngridNo ratings yet
- HUMAN TISSUE PRESENTATIONDocument47 pagesHUMAN TISSUE PRESENTATIONAngelo Cadenas75% (4)
- CH 7 - Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument8 pagesCH 7 - Structural Organisation in AnimalsLaxmiNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheets Animal Cell TypesDocument4 pagesFact Sheets Animal Cell Typessamsung picturesNo ratings yet
- MAHANDocument9 pagesMAHANKANT JAMES D. MAHANNo ratings yet
- BIO122 - CHAPTER 7 Part 1Document53 pagesBIO122 - CHAPTER 7 Part 1lili100% (1)
- 1.1 Animal's Specialized StructuresDocument58 pages1.1 Animal's Specialized StructuresNathaliabee100% (1)
- Tissue Types and FunctionsDocument31 pagesTissue Types and Functionsaliyyah aswinanda100% (1)
- Tissues Level OrganizationDocument60 pagesTissues Level OrganizationHilman YusriNo ratings yet
- The Four Major Tissue Types: Epithelial, Connective, Muscle and Nervous (less than 40 charsDocument29 pagesThe Four Major Tissue Types: Epithelial, Connective, Muscle and Nervous (less than 40 charsGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in Animals Revision NotesDocument10 pagesStructural Organisation in Animals Revision NotesHarismita AlagurajNo ratings yet
- Structural Organization in AnimalsDocument7 pagesStructural Organization in AnimalsVedant BondeNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Tissues - ObjectivesDocument7 pagesPlant and Animal Tissues - ObjectivesSyedrijal AkberNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganizationDocument8 pagesCell OrganizationKiele Nicole Calansingin100% (1)
- 3 Animal Tissues Structure and FunctionDocument16 pages3 Animal Tissues Structure and FunctionIce ShadowNo ratings yet
- Tissue Membranes GuideDocument4 pagesTissue Membranes GuideElleNo ratings yet
- Tissues NTBDocument39 pagesTissues NTBAuthor ClubNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 7Document10 pages11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 7Saurav Soni100% (1)
- Zoology Notes: 007 Chapter 4Document4 pagesZoology Notes: 007 Chapter 4humanupgradeNo ratings yet
- BIOL223-Lab 9Document53 pagesBIOL223-Lab 9chicken fries100% (1)
- Lesson 6 - Tissues PDFDocument70 pagesLesson 6 - Tissues PDFVjay Payumo100% (1)
- Chapter 6Document36 pagesChapter 6Nur-aine Hajijul100% (1)
- Chapter 7 Points To RememberDocument7 pagesChapter 7 Points To RememberNANDA KISHORE S X A AD : 1 0 6 4 4100% (1)
- Cell TissuesDocument28 pagesCell TissuesStifany Dianne VillasNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument6 pagesAnimal TissueSarveshrau MagentharauNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Chapter 4Document4 pagesAnaphy Chapter 4Riy KimNo ratings yet
- Tissue of The BodyDocument12 pagesTissue of The BodyJuliet Aira Cabero Quibilan100% (1)
- Tissues, Glands and Membranes: A. FunctionsDocument4 pagesTissues, Glands and Membranes: A. FunctionsRyan Cadorna FontanillaNo ratings yet
- BIOL 1409 - Animal - Tissues - LR - Lab Report 4Document11 pagesBIOL 1409 - Animal - Tissues - LR - Lab Report 4Tonya Oliver100% (1)
- 9 Biology - Tissues (Animal Tissues) - Notes & Video LinkDocument9 pages9 Biology - Tissues (Animal Tissues) - Notes & Video Linksaragrover095No ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument14 pagesAnimal TissueSagar GavasNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - TissuesDocument43 pagesAnatomy - TissuesGleceree Filomeno100% (1)
- Answers UNIT 2 Lesson 2.2 Structures of Animal CellsDocument7 pagesAnswers UNIT 2 Lesson 2.2 Structures of Animal CellsKatznjammrNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue TypesDocument17 pagesAnimal Tissue TypesMuskan Shree100% (1)
- Biology 1Document11 pagesBiology 1Francois Isabelo EspirituNo ratings yet
- Tissue Structure & FunctionDocument74 pagesTissue Structure & FunctionTaufiqurrahman Sidqi100% (1)
- ANIMAL-CELL group 2Document35 pagesANIMAL-CELL group 2mjecbjNo ratings yet
- Physiology - 4th SemDocument76 pagesPhysiology - 4th SemSandeep AdapalaNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument61 pagesStructural Organisation in AnimalsGanesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Genzoo Reviewer 1st SemDocument4 pagesGenzoo Reviewer 1st SememilpauloquibilanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes CBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-07 Structural Organization in AnimalsDocument11 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes CBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-07 Structural Organization in AnimalsjituxNo ratings yet
- Tissues - Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesTissues - Anatomy and PhysiologyHan CallejaNo ratings yet
- Histology: The Study of TissuesDocument39 pagesHistology: The Study of TissuesEla Santos100% (1)
- Cell Organisation NotesDocument15 pagesCell Organisation Notessylent gohNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6 Tissues Animal Tissues: Tissue Is A Cellular Organizational Level Intermediate Between Cells andDocument5 pagesChapter-6 Tissues Animal Tissues: Tissue Is A Cellular Organizational Level Intermediate Between Cells andMonika MehanNo ratings yet
- Structural Organization in Animals Animal TissuesDocument3 pagesStructural Organization in Animals Animal TissuesHadiya FatimaNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument44 pagesAnimal TissuesMary Sutingco100% (1)
- M 1 PPT-PDF XI Bio CH 7 Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument39 pagesM 1 PPT-PDF XI Bio CH 7 Structural Organisation in Animalsamarendrar87No ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document18 pagesGeneral Biology 2ayah eliviaNo ratings yet
- 1.2. Support and Movement SystemsDocument16 pages1.2. Support and Movement SystemssamiktshyagiriNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument2 pagesTissuesDinesh0% (1)
- The Four Primary Tissue Types:: Epithelial (Covering) Connective Tissue (Support) Muscle (Movement) Nervous (Control)Document33 pagesThe Four Primary Tissue Types:: Epithelial (Covering) Connective Tissue (Support) Muscle (Movement) Nervous (Control)Maira Garcia C.100% (2)
- Histologi Dasar (Jaringan Tubuh) : Bioetical Focus: Transplantasi Organ Tubuh Dan Bedah PlastikDocument19 pagesHistologi Dasar (Jaringan Tubuh) : Bioetical Focus: Transplantasi Organ Tubuh Dan Bedah PlastikKristin Natal Riang GeaNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue PPT by KanishkaDocument20 pagesAnimal Tissue PPT by KanishkaKanishka SharmaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4. AnswersDocument5 pagesExperiment 4. AnswersChristian Roy CNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues 2023Document70 pagesAnimal Tissues 2023yxcz.rzNo ratings yet
- Exercises 1 Tissues: 1. Define What Tissues AreDocument9 pagesExercises 1 Tissues: 1. Define What Tissues AreMaria MarmitaNo ratings yet
- Amity International School, Noida: Phone(s) : 4399000, 4399135 ReceiptDocument1 pageAmity International School, Noida: Phone(s) : 4399000, 4399135 ReceiptL.C. GOYALNo ratings yet
- Amity International School, Noida: Phone(s) : 4399000, 4399135 ReceiptDocument1 pageAmity International School, Noida: Phone(s) : 4399000, 4399135 ReceiptL.C. GOYALNo ratings yet
- Triangular Excavation and Then Refilling With 2B Material in 12Document1 pageTriangular Excavation and Then Refilling With 2B Material in 12L.C. GOYALNo ratings yet
- Amity International School, Noida: Phone(s) : 4399000, 4399135 ReceiptDocument1 pageAmity International School, Noida: Phone(s) : 4399000, 4399135 ReceiptL.C. GOYALNo ratings yet
- Student Fee ReceiptDocument1 pageStudent Fee ReceiptL.C. GOYALNo ratings yet
- Student Fee ReceiptDocument1 pageStudent Fee ReceiptL.C. GOYALNo ratings yet
- Amity International School, Noida: Phone(s) : 4399000, 4399135 ReceiptDocument1 pageAmity International School, Noida: Phone(s) : 4399000, 4399135 ReceiptL.C. GOYALNo ratings yet
- QewqDocument1 pageQewqL.C. GOYALNo ratings yet
- Amity International School, Noida: Phone(s) : 4399000, 4399135 ReceiptDocument1 pageAmity International School, Noida: Phone(s) : 4399000, 4399135 ReceiptL.C. GOYALNo ratings yet
- A New Approach in Determining The Load Transfer Mechanism in Fully Grouted BoltsDocument45 pagesA New Approach in Determining The Load Transfer Mechanism in Fully Grouted BoltsL.C. GOYALNo ratings yet
- QewqDocument1 pageQewqL.C. GOYALNo ratings yet
- EwfjhjkewhnjkewDocument2 pagesEwfjhjkewhnjkewL.C. GOYALNo ratings yet
- MARCH 2003 Comments:: Everest Power Private Limited Detailed ProjectDocument10 pagesMARCH 2003 Comments:: Everest Power Private Limited Detailed ProjectL.C. GOYALNo ratings yet
- MARCH 2003 Comments:: Everest Power Private Limited Detailed ProjectDocument10 pagesMARCH 2003 Comments:: Everest Power Private Limited Detailed ProjectL.C. GOYALNo ratings yet
- Histological Techniques and Principles Behind Micros Copies (LM TEM)Document7 pagesHistological Techniques and Principles Behind Micros Copies (LM TEM)Aslak TorgersenNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues Lab SlidesDocument21 pagesAnimal Tissues Lab SlidesMichaelNo ratings yet
- Histotechnology Reading ListDocument1 pageHistotechnology Reading ListHassan Gill100% (1)
- Plant and Animal Cell WorksheetDocument3 pagesPlant and Animal Cell WorksheetCorey ColeNo ratings yet
- 01 01aLectureNotesDocument16 pages01 01aLectureNotesRosalie Jane OrtizNo ratings yet
- Lab ReviewerDocument3 pagesLab Reviewerryana cabreraNo ratings yet
- Quality Control in Histopathology - PPTX Edited - PPTX No 1Document30 pagesQuality Control in Histopathology - PPTX Edited - PPTX No 1Medicine 0786No ratings yet
- Connective TissuesstudDocument53 pagesConnective TissuesstudDanial Sharizul100% (1)
- Aging Skin Histology Physiology and PathologyDocument6 pagesAging Skin Histology Physiology and PathologyyadNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument21 pagesMorphology of Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDhanush VNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1: Bacteria: Course: B.Sc. Biotechnology Semester IiiDocument24 pagesUNIT 1: Bacteria: Course: B.Sc. Biotechnology Semester IiiPriya PankajNo ratings yet
- Cells Webquest Student HandoutDocument5 pagesCells Webquest Student Handoutapi-329978763No ratings yet
- Cell Structure Review QuizDocument2 pagesCell Structure Review QuizAbdulkarim AlrefaeNo ratings yet
- Cell AnalogyDocument2 pagesCell AnalogyAlessandra AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Revised syllabus for anatomy and physiology coursesDocument40 pagesRevised syllabus for anatomy and physiology coursesSrikutty DevuNo ratings yet
- Histology Report 10-06-2022Document2 pagesHistology Report 10-06-2022chloedee30No ratings yet
- Formatif - C2 Cell Biology and Organisation KSSMDocument22 pagesFormatif - C2 Cell Biology and Organisation KSSMadamNo ratings yet
- Bone DevelopmentDocument25 pagesBone DevelopmentZeyNo ratings yet
- 01 Animal TissueDocument8 pages01 Animal TissueRohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants - Mind MapsDocument2 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plants - Mind MapsanmolthegreatwarriorNo ratings yet
- Biology 223 Exam 1 Study GuideDocument6 pagesBiology 223 Exam 1 Study GuideMartina MicicNo ratings yet
- Decalcification: MR G.P. Tiwari Technologist Tata Memorial HospitalDocument42 pagesDecalcification: MR G.P. Tiwari Technologist Tata Memorial HospitalGulab Chand Tiwari Tiwari100% (5)
- Hematology 1 (Laboratory) - Week 10-11 ModuleDocument8 pagesHematology 1 (Laboratory) - Week 10-11 ModuleJam RamosNo ratings yet
- Bio411 Lab Report 2Document25 pagesBio411 Lab Report 2Nur Aqillah100% (1)
- Penampakan Paramoeba Dan NeoparamoebaDocument3 pagesPenampakan Paramoeba Dan NeoparamoebaSyarif Hidayat AmrullahNo ratings yet
- Hem Lab6 RBC Morph Incl F12Document7 pagesHem Lab6 RBC Morph Incl F12Elvan Dwi WidyadiNo ratings yet
- Mus Phys PartDocument13 pagesMus Phys PartJAGDEV PANESARNo ratings yet
- ABO and RH Blood GroupsDocument7 pagesABO and RH Blood GroupsShum Wing Hei JoanneNo ratings yet
- DG Gel Studies Reference Book (English)Document72 pagesDG Gel Studies Reference Book (English)Endah LestariNo ratings yet
- Atlas Diggs BiruDocument128 pagesAtlas Diggs Biruninik yosida71% (7)