Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CI-01 Mar06
Uploaded by
Aby BabuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CI-01 Mar06
Uploaded by
Aby BabuCopyright:
Available Formats
CIRCUIT
IDEAS
INFRARED BUG S.C. DW
IVEDI
T.K. HAREENDRAN cuit, in principle, con-
verts the IR signal pulse
T
his circuit can be used to de- trains into noticeable au-
tect the presence of modulated ral notes.
infrared signals in its vicinity S1 is used to switch
from any electronic source, for in- on/off mains power and
stance, an IR handheld remote control- LED1 indicates power-
ler. It can also be used for testing IR ‘on.’ Resistor R4 and
burglar alarm systems. zener diode ZD2 form
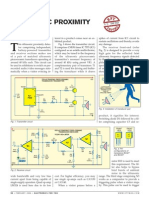
Fig. 1 shows the circuit of the in- a low-current voltage Fig. 2: Pin configurations of LM386, BC547/337 and UM66
frared bug. Besides the power supply stabiliser for providing
(one 9V PP3/6F22 compact battery steady 5.1V DC to the small signal- T2. The amplified signal is fed to the
pack), it consists of an infrared preamplifier circuit. IR LED1 is the melody generator via resistor R5. The
signal detector-cum-preamplifier main sensing element. output of the melody generator is fed
followed by a melody generator The IR signal detected by IR LED1 to LM386 low-power audio amplifier
and a tiny audio amplifier. The cir- is amplified by npn transistors T1 and (IC2) via variable resistor VR1, which
works as the volume control.
The loudspeaker sounds to in-
dicate the presence of IR signal
near the circuit.
IC LM386 is wired as a
minimum-parts amplifier with
a voltage gain of ‘20,’ which is
sufficient for this application.
Capacitor C3 is used for
decoupling of the positive rail
and the R-C combination net-
work comprising C4 and R7
bypasses high frequency to
ground.
The circuit can be easily
wired on a small veroboard or
any general-purpose PCB. Pin
configurations of IC LM386,
transistor BC547 and melody
generator UM66 are shown in
Fig. 2. A miniature metallic
cabinet may be used for enclos-
Fig. 1: Infrared bug ing the gadget. z
100 • MARCH 2006 • ELECTRONICS FOR YOU WWW.EFYMAG.COM
CMYK
You might also like
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Power Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsFrom EverandPower Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Project Parameters Control Panel: Pre-Define Input ParametersDocument11 pagesProject Parameters Control Panel: Pre-Define Input ParametersAzmiNo ratings yet
- Basics of Audio ElectronicsDocument8 pagesBasics of Audio ElectronicsPratibhaBhaskarNo ratings yet
- OBE Syllabus For Computer Programming 1Document6 pagesOBE Syllabus For Computer Programming 1LoiDa FloresNo ratings yet
- The ElektorDSP Radio Part 1Document6 pagesThe ElektorDSP Radio Part 1testNo ratings yet
- Training Manual: SAMSUNG Washing MachineDocument44 pagesTraining Manual: SAMSUNG Washing MachineCristobal Martinez100% (1)
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1From EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Laser Communication SystemDocument4 pagesLaser Communication Systemjose273No ratings yet
- Musical Light Chaser: IdeasDocument2 pagesMusical Light Chaser: IdeasJaveed AhamedNo ratings yet
- Using The Ne 602Document9 pagesUsing The Ne 602takajov540No ratings yet
- Spy EarDocument1 pageSpy EarAsad AbbasNo ratings yet
- 2-Pound RLC Meter Measures Impedance Using Sound CardDocument5 pages2-Pound RLC Meter Measures Impedance Using Sound Cardlm741No ratings yet
- Ultrasonic DetectorDocument2 pagesUltrasonic DetectorRev. Matthew100% (3)
- Add A Composite Video Input To A TVDocument6 pagesAdd A Composite Video Input To A TVEnya Andrea Ribba HernandezNo ratings yet
- Electronic Watch Dog - OptDocument2 pagesElectronic Watch Dog - OptJishu MojumderNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Block Diagram With Explanation:: Chapter-1Document27 pages1.2 Block Diagram With Explanation:: Chapter-1Vamshi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Designing For High Common-Mode Rejection in Balanced Audio InputsDocument7 pagesDesigning For High Common-Mode Rejection in Balanced Audio Inputsarness22No ratings yet
- BiDirectional Visitor CounterDocument4 pagesBiDirectional Visitor CounterashusvcstNo ratings yet
- 70501diDocument5 pages70501diDaniel EsquinaNo ratings yet
- Maplin Magazine-1986-12-1987-02-IDX-28Document1 pageMaplin Magazine-1986-12-1987-02-IDX-28thomtubesNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Read Range in RFID Systems: DesignfeatureDocument7 pagesOptimizing Read Range in RFID Systems: DesignfeaturePrajeesh RaviNo ratings yet
- Generate Melodies Using M348X ICDocument9 pagesGenerate Melodies Using M348X ICMagesh KumarNo ratings yet
- (Microchip) RFID Coil DesignDocument20 pages(Microchip) RFID Coil Designolaolaolaola123No ratings yet
- Project Report On Infra Red Remote ControlDocument19 pagesProject Report On Infra Red Remote ControlDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATE88% (8)
- A Low-Cost Surface Mount PIN Diode Attenuator: Application Note 1048Document6 pagesA Low-Cost Surface Mount PIN Diode Attenuator: Application Note 1048parsa mahvisNo ratings yet
- TesTer For RemoTe ConTrolCI-03 - Feb08Document1 pageTesTer For RemoTe ConTrolCI-03 - Feb08Alagappan Arunachalam100% (1)
- Stereo Peak Indicator: Small CircuitscollectionDocument1 pageStereo Peak Indicator: Small CircuitscollectionTariq Zuhluf100% (1)
- May 2003 Ray Marston - Understanding and Using OTA OP-Amps - Part 2Document5 pagesMay 2003 Ray Marston - Understanding and Using OTA OP-Amps - Part 2MeatheadMerlinNo ratings yet
- Adi Esr Allan Willcox 2Document3 pagesAdi Esr Allan Willcox 2Marincus AdrianNo ratings yet
- Build an AM or FM audio receiverDocument5 pagesBuild an AM or FM audio receiverTEDY-RNo ratings yet
- A Compact Network For Eliminating Parametric Oscillations in HigDocument4 pagesA Compact Network For Eliminating Parametric Oscillations in HigĐạt Trần DoãnNo ratings yet
- A Low-Cost Surface Mount PIN Diode π Attenuator PDFDocument8 pagesA Low-Cost Surface Mount PIN Diode π Attenuator PDFerdemsecenNo ratings yet
- Clap-activated switch using microphone and timer ICsDocument1 pageClap-activated switch using microphone and timer ICssulayajannyNo ratings yet
- Non Contact AC Power MonitorDocument1 pageNon Contact AC Power MonitorRev. MatthewNo ratings yet
- RF Signal Detector - PPTX 31005 & 31003Document10 pagesRF Signal Detector - PPTX 31005 & 31003SudheerSharmaShubhamNo ratings yet
- Electronic Car HornDocument2 pagesElectronic Car HornViraj ShirodkarNo ratings yet
- RCA-Ham - 8122 PADocument8 pagesRCA-Ham - 8122 PAFrancis BartheNo ratings yet
- Letterbox Letter CounterDocument27 pagesLetterbox Letter CounterSAMEULNo ratings yet
- Fig2 - Circuit-Nov 14 (Monitor For 6V - Page 83)Document1 pageFig2 - Circuit-Nov 14 (Monitor For 6V - Page 83)Alberto Del BosqueNo ratings yet
- Infrared Remote Control Receiver Module IRM-2638T: FeaturesDocument10 pagesInfrared Remote Control Receiver Module IRM-2638T: FeaturesDaniel Nicolae CiufudeanNo ratings yet
- A Low Power Bandgap Voltage Reference CircuitDocument4 pagesA Low Power Bandgap Voltage Reference Circuitpraben00001No ratings yet
- DESIGN GUIDE FOR THE Si3210Document16 pagesDESIGN GUIDE FOR THE Si3210Hinnich SaidNo ratings yet
- ALERT BIKE OWNERS OF THEFT WITH ANTI-THEFT ALARM CIRCUITDocument10 pagesALERT BIKE OWNERS OF THEFT WITH ANTI-THEFT ALARM CIRCUITMasood Anwar KhanNo ratings yet
- Motorola: Semiconductor Products NCDocument10 pagesMotorola: Semiconductor Products NCjm1503_772868557No ratings yet
- His Low-Cost Cordless Bug Can Transmit Voice Signals in FMDocument3 pagesHis Low-Cost Cordless Bug Can Transmit Voice Signals in FMDevadas100% (2)
- Circuit Ideas for a Brake Failure IndicatorDocument1 pageCircuit Ideas for a Brake Failure IndicatorBhagya ParmarNo ratings yet
- Intruder Alert Radio System Transmits Emergency MessageDocument1 pageIntruder Alert Radio System Transmits Emergency MessageShrivlsi RamNo ratings yet
- Fun Projects 32 ChapterDocument3 pagesFun Projects 32 ChaptertihomihoNo ratings yet
- DeepaksharmaDocument1 pageDeepaksharmaKumar AbhishekNo ratings yet
- 60 GHZ Transmitter Circuits in 65Nm Cmos: Rtuif-18Document4 pages60 GHZ Transmitter Circuits in 65Nm Cmos: Rtuif-18Ganagadhar CHNo ratings yet
- Fig 5Document1 pageFig 5Stand CostoNo ratings yet
- User Manual - ItDocument13 pagesUser Manual - ItBrayan OchoaNo ratings yet
- Mini Project ReportDocument15 pagesMini Project ReportShirsendu AcharyyaNo ratings yet
- CK1620 - Door Minder: ConstructionDocument3 pagesCK1620 - Door Minder: ConstructionIon GrigorashNo ratings yet
- 1 Level 1. LED Chaser: 74ls138 74ls163Document5 pages1 Level 1. LED Chaser: 74ls138 74ls163Sahil BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Double-Balanced Mixer and Oscillator: Philips SemiconductorsDocument12 pagesDouble-Balanced Mixer and Oscillator: Philips SemiconductorsAle MmsNo ratings yet
- Gigahertz Signal DetectorDocument2 pagesGigahertz Signal DetectorRamonNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: Afct-5941XtxzDocument15 pagesData Sheet: Afct-5941XtxzAnonymous G1iPoNOKNo ratings yet
- Luggage Security Alarm Using IC UM3561: Aman Chadha, and Abhijeet Ballani, TE, EXTCDocument5 pagesLuggage Security Alarm Using IC UM3561: Aman Chadha, and Abhijeet Ballani, TE, EXTCgobimohanNo ratings yet
- Build A Linear 2 Meter 80 W All Mode AmplifierDocument5 pagesBuild A Linear 2 Meter 80 W All Mode AmplifierMircea PetrescuNo ratings yet
- Petroleum RefiningDocument5 pagesPetroleum Refiningsandy2099No ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Plants: Understanding RadiationDocument4 pagesNuclear Power Plants: Understanding RadiationKunal MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- ECS2z SelfCD Wiring DiagramsDocument3 pagesECS2z SelfCD Wiring DiagramsAby Babu100% (1)
- Fan RegulatorDocument1 pageFan Regulatorvishnuu06No ratings yet
- DevOps Architect with 15+ Years Experience in AWS Migrations and CI/CDDocument2 pagesDevOps Architect with 15+ Years Experience in AWS Migrations and CI/CDMadhu DDDNo ratings yet
- APIs That SortDocument18 pagesAPIs That Sortrachmat99No ratings yet
- Real Time Delivery ReportDocument7 pagesReal Time Delivery Reportimtiyaz khanNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On "Payroll Management System "Document25 pagesA Project Report On "Payroll Management System "harsh talpadaNo ratings yet
- AcronisCyberProtect 15Document582 pagesAcronisCyberProtect 15Ivn Echegoyen RivasNo ratings yet
- Nexgenie Product BasketDocument16 pagesNexgenie Product BasketSonuOm0% (1)
- College Management System Project SrsDocument76 pagesCollege Management System Project Srslokesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Oracle FLEXCUBE Universal Banking 14-2-0 0 0 ReleaseNotesDocument21 pagesOracle FLEXCUBE Universal Banking 14-2-0 0 0 ReleaseNotesiyyanar135No ratings yet
- Electric Circuits PDFDocument9 pagesElectric Circuits PDFNancyNo ratings yet
- Pyronix Conqueror User GuideDocument8 pagesPyronix Conqueror User GuideAntonio LopezNo ratings yet
- Tps 65167 ADocument42 pagesTps 65167 AVikas Deoarshi100% (1)
- MCQ'sDocument10 pagesMCQ'ssjprabakarsathyNo ratings yet
- SSC GR 10 Electronics Q4 Module 1 WK 1 - v.01-CC-released-22May2021Document20 pagesSSC GR 10 Electronics Q4 Module 1 WK 1 - v.01-CC-released-22May2021Vj AleserNo ratings yet
- IoT Based Automated Indoor Agriculture SystemDocument6 pagesIoT Based Automated Indoor Agriculture SystemagitatedmorseNo ratings yet
- MVVM Vs MVP Vs MVCDocument5 pagesMVVM Vs MVP Vs MVCAnonymous YQSvqcQ6No ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Threads Chapter 4: Threads: Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts - 9 EditionDocument25 pagesChapter 4: Threads Chapter 4: Threads: Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts - 9 EditionJai KumarNo ratings yet
- Teradata FastExport: Export Data Lightning FastDocument11 pagesTeradata FastExport: Export Data Lightning FastKumar SattiNo ratings yet
- Fault Tolerance in Distributed SystemsDocument6 pagesFault Tolerance in Distributed SystemsHeidar Usmael JundiNo ratings yet
- Wiring Diagram PDFDocument1 pageWiring Diagram PDFNehal RaiNo ratings yet
- Requirements For Installing Oracle10gR2 On RHEL 5 OL 5 (x86 - 64) (Doc ID 421308.1)Document5 pagesRequirements For Installing Oracle10gR2 On RHEL 5 OL 5 (x86 - 64) (Doc ID 421308.1)elcaso34No ratings yet
- DesignDocument126 pagesDesignbelayNo ratings yet
- Ch4 Nodal and MeshDocument39 pagesCh4 Nodal and MeshAjmal BhattiNo ratings yet
- Vision and Scope Document For Chess GameDocument8 pagesVision and Scope Document For Chess Gamejacktheking20100% (2)
- EziView Brochure PDFDocument2 pagesEziView Brochure PDFharisNo ratings yet
- Norton TheoremDocument5 pagesNorton TheoremShameek PathakNo ratings yet
- ISC Computer Viva QuestionDocument7 pagesISC Computer Viva QuestionJojo Charles Xavier100% (2)
- Ic108a Ic109a R3 - 1 05 PDFDocument32 pagesIc108a Ic109a R3 - 1 05 PDFAlejandro MagnoNo ratings yet