Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fea Assignment 2
Uploaded by
Misbah PatelCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fea Assignment 2
Uploaded by
Misbah PatelCopyright:
Available Formats
Finite Element Analysis 2017-18
Assignment No.2
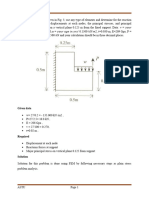
Title: Computer program for stress analysis of 2-D truss subjected to plane forces.
Aim: To perform displacement and stress analysis for the given 2D truss using MATLAB and
analytical expressions.
Problem Description:
For the Truss shown in Figure No.1 find the displacement of nodes, support reactions and
elemental stresses. Assume young modulus for truss material, E=210GPa and cross section
of each member is, A= 10*10^4 mm2. Also, solve the above truss problem using ANSYS to
validate the results.
`
Figure 1.1: 2D truss
Node Nos. x-coordinate (m) Y-coordinate (m)
1 0 0
2 1500 0
3 3000 0
4 2250 1250
5 750 1250
PES MCOE, Pune | Department of Mechanical Engineering 1
Finite Element Analysis 2017-18
MATLAB Program for 2-D Truss
%7-member truss practical assignment%
clc;
clear all;
E = 210*10^3;
A = 10*10^4;
L1 = ElementLength(0,0,1500,0)
L2 = ElementLength(1500,0,3000,0)
L3 = ElementLength(3000,0,2250,1250)
L4 = ElementLength(2250,1250,1500,0)
L5 = ElementLength(2250,1250,750,1250)
L6 = ElementLength(750,1250,1500,0)
L7 = ElementLength(750,1250,0,0)
theta1 = 0;
theta2 = 0;
theta3 = pi-tan(1250/750);
theta4 = tan(1250/750);
theta5 = 0;
theta6 = pi -tan(1250/750);
theta7 = tan(1250/750);
%Element Stiffness Matrices
K1 = ElementStiffness(E,A,L1,theta1)
K2 = ElementStiffness(E,A,L2,theta2)
K3 = ElementStiffness(E,A,L3,theta3)
K4 = ElementStiffness(E,A,L4,theta4)
K5 = ElementStiffness(E,A,L5,theta5)
K6 = ElementStiffness(E,A,L6,theta6)
K7 = ElementStiffness(E,A,L7,theta7)
kk1=zeros(10,10);
kk2=zeros(10,10);
kk3=zeros(10,10);
kk4=zeros(10,10);
kk5=zeros(10,10);
kk6=zeros(10,10);
kk7=zeros(10,10);
x=1;
kk1=make10by10(x,K1);
x=2;
kk2=make10by10(x,K2);
x=3;
kk3=make10by10(x,K3);
x=4;
kk4=make10by10(x,K4);
x=5;
kk5=make10by10(x,K5);
x=6;
kk6=make10by10(x,K6);
x=7;
kk7=make10by10(x,K7);
Kg=kk1+kk2+kk3+kk4+kk5+kk6+kk7
PES MCOE, Pune | Department of Mechanical Engineering 2
Finite Element Analysis 2017-18
% Boundary Conditions
Kr=[Kg(3,3) Kg(3,4) Kg(3,5) Kg(3,7) Kg(3,8) Kg(3,9) Kg(3,10);
Kg(4,3) Kg(4,4) Kg(4,5) Kg(4,7) Kg(4,8) Kg(4,9) Kg(4,10);
Kg(5,3) Kg(5,4) Kg(5,5) Kg(5,7) Kg(5,8) Kg(5,9) Kg(5,10);
Kg(7,3) Kg(7,4) Kg(7,5) Kg(7,7) Kg(7,8) Kg(7,9) Kg(7,10);
Kg(8,3) Kg(8,4) Kg(8,5) Kg(8,7) Kg(8,8) Kg(8,9) Kg(8,10);
Kg(9,3) Kg(9,4) Kg(9,5) Kg(9,7) Kg(9,8) Kg(9,9) Kg(9,10);
Kg(10,3) Kg(10,4) Kg(10,5) Kg(10,7) Kg(10,8) Kg(10,9) Kg(10,10)]
%Force Vector
F=[0;-8000;0;0;-5000;0;-10000];
%Displacement Vector
u=Kr\F
%Global Displacement Vector
U=[0;0;u(1,1);u(2,1);u(3,1);0;u(4,1);u(5,1);u(6,1);u(7,1)]
%Support Reaction
F=Kg*U
%Local Displacement Vectors
u1=U(1:4);
u2=U(3:6);
u3=U(5:8);
u4=[U(3,1);U(4,1);U(7,1);U(8,1)];
u5=U(7:10);
u6=[U(3,1);U(4,1);U(9,1);U(10,1)];
u7=[U(1,1);U(2,1);U(9,1);U(10,1)];
%Element Stresses
sigma1=ElementStress(E,L1,theta1,u1)
sigma2=ElementStress(E,L2,theta2,u2)
sigma3=ElementStress(E,L3,theta3,u3)
sigma4=ElementStress(E,L3,theta4,u4)
sigma5=ElementStress(E,L4,theta5,u5)
sigma6=ElementStress(E,L5,theta6,u6)
sigma7=ElementStress(E,L7,theta7,u7)
%Functions%
1. Element length
function [y] = ElementLength(x1,y1,x2,y2)
y = sqrt((x2-x1)^2+(y2-y1)^2);
end
2. Element stiffness
function [y] = ElementStiffness(E,A,L,theta)
c = cos(theta);
s = sin(theta);
y = ((E*A)/L)*[c*c c*s -c*c -c*s; c*s s*s -c*s -s*s; -c*c -c*s c*c c*s; -c*s -s*s c*s s*s];
end
PES MCOE, Pune | Department of Mechanical Engineering 3
Finite Element Analysis 2017-18
3. Makek10by10
function [y] = make10by10(x,K)
if (x==1)
i=1;j=2;m=3;n=4;
else
if (x==2)
i=3;j=4;m=5;n=6;
else
if (x==3)
i=5;j=6;m=7;n=8;
else
if (x==4)
i=3;j=4;m=7;n=8;
else
if (x==5)
i=7;j=8;m=9;n=10;
else
if (x==6)
i=3;j=4;m=9;n=10;
else
i=1;j=2;m=9;n=10;
end
end
end
end
end
end
kk=zeros(10,10);
kk(i,i)=K(1,1);
kk(i,j)=K(1,2);
kk(i,m)=K(1,3);
kk(i,n)=K(1,4);
kk(j,i)=K(2,1);
kk(j,j)=K(2,2);
kk(j,m)=K(2,3);
kk(j,n)=K(2,4);
kk(m,i)=K(3,1);
kk(m,j)=K(3,2);
kk(m,m)=K(3,3);
kk(m,n)=K(3,4);
kk(n,i)=K(4,1);
kk(n,j)=K(4,2);
kk(n,m)=K(4,3);
kk(n,n)=K(4,4);
y=kk;
end
4. Element Stress
function [y] = ElementStress(E,L,theta,u)
C=cos(theta);
S=sin(theta);
y=(E/L)*[-C -S C S]*u;
end
PES MCOE, Pune | Department of Mechanical Engineering 4
Finite Element Analysis 2017-18
OUTPUT
E = 2.1000e+11
A = 1.0000e-03
L1 = 1500
L2 = 1500
L3 = 1.4577e+03
L4 = 1.4577e+03
L5 = 1500
L6 = 1.4577e+03
L7 = 1.4577e+03
K1 =
14000000 0 -14000000 0
0 0 0 0
-14000000 0 14000000 0
0 0 0 0
K2 =
14000000 0 -14000000 0
0 0 0 0
-14000000 0 14000000 0
0 0 0 0
K3 = 1.0e+06 *
4.5499 6.6966 -4.5499 -6.6966
6.6966 9.8559 -6.6966 -9.8559
-4.5499 -6.6966 4.5499 6.6966
-6.6966 -9.8559 6.6966 9.8559
K4 = 1.0e+06 *
4.5499 -6.6966 -4.5499 6.6966
-6.6966 9.8559 6.6966 -9.8559
-4.5499 6.6966 4.5499 -6.6966
6.6966 -9.8559 -6.6966 9.8559
PES MCOE, Pune | Department of Mechanical Engineering 5
Finite Element Analysis 2017-18
K5 =
14000000 0 -14000000 0
0 0 0 0
-14000000 0 14000000 0
0 0 0 0
K6 = 1.0e+06 *
4.5499 6.6966 -4.5499 -6.6966
6.6966 9.8559 -6.6966 -9.8559
-4.5499 -6.6966 4.5499 6.6966
-6.6966 -9.8559 6.6966 9.8559
K7 = 1.0e+06 *
4.5499 -6.6966 -4.5499 6.6966
-6.6966 9.8559 6.6966 -9.8559
-4.5499 6.6966 4.5499 -6.6966
6.6966 -9.8559 -6.6966 9.8559
Kg = 1.0e+07 *
1.8550 -0.6697 -1.4000 0 0 0 0 0 -0.4550 0.6697
-0.6697 0.9856 0 0 0 0 0 0 0.6697 -0.9856
-1.4000 0 3.7100 -0.0000 -1.4000 0 -0.4550 0.6697 -0.4550 -0.6697
0 0 -0.0000 1.9712 0 0 0.6697 -0.9856 -0.6697 -0.9856
0 0 -1.4000 0 1.8550 0.6697 -0.4550 -0.6697 0 0
0 0 0 0 0.6697 0.9856 -0.6697 -0.9856 0 0
0 0 -0.4550 0.6697 -0.4550 -0.6697 2.3100 -0.0000 -1.4000 0
0 0 0.6697 -0.9856 -0.6697 -0.9856 -0.0000 1.9712 0 0
-0.4550 0.6697 -0.4550 -0.6697 0 0 -1.4000 0 2.3100 -0.0000
0.6697 -0.9856 -0.6697 -0.9856 0 0 0 0 -0.0000 1.9712
PES MCOE, Pune | Department of Mechanical Engineering 6
Finite Element Analysis 2017-18
Kr = 1.0e+07 *
3.7100 -0.0000 -1.4000 -0.4550 0.6697 -0.4550 -0.6697
-0.0000 1.9712 0 0.6697 -0.9856 -0.6697 -0.9856
-1.4000 0 1.8550 -0.4550 -0.6697 0 0
-0.4550 0.6697 -0.4550 2.3100 -0.0000 -1.4000 0
0.6697 -0.9856 -0.6697 -0.0000 1.9712 0 0
-0.4550 -0.6697 0 -1.4000 0 2.3100 -0.0000
-0.6697 -0.9856 0 0 0 -0.0000 1.9712
u=
-0.0006
-0.0025
-0.0011
-0.0002
-0.0017
-0.0010
-0.0019
U=
-0.0006
-0.0025
-0.0011
-0.0002
-0.0017
-0.0010
-0.0019
PES MCOE, Pune | Department of Mechanical Engineering 7
Finite Element Analysis 2017-18
F = 1.0e+04 *
-0.0000
1.2750
0.0000
-0.8000
1.0250
-0.5000
0.0000
-1.0000
sigma1 = -0.0866
sigma2 = -0.0696
sigma3 = -0.1239
sigma4 = 0.0635
sigma5 = -0.1084
sigma6 = 0.0323
sigma7 = -0.1541
PES MCOE, Pune | Department of Mechanical Engineering 8
Finite Element Analysis 2017-18
ANSYS REPORT
1. Modeling:-
a. Generation of Key points:
Preprocessor>Modeling>Create>Key points>In active CS.
Sr.No. Key point No. Co-ordinates (x,y)
1 1 (0,0)
2 2 (1500,0)
3 3 (3000,0)
4 4 (2250,1250)
5 5 (750,1250)
b. Create Lines:
Preprocessor>Modeling>Create>Lines>Straight Line>In active CS.
2.Assign the Element:
Preprocessor>Element type>Add /Edit /Delete>Link
Element assigned :-3D finitstn 180
3.Apply the real Constants:
Preprocessor>Real Constants>Add /Edit /Delete
Cross Sectional Area = 10*10^4 mm2
4. Apply Material Properties:
Preprocessor>Material Properties>Material models>Structural>Linear>Isotropic
Young’s Modulus = 210 GPa
Poisson’s Ratio = 0.3
5. Meshing:
Preprocessor>Meshing>Mesh>Line>Select the Lines>Mesh>OK.
1
ELEMENTS
MAR 14 2018
10:43:40
Y
Z X
Fig. 1.2:Generation of Elements
PES MCOE, Pune | Department of Mechanical Engineering 9
Finite Element Analysis 2017-18
B) Solver:-In this step the solution type and loads are defined.
a. Give solution type:
Solution>Analysis type>New Analysis>Static>OK.
b. Define Loads (Boundary Conditions):
1. Apply Displacement:
Solution> Define Loads> Apply>Structural>Displacement>All DOF= 0 on Node
no.1 (because they are fixed).
2. Apply Load:
Solution>Define Loads>Apply>Structural>Force/Moment→Force = -10000 N on
node no. 5, -8000 on node 2 and -5000 on node 4.
1
E-N
U
F
MAR 14 2018
09:44:47
Y
Z X
Fig. 1.3 Applying the Boundary Conditions
c. Solve the FEA Model:
Solution – Solve – Current LS.
C)Post processing:-In the post processing step the Deflection and stress plot are taken
and also the reaction values are taken.
Go to General Postproc>Read results>Last set.
a. Nodal displacement values plot:
PRINT U NODAL SOLUTION PER NODE
***** POST1 NODAL DEGREE OF FREEDOM LISTING *****
LOAD STEP= 0 SUBSTEP= 1
TIME= 1.0000 LOAD CASE= 0
THE FOLLOWING DEGREE OF FREEDOM RESULTS ARE IN THE GLOBAL COORDINATE SYSTEM
NODE UX UY UZ USUM
1 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000
2 0.54643E-03-0.21576E-02 0.0000 0.22257E-02
3 0.98571E-03 0.0000 0.0000 0.98571E-03
4 0.18750E-03-0.14466E-02 0.0000 0.14587E-02
5 0.85179E-03-0.17147E-02 0.0000 0.19147E-02
MAXIMUM ABSOLUTE VALUES
NODE 3 2 0 2
VALUE 0.98571E-03-0.21576E-02 0.0000 0.22257E-02
PES MCOE, Pune | Department of Mechanical Engineering 10
Finite Element Analysis 2017-18
b. Support Reactions:
PRINT REACTION SOLUTIONS PER NODE
***** POST1 TOTAL REACTION SOLUTION LISTING *****
LOAD STEP= 0 SUBSTEP= 1
TIME= 1.0000 LOAD CASE= 0
THE FOLLOWING X,Y,Z SOLUTIONS ARE IN THE GLOBAL COORDINATE SYSTEM
NODE FX FY FZ
1 -0.18190E-11 12750. 0.0000
3 10250.
TOTAL VALUES
VALUE -0.18190E-11 23000. 0.0000
c. Elemental stresses:
PRINT ELEMENT TABLE ITEMS PER ELEMENT
***** POST1 ELEMENT TABLE LISTING *****
STAT CURRENT
ELEM LS1
1 0.76500E-01
2 0.61500E-01
3 -0.11953
4 0.61225E-01
5 -0.93000E-01
6 0.32070E-01
7 -0.14869
MINIMUM VALUES
ELEM 7
VALUE -0.14869
MAXIMUM VALUES
ELEM 1
VALUE 0.76500E-01
PES MCOE, Pune | Department of Mechanical Engineering 11
Finite Element Analysis 2017-18
Conclusion:-
Result Matlab Ansys
Nodal Displacement Ux Uy Ux Uy
Element 1 0.0000000 0.0000000 0.0000 0.0000
Element 2 0.0005464 0.0021576 -0.0006 -0.0025
Element 3 0.0009857 0.0000000 -0.0011 0.0000
Element 4 0.0001875 0.0014466 -0.0002 -0.0019
Element 5 0.0008517 0.0017147 -0.0010 -0.0017
Element stress Sigma Sigma
0.07650 -0.0866
0.06150 -0.0696
-0.11953 -0.1239
0.06122 0.0635
-0.09300 -0.1084
0.03207 0.0323
-0.14869 -0.1541
Support Reaction Rx Ry Rx Ry
Node 1 0 12750 -0.18190E-11 12750
Node 3 0 10250 0 10250
PES MCOE, Pune | Department of Mechanical Engineering 12
You might also like
- Advanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionFrom EverandAdvanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionNo ratings yet
- Solving Trusses Including InclinedDocument24 pagesSolving Trusses Including Inclinedjikijoker0% (2)
- Computer Implementation (Matlab) 5 Bar Truss Assembly: Gpa and The Last One With E 70 Gpa. The Applied Load P 150 KNDocument2 pagesComputer Implementation (Matlab) 5 Bar Truss Assembly: Gpa and The Last One With E 70 Gpa. The Applied Load P 150 KNNeymarNo ratings yet
- Deber 1 OptimizacionDocument9 pagesDeber 1 OptimizacionAndrés ToalaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Algorithm Homework 1: Result and SolutionDocument5 pagesAdvanced Algorithm Homework 1: Result and Solutionkranthi chaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Computational AssignmentDocument16 pagesComputational AssignmentAshebirNo ratings yet
- TUGASDocument16 pagesTUGASAnggaNo ratings yet
- Flight Mechanics Tutorial Assignment AnalysisDocument16 pagesFlight Mechanics Tutorial Assignment AnalysisNicholas GiannelisNo ratings yet
- Caringal Activity 9 Application of System of Linear EquationDocument13 pagesCaringal Activity 9 Application of System of Linear EquationDummy AccNo ratings yet
- Submission of Term Work': Subject - CpmsDocument25 pagesSubmission of Term Work': Subject - CpmsPrakharNo ratings yet
- Exercise Prod Design PracticingDocument9 pagesExercise Prod Design PracticingLaura AlósNo ratings yet
- 26. ជា គីមហេងDocument5 pages26. ជា គីមហេងMaxc MixNo ratings yet
- High-Order Embedded Runge-Kutta-Nystrom FormulaeDocument10 pagesHigh-Order Embedded Runge-Kutta-Nystrom FormulaeMomentod'InerziaNo ratings yet
- Psa Lab 9.: Aim: Development of A Generalized Program For Load Flow Analysis Using Gauss SeidalDocument5 pagesPsa Lab 9.: Aim: Development of A Generalized Program For Load Flow Analysis Using Gauss SeidalYashodhan JaltareNo ratings yet
- EC Department Government Engineering College, RajkotDocument8 pagesEC Department Government Engineering College, RajkotArjunAgharaNo ratings yet
- Homework Assignment 3 Homework Assignment 3Document10 pagesHomework Assignment 3 Homework Assignment 3Ido AkovNo ratings yet
- DFGDDocument14 pagesDFGD北科大-劉千榮No ratings yet
- Linear Regression: Best Fit LineDocument4 pagesLinear Regression: Best Fit LinePAWAN TIWARINo ratings yet
- Tanagra Data Mining: SOM and Cluster AnalysisDocument21 pagesTanagra Data Mining: SOM and Cluster AnalysisVbg DaNo ratings yet
- ODE Curve Fitting & InterpolationDocument58 pagesODE Curve Fitting & InterpolationMelih TecerNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document10 pagesAssignment 1Farrina Aziz100% (1)
- Quiz 2-2engDocument2 pagesQuiz 2-2engOmar MamedovNo ratings yet
- Lucrarea 1 Si 2 Engleza Stancioiu Tg-JiuDocument10 pagesLucrarea 1 Si 2 Engleza Stancioiu Tg-JiuamocatoNo ratings yet
- 2 Linear RegressionDocument5 pages2 Linear RegressionRushabh VashikarNo ratings yet
- Matrices MatlabDocument10 pagesMatrices Matlabjose rubenNo ratings yet
- Crank and slider mechanism lab experiment resultsDocument18 pagesCrank and slider mechanism lab experiment resultsAfif HaziqNo ratings yet
- AE3110 Take-Home Test 1 Wing AnalysisDocument11 pagesAE3110 Take-Home Test 1 Wing AnalysisMuhammad Rizki ZuhriNo ratings yet
- Trial SBP SPM 2014 ADD MATH K2Document21 pagesTrial SBP SPM 2014 ADD MATH K2Cikgu Faizal100% (2)
- Test 3Document7 pagesTest 3Prashant ChaubeyNo ratings yet
- 7 LastDocument28 pages7 LastNand KumarNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Simulation Analysis and Trajectory Planning of A Moving Robot Based On ADAMSDocument7 pagesKinematics Simulation Analysis and Trajectory Planning of A Moving Robot Based On ADAMS阳智No ratings yet
- PEME200001 Mathematical Techniques 2Document10 pagesPEME200001 Mathematical Techniques 2Andrew AndersonNo ratings yet
- Multi-Field Formulations For Beam Elements: Chapter FourDocument6 pagesMulti-Field Formulations For Beam Elements: Chapter FourWeight lossNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication LabDocument83 pagesDigital Communication Labspicypoova_899586184No ratings yet
- Nama: Salwa Fasha Wijaya NPM: A1A020089 Kelas: 4C Prodi: Pendidikan Bahasa IndonesiaDocument12 pagesNama: Salwa Fasha Wijaya NPM: A1A020089 Kelas: 4C Prodi: Pendidikan Bahasa IndonesiaSalwa fasha WijayaNo ratings yet
- Nama: Faldi Hadi Prabowo NIM:11189070000032 Modul: Radiasi Benda Hitam Tanggal: 9 Desember 2020Document5 pagesNama: Faldi Hadi Prabowo NIM:11189070000032 Modul: Radiasi Benda Hitam Tanggal: 9 Desember 2020faldi irfanNo ratings yet
- Least Square LineDocument6 pagesLeast Square LineProfessor SaadNo ratings yet
- Tubes Anstruk Betul SekaliDocument113 pagesTubes Anstruk Betul Sekaliluqman HarunNo ratings yet
- m4l28 Lesson 28 The Direct Stiffness Method: Beams (Continued)Document15 pagesm4l28 Lesson 28 The Direct Stiffness Method: Beams (Continued)Vitor ValeNo ratings yet
- Exercises: C A+B D A-B E A B F A. BDocument9 pagesExercises: C A+B D A-B E A B F A. BDen CelestraNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Computer Graphics and Multimedia - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument9 pagesUnit 2 - Computer Graphics and Multimedia - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inPurvi MajokaNo ratings yet
- Trocio, Joshua ECE 412 Exp1Document6 pagesTrocio, Joshua ECE 412 Exp1Joshua TrocioNo ratings yet
- Basic Simulation Lab File 2Document40 pagesBasic Simulation Lab File 2test 1831No ratings yet
- Pedroni MITPress 2ndedition Solution Samples v3Document25 pagesPedroni MITPress 2ndedition Solution Samples v3Squall_DA0% (1)
- CE Conc. Manag.Document4 pagesCE Conc. Manag.CE20B1019 PradeebNo ratings yet
- A2 - Risk and Return & CAPM Jose SolivanDocument3 pagesA2 - Risk and Return & CAPM Jose SolivanJose Javier Solivan RiveraNo ratings yet
- Final Presentation of Dynamic StructuresDocument22 pagesFinal Presentation of Dynamic StructuresAdiprabowo WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Fourier Series: ECE 350 - Linear Systems I MATLAB Tutorial #6Document7 pagesTrigonometric Fourier Series: ECE 350 - Linear Systems I MATLAB Tutorial #6CatNo ratings yet
- Mumba Individual AlgosDocument5 pagesMumba Individual AlgosMusariri TalentNo ratings yet
- Advanced Statistics With MatlabDocument5 pagesAdvanced Statistics With MatlabRohit Vishal Kumar100% (2)
- Data Mining PortfolioDocument19 pagesData Mining PortfolioJohnMaynardNo ratings yet
- A Presentation ON Solving LPP BY Graphical Method: Submitted By: Kratika Dhoot MBA-2 SemDocument25 pagesA Presentation ON Solving LPP BY Graphical Method: Submitted By: Kratika Dhoot MBA-2 SemkratikadhootNo ratings yet
- Advanced AutoCAD® 2017: Exercise WorkbookFrom EverandAdvanced AutoCAD® 2017: Exercise WorkbookRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Mathematics for Electrical Engineering and ComputingFrom EverandMathematics for Electrical Engineering and ComputingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- Advanced Electric Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionFrom EverandAdvanced Electric Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionNo ratings yet
- International Maths Olympiad - Class 10 (With CD): Theories with examples, MCQs & solutions, Previous questions, Model test papersFrom EverandInternational Maths Olympiad - Class 10 (With CD): Theories with examples, MCQs & solutions, Previous questions, Model test papersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYFrom EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNo ratings yet
- V12 04 07 Hac From Mme PDFDocument18 pagesV12 04 07 Hac From Mme PDFHariharanNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Modified Oleo Strut Shock Absorber System in Aircraft Landing GearDocument4 pagesDesign and Analysis of Modified Oleo Strut Shock Absorber System in Aircraft Landing GearMisbah PatelNo ratings yet
- PPC Notes PDFDocument36 pagesPPC Notes PDFIbrahim UjjainwalaNo ratings yet
- PsychrometryDocument8 pagesPsychrometryMisbah PatelNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Design and Linear Static Analysis of Nose GearDocument8 pagesConceptual Design and Linear Static Analysis of Nose GearMisbah PatelNo ratings yet
- RPDocument10 pagesRPpatilsspNo ratings yet
- PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL-PPC NotesDocument128 pagesPRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL-PPC NotesDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATE100% (31)
- Numerical Investigation of Structural Design of Torsion Links in A Landing Gear Retraction MechanismDocument7 pagesNumerical Investigation of Structural Design of Torsion Links in A Landing Gear Retraction MechanismMisbah PatelNo ratings yet
- FE Analysis For Landing Gear of Test Air CraftDocument9 pagesFE Analysis For Landing Gear of Test Air CraftMisbah PatelNo ratings yet
- Ch03 Section14 Pressure Vessel Design PDFDocument10 pagesCh03 Section14 Pressure Vessel Design PDFrafaelkiNo ratings yet
- May Jun 2016Document3 pagesMay Jun 2016Misbah PatelNo ratings yet
- CH1 Production Planning& Control PDFDocument46 pagesCH1 Production Planning& Control PDFDharma RajaNo ratings yet
- Sampling & QuantizingDocument28 pagesSampling & QuantizingMisbah PatelNo ratings yet
- Love Me Do - The Beatles-Guitar Strumming Pattern: (Swung) D DududuDocument1 pageLove Me Do - The Beatles-Guitar Strumming Pattern: (Swung) D DududuMisbah PatelNo ratings yet
- MethodologyDocument1 pageMethodologyMisbah PatelNo ratings yet
- Competition Car Aerodynamics GuideDocument2 pagesCompetition Car Aerodynamics GuideMisbah Patel100% (1)
- Future ScopeDocument1 pageFuture ScopeMisbah PatelNo ratings yet
- ReadmeDocument1 pageReadmeMisbah PatelNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument3 pagesGlobal WarmingMisbah PatelNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic PropulsionDocument16 pagesElectromagnetic PropulsionMisbah PatelNo ratings yet
- The ENERGY MANAGEMENT PROFESSION Energy Management Skills Are Important To People in Many OrganizationsDocument3 pagesThe ENERGY MANAGEMENT PROFESSION Energy Management Skills Are Important To People in Many OrganizationsMisbah PatelNo ratings yet
- Synopsis FormatDocument2 pagesSynopsis FormatMisbah PatelNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument40 pagesPDFMisbah PatelNo ratings yet
- Abstract:: Savitribai Phule Pune UniversityDocument1 pageAbstract:: Savitribai Phule Pune UniversityMisbah PatelNo ratings yet
- TITLE - Ultrasonic Time of Flight Diffraction Technique For Weld DefectsDocument2 pagesTITLE - Ultrasonic Time of Flight Diffraction Technique For Weld DefectsMisbah PatelNo ratings yet
- PPTDocument23 pagesPPTMisbah PatelNo ratings yet
- Mini ProjectDocument9 pagesMini ProjectMisbah PatelNo ratings yet
- PPTDocument26 pagesPPTMisbah PatelNo ratings yet
- Ep PDFDocument18 pagesEp PDFMisbah PatelNo ratings yet
- Bosch L Jetronic Injection Technical Instructions PDFDocument40 pagesBosch L Jetronic Injection Technical Instructions PDFjorge Angel LopeNo ratings yet
- Practice Chapter 18 Carboxylic AcidsDocument0 pagesPractice Chapter 18 Carboxylic AcidsRochelle BartiletNo ratings yet
- Applications of Nano Biotechnology in Wastewater Treatment PDFDocument9 pagesApplications of Nano Biotechnology in Wastewater Treatment PDFswaroop_exlncNo ratings yet
- Francis Bacon, Logic of SensationDocument2 pagesFrancis Bacon, Logic of SensationShrankhla NaryaNo ratings yet
- Mousavi, Aliha, Imani - 2020 - On The Use of Edge Cracked Short Bend Beam Specimen For PMMA Fracture Toughness Testing Under Mixed-ModeDocument1 pageMousavi, Aliha, Imani - 2020 - On The Use of Edge Cracked Short Bend Beam Specimen For PMMA Fracture Toughness Testing Under Mixed-ModeMorteza AtaeiNo ratings yet
- Purmelt QR 3317 BR 2Document2 pagesPurmelt QR 3317 BR 2Mikel Pacheco IglesiasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Dynamics of Robotics SystemDocument38 pagesChapter 3 Dynamics of Robotics SystemAddisuSaafooNo ratings yet
- Atlas Copco: Parts ListDocument152 pagesAtlas Copco: Parts ListChathura SenanayakeNo ratings yet
- Appendix JA2 Reference Weather and Climate Zone DataDocument66 pagesAppendix JA2 Reference Weather and Climate Zone DataJoseph DavidNo ratings yet
- HW2 Solutions FinalDocument5 pagesHW2 Solutions Finalpande_100No ratings yet
- Is.1875 1992Document14 pagesIs.1875 1992Sadashiva sahooNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Magazine Abril 2009 PDFDocument108 pagesChemical Engineering Magazine Abril 2009 PDFFélix Vargas Santillán100% (1)
- Unit Hydrograph DerivationDocument7 pagesUnit Hydrograph DerivationSudharsananPRSNo ratings yet
- Oversized Particles in Emulsified Asphalts (Sieve Test) : Standard Test Method ForDocument2 pagesOversized Particles in Emulsified Asphalts (Sieve Test) : Standard Test Method Forمحمد سليمان بن عمرNo ratings yet
- Fluidized Bed CombustionDocument600 pagesFluidized Bed Combustionvikasnar100% (7)
- Topic 4 - Probability (Old Notes)Document22 pagesTopic 4 - Probability (Old Notes)Pradeep100% (1)
- Lab Report 5Document6 pagesLab Report 5Sarwar Hosen SimonNo ratings yet
- Time Allowed: 20 Minutes Marks: 12: Section - ADocument3 pagesTime Allowed: 20 Minutes Marks: 12: Section - AAliNo ratings yet
- Materials I: Lecture Course 5 Phase Diagrams. Fe-C Diagram. Crystallisation of Alloys in Fe - Fe C SystemDocument24 pagesMaterials I: Lecture Course 5 Phase Diagrams. Fe-C Diagram. Crystallisation of Alloys in Fe - Fe C SystemTiger ClaudiuNo ratings yet
- Making and Curing Concrete Test Specimens in The Laboratory: Standard Practice ForDocument8 pagesMaking and Curing Concrete Test Specimens in The Laboratory: Standard Practice ForAhmed AbidNo ratings yet
- McCabe-Thiele Diagrams For Binary DistillationDocument8 pagesMcCabe-Thiele Diagrams For Binary DistillationwetcoNo ratings yet
- A Method of Solving Certain Nonlinear DiophantineDocument3 pagesA Method of Solving Certain Nonlinear DiophantineArsh TewariNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Soil Structure Interaction - 01 - Chapter 1 - NaganoDocument42 pagesDynamic Soil Structure Interaction - 01 - Chapter 1 - Naganonevam21100% (1)
- Schrodinger Equation DerivationDocument12 pagesSchrodinger Equation DerivationAndrés López Martínez100% (1)
- CAD/CAM Geometric Modelling RepresentationsDocument34 pagesCAD/CAM Geometric Modelling Representationsshantikiran shantikiranNo ratings yet
- Flux 10 4 New Features Presentation ValideDocument22 pagesFlux 10 4 New Features Presentation ValideleelNo ratings yet
- NTMM LAB: MATERIAL REMOVAL RATE TEST ON ULTRASONIC MACHINEDocument23 pagesNTMM LAB: MATERIAL REMOVAL RATE TEST ON ULTRASONIC MACHINETarundeep SinghNo ratings yet
- The D and F Block Elements PDFDocument8 pagesThe D and F Block Elements PDFTr Mazhar PunjabiNo ratings yet
- Soil Nail Wall - Soil Nailing - Deep ExcavationDocument7 pagesSoil Nail Wall - Soil Nailing - Deep ExcavationAlok Mehta0% (1)
- 176-fc4731 Fault CodeDocument3 pages176-fc4731 Fault CodeHamilton MirandaNo ratings yet