Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Tense Chart Explained
Uploaded by
Jessi FernandezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Tense Chart Explained
Uploaded by
Jessi FernandezCopyright:
Available Formats
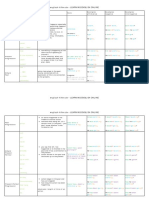
The Tense Chart
Examples Examples Examples
Tense Signal words Use Form
affirmative negative question
every day
always - something happens
sometimes repeatedly (routine) I work. I don't work. Do I work?
Simple usually - how often something He works. He doesn't work. Does he work?
I /we /they /you + V1 he/she/it + V1+s
Present often happens I go. I don't go. Do I go?
hardly - one action follows another He goes. He doesn't go. Does he go?
never - things in general
first ... then
I'm working. I'm not working. Am I working?
Now I am He's working. He isn't working. Is he working?
These days - something is happening at We’re working We aren’t working Are we going home?
Present
At the moment the same time of speaking or he/she/it is + V-ing
Continuous
Look! around it I'm going home I'm not going home. Am I going home?
Listen! we/they/you are He's going home. He isn't going home Is he going home?
We’re going home We aren’t going home Are we going home?
Subject + V2
last ... action took place in the past, I worked. I didn't work. Did I work?
--------------------------
Simple ... ago connected with an expression He worked. He didn't work. Did he work?
V2 = (* regular: V1+ ed)
Past in 1990 of time (no connection to the I went. I didn't go. Did I go?
V2= (* irregular: Look at the table
yesterday present) He went. He didn't go. Did he go?
of irregular verbs)
I was working. I was not working. Was I working?
- an action happened in the I was He was working. He was not working. Was he working?
middle of another action We were working We were not working Were we going home?
Past
while - someone was doing he/she/it was + V-ing
Continuous
something at a certain time I was going home I was not going home. Was I going home?
(in the past) - you don't know we/they/you were He was going home. He was not going home Was he going home?
whether it was finished or not We were going home We were not going home. Were we going home?
The verb “be” can be an auxiliary verb (helping verb) or a main verb in English.
“be” as a main verb in the Simple Present (am, are, is) “be” as a main verb in the Simple Past (was, were)
affirmative negative yes/no question affirmative negative yes/no question
I: I:
I am from England. I am not from England. Am I from England? I was here. I was not here. Was I here?
he, she, it: he, she, it:
He is from England. He is not from England. Is he from England? He was here. He was not here. Was he here?
we, you, they: we, you, they:
We are from England. We are not from England. Are we from England We were here. We were not here. Were we here?
“be” as a helping verb in the Present Continuous (am, are, is) +Ving
affirmative negative yes/no question
I:
I am reading a book. I am not reading a book. Am I reading a book?
he, she, it:
He is reading a book. He is not reading a book. Is he reading a book?
we, you, they:
We are reading a book. We are not reading a book. Are we reading a book
“be” as a helping verb in the Past Continuous (was, were) +Ving
affirmative negative yes/no question
I:
I was reading a book. I was not reading a book. Was I reading a book?
he, she, it:
He was reading a book. He was not reading a book. Was he reading a book?
we, you, they:
We were reading a book. We were not reading a book. Were we reading a book
You might also like
- Ruling party member's child abducted prior to electionDocument117 pagesRuling party member's child abducted prior to electionAvik Das100% (1)
- English LanguageDocument2 pagesEnglish LanguageVinayak NegiNo ratings yet
- Dependent and Independent ClausesDocument59 pagesDependent and Independent ClausesJolan DesmedtNo ratings yet
- Heavy MachineryDocument18 pagesHeavy MachineryJessi Fernandez100% (1)
- ABRSM Grade 8 2023-2024 and ARSM SyllabusDocument13 pagesABRSM Grade 8 2023-2024 and ARSM Syllabusdeadlymajesty0% (2)
- English Verbs FormsDocument30 pagesEnglish Verbs FormsM MNo ratings yet
- PFC Level Wordlist PDFDocument45 pagesPFC Level Wordlist PDFRivaldo Júnior100% (1)
- English Tenses TableDocument1 pageEnglish Tenses Tableパス•クシメナ100% (1)
- English 11 MLMDocument138 pagesEnglish 11 MLMVishwanath PeddanollaNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary and Spelling - Glencoe - McGraw-Hill (PDFDrive)Document30 pagesVocabulary and Spelling - Glencoe - McGraw-Hill (PDFDrive)Sherry JiangNo ratings yet
- English Grammar NotesDocument151 pagesEnglish Grammar NotesLiibaan A/karinNo ratings yet
- Assertive Advocate (INFJ-A)Document6 pagesAssertive Advocate (INFJ-A)kawaiilaitue100% (1)
- Why Isn't Phonetic' Spelled The Way It Sounds??: Or, As It Is More Commonly Known, Our "Spelling Rules Book"Document13 pagesWhy Isn't Phonetic' Spelled The Way It Sounds??: Or, As It Is More Commonly Known, Our "Spelling Rules Book"bblianceNo ratings yet
- Past Tense Irregular Verbs List: English Grammar NotesDocument9 pagesPast Tense Irregular Verbs List: English Grammar NotesxarethNo ratings yet
- Twinkl Modal VerbsDocument8 pagesTwinkl Modal VerbsKure RukminiNo ratings yet
- Preposition Exercises1Document6 pagesPreposition Exercises1Nisa Shining0% (1)
- Bahasa Inggris - Main Idea - IzzaDocument21 pagesBahasa Inggris - Main Idea - IzzaNandita Diva ChintikaNo ratings yet
- Phrasal VerbDocument19 pagesPhrasal VerbPhương UyênNo ratings yet
- Erica Grammar DSAT - RemovedDocument101 pagesErica Grammar DSAT - RemovedViet Nguyen Trong100% (1)
- 4000 English Words (Part-3)Document197 pages4000 English Words (Part-3)hemang.shroffNo ratings yet
- Adjective / Adverb + Past Participle: Compound Adjectives With NumbersDocument5 pagesAdjective / Adverb + Past Participle: Compound Adjectives With NumbersKrishna Veena KosuruNo ratings yet
- The Basic Types of Adjectives: 1 Which Is The Correct Order?Document2 pagesThe Basic Types of Adjectives: 1 Which Is The Correct Order?Alina BertyNo ratings yet
- Future Tense With "Going To" - What Is Sara Going To Do?Document10 pagesFuture Tense With "Going To" - What Is Sara Going To Do?Jhonn DhzNo ratings yet
- Aef Starter Repaso Units 1-6Document7 pagesAef Starter Repaso Units 1-6Jessi Fernandez100% (1)
- Grammar For WrittingDocument34 pagesGrammar For WrittingDuy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Creative TeachingDocument254 pagesCreative TeachingYusuf Rizal100% (1)
- Pre Intermediate Grammar Ebook SampleDocument14 pagesPre Intermediate Grammar Ebook SampleAye Pyae SoneNo ratings yet
- Reading Year 6 KSSRDocument43 pagesReading Year 6 KSSRnorhasniNo ratings yet
- AEF0 File7 QuickTest PDFDocument2 pagesAEF0 File7 QuickTest PDFJessi Fernandez100% (2)
- Activity Proposal For Graduation 2023Document2 pagesActivity Proposal For Graduation 2023Jahzeel Rubio100% (1)
- Canterville Ghost TestDocument2 pagesCanterville Ghost TestAndreia LourençoNo ratings yet
- Cot2 DLL - 2023Document3 pagesCot2 DLL - 2023Haidi Lopez100% (1)
- Math Vocabulary PDFDocument1 pageMath Vocabulary PDFreadwritesing0% (1)
- 2000 Vocabulary PDF For Editorial 95Document205 pages2000 Vocabulary PDF For Editorial 95Raja Sandeep VubaNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses ExplainedDocument3 pagesVerb Tenses Explainedmanisha_bhavsarNo ratings yet
- Identifying Interjections WorksheetDocument1 pageIdentifying Interjections WorksheetAadishree JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension Skills - English StudiesDocument5 pagesReading Comprehension Skills - English StudiesBenbouhia IhssanNo ratings yet
- K Kundan: DictionDocument27 pagesK Kundan: Dictionorchid21No ratings yet
- Year 4 Grammar Review: Exercise 2Document4 pagesYear 4 Grammar Review: Exercise 2Ivan HoNo ratings yet
- Adjectives and Adverbs: Here Starts The Lesson!Document23 pagesAdjectives and Adverbs: Here Starts The Lesson!Katherine Caballero RiveroNo ratings yet
- Verbs Guide: Types, Examples & IdentificationDocument9 pagesVerbs Guide: Types, Examples & IdentificationMuhammad Hadikz100% (1)
- Verb Tenses and Forms On SAT WritingDocument24 pagesVerb Tenses and Forms On SAT WritingJoe Marie Peter BaddongonNo ratings yet
- Adverbs EnglishDocument7 pagesAdverbs EnglishAlina PeticNo ratings yet
- English GrammarDocument45 pagesEnglish GrammarAnonymous ZCb9xzNo ratings yet
- CDC2017 EnglishGrade-3 PDFDocument103 pagesCDC2017 EnglishGrade-3 PDFRanjanNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Good ParagraphDocument15 pagesHow To Write A Good ParagraphLala FridaNo ratings yet
- 2016 Spelling Bee Words Webber Academy PDFDocument8 pages2016 Spelling Bee Words Webber Academy PDFdhonakakaNo ratings yet
- There Is There Are PPT Fun Activities Games Grammar Drills Grammar Guides - 41089Document28 pagesThere Is There Are PPT Fun Activities Games Grammar Drills Grammar Guides - 41089Anonymous LoSljH8nQNo ratings yet
- Asking Questions in English: Write Questions For The Underlined WordsDocument2 pagesAsking Questions in English: Write Questions For The Underlined WordsFatima VazquezNo ratings yet
- 7 Grammar Rules You Need To GeDocument7 pages7 Grammar Rules You Need To GeHarpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- 7 Types of English Adjectives Every ESL Student Must KnowDocument3 pages7 Types of English Adjectives Every ESL Student Must KnowBenny James CloresNo ratings yet
- SuffixDocument3 pagesSuffixBharat SaiNo ratings yet
- Notes - English (Grammar)Document3 pagesNotes - English (Grammar)Angeline BruceNo ratings yet
- MBA English Lec 1 (N)Document23 pagesMBA English Lec 1 (N)Usa 2021No ratings yet
- All Tense Rule Chart or Table in EnglishDocument7 pagesAll Tense Rule Chart or Table in EnglishHammad Ali ShahzadNo ratings yet
- English Vocabulary Crossword Puzzle - Google 搜索Document2 pagesEnglish Vocabulary Crossword Puzzle - Google 搜索kusingbarNo ratings yet
- OXFORD Thesaurus - AbilityDocument3 pagesOXFORD Thesaurus - Abilityharwan_sNo ratings yet
- Participle PhrasesDocument13 pagesParticiple PhrasesAimee TamonanNo ratings yet
- Oc ApplicpackDocument10 pagesOc ApplicpackRaviNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Forming Questions - WhereDocument1 pageIntermediate Forming Questions - WherePablo PasqualiniNo ratings yet
- Grammar Cheat Sheet 2016Document3 pagesGrammar Cheat Sheet 2016임민수No ratings yet
- Reading ComprehensionDocument6 pagesReading ComprehensionFebe faeganeNo ratings yet
- Big Grammar Book Intermediate Level - 311pDocument311 pagesBig Grammar Book Intermediate Level - 311pbblanca23No ratings yet
- Czasy TabelkaDocument6 pagesCzasy TabelkaAgnieszkaNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument5 pagesEnglish TensesI. N.No ratings yet
- Material 201551 LNG400 13 49698Document5 pagesMaterial 201551 LNG400 13 49698Jacqueline Mejía LunaNo ratings yet
- Tenses TableDocument5 pagesTenses Tablebarathi subburamNo ratings yet
- Tenses TableDocument5 pagesTenses TableKamahabzanizam Abd KadirNo ratings yet
- Ejemplo Task 2 Offering A Full MenuDocument1 pageEjemplo Task 2 Offering A Full MenuJessi FernandezNo ratings yet
- Repaso Examinacion Nacional Basico 1 2019-1Document4 pagesRepaso Examinacion Nacional Basico 1 2019-1Jessi FernandezNo ratings yet
- AEF - Starter - 5A - Grammar - Bank (Solo Lectura) (Modo de Compatibilidad)Document2 pagesAEF - Starter - 5A - Grammar - Bank (Solo Lectura) (Modo de Compatibilidad)Jessi FernandezNo ratings yet
- Ejemplo Task 1 Describing FoodDocument2 pagesEjemplo Task 1 Describing FoodJessi FernandezNo ratings yet
- Repaso Ett Basico 1 AefDocument5 pagesRepaso Ett Basico 1 AefJessi FernandezNo ratings yet
- Sleepy Hollow: Name: - DateDocument1 pageSleepy Hollow: Name: - DateJessi FernandezNo ratings yet
- Lista de Verbos Regulares e Irregulares en Ingles Libro American English File StarterDocument2 pagesLista de Verbos Regulares e Irregulares en Ingles Libro American English File StarterJessi FernandezNo ratings yet
- Bar Utensils and InstructionsDocument5 pagesBar Utensils and InstructionsJessi FernandezNo ratings yet
- Drink Ingredients and PreparationsDocument4 pagesDrink Ingredients and PreparationsJessi FernandezNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Review Intermediate English 1Document5 pagesFinal Exam Review Intermediate English 1Jessi FernandezNo ratings yet
- (Be) Going To - Future PDFDocument2 pages(Be) Going To - Future PDFJessi FernandezNo ratings yet
- Object Pronouns Basico 2Document2 pagesObject Pronouns Basico 2Jessi FernandezNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Handling ComplaintsDocument19 pagesUnit 2 Handling ComplaintsJessi FernandezNo ratings yet
- Repaso Examinacion Nacional Basico 1 2019-1Document4 pagesRepaso Examinacion Nacional Basico 1 2019-1Jessi FernandezNo ratings yet
- Name: María Jesús Farías Bittner. Grade: 5º "A''Document11 pagesName: María Jesús Farías Bittner. Grade: 5º "A''Jessi FernandezNo ratings yet
- 8Th Grade: Unit 4: Future MattersDocument8 pages8Th Grade: Unit 4: Future MattersJessi Fernandez100% (1)
- Verb To Be PresentDocument4 pagesVerb To Be PresentJessi FernandezNo ratings yet
- 8th Grade Unit 4 Future Life VocabularyDocument15 pages8th Grade Unit 4 Future Life VocabularyJessi Fernandez100% (1)
- Repaso Ett Basico 2 AefDocument5 pagesRepaso Ett Basico 2 AefJessi FernandezNo ratings yet
- Repaso MTT Basico 1 AefDocument5 pagesRepaso MTT Basico 1 AefJessi FernandezNo ratings yet
- Rubrica DialogoDocument1 pageRubrica DialogoJessi FernandezNo ratings yet
- Assessed Handout Units 5-6 Tecnico Deportivo PDFDocument5 pagesAssessed Handout Units 5-6 Tecnico Deportivo PDFJessi FernandezNo ratings yet
- Assessed Handout Units 5-6 Tecnico DeportivoDocument5 pagesAssessed Handout Units 5-6 Tecnico DeportivoJessi FernandezNo ratings yet
- Dialogue Ingles 1Document2 pagesDialogue Ingles 1Jessi FernandezNo ratings yet
- Repaso Basico 2Document4 pagesRepaso Basico 2Jessi FernandezNo ratings yet
- Stanford University Latex Thesis Style FileDocument5 pagesStanford University Latex Thesis Style Filejuliewebsterwashington100% (2)
- Sekolah Kebangsaan Batu Kawan 14110 Simpang Ampat Seberang Perai Selatan Senarai Nama Murid Tunas Kadet Remaja Sekolah (2014)Document10 pagesSekolah Kebangsaan Batu Kawan 14110 Simpang Ampat Seberang Perai Selatan Senarai Nama Murid Tunas Kadet Remaja Sekolah (2014)seetharaman78No ratings yet
- Eapp Summative Test 2023 2024Document5 pagesEapp Summative Test 2023 2024Ed Vincent M. YbañezNo ratings yet
- BSC Applied Accounting OBU SpecificationsDocument8 pagesBSC Applied Accounting OBU SpecificationsArslanNo ratings yet
- 013285242X - PP CH 2Document15 pages013285242X - PP CH 2magesNo ratings yet
- Academic Resources Worksheet Maya TraceyDocument1 pageAcademic Resources Worksheet Maya Traceyapi-340525387No ratings yet
- Blacklight Dress Rehearsal and Tentative Final PerformanceDocument5 pagesBlacklight Dress Rehearsal and Tentative Final Performanceapi-496802644No ratings yet
- School Report CardsDocument80 pagesSchool Report CardswindsorstarNo ratings yet
- Databaseplan 1Document3 pagesDatabaseplan 1api-689126137No ratings yet
- DOMDocument2 pagesDOMnea317No ratings yet
- 0511 English As A Second Language: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2013 SeriesDocument13 pages0511 English As A Second Language: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2013 SeriesEthanNo ratings yet
- Club Proposal FormDocument3 pagesClub Proposal FormSyed Fahim RahmanNo ratings yet
- 11% - HR Stargey HeritageDocument51 pages11% - HR Stargey HeritageMohmmedKhayyumNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Internationa Kampala Uganda Annual Planner 23 24 CirculationDocument2 pagesDelhi Public School Internationa Kampala Uganda Annual Planner 23 24 Circulationgaurang1111No ratings yet
- BUS 102 Fundamentals of Buiness II 2022Document4 pagesBUS 102 Fundamentals of Buiness II 2022Hafsa YusifNo ratings yet
- Tally Sheet (Check Sheet) : TemplateDocument7 pagesTally Sheet (Check Sheet) : TemplateHomero NavarroNo ratings yet
- Secret Path Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesSecret Path Lesson Planapi-394112616100% (1)
- 620 001 Econ Thought Syllabus Fall08 Wisman PDFDocument4 pages620 001 Econ Thought Syllabus Fall08 Wisman PDFJeff KruseNo ratings yet
- 3D Terrain Car Racing GameDocument38 pages3D Terrain Car Racing Gamerao sbNo ratings yet
- R22 - IT - Python Programming Lab ManualDocument96 pagesR22 - IT - Python Programming Lab ManualJasmitha BompellyNo ratings yet
- HBET1303Document216 pagesHBET1303Tce ShikinNo ratings yet
- Indian states with highest and lowest dropout ratesDocument23 pagesIndian states with highest and lowest dropout ratesAJIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- How Social Class Impacts EducationDocument5 pagesHow Social Class Impacts Educationnor restinaNo ratings yet
- Sci GDocument12 pagesSci GEvans KipyegoNo ratings yet