Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Law of segregation & independent assortment
Uploaded by
FiqahhyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Law of segregation & independent assortment
Uploaded by
FiqahhyCopyright:
Available Formats
Law of segregation
Due to the presence of Chromosomes undergo segregation
recessive alleles on the X & independent assortment
chromosomes
Law of Independent
Assortment
Recessive disorders:
Colour blindness Eg: In fruitflies, gene for eye
Mendelian genes have specific
A gene is located on colour located on the X
loci (positions) on chromosomes
Duchenne muscular dystrophy either sex chromosome chromosome
progressive: weakening of (usually X chromosomes)
muscles 1
Wild type female (Red eyes)
Haemophilia: absence of blood- Chromosome Theory of
clotting proteins Inheritance x
Sex-Linked Genes 2
Mutant Male (White eyes)
F2 gen:
Chromosomal Basis of
½ X chromosomes in each cell is
randomly inactivated during 3 Inheritance (Part I) 3 red:1 white (Only male has
embryonic dev. white eyes)
X Inactivation in
The inactivated X chromosome: female mammals
inactive X → Barr body
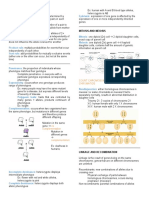
4 Linked Genes 5 Unlinked Genes
Allele for orange & black fur Wild type (gray body, normal
in cats: If the female cat is wings) Genes located on the same
heterozygous : the cat will be If genes located on different
chromosome that tend to be
mosaic for that character X chromosome, UNLINKED
inherited together
Double Mutant (Black body, 1 : 1 : 1 : 1
vestigial wings)
Eg: In fruitflies, flies with
F1 dihybrid: All wild type Incomplete linkage as evident
differed body colour & wing
from recombinant phenotypes:
size were crossed
F1 dihybrid x Double mutant crossing-over between
homologous chromosomes
If genes located on the same
chromosome + parental alleles Recombinant Frequency:
inherited together, LINKED
Total recombinants x
1 : 1 : 0 : 0 100
*Recombinants produced (non- Total of all phenotypes
parental phenotypes)
You might also like
- Genetics Notes 1Document7 pagesGenetics Notes 1Hi HiNo ratings yet
- NOTES - CH 15 - Sex Determination - Linkage - SlideshowDocument59 pagesNOTES - CH 15 - Sex Determination - Linkage - Slideshowkaren milloNo ratings yet
- DevPsy_1_PrenatalDocument6 pagesDevPsy_1_PrenatalIvy Marie ToyonganNo ratings yet
- Devpsych Reviewer 1Document56 pagesDevpsych Reviewer 1Joshua MalloNo ratings yet
- Example: Aa: AdbcbdDocument4 pagesExample: Aa: AdbcbdHannah MeloNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Unit 7: Genetics Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument1 pageAP Biology Unit 7: Genetics Cheat Sheet: by ViaJ15No ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Bio-Zoology Unit II Surya Biology Guide emDocument75 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Bio-Zoology Unit II Surya Biology Guide emDhanush RamanNo ratings yet
- DevPsy 1 PrenatalDocument7 pagesDevPsy 1 PrenatalninamaedamilesNo ratings yet
- 17 - InheritanceDocument4 pages17 - InheritanceAvyay TopraniNo ratings yet
- Genetics Diy-LectureDocument14 pagesGenetics Diy-LectureRoselyn LacernaNo ratings yet
- Ndsi BioDocument26 pagesNdsi BioMarc Augustine BelgaNo ratings yet
- Genetics in 40 CharactersDocument28 pagesGenetics in 40 CharactersNicolas JayNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal AbnormalitiesDocument7 pagesChromosomal Abnormalitiesmax delvalleNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics Lecture 06Document4 pagesCytogenetics Lecture 06Dianne NolascoNo ratings yet
- What You Must Know:: Chromosome Theory of InheritanceDocument2 pagesWhat You Must Know:: Chromosome Theory of Inheritanceapi-327705163No ratings yet
- Chapter 13 BIO 1510Document22 pagesChapter 13 BIO 1510Chachi CNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Sex LinkageDocument4 pagesA Guide To Sex LinkageTamicka BonnickNo ratings yet
- Tasmanian Devil Karyotype (Remote)Document8 pagesTasmanian Devil Karyotype (Remote)pijus mickevičiusNo ratings yet
- M1 Introdcution To GeneticsDocument4 pagesM1 Introdcution To GeneticsBrylle Angelo PolintanNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document16 pagesGeneral Biology 2libbyNo ratings yet
- Matters of Sex LongDocument3 pagesMatters of Sex Longjenifer lolaNo ratings yet
- LS 107 - Midterm 1 Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesLS 107 - Midterm 1 Cheat SheetAudrie L.No ratings yet
- AP Biology Review SheetDocument3 pagesAP Biology Review Sheetapi-286357921No ratings yet
- GENETIKA: MENDELIAN AND CHROMOSOMAL BASIS OF HEREDITYDocument27 pagesGENETIKA: MENDELIAN AND CHROMOSOMAL BASIS OF HEREDITYwokadwojuehfaokdwaNo ratings yet
- Genetics 2024Document63 pagesGenetics 2024davidmajutla87No ratings yet
- Week 4 - Human GeneticsDocument5 pagesWeek 4 - Human GeneticsTEDDY BEAR PRODUCTIONNo ratings yet
- B5 Principles of InheritanceDocument1 pageB5 Principles of InheritanceHarsh MittalNo ratings yet
- Heredity For JHSDocument21 pagesHeredity For JHSKrisnhaliani100% (1)
- Reviewer in General Biology Ii - KmbsDocument5 pagesReviewer in General Biology Ii - KmbsKSNo ratings yet
- Genotypes and DominanceDocument13 pagesGenotypes and Dominancecv5mv6w4htNo ratings yet
- Genetics Vocab Flashcards 2017Document4 pagesGenetics Vocab Flashcards 2017Ryleigh SmithNo ratings yet
- Morgan's fruit fly experiments reveal gene linkageDocument23 pagesMorgan's fruit fly experiments reveal gene linkagezahuuNo ratings yet
- Genetics Transmission GuideDocument15 pagesGenetics Transmission GuidefsadfNo ratings yet
- Similar To Mitosis Interphase. S Phase IdenticalDocument22 pagesSimilar To Mitosis Interphase. S Phase IdenticalEvangeline WongNo ratings yet
- Ch-8 Heredity and EvokutionDocument14 pagesCh-8 Heredity and Evokutioneekshi0003No ratings yet
- Mendelian, Pedigree and Modification NotesDocument7 pagesMendelian, Pedigree and Modification NotesJoyceNo ratings yet
- Genes and DiseasesDocument31 pagesGenes and DiseasesT FNo ratings yet
- 4 - Q - Genetic InheritanceDocument22 pages4 - Q - Genetic InheritanceNOOR JANNAH FIRDOUSE BINTI ISMAIL KM-Pensyarah100% (1)
- Sex Chromosomes and TraitsDocument4 pagesSex Chromosomes and TraitsZaida RectoNo ratings yet
- 7 Priciple of Genetic 1Document22 pages7 Priciple of Genetic 1beyonduckNo ratings yet
- Genetics NotesDocument20 pagesGenetics Noteslebohangcandy8No ratings yet
- Genbio 2 ReviewerDocument8 pagesGenbio 2 ReviewerLarvin Andrei E. BechaydaNo ratings yet
- 18 InheritanceDocument46 pages18 Inheritances1139221No ratings yet
- Terms To Know in Mendelian GeneticsDocument2 pagesTerms To Know in Mendelian GeneticsDoris C. Brucales100% (1)
- BIO-2-2nd-semDocument7 pagesBIO-2-2nd-semKelly Misha NoolNo ratings yet
- 19-04 CytogeneticsDocument39 pages19-04 CytogeneticsMichael John AguilarNo ratings yet
- General Biology Genetics, Proteins, Origins of Life & BiotechnologyDocument31 pagesGeneral Biology Genetics, Proteins, Origins of Life & BiotechnologyAlexis Carla GahumanNo ratings yet
- U4 Chapter 13 The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance and Human Genetics - TaggedDocument54 pagesU4 Chapter 13 The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance and Human Genetics - Tagged1968405546No ratings yet
- What If?: Aberrations in Cell CycleDocument7 pagesWhat If?: Aberrations in Cell CycleJasper CasayuranNo ratings yet
- Sex Determination And ChromosomesDocument11 pagesSex Determination And ChromosomesBismarck John Salazar100% (1)
- SY12202 Variation in Chromosome Number StructureDocument49 pagesSY12202 Variation in Chromosome Number StructureMasni Shah NingNo ratings yet
- Outline: The Chromosomal Basis of InheritanceDocument4 pagesOutline: The Chromosomal Basis of InheritanceGizem OsmanogluNo ratings yet
- Laws of Inheritance Law of Segregation: Sperm Carries Half Their Chromosomes 2 Sex Cells 50% Chance of FertilizingDocument5 pagesLaws of Inheritance Law of Segregation: Sperm Carries Half Their Chromosomes 2 Sex Cells 50% Chance of FertilizingkimNo ratings yet
- Chapter_10__Patterns_of_Inheritance.docxDocument4 pagesChapter_10__Patterns_of_Inheritance.docxsherlynmamac98No ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles.Document5 pagesChapter 13 - Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles.Juan Miguel Calvelo BelzaNo ratings yet
- "Mendelian Genetics": General Biology 2 ReviewerDocument5 pages"Mendelian Genetics": General Biology 2 ReviewerFayza Jalil Balading100% (1)
- 8.1 Meiosis: EQ: How Are Sex Cells Different From Non-Sex Cells Genome - All of A Cell's Genetic Info (DNA)Document2 pages8.1 Meiosis: EQ: How Are Sex Cells Different From Non-Sex Cells Genome - All of A Cell's Genetic Info (DNA)ZJC 2333No ratings yet
- 8.1 Meiosis: EQ: How Are Sex Cells Different From Non-Sex Cells Genome - All of A Cell's Genetic Info (DNA)Document2 pages8.1 Meiosis: EQ: How Are Sex Cells Different From Non-Sex Cells Genome - All of A Cell's Genetic Info (DNA)ZJC 2333No ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument3 pagesGeneticsKenjie Darilag0% (1)
- L-7SCIENCE REVISION WORKSHEET ReproductionDocument3 pagesL-7SCIENCE REVISION WORKSHEET Reproductionmaanvikashyap98No ratings yet
- And She Became A Man Sexual MetamorpDocument19 pagesAnd She Became A Man Sexual Metamorpmaria.basta2No ratings yet
- Shakespeare Guardian Article - D PattersonDocument13 pagesShakespeare Guardian Article - D Pattersonapi-231816447No ratings yet
- How To Fill Up Your Dating FunnelDocument79 pagesHow To Fill Up Your Dating FunnelDominic dominicNo ratings yet
- Susan McClaryDocument7 pagesSusan McClaryjames823838aNo ratings yet
- Have You Really Loved A WomanDocument1 pageHave You Really Loved A Womanjuli-10No ratings yet
- ChromosomeDocument25 pagesChromosomenebullaNo ratings yet
- Case Neg - Sex Workers (Dartmouth Camp)Document18 pagesCase Neg - Sex Workers (Dartmouth Camp)EllenDymitNo ratings yet
- Movie Reflection Paper ofDocument2 pagesMovie Reflection Paper ofChriszalyn QuiselNo ratings yet
- Magnum Opus MeditationDocument5 pagesMagnum Opus MeditationChompek840% (1)
- The Third Sex: On The Fringes of SocietyDocument8 pagesThe Third Sex: On The Fringes of SocietyMalaika VardakNo ratings yet
- Boysdon'tcrydocxDocument591 pagesBoysdon'tcrydocxAriana ColeNo ratings yet
- Fenrir Journal of The Sinister Vol 5 Iss 1Document40 pagesFenrir Journal of The Sinister Vol 5 Iss 1ulfheidner9103100% (2)
- Bershady, Isaac Sexual Deviancy and Deviant Sexuality in Medieval England PDFDocument6 pagesBershady, Isaac Sexual Deviancy and Deviant Sexuality in Medieval England PDFMarcela Cubillos PobleteNo ratings yet
- Sexual DysfunctionsDocument25 pagesSexual Dysfunctionshanna endinoNo ratings yet
- People vs. Lizada - GR 143468-71 - Case DigestDocument2 pagesPeople vs. Lizada - GR 143468-71 - Case DigestJohn100% (2)
- Pamphlet 2Document2 pagesPamphlet 2api-345915599100% (1)
- The Effects of Violent Music Content On TeensDocument2 pagesThe Effects of Violent Music Content On TeensJoyce GohNo ratings yet
- FeminismDocument19 pagesFeminismapi-255339657No ratings yet
- Pelvic ExamDocument3 pagesPelvic ExamLouis Gabriel LuchingNo ratings yet
- The Lunar InfluenceDocument12 pagesThe Lunar Influencedragosbalaniuc100% (2)
- Sex Related TraitsDocument38 pagesSex Related Traitsirah jane valentinoNo ratings yet
- Concepts in Biology 14th Edition Enger Test BankDocument47 pagesConcepts in Biology 14th Edition Enger Test Bankdominiccosimawye100% (32)
- Straight Talk, September 2009Document4 pagesStraight Talk, September 2009Straight Talk FoundationNo ratings yet
- Inanna RetursDocument202 pagesInanna Retursborntobemild75% (4)
- Masaan: Film ReviewDocument3 pagesMasaan: Film ReviewSnigdha ShahiNo ratings yet
- The Gender Crisis in Professional PhotojournalismDocument11 pagesThe Gender Crisis in Professional PhotojournalismMatea PetrovićNo ratings yet
- HijraDocument20 pagesHijraabidahqadirNo ratings yet
- I F Ked Your Boyfriend (BOOK)Document165 pagesI F Ked Your Boyfriend (BOOK)Anonymous MLRQjQAYDDNo ratings yet
- Affidavit Witness 2Document2 pagesAffidavit Witness 2harriet virtudazoNo ratings yet