Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HERIC
Uploaded by
yasinCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HERIC
Uploaded by
yasinCopyright:
Available Formats
Photovoltaic Inverter Structures 13
2.2.3 HERIC Inverter (Sunways)
In 2006, Sunways patented a new topology also derived from the classical H-bridge called
HERIC (highly efficient and reliable inverter concept) by adding a bypass leg in the AC side
using two back-to-back IGBTs (insulated gate bipolar transistors), as shown in Figure 2.7 [6].
The AC bypass provides the same two vital functions as the fifth switch in case of the H5
topology:
r Prevents the reactive power exchange between L 1(2) and CPV during the zero voltage state,
thus increasing efficiency.
r Isolates the PV module from the grid during the zero voltage state, thus eliminating the
high-frequency content of VPE .
The switching states for positive and negative generated AC currents are depicted in
Figure 2.8.
The main features of this converter are:
r S1–S4 and S2–S3 are switched at high frequency and S+ (S−) at grid frequency.
r Two zero output voltage states are possible: S+ = on and S− = on (providing the bridge is
switched off).
Advantages:
r Voltage across the filter is unipolar (0 → +VPV → 0 → −VPV → 0), yielding lower core
losses.
r Higher efficiency of up to 97 % is due to no reactive power exchange between L 1(2) and CPV
during zero voltage and to lower frequency switching in one leg.
r VPE has only a grid frequency component and no switching frequency components, yielding
very low leakage current and EMI.
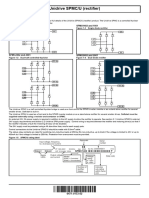
PV Array Filter HERIC FB inverter Filter Grid
D1 D3
S1 S3
VPV L1
S+ D− L
Vg
CPV
D+ S− L2 N
D2 D4
S2 S4
VPE
Figure 2.7 HERIC topology (Sunways)
14 Grid Converters for Photovoltaic and Wind Power Systems
PV Array Filter HERIC FB inverter Filter Grid PV Array Filter HERIC FB inverter Filter Grid
D1 D3 VAB = + VPV D1 D3 VAB = − VPV
VPV S1 S3 VPV S1 S3
L1 L1
A A
S+ D+ Vg L S+ D+ Vg L
CPV CPV
D− S− L N D− S− L N
2 B 2
B
D2 D4 D2 D4
S2 S4 S2 S4
VPE Vg > 0. S1 and S4 = ON, S+ = ON VPE V g < 0. S2 and S3 = ON. S– = ON
S1 and S4 are switched at high frequency. S+ is switched at line frequency S2 and S3 are switched at high frequency. S- is switched at line frequency
PV Array Filter HERIC FB inverter Filter Grid PV Array Filter HERIC FB inverter Filter Grid
D1 D3 VAB = 0 D1 D3 VAB = 0
VPV S1 S3 VPV S1 S3 L1
L1
A A
S+ D+ Vg L S+ D+ Vg L
CPV CPV
D− S − L2 D− S− L
N 2 N
B B
D2 D4 D2 D4
S2 S4 S2 S4
VPE Vg > 0. S1 and S4 = OFF. S + and D- = ON VPE Vg < 0. S2 and S3 = OFF. S- and D+ = ON
S5 and S4 are switched at high frequency. S+ is switched at line frequency S2 and S3 are switched at high frequency. S- is switched at line frequency
(a) (b)
Figure 2.8 The switching states of the HERIC inverter in the case of generating: (a) positive current
and (b) negative current
Drawbacks:
r Two extra switches.
Remark:
The HERIC improves the performance of FB with BP modulation by adding the
zero voltage obtained with the AC bypass, thus increasing the efficiency. This
topology is therefore very suitable for use in transformerless PV applications due
to high efficiency and low leakage current and EMI. It is currently commercialized
by Sunways in the AT series (2.7–5 kW) with reported European efficiency of 95 %
and maximum efficiency of 95.6 % (Photon International, July 2008).
The behavior of HERIC and H5 are quite similar as both realize the decoupling of the PV
generator from the grid during the zero voltage state on the AC side and DC side respectively.
They both use two switches switched at high frequency and one switched at grid frequency,
and H5 has three switches conducting at the same time, while HERIC has only two.
You might also like
- Converter Circuits University of Colorado, Boulder Prof. Robert EricksonDocument4 pagesConverter Circuits University of Colorado, Boulder Prof. Robert EricksonThinh NguyenNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING: PAPER REVIEW AND QUESTIONSDocument62 pagesELECTRICAL ENGINEERING: PAPER REVIEW AND QUESTIONSDivyang GautamNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6Document2 pagesTutorial 6Saransh MittalNo ratings yet
- L16Document41 pagesL16Deepti SaraswatNo ratings yet
- C&S 2 - Series Circuits, Parallel Circuits and Series-Parallel Circuits Ganjil 1920Document5 pagesC&S 2 - Series Circuits, Parallel Circuits and Series-Parallel Circuits Ganjil 1920Ambleh AmblehNo ratings yet
- Uni SPMC_U Sheet Issue 2 (0471-0153-02)_ApprovedDocument20 pagesUni SPMC_U Sheet Issue 2 (0471-0153-02)_ApprovedmarkNo ratings yet
- Flyback Converter: J. FisherDocument16 pagesFlyback Converter: J. FisherDaniel NimabwayaNo ratings yet
- AN-4104 Fairchild Elenota - PLDocument18 pagesAN-4104 Fairchild Elenota - PLdavidthijsNo ratings yet
- CH 6 SlidesDocument95 pagesCH 6 SlidesEmre DemirNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Operational Amplifiers (Op Amps) and Its ApplicationsDocument11 pagesUnit - 1 Operational Amplifiers (Op Amps) and Its ApplicationsVishalini PNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document41 pagesLecture 2trongnhansuper1No ratings yet
- Half Controlled Bridge Converter ExperimentDocument4 pagesHalf Controlled Bridge Converter ExperimentAbdullah MohammedNo ratings yet
- Signal Conditioning Techniques for Measurement SystemsDocument20 pagesSignal Conditioning Techniques for Measurement SystemsKelkiyas TaurusNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2019-20 EEE3002 ETH VL2019201001056 Reference Material I 12-Jul-2019 UNIT-2-op-amp ApplicationsDocument66 pagesFALLSEM2019-20 EEE3002 ETH VL2019201001056 Reference Material I 12-Jul-2019 UNIT-2-op-amp ApplicationsKumar RishabhNo ratings yet
- (0825 - 2) P BM PSPICE-6 (Schematic)Document6 pages(0825 - 2) P BM PSPICE-6 (Schematic)ayanavakarNo ratings yet
- Practical Op Amps AC Lecture1 Apn1Document51 pagesPractical Op Amps AC Lecture1 Apn1gpay121045No ratings yet
- Controller Design For BLDC MotorDocument15 pagesController Design For BLDC MotorAnonymous SdIsxrNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document2 pagesTutorial 4Saransh MittalNo ratings yet
- 11 Inverter 1Document68 pages11 Inverter 1KemasAlsyaAfrilianNo ratings yet
- New High Voltage Gain DC-DC Converter Based On Modified Quasi Z-Source NetworkDocument6 pagesNew High Voltage Gain DC-DC Converter Based On Modified Quasi Z-Source NetworkHussain K. SayedNo ratings yet
- 4 - JEE - Physics - Modern Physics - Valve Electronics - Diode ValveDocument4 pages4 - JEE - Physics - Modern Physics - Valve Electronics - Diode ValvescholasticaoffiahNo ratings yet
- ECEN 325 Lab 4: Operational Amplifiers - Part IIDocument4 pagesECEN 325 Lab 4: Operational Amplifiers - Part IISam AlbaNo ratings yet
- Matecconf Eureca2020 02007Document12 pagesMatecconf Eureca2020 02007Lim Chia SeangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Asymmetrical Pulse Width Modulation ControlDocument18 pagesChapter 4: Asymmetrical Pulse Width Modulation Controlsantosh_babar_26No ratings yet
- DC to AC Conversion Using InvertersDocument24 pagesDC to AC Conversion Using InvertersABHISHEK KUMARNo ratings yet
- Examples of Diode Circuits: Rectifier CircuitsDocument29 pagesExamples of Diode Circuits: Rectifier CircuitsJasleen KaurNo ratings yet
- SMPS ForwardConverterTypePCDocument17 pagesSMPS ForwardConverterTypePCNAYEEMNo ratings yet
- Voltage & Current DividerDocument28 pagesVoltage & Current DividerArsal Javed ButtNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Op AmpDocument14 pagesChapter 6 Op AmpAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- 08 Vertical Curves PDFDocument60 pages08 Vertical Curves PDFRey Benedict SalveNo ratings yet
- OP AMP APPLICATIONS LABDocument88 pagesOP AMP APPLICATIONS LABkrishna goggiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document3 pagesTutorial 5Saransh MittalNo ratings yet
- 2017 Ee Solved Paper PDFDocument94 pages2017 Ee Solved Paper PDFsunny55krNo ratings yet
- SRSDocument4 pagesSRSFix Gps GarminNo ratings yet
- Diode circuit analysisDocument1 pageDiode circuit analysisSuseel MenonNo ratings yet
- L6 Cuk ConverterDocument20 pagesL6 Cuk ConverterKarthickNo ratings yet
- CE 12 HIGHER SURVEYING Route Surveying V PDFDocument60 pagesCE 12 HIGHER SURVEYING Route Surveying V PDFArkai ParillasNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Amplifier: EXP - NO: 03Document4 pagesInstrumentation Amplifier: EXP - NO: 03Naveen GNo ratings yet
- Multivibrators Explained: Types, Operation & DesignDocument39 pagesMultivibrators Explained: Types, Operation & DesignAjdin BuljubasicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document26 pagesChapter 3rushimunde1212No ratings yet
- KMC Main control contactor wiring diagramDocument14 pagesKMC Main control contactor wiring diagramthanggimme.phanNo ratings yet
- OP Amp 1Document14 pagesOP Amp 1Hesham EbrahimNo ratings yet
- FinalExam ENM061 2021 04 07Document3 pagesFinalExam ENM061 2021 04 07Kostas GekasNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifiers Lab ExperimentDocument5 pagesOperational Amplifiers Lab ExperimentSandesh DalviNo ratings yet
- Redwan Ahmed Miazee - HW - 1Document3 pagesRedwan Ahmed Miazee - HW - 1REDWAN AHMED MIAZEENo ratings yet
- Lecture 100 (Instrumentation Amplifier)Document3 pagesLecture 100 (Instrumentation Amplifier)ShubamNo ratings yet
- 376 Ahf Manual (Vi)Document13 pages376 Ahf Manual (Vi)Quang Thịnh BùiNo ratings yet
- ECE Dept's Basic Electronics CourseDocument31 pagesECE Dept's Basic Electronics CoursePaul Tan RegalaNo ratings yet
- That Corporation Grsign Note 109Document2 pagesThat Corporation Grsign Note 109Anonymous Wyb8Y10% (1)
- DA Converters: DigitalelectronicsiicourseDocument24 pagesDA Converters: DigitalelectronicsiicourseLeonardo Franzua Giraldo CardosoNo ratings yet
- Week1 NotesDocument53 pagesWeek1 NoteskkkprotNo ratings yet
- Converter CircuitsDocument101 pagesConverter CircuitsBruh HDHDNo ratings yet
- TI - 20180906 - SG125HV-20 - User Manual - V1 - ENDocument110 pagesTI - 20180906 - SG125HV-20 - User Manual - V1 - ENMauricio ChinarelliNo ratings yet
- Research On Totem - Pole Bridgeless PFC Based On Synchronous Reference FrameDocument6 pagesResearch On Totem - Pole Bridgeless PFC Based On Synchronous Reference FrameTedNo ratings yet
- OP AMP AssignmentDocument8 pagesOP AMP AssignmentPradeep ChauhanNo ratings yet
- School of Electrical and Computer EngineeringDocument54 pagesSchool of Electrical and Computer EngineeringRafaellaNo ratings yet
- Belimo EP..R K.. Installation-InstructionsDocument2 pagesBelimo EP..R K.. Installation-InstructionsSiddiqNo ratings yet
- Advanced Electronics: Wave Shaping & Generating CircuitsDocument19 pagesAdvanced Electronics: Wave Shaping & Generating CircuitsGelvie LagosNo ratings yet
- 05 DC-DC Converter - AllDocument99 pages05 DC-DC Converter - AllAsad AzharNo ratings yet
- 06533376Document6 pages06533376yasinNo ratings yet
- Energies 11 00458Document16 pagesEnergies 11 00458yasinNo ratings yet
- Divyesh PaperDocument6 pagesDivyesh PaperyasinNo ratings yet
- Harmonics Optimization in Multilevel Inverter Using Real Coded Genetic AlgorithmDocument8 pagesHarmonics Optimization in Multilevel Inverter Using Real Coded Genetic AlgorithmyasinNo ratings yet
- 3.2 International Regulations: 3.2.1 IEEE 1547 Interconnection of Distributed GenerationDocument1 page3.2 International Regulations: 3.2.1 IEEE 1547 Interconnection of Distributed GenerationyasinNo ratings yet
- Help General DLL BlockDocument12 pagesHelp General DLL BlockĐào Vĩnh QuốcNo ratings yet
- DIALux Direct3D InformationDocument2 pagesDIALux Direct3D InformationyasinNo ratings yet
- TRPP1 de 1Document242 pagesTRPP1 de 1yasinNo ratings yet
- ReadmeDocument9 pagesReadmewatzzupNo ratings yet
- Page 45Document1 pagePage 45yasinNo ratings yet
- April in Moscow Ballet DreamDocument11 pagesApril in Moscow Ballet DreamyasinNo ratings yet
- Adjective by YassoDocument2 pagesAdjective by YassoyasinNo ratings yet
- Page 22Document1 pagePage 22yasinNo ratings yet
- SmartCtrl PresentationDocument25 pagesSmartCtrl PresentationyasinNo ratings yet
- Level 2 - Moby Dick - Penguin ReadersDocument32 pagesLevel 2 - Moby Dick - Penguin Readersourbook86% (36)
- George Mikes - How To Be An AlienDocument25 pagesGeorge Mikes - How To Be An AlienDragana ModestyNo ratings yet
- Aitbs2018 - ProgramıDocument27 pagesAitbs2018 - ProgramıyasinNo ratings yet
- Verify HDL Implementation of PID Controller Using FPGADocument15 pagesVerify HDL Implementation of PID Controller Using FPGAyasinNo ratings yet
- RET 630 Differential ProtectionDocument33 pagesRET 630 Differential ProtectionNarvin Raj ChandraNo ratings yet
- Capstone MicroTurbine Electrical Installation GuideDocument31 pagesCapstone MicroTurbine Electrical Installation GuideMaría MartinezNo ratings yet
- TABLE 1.10 Limiting Effect Cable Short-Circuit Currents 208 Volts, Three PhaseDocument23 pagesTABLE 1.10 Limiting Effect Cable Short-Circuit Currents 208 Volts, Three PhaseJuan Carlos Perez ParraNo ratings yet
- Armature Reaction in Direct Current Machines: Pereira, Colombia Julianesteban - Garcia@utp - Edu.coDocument3 pagesArmature Reaction in Direct Current Machines: Pereira, Colombia Julianesteban - Garcia@utp - Edu.coJulian GarciaNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase Intelligent Energy Meter User Manual: ES925 SeriesDocument4 pages3 Phase Intelligent Energy Meter User Manual: ES925 SeriesMbgardNo ratings yet
- Aditya Academy Secondary Physics ProjectDocument5 pagesAditya Academy Secondary Physics Projectaaldin DudeNo ratings yet
- Product Information: Rotanode™ E7290AXDocument14 pagesProduct Information: Rotanode™ E7290AXKamilNo ratings yet
- Cable HarnessesDocument7 pagesCable HarnessesdanielNo ratings yet
- ERRU (Electronic Rectification and Regulating Unit)Document19 pagesERRU (Electronic Rectification and Regulating Unit)Dilpal50% (2)
- TP Elec PDFDocument3 pagesTP Elec PDFchroeun sokayNo ratings yet
- Technology and Livelihood Education: Industrial Arts-Electrical Installation and Maintenance Quarter 2 - Module 1Document35 pagesTechnology and Livelihood Education: Industrial Arts-Electrical Installation and Maintenance Quarter 2 - Module 1Benjamin Fallet100% (6)
- IEC 60255 Electrical RelaysDocument1 pageIEC 60255 Electrical RelaysJeya Kannan0% (4)
- Fundamentals of Distance Protection and Transmission LinesDocument111 pagesFundamentals of Distance Protection and Transmission Linesmuaz_aminu1422100% (1)
- Cable sizing tables for PVC and XLPE insulated conductorsDocument3 pagesCable sizing tables for PVC and XLPE insulated conductorsLucky MalihanNo ratings yet
- Safepad 02 03 Tech EssaysDocument2 pagesSafepad 02 03 Tech EssaysnikecerreroNo ratings yet
- What Is CALCTP?Document1 pageWhat Is CALCTP?Kathryn R. ThompsonNo ratings yet
- FirstRanker's Choice 1Document8 pagesFirstRanker's Choice 1Jaipaul CheernamNo ratings yet
- STR-X6400 Application GuideDocument24 pagesSTR-X6400 Application Guidekorodiferenc9258No ratings yet
- TIP Application Manual - Part 1 Basic Data and Preliminary PlanningDocument166 pagesTIP Application Manual - Part 1 Basic Data and Preliminary PlanningAyman SaberNo ratings yet
- Mitsubhishi S500 ManualDocument200 pagesMitsubhishi S500 ManualDeepak GuptaNo ratings yet
- Energy Meter Installation Guidelines PDFDocument23 pagesEnergy Meter Installation Guidelines PDFAkramNo ratings yet
- Design and Performance Analysis of A Universal Motor For Industrial Alarm SystemsDocument5 pagesDesign and Performance Analysis of A Universal Motor For Industrial Alarm SystemsNoel BactonNo ratings yet
- P6112 Alstom PG9171E PowerPlant SpecificationsDocument1 pageP6112 Alstom PG9171E PowerPlant SpecificationsSunario YapNo ratings yet
- 15 - Omar Et AlDocument13 pages15 - Omar Et AlFlogamagNo ratings yet
- 404 Bus 2 CVT 181021030334Document6 pages404 Bus 2 CVT 181021030334SARAVANAN ANo ratings yet
- Lithium Battery Catalogue 10-03-2024Document7 pagesLithium Battery Catalogue 10-03-2024ASHUTOSH MOHAPATRA ROLL 24 VINo ratings yet
- Decentralized Inverter Guide for Large Solar PlantsDocument48 pagesDecentralized Inverter Guide for Large Solar PlantsPablo Omar Luz PedemonteNo ratings yet
- A - Learning - Report - On - Load - Flow - Studies - From - IEEE - 399 - 1658137826 2022-07-18 09 - 50 - 32Document7 pagesA - Learning - Report - On - Load - Flow - Studies - From - IEEE - 399 - 1658137826 2022-07-18 09 - 50 - 32Mohammad SamourNo ratings yet
- WO 33-4 Shastri Bridge Panel Cost R0 25.09.2021 - FINALDocument27 pagesWO 33-4 Shastri Bridge Panel Cost R0 25.09.2021 - FINALJayashree GopalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Konzen Electric Pulse MotorDocument6 pagesKonzen Electric Pulse Motorfreiwild100% (1)