Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Continuum Expectations - Chart Form Academic and University
Uploaded by
api-3952630970 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views6 pagesOriginal Title
continuum expectations - chart form academic and university
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views6 pagesContinuum Expectations - Chart Form Academic and University
Uploaded by
api-395263097Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
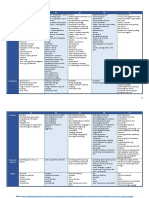
Grammar
Unit – Grade 9 to 12 Academic/University
Grade 9 Grade 10 Grade 11 Grade 12
Content Expectations Content Expectations Content Expectations Content Expectations
• Parsing symbols 3.3 use punctuation • Parts of speech 3.3 use punctuation • Review of parsing. 3.3 use punctuation • Continual review of 3.3 use punctuation
• Parts of speech – nouns, correctly to (review from grade correctly to • Development of correctly to all skills since grade correctly to
verbs, pronouns, communicate nine) – nouns, verbs, communicate sentence structure – communicate nine. communicate
adjectives, adverbs, their intended pronouns, adjectives, their intended meaning use of clauses, varied their intended meaning their intended meaning
prepositions, conjunctions, meaning adverbs, prepositions, sentences, etc.
interjections. conjunctions, 3.4 use grammar • Common writing 3.4 use grammar 3.4 use grammar
• Parts of the sentence – 3.4 use grammar interjections. conventions correctly problems/usage: conventions correctly conventions correctly
subjects, linking/action conventions correctly • Parts of the sentence to commu- parallel structure, to commu- to commu-
verbs, adjectives, adverbs, to commu- (review from grade nicate their intended misplaced modifiers, nicate their intended nicate their intended
prepositional clauses, nicate their intended nine) – subjects, meaning clearly dangling participles, meaning clearly meaning clearly
direct/indirect objects, meaning clearly linking/action verbs, comma splices,
object of the prepositions, adjectives, adverbs, Oral Communciation: apostrophe usage, Oral Communciation: Oral Communciation:
adverb phrases, adjective Oral prepositional clauses, 1.8 identify the semi-colons, colons, 1.8 identify the 1.8 identify the
phrases, clauses – noun, Communciation: direct/indirect objects, perspectives and/or etc. perspectives and/or perspectives and/or
adverb, adjective, 1.8 identify the object of the biases evident biases evident biases evident
subordinate, independent, perspectives and/or prepositions, adverb in both simple and in both simple and in both simple and
subordinate clause signals, biases evident phrases, adjective complex oral texts and complex oral texts and complex oral texts and
conjunctions, verbals – in both simple and phrases, clauses – comment on any comment on any comment on any
gerunds, infinitives, complex oral texts noun, adverb, questions they may questions they may questions they may
participles. and comment on any adjective, subordinate, raise about beliefs, raise about beliefs, raise about beliefs,
• Continual parsing questions they may independent, values, and identity values, and identity values, and identity
throughout the year. raise about beliefs, subordinate clause 2.2 demonstrate an 2.2 demonstrate an 2.2 demonstrate an
values, and identity signals, conjunctions, understanding of understanding of understanding of
2.2 demonstrate an verbals – gerunds, several different several different several different
understanding of infinitives, participles. interpersonal speaking interpersonal speaking interpersonal speaking
several different • Word usage: strategies strategies strategies
interpersonal affect/effect, etc. and adapt them to suit and adapt them to suit and adapt them to suit
speaking strategies • Verb-subject the purpose, situation, the purpose, situation, the purpose, situation,
and adapt them to agreement. and audience, and audience, and audience,
suit the purpose, • Punctuation – semi- exhibiting sensitivity to exhibiting sensitivity to exhibiting sensitivity to
situation, and colon, apostrophes, cultural cultural cultural
audience, exhibiting etc. differences differences differences
sensitivity to cultural
differences
Writing/Essay Unit – Grade 9 to 12 Academic/University
Grade 9 Grade 10 Grade 11 Grade 12
Content Expectations Content Expectations Content Expectations Content Expectations
• Giving specific details. 1.1 identify the topic, • MLA format. 1.4 identify, sort, and • Formal voice, formal 1.3 locate and select • Formal voice, formal 2.1 write for different
• Inference reading will lead purpose, and • Moving beyond a five order main ideas and structure. information to support structure. purposes and
to more analytical writing. audience for paragraph essay. supporting • Literary insight paper ideas • Literary insight paper audiences using several
• Difference between several different One point in details for writing and its components – for writing, using and its components – different literary,
summarizing and types of writing tasks directional sentence tasks, using several subject based on first several different subject based on first informational,
analyzing. 1.4 identify, sort, and can lead to several different strategies and major genre done in strategies major genre done in and graphic forms
• Using quotes/examples to order main ideas and paragraphs. organizational patterns the year. and print, electronic, the year. 2.2 establish an
exemplify answers. supporting • Specific details in suited to the content • Development of a and other resources, as • Development of a identifiable voice in
• Five components of the details for writing writing - use and purpose for writing thesis from a topic, appropriate thesis from a topic, their writing,
essay: introduction, tasks, using several examples and quotes 2.4 write complete not a question. 1.5 determine whether not a question. modifying language
thesis, directional different strategies to back up answer. sentences that • Essay structure and the ideas and • Essay structure and and tone to suit the
sentence, body, and organizational • Vary sentence communicate its development for a information gathered its development for a form, audience, and
conclusion. patterns suited to structure for effect. their meaning clearly longer piece. are relevant to the longer piece. purpose for writing
• Five paragraph essay the content and • How to write a and accurately, varying • How to write a topic, sufficient for the • How to write a 2.3 use appropriate
format – by the end of the purpose for writing comparative piece. sentence type, comparative piece. purpose, and meet the comparative piece. descriptive and
year they can move away 2.4 write complete structure, and length requirements of the evocative words,
from this form and are sentences that for different writing task phrases, and
expected to go beyond communicate purposes and making 2.5 explain how their expressions to make
their meaning clearly logical transitions own beliefs, values, and their writing clear and
this in grade ten. experiences are revealed
• How to form a thesis from and accurately, between ideas in their writing vivid for their intended
the question asked. varying sentence 2.7 produce revised 2.7 produce revised audience
• MLA format – final, type, structure, and drafts of both simple drafts of both simple 2.5 explain how their
polished essay in last length for different and and own beliefs, values,
genre (usually purposes and making 3.5 proofread and 3.5 proofread and and experiences are
Shakespeare). logical transitions correct their writing, correct their writing, revealed in their
between ideas using using writing
2.7 produce revised guidelines developed guidelines developed 4.1 describe several
drafts of both simple with the teacher and with the teacher and different strategies
and peers peers they used before,
complex texts 3.7 produce pieces of 3.7 produce pieces of during, and after
written to meet published work to published work to writing; and identify
criteria identified meet criteria identified meet criteria identified several specific steps
by the teacher, based by the teacher, based by the teacher, based they can take to
on the curriculum on the curriculum on the curriculum improve as writers
expectations expectations expectations
Short Stories/Mythology/Debate – Grade 9 to 12 Academic/University
Grade 9 Grade 10 Grade 11 Grade 12
Content Expectations Content Expectations Content Expectations Content Expectations
Short Stories: 1.4 make and explain Mythology 1.4 make and explain Short Stories: 1.4 make and explain Archetypes: 1.4 make and explain
• Responding to Reading inferences about both • Common ones used inferences about both • Viewpoints inferences about both • Common, inferences about both
• Inference reading simple and complex that tie in with simple and complex • Short story simple recognizable simple and complex
• Short story components texts, supporting their literature – Cupid, texts, supporting their components, literary and complex texts, archetypes – keep texts, supporting their
• Common figures of speech explanations Achilles, etc. explanations devices, figures of supporting their them relevant to explanations
(metaphor, simile, etc.) with stated and • Same story, different with stated and implied speech explanations genres studied with stated and implied
• Common literary devices implied ideas from the versions according to ideas from the texts • Writing assignments: with stated and implied • Archetypes can be ideas from the texts
(foreshadowing, irony, texts culture. 1.6 analyse texts in response journals – ideas from the texts manipulated and 1.6 analyse texts in
symbols, etc.) 1.6 analyse texts in • Hero quest. terms of the feeds the literary 1.6 analyse texts in changed terms of the
• Use of voice terms of the information, ideas, insight paper and terms of the information, ideas,
information, ideas, Debates: issues, or themes they independent study. information, ideas, issues, or themes they
issues, or themes they • Oral argument – same explore, examining issues, or themes they explore, examining
explore, examining structure as written how various aspects of explore, examining how various aspects of
how various aspects argument. the texts contribute to how various aspects of the texts contribute to
of the texts contribute • Examples/details the presentation or the texts contribute to the presentation or
to the presentation or must be used. development of these the presentation or development of these
development of these • Backing up points elements development of these elements
elements with research. 1.8 identify the elements 1.8 identify the
1.8 identify the perspectives and/or 2.2 identify several perspectives and/or
perspectives and/or biases evident different text features biases evident
biases evident in both simple and and explain how they in both simple and
in both simple and complex texts help communicate complex texts and
complex texts and 2.2 identify several meaning comment on any
comment on any different text features Writing: questions they may
questions they may and explain how they 2.5 explain how their raise about beliefs,
raise about beliefs, help communicate own beliefs, values, values, and identity
values, and identity meaning and 2.2 identify several
2.2 identify several Oral Communication: experiences are different text features
different text features 2.1 communicate orally revealed in their and explain how they
and explain how they for a range of writing help communicate
help communicate purposes, meaning
meaning using language
appropriate for the
intended audience
Novel Study – Grade 9 to 12 Academic/University
Grade 9 Grade 10 Grade 11 Grade 12
Content Expectations Content Expectations Content Expectations Content Expectations
To Kill A Mockingbird: 1.4 make and explain Lord of the Flies: 1.4 make and explain Wuthering Heights: 1.4 make and explain Fifth Business: 1.4 make and explain
• Narrative structure inferences about both • Themes – innocence, inferences about both • Use of reliable inferences about both • Themes: guilt; inferences about both
• Themes: simple and complex growth, appearance simple and complex narrator. simple appearance(illusion) simple and complex
prejudice/racism, texts, supporting their versus reality texts, supporting their • Plot structure: Classic and complex texts, versus reality texts, supporting their
innocence/growth explanations (disguises/masks), explanations literature gives basis supporting their • Foils explanations
• Literary devices/figures of with stated and evil in man with stated and implied for other pieces – i.e. explanations • Narrative: point of with stated and implied
speech – symbols, implied ideas from the • Symbols/archetypes ideas from the texts To Kill A Mockingbird with stated and implied view, reliability ideas from the texts
foreshadowing, irony, texts • Narrative structure – 1.6 analyse texts in • Characterization and ideas from the texts • Perspective: 1.6 analyse texts in
metaphor, simile, etc. 1.6 analyse texts in point of view terms of the foils. 1.6 analyse texts in challenge it terms of the
• Foils terms of the • Literary techniques – information, ideas, • Themes: love, hate, terms of the • Imagery information, ideas,
• Characterization information, ideas, foreshadowing, irony, issues, or themes they revenge, information, ideas, • Allusions: saints, issues, or themes they
• Vocabulary building issues, or themes they etc. explore, examining supernatural, issues, or themes they Jung, Freud, etc. explore, examining
• Oral communication – explore, examining • Elements of literature how various aspects of ambition, etc. explore, examining • Archetypes how various aspects of
debate how various aspects • Writing strategies – the texts contribute to • Minor characters – how various aspects of the texts contribute to
• Essays on tests of the texts contribute formal/informal the presentation or use, etc. the texts contribute to the presentation or
to the presentation or voice, detail in development of these • Literary devices – the presentation or development of these
development of these writing elements symbols (animals, development of these elements
elements • Essay writing on 1.8 identify the nature, etc.), elements 1.8 identify the
1.8 identify the tests. perspectives and/or foreshadowing, irony, 2.2 identify several perspectives and/or
perspectives and/or biases evident etc. different text features biases evident
biases evident in both simple and and explain how they in both simple and
in both simple and complex texts and help communicate complex texts and
complex texts and comment on any meaning comment on any
comment on any questions they may questions they may
questions they may raise about beliefs, raise about beliefs,
raise about beliefs, values, and identity values, and identity
values, and identity 2.2 identify several 2.2 identify several
2.2 identify several different text features different text features
different text features and explain how they and explain how they
and explain how they help communicate help communicate
help communicate meaning meaning
meaning
Drama Study – Grade 9 to 12 Academic/University
Grade 9 Grade 10 Grade 11 Grade 12
Content Expectations Content Expectations Content Expectations Content Expectations
A Midsummer Night’s 1.4 make and explain Romeo and Juliet: 1.4 make and explain Macbeth: 1.4 make and explain Hamlet: 1.4 make and explain
Dream: inferences about both • Sonnet/prologue. inferences about both • Themes: honour, inferences about both • Themes; appearance inferences about both
• Shakespearean devices: simple and complex • Shakespearean simple and complex revenge, ambition, simple versus reality, honour simple and complex
use of soliloquy, asides, texts, supporting their techniques – prose, texts, supporting their supernatural, etc. and complex texts, and revenge texts, supporting their
dramatic structure (crisis explanations blank verse, rhyming explanations • Foils supporting their • Foils explanations
is always in Act III), with stated and implied schemes, cadence, with stated and implied • Shakespearean explanations • Shakespearean with stated and implied
prose (madness) and ideas from the texts metre, etc. ideas from the texts devices: use of with stated and implied devices: use of ideas from the texts
blank verse (sanity), 1.6 analyse texts in • Literary techniques – 1.6 analyse texts in soliloquy to develop ideas from the texts soliloquy to develop 1.6 analyse texts in
Elizabethan humours, terms of the foreshadowing, terms of the character and 1.6 analyse texts in character and terms of the
etc. information, ideas, dramatic irony, irony, information, ideas, thought, dramatic terms of the thought, dramatic information, ideas,
• Personal opinion piece. issues, or themes they etc. issues, or themes they structure, prose information, ideas, structure, prose issues, or themes they
• MLA formatted essay – explore, examining • Figurative language – explore, examining (madness) and blank issues, or themes they (madness) and blank explore, examining
formal, minor literary how various aspects of oxymorons, how various aspects of verse (sanity), explore, examining verse (sanity), how various aspects of
insight paper, driven by the texts contribute to metaphors, etc. the texts contribute to Elizabethan humours, how various aspects of Elizabethan humours, the texts contribute to
specific topic/question the presentation or • Themes – innocence, the presentation or etc. the texts contribute to • Mood and the presentation or
given by teacher. development of these growth, appearance development of these • Mood and the presentation or atmosphere development of these
• Essay on tests. elements versus reality elements atmosphere development of these • Imagery: disease, elements
1.8 identify the • Elizabethan humours 1.8 identify the • Imagery: blood, elements harlot 1.8 identify the
perspectives and/or • Formal essay – minor perspectives and/or animals, colours, etc 2.2 identify several • Archetypes perspectives and/or
biases evident literary insight paper biases evident • Minor characters – different text features • Perspective: biases evident
in both simple and – MLA format. in both simple and use, etc. and explain how they challenge it; is in both simple and
complex texts complex texts • Archetypes help communicate Hamlet’s reliable? complex texts
2.2 identify several 2.2 identify several • Figures of speech meaning • Faults of man 2.2 identify several
different text features different text features Media different text features
• Literary insight paper • Figures of speech
and explain how they and explain how they – if this genre done 2.7 use a variety of and explain how they
• Literary insight paper
help communicate help communicate first audio-visual aids help communicate
– if this genre done
meaning meaning appropriately meaning
first
Media Media to support and Media
2.7 use a variety of 2.7 use a variety of enhance oral 2.7 use a variety of
audio-visual aids audio-visual aids presentations and audio-visual aids
appropriately appropriately to engage an audience appropriately
to support and enhance to support and to support and
oral presentations and enhance oral enhance oral
to engage an audience presentations and presentations and
to engage an audience to engage an audience
You might also like
- Latin American Spanish: All-Round Confidence LanguageDocument291 pagesLatin American Spanish: All-Round Confidence LanguageDavid Langarica100% (2)
- Subject Verb AgreementDocument24 pagesSubject Verb AgreementJoiche Itallo LunaNo ratings yet
- Active Passive VoiceDocument14 pagesActive Passive VoiceAbhieey Choi Soo HyunNo ratings yet
- Plural Forms of Compound NounsDocument6 pagesPlural Forms of Compound NounsJannice Coscolluela Canlas100% (1)
- English Tonality/tonicityDocument22 pagesEnglish Tonality/tonicitynomichui100% (3)
- Language Arts Activity Cards for School and Home, Grade 1From EverandLanguage Arts Activity Cards for School and Home, Grade 1No ratings yet
- K to 12 English Curriculum GuideDocument31 pagesK to 12 English Curriculum GuideHoneyBee Banagan75% (16)
- MTB - MLE 1-QUARTER-4 Week 1Document8 pagesMTB - MLE 1-QUARTER-4 Week 1Kathsmae SuazoNo ratings yet
- VocabuLearn foreign language learning program divides cassettes and promotes fast learningDocument21 pagesVocabuLearn foreign language learning program divides cassettes and promotes fast learningamaliab0% (1)
- Grammar Practice Simplified: Guided Practice in Basic Skills (Book B, Grades 3-4): Sentences, Verbs, Nouns, Pronouns, Capitalization, Subjects, Predicates, and MoreFrom EverandGrammar Practice Simplified: Guided Practice in Basic Skills (Book B, Grades 3-4): Sentences, Verbs, Nouns, Pronouns, Capitalization, Subjects, Predicates, and MoreNo ratings yet
- English For NursesDocument214 pagesEnglish For NursesLeonte Știrbu86% (7)
- Verbs Information SheetDocument2 pagesVerbs Information SheetLen Vicente - FerrerNo ratings yet
- Delta Module One Report June 2010Document62 pagesDelta Module One Report June 2010AlchemisterNo ratings yet
- Performance TaskDocument2 pagesPerformance TaskLaarni Antiola SardeaNo ratings yet
- Eng8 Wk4.1Document8 pagesEng8 Wk4.1Jepoy D VloggerNo ratings yet
- Q4 Week1 English 7Document8 pagesQ4 Week1 English 7mads caasiNo ratings yet
- Week 1 English 9 and 7 Very FinalDocument7 pagesWeek 1 English 9 and 7 Very FinalCristy Gasco SumpayNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Part 1 1Document1 pageModule 1 - Part 1 1api-512818325No ratings yet
- WritingDocument12 pagesWritingapi-459118418No ratings yet
- CIE Prior - American Language Program Grammar PDFDocument4 pagesCIE Prior - American Language Program Grammar PDFionelabNo ratings yet
- Eng8 Wk4.2Document8 pagesEng8 Wk4.2Jepoy D VloggerNo ratings yet
- DLL Week 7 Eng VDocument14 pagesDLL Week 7 Eng VRicky UrsabiaNo ratings yet
- Language Functions and Forms: WWW - Ode.state - Or.us/teachlearn/real/standardsDocument11 pagesLanguage Functions and Forms: WWW - Ode.state - Or.us/teachlearn/real/standardsBayu CrazzieNo ratings yet
- Activity On Worksheet DesigningDocument2 pagesActivity On Worksheet DesigningSharen Faye E. LaoNo ratings yet
- English Progression MapDocument14 pagesEnglish Progression MapAditiNo ratings yet
- Grade 1 English Lesson Plan Week 7 Q3 SY 2018-2019Document24 pagesGrade 1 English Lesson Plan Week 7 Q3 SY 2018-2019jenilynNo ratings yet
- Baldwin-Wallace University School of Education Unit Plan TemplateDocument7 pagesBaldwin-Wallace University School of Education Unit Plan Templateapi-422625647No ratings yet
- Relacion Objetivos y ContenidosDocument4 pagesRelacion Objetivos y ContenidosTeresa MarhuendaNo ratings yet
- DLL - MTB 1 - Q4 - W6 - For MergeDocument11 pagesDLL - MTB 1 - Q4 - W6 - For MergeTser LodyNo ratings yet
- Reading Content Domains ProgressionDocument6 pagesReading Content Domains ProgressionRemNo ratings yet
- Ac9 English Prep-Yr6 As SequenceDocument2 pagesAc9 English Prep-Yr6 As SequenceDavidNo ratings yet
- Week7 English2Document1 pageWeek7 English2Leilani SantiagoNo ratings yet
- MTB - MLE 1-QUARTER-4 Week 1Document8 pagesMTB - MLE 1-QUARTER-4 Week 1hazelkia adrosallivNo ratings yet
- DLL Q1eng5-W3Document4 pagesDLL Q1eng5-W3Neriza JeanNo ratings yet
- SEM1 SESI 1718 - UHF2111 - Speaking Test 1 - V2 - StudentDocument6 pagesSEM1 SESI 1718 - UHF2111 - Speaking Test 1 - V2 - StudentNazrul Haffiz Mohd BahrudinNo ratings yet
- 10 International English: Language CompetitionDocument6 pages10 International English: Language Competitionhweta173No ratings yet
- UHF2111 - Speaking Test 1Document6 pagesUHF2111 - Speaking Test 1mierulsNo ratings yet
- DLL-WEEK 8 ENGLISH 3rd QDocument6 pagesDLL-WEEK 8 ENGLISH 3rd QAis Agon AcebucheNo ratings yet
- Week 3 English 8 and 10 Very FinalDocument6 pagesWeek 3 English 8 and 10 Very FinalCristy Gasco SumpayNo ratings yet
- Rubric - Language Arts: 3 Meets StandardDocument5 pagesRubric - Language Arts: 3 Meets Standardapi-350278355No ratings yet
- MTB Week 6Document8 pagesMTB Week 6Janneth Alquizar ImperialNo ratings yet
- Oxburgh Academy English Scheme of Work 2017/2018Document30 pagesOxburgh Academy English Scheme of Work 2017/2018Tisha Nair ടിഷ നായര്No ratings yet
- Thematic Curriculum For The 11 GradeDocument39 pagesThematic Curriculum For The 11 GradeBoloroo ErdenebilegNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH 5 Q1 Week 4Document14 pagesENGLISH 5 Q1 Week 4Junelle Joy CatbaganNo ratings yet
- Actividad Oral - Corte 1 - Ingles IvDocument2 pagesActividad Oral - Corte 1 - Ingles IvJ David BrunalNo ratings yet
- Week2 DLL EnglishDocument7 pagesWeek2 DLL EnglishVirgil Acain GalarioNo ratings yet
- WEEk 11 remediationGRADE IVDocument3 pagesWEEk 11 remediationGRADE IVRhey GalarritaNo ratings yet
- CLIL and Evaluating Materials - 3 - British Council-EAQUALS Core InventoryDocument2 pagesCLIL and Evaluating Materials - 3 - British Council-EAQUALS Core Inventorykataky100% (1)
- 9 - 12 Argument Common RubricDocument3 pages9 - 12 Argument Common Rubricapi-253387038No ratings yet
- Unpacking The Standards For Understanding: SUBJECT: English Content Standard Performance Standard CompetenciesDocument4 pagesUnpacking The Standards For Understanding: SUBJECT: English Content Standard Performance Standard CompetenciesPaul Daniel GalangNo ratings yet
- Week3 English2Document1 pageWeek3 English2Leilani SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Melbourne Girls Grammar Chinese SAC 1 Role-playDocument4 pagesMelbourne Girls Grammar Chinese SAC 1 Role-playjingNo ratings yet
- Year 4 Curriculum Handbook 2020-2021Document22 pagesYear 4 Curriculum Handbook 2020-2021fm100No ratings yet
- 2nd Rws QuizDocument1 page2nd Rws QuizZyren Joy SamillanoNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Rubric - SpeakingDocument1 pageEvaluation Rubric - SpeakingJohny StarkNo ratings yet
- Oral Presentation Scoring RubricDocument2 pagesOral Presentation Scoring RubricHanna PertiwiNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 1 - Q4 - W5Document6 pagesDLL - English 1 - Q4 - W5hazelkia adrosallivNo ratings yet
- November DLL Oral-CommDocument4 pagesNovember DLL Oral-CommSophia Joy A. FajardoNo ratings yet
- Stubbington Rti LiteracyDocument2 pagesStubbington Rti Literacyapi-420601149No ratings yet
- Week4 English2Document1 pageWeek4 English2Leilani SantiagoNo ratings yet
- DLL Eng9Document5 pagesDLL Eng9Anicia Sabrina Pongco Minon100% (1)
- DLL SampleDocument6 pagesDLL SampleRACHELL SATSATINNo ratings yet
- Mastermind 1 Practice OnlinexDocument9 pagesMastermind 1 Practice OnlinexGrecia Ugarte ArchondoNo ratings yet
- Language Functions and FormsDocument11 pagesLanguage Functions and FormsMaddalineNo ratings yet
- Oralcom Las4calopezDocument5 pagesOralcom Las4calopezFebie Jean Gelantaga-anNo ratings yet
- Oralcom Las4calopezDocument5 pagesOralcom Las4calopezFebie Jean Gelantaga-anNo ratings yet
- TabLang elementary school weekly English lessonDocument7 pagesTabLang elementary school weekly English lessonPatricia Ann MacaraegNo ratings yet
- California A3 ComparisonDocument12 pagesCalifornia A3 Comparisonsurnam63No ratings yet
- Grade 1 DLL MTB Q4 Week 9Document6 pagesGrade 1 DLL MTB Q4 Week 9Chat DivineNo ratings yet
- Past Simple TenseDocument17 pagesPast Simple TenseAPRILIA NURULNo ratings yet
- Sra Imagine It Year OverviewDocument6 pagesSra Imagine It Year Overviewapi-327764415No ratings yet
- SEC A - Time allowed: 20 minutesDocument3 pagesSEC A - Time allowed: 20 minutesanasgiNo ratings yet
- Futebol em Minutos Livro de Regras em Ingles 55217Document2 pagesFutebol em Minutos Livro de Regras em Ingles 55217PedroNo ratings yet
- Modal-Like Verbs: Dora Abigail Mejía GarciaDocument11 pagesModal-Like Verbs: Dora Abigail Mejía GarciaAbigailNo ratings yet
- Syntactic Change SummaryDocument5 pagesSyntactic Change SummaryZulbitah SidekNo ratings yet
- List of Comparatives and SuperlativesDocument13 pagesList of Comparatives and SuperlativesDina Narváez83% (6)
- Rules For Reported SpeechDocument7 pagesRules For Reported SpeechPannaNo ratings yet
- 200 Verbos en Ingles Con TraduccionDocument8 pages200 Verbos en Ingles Con TraduccionEmanuel Gonzalez Jerez0% (1)
- Marriage Agreement Validity When Not RegisteredDocument21 pagesMarriage Agreement Validity When Not RegisteredAjeng cintyaaNo ratings yet
- PrepositionsDocument15 pagesPrepositionsParameswari PerumalNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Tense: Presented by Indah Dwi Permanawati 1305020082Document7 pagesSimple Past Tense: Presented by Indah Dwi Permanawati 1305020082Indah Dwi PNo ratings yet
- Grammaticality, Acceptability, Possible Words and Large Corpora-4Document21 pagesGrammaticality, Acceptability, Possible Words and Large Corpora-4Ντάνιελ ΦωςNo ratings yet
- Content and Function Words DefinedDocument2 pagesContent and Function Words DefinedjudeeanneNo ratings yet
- Review: Imperatives: Infinitive Simple FormDocument35 pagesReview: Imperatives: Infinitive Simple FormnayunasaNo ratings yet
- Business Law/Rfbt: Atty. Macmod 2018 EditionDocument35 pagesBusiness Law/Rfbt: Atty. Macmod 2018 EditionKira LimNo ratings yet
- Football ModuleDocument5 pagesFootball ModuleRijah VenzonNo ratings yet
- Non-Linear Reading Path: Espen Aarseth "Nonlinearity and Literary Theory,"Document3 pagesNon-Linear Reading Path: Espen Aarseth "Nonlinearity and Literary Theory,"Genelle SorianoNo ratings yet
- Learn To Read Latin: Ch. 12 OutlineDocument3 pagesLearn To Read Latin: Ch. 12 OutlineJessica ChaseNo ratings yet
- Unit 8: Hypothetical or Imaginary Situations.: Form 1Document4 pagesUnit 8: Hypothetical or Imaginary Situations.: Form 1Emely Gabriela FNo ratings yet
- Substantivul A) GenulDocument3 pagesSubstantivul A) GenulLacraNo ratings yet