Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ccccccccccop
Uploaded by
isaacOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ccccccccccop
Uploaded by
isaacCopyright:
Available Formats
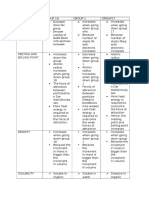
General Chemistry Atomic Theory Periodic T?
ends
Besides reacting with oxygen, alkaline earth metals can also be oxidized by
halogens, nitrogen, and hydrogen. Reactions 2.I2, 2.I9,2.I4, and 2.1.5 arc a
random sampling of these reactions:
Mg(s) + 2 HCI(aq) ----+ MgCl2(aq) + Hz(g)
Reaction 2.L2
3 Sr(s) + 2 N2(g) ---'€- 2 Sr3N2(s)
Reaction 2.13
T
Be(s)+Hz(g)+ BeH2(s)
Reaction 2.L4
0
Ba(s) + I2(g) -+ BaI2(s)
x
Reaction 2.15 "I
it
Chalcogens (Group VI) lil
Chalcogens are metalloids and non-metals from the sixth column of the periodic
rH
table. Included are oxygen, sulfur, selenium, tellurium, and polonium. Oxygen,
W
sulfur, and selenium are non-metals, while tellurium and polonium are
metalloids. The common feature is that their valence shell is ns2np4. They form
s
several covalent molecules with non-metals. As neutral elements, they are
oxidizing agents, because they gain two electrons to become a -2 anion with a
,{
filled octet. However, their reactivity decreases as you descend the column,
,0
because the first and second electron affinities are not as great. They are often
r@
insoluble, although it varies with their counterion (cation). Oxygen exists as a
rS
diatomic molecule (O), sulfur and selenium exist as octatomic molecules (sg and
dt
Se6), and tellurium and polonium exist in vast molecular matrices.
D
Halogens (Group VII) di
Halogens are non-metals from the seventh column of the periodic table. #
Included are fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine. The common
feature is that their valence shell is ns2np5. They form covalent molecules with
non-metals and ionic compounds with metals. As neutral elements, they are
strong oxidizing agents, because they readily gain an electron to become a -1
anion with a filled octet. However, their reactivity decreases as you descend the
column, because the electron affinity is not as great. They are often soluble"
although it varies with their counterion (cation). They all exist as a diatomic
molecules (X2), although little is known of astatine due to its radioactivity.
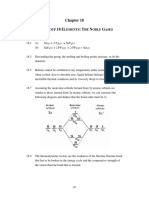
Noble Gases (Group VIII)
Noble gases are non-metals from the eighth (and last) column of the periodic
table. Included are helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon. The
common feature is that their valence shell is complete at ns2np6. For the mosl
part, they form no bonds and exist as monatomic atoms. Thanks to the work of
Neil Bartlett of U.C. Berkeley, xenon and krypton are known to form compoun&
with halogens. The compounds with fluorine show more electron densitn
around fluorine, implying that fluorine is more electronegative than either xenor"
or krypton.
Copyright @ by The Berkeley Review loa The Berkeley Reviw
You might also like
- Systools Demo: Kcse Cluster Test 14Document4 pagesSystools Demo: Kcse Cluster Test 14isaacNo ratings yet
- Systools Demo: Kcse Cluster Tests 12Document4 pagesSystools Demo: Kcse Cluster Tests 12isaacNo ratings yet
- Once You Upload An Approved Document, You Will Be Able To Download The Document IGCSE Physics WorkbookDocument1 pageOnce You Upload An Approved Document, You Will Be Able To Download The Document IGCSE Physics WorkbookisaacNo ratings yet
- Surveying Volume 2 by Dr. B.C.Punmia, Ashok Kumar Jain, Arun Kumar Jain - Laxmi Publications - Free Download PDFDocument1 pageSurveying Volume 2 by Dr. B.C.Punmia, Ashok Kumar Jain, Arun Kumar Jain - Laxmi Publications - Free Download PDFisaacNo ratings yet
- Systools Demo: Kcse Cluster Tests 12Document4 pagesSystools Demo: Kcse Cluster Tests 12isaacNo ratings yet
- Problems And: Surveying SolutionsDocument1 pageProblems And: Surveying SolutionsisaacNo ratings yet
- I&II - Agricultural EngineeringDocument1 pageI&II - Agricultural EngineeringisaacNo ratings yet
- Measurement: LinearDocument1 pageMeasurement: LinearisaacNo ratings yet
- Problems And: Surveying SolutionsDocument1 pageProblems And: Surveying SolutionsisaacNo ratings yet
- Testing and Adjustment of A LevelDocument1 pageTesting and Adjustment of A LevelisaacNo ratings yet
- Activity Activity Description Key Performance Indicator Risk Supervisor's CommentsDocument1 pageActivity Activity Description Key Performance Indicator Risk Supervisor's CommentsisaacNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry: SurveyingDocument1 pageTrigonometry: SurveyingisaacNo ratings yet
- Points To Remember: Voucher Entry in Tally - ERP 9Document1 pagePoints To Remember: Voucher Entry in Tally - ERP 9isaacNo ratings yet
- 2.3.2 Base Currency Information: Fundamentals of Tally - ERP 9Document1 page2.3.2 Base Currency Information: Fundamentals of Tally - ERP 9isaacNo ratings yet
- Problems: SolutionsDocument1 pageProblems: SolutionsisaacNo ratings yet
- Instrumental: OpticsDocument1 pageInstrumental: OpticsisaacNo ratings yet
- AND Curves: Vertical TransitionDocument1 pageAND Curves: Vertical TransitionisaacNo ratings yet
- Surveying Solutions: Problems andDocument1 pageSurveying Solutions: Problems andisaacNo ratings yet
- Problems AND: Surveying SolutionsDocument1 pageProblems AND: Surveying SolutionsisaacNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Creation/ Setting Up of Company in Tally - ERP 9Document1 page2.3 Creation/ Setting Up of Company in Tally - ERP 9isaacNo ratings yet
- VBM PDFDocument1 pageVBM PDFisaacNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Basics of AccountingDocument1 pageLesson 1: Basics of AccountingisaacNo ratings yet
- Advanced Accounting in Tally - ERP 9: Figure 6.1 Ledger CreationDocument1 pageAdvanced Accounting in Tally - ERP 9: Figure 6.1 Ledger CreationisaacNo ratings yet
- NMBYDocument1 pageNMBYisaacNo ratings yet
- 5.3.3 Walk-Through To Create An Account InvoiceDocument3 pages5.3.3 Walk-Through To Create An Account InvoiceisaacNo ratings yet
- Er 9Document2 pagesEr 9isaacNo ratings yet
- Goo ErpDocument1 pageGoo ErpisaacNo ratings yet
- Continental Slope Continental Crust Sedimentary RockDocument1 pageContinental Slope Continental Crust Sedimentary RockisaacNo ratings yet
- Relation To Academic Performance: Courtesy: Deccan HeraldDocument1 pageRelation To Academic Performance: Courtesy: Deccan HeraldisaacNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Bangladesh International School, Dammam The Periodic Table An Overview of The Periodic TableDocument4 pagesBangladesh International School, Dammam The Periodic Table An Overview of The Periodic TableSIAM PLAZ YTNo ratings yet
- Elements Matching Game CardsDocument4 pagesElements Matching Game CardsMoath AlsaidNo ratings yet
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesDocument3 pagesClassification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesBurhanuddin SlatewalaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes Form 4 Chapter 4Document5 pagesChemistry Notes Form 4 Chapter 4lenovosubaNo ratings yet
- 2.3. Periodic Table and Trends NotesDocument12 pages2.3. Periodic Table and Trends Noteschunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- Water Disassociation Using Zero Point EnergyDocument99 pagesWater Disassociation Using Zero Point Energyshizuye100% (2)
- MODULE 1-Pharmaceutical Chemistry: Prepared By: Florence Claire MarceloDocument3 pagesMODULE 1-Pharmaceutical Chemistry: Prepared By: Florence Claire MarceloellysayusopNo ratings yet
- Official Soldier GD Paper - (Katihar) - 23 Feb 2020 EnglishDocument62 pagesOfficial Soldier GD Paper - (Katihar) - 23 Feb 2020 Englishs saravanaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Noble GasesDocument26 pagesChemistry of Noble GasesjaqNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE PMR Notes and ExperimentsDocument221 pagesSCIENCE PMR Notes and ExperimentsAzlina Ahmad100% (1)
- Chemistry Notes Form 4 PDF Free PDFDocument28 pagesChemistry Notes Form 4 PDF Free PDFJane DoeNo ratings yet
- A History of Rife's Instruments and FrequenciesDocument111 pagesA History of Rife's Instruments and Frequenciesacuario33No ratings yet
- Important Notice: Additional Combined Science 5130 GCE O Level 2007Document37 pagesImportant Notice: Additional Combined Science 5130 GCE O Level 2007rodel.verzosaNo ratings yet
- OMAR IBRAHIM 3 - Students - ANALYZING DATA - Physical Properties of Gaseous ElementsDocument4 pagesOMAR IBRAHIM 3 - Students - ANALYZING DATA - Physical Properties of Gaseous ElementsOmar Ibrahim LNo ratings yet
- Class 8th - Periodic TableDocument2 pagesClass 8th - Periodic TableUniyals AcademyNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 IB Bridging Course - Chemistry: Topic 1 Atomic Structure Part 3 Electron ArrangementDocument9 pagesGrade 10 IB Bridging Course - Chemistry: Topic 1 Atomic Structure Part 3 Electron ArrangementMarc LoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding-NotesDocument47 pagesChemical Bonding-NotesHimanshu Meena100% (3)
- Revision Notes On P-Block Elements:: BoronDocument15 pagesRevision Notes On P-Block Elements:: BoronKarthikayan BalajiNo ratings yet
- S2 Is 1st WorkbookDocument84 pagesS2 Is 1st WorkbookWinnie ChanNo ratings yet
- ch18 OddDocument4 pagesch18 OddatiqahNo ratings yet
- Group I Elements Aka The Alkali Metals: K(S) +O2 (G) KO2(s)Document3 pagesGroup I Elements Aka The Alkali Metals: K(S) +O2 (G) KO2(s)nNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering MCQsDocument4 pagesChemical Engineering MCQsRexel ReedusNo ratings yet
- NSSCO Chemistry SyllabusDocument52 pagesNSSCO Chemistry SyllabusEbic GamerNo ratings yet
- Gas & Dye LasersDocument39 pagesGas & Dye LasersDivya AseejaNo ratings yet
- BC Science 9 Chemistry Unit Study GuideDocument2 pagesBC Science 9 Chemistry Unit Study Guideerinyth100% (2)
- Chapter 2 Chemistry For Engineers Final Module 2Document26 pagesChapter 2 Chemistry For Engineers Final Module 2Alex Jr. Rosadiño C.No ratings yet
- Unit 01 NotesDocument32 pagesUnit 01 Notesapi-336093393No ratings yet
- Eng Periodic-92 PDFDocument11 pagesEng Periodic-92 PDFPepe MNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 q2 Module 2Document36 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 q2 Module 2Akizy Clauken100% (1)
- Be ChemDocument30 pagesBe ChemSka dooshNo ratings yet