Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acoustics 03
Uploaded by
Pau Orteza0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views1 pageAcoustics informations
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAcoustics informations
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views1 pageAcoustics 03
Uploaded by
Pau OrtezaAcoustics informations
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
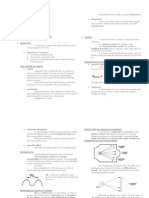
ACCOUSTICS 3.
Amplitude - maximum displacement
SCIENCE & TREATMENT OF SOUND
4. Velocity - speed of sound
ELEMENTS:
5. Wavelength - distance
1. Source
2. Transmission path
6. Pure tone - one energy one frequency
3. Receiver
7. Musical Tone - many pre tones
POROUS ABSORBENT
Best for lower band frequency
8. Intensity - rate of flow at sound energy
ECHO
The repetition of a sound produced by the reflection of sound waves from
QUALITY OF SOUND
an obstructing surface, loud enough and received late enough to be perceived as
distinct from the source
1. Reverberation - the prolonging of sound
RESONANCE
The intensification and prolongation of sound produced by sympathetic 2. Echo - repetition of sound, with magnitude and delay
vibration
3. Flutter - rapid succession of echoes caused by the reflection of
PHON sound waves back and forth between two parallel surfaces
Unit of loudness level
4. Creep/ Crawl - reflection of sound from a curved surface
SOUND ABSORPTION
Process of dissipating sound energy by converting it into heat 5. Sound Foci
SOUND 6. Diffusion - sound is everywhere
Fluctuation in pressure, particle displacement in elastic medium
7. Refraction - when traveling forward in a straight path, it changes
SABIN direction as it passes through different density and causes
unit of absorption equivalent to 1 sq ft of perfectly absorptive material sound wave to bend
8. Diffraction - acoustic phenomenon which causes sound wave to bend
Frequency - expressed in hertz
Decibel - unit of sound 9. Focusing - sound waves reflected from a concave surface
Noise - unwanted sound
Decay time - reverberation tie
Hertz - the Si unit of frequency
CHARACTER OF SOUND
1. Cycle - full circuit of particle
____________________________________________www.architectscube.com
2. Frequency - number of times a cycle is repeated
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Acoustics and Lighting: FrequenciesDocument15 pagesAcoustics and Lighting: FrequenciesPau OrtezaNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Scope and DelimitationDocument3 pagesScope and DelimitationPau OrtezaNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Related Literature ReferencesDocument1 pageRelated Literature ReferencesPau OrtezaNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- dOOR hARDWAREDocument385 pagesdOOR hARDWAREPau OrtezaNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Admin Dept.: Ticketing Office Finance DeptDocument3 pagesAdmin Dept.: Ticketing Office Finance DeptPau OrtezaNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Sustainable Architecture - Is: Green Architecture, Philosophy ofDocument1 pageSustainable Architecture - Is: Green Architecture, Philosophy ofPau OrtezaNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Waves - Worksheet 2Document7 pagesWaves - Worksheet 2Ricardo Johnson0% (2)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Understanding & Using Ansel Adam's Zone System PDFDocument19 pagesUnderstanding & Using Ansel Adam's Zone System PDFPremanand Velu100% (4)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Position, Velocity and AccelerationDocument12 pagesPosition, Velocity and AccelerationawbNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- ABSTRACT On HolographyDocument4 pagesABSTRACT On HolographyAftab Popatia80% (5)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- FOC Drum Test ReportDocument3 pagesFOC Drum Test ReportMinoj SarasanNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Non-Destructive Testing Applications in Commercial Aircraft MaintenanceDocument9 pagesNon-Destructive Testing Applications in Commercial Aircraft MaintenanceEdgardo José Tamaronis LeonettNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument23 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectPurva Shyama100% (1)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Astronomy Today 7Th Edition: Chaisson/McmillanDocument28 pagesAstronomy Today 7Th Edition: Chaisson/Mcmillanvenkat_09No ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Universe: Glocielle F. Molabola Department of Biology College of Science Polytechnic University of The PhilippinesDocument16 pagesThe Universe: Glocielle F. Molabola Department of Biology College of Science Polytechnic University of The PhilippinesPaul Symon CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- STPM Physics Sem 1 Circular MotionDocument5 pagesSTPM Physics Sem 1 Circular MotionChong Yin Ping0% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- International Military Catalogue 2008 Night Vision ProductsDocument34 pagesInternational Military Catalogue 2008 Night Vision Productsnadeem_skNo ratings yet
- Physics Final ProblemsDocument17 pagesPhysics Final ProblemsCheldon BigDaddy Banks100% (1)
- Lighting Design2010Document26 pagesLighting Design2010Ganesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Photonics Chapter 1Document59 pagesFundamentals of Photonics Chapter 1orhan şentürk100% (1)
- Vectors MCQDocument1 pageVectors MCQAbduŕ RehmanNo ratings yet
- Physics WaecDocument31 pagesPhysics WaecTunde IpayeNo ratings yet
- Remote Sensing and GisDocument17 pagesRemote Sensing and Gismd khajaNo ratings yet
- 019503016Document5 pages019503016alephiiNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- PHYSICAL SCIENCE Quarter II - Week 5 Light PhenomenaDocument1 pagePHYSICAL SCIENCE Quarter II - Week 5 Light PhenomenaSamantha AlzateNo ratings yet
- Gjyxch 8 Core FTTH Drop Cable: PecificationDocument2 pagesGjyxch 8 Core FTTH Drop Cable: PecificationluiggiNo ratings yet
- D'Alembert's MechanicsDocument1 pageD'Alembert's MechanicsridwanphyNo ratings yet
- Potential Energy PDFDocument14 pagesPotential Energy PDFCancele RoleNo ratings yet
- Phys222 Pretest PDFDocument8 pagesPhys222 Pretest PDFDanNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Gravitation 150820160911 Lva1 App6892 PDFDocument22 pagesGravitation 150820160911 Lva1 App6892 PDFAshutosh Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Test-21 Law of Motion Fricton Circular E WADocument4 pagesTest-21 Law of Motion Fricton Circular E WAAditya RajputNo ratings yet
- FRQ Modern PhysicsDocument22 pagesFRQ Modern PhysicsIvycrazeNo ratings yet
- Physics Experiment - Estimating The Wavelengths of Light Using A Plane Diffraction GratingDocument3 pagesPhysics Experiment - Estimating The Wavelengths of Light Using A Plane Diffraction GratingYAN YI LAMNo ratings yet
- UV VIS Phenol LabDocument6 pagesUV VIS Phenol LabJoão Paulo FioriNo ratings yet
- Complex Problems 2nd LawDocument8 pagesComplex Problems 2nd LawRenzdy MejillaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE (9-1) : Physics 0972/22Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE (9-1) : Physics 0972/22Tristan GrahamNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)