Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Manage Product Delivery (MP) Manage Product Delivery (MP) : & Benefit Review Plan
Uploaded by
Anonymous SmYjg7gOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Manage Product Delivery (MP) Manage Product Delivery (MP) : & Benefit Review Plan
Uploaded by
Anonymous SmYjg7gCopyright:
Available Formats
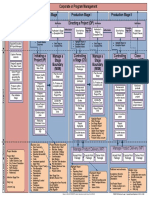
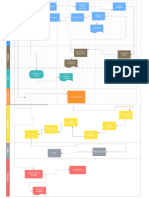
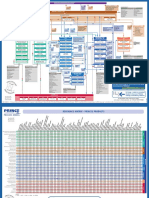
Corp/Program
Corporate or Program Management
Project
Mandate Pre-Project Initiation Stage Delivery Stage I Delivery Stage II
Starting Up a Notification Notification Directing a Project (DP) Notification Notification
Project (SU) Authorize A Authorization
Premature Authorize A Authorization Premature Authorize
Authorize Authorize Give Ad-Hoc Stage End Give Ad-Hoc Stage End
Direction
Project Brief Stage or Stage or Project
Initiation The Project Direction Direction
Initiation Stage Plan Exception Plan Exception Plan Closure
Project Initiation Highlight Report or
Appoint Exec & Next Stage or Next Stage or Highlight Report or
Document Exception Report
ExceptionPlan ExceptionPlan Exception Report
PM & Benefit Review Escalated Issues
Plan
Capture Previous
Lessons Initiating a Manage a Controlling Manage a Controlling Close
Project (IP) Stage a Stage (CS) Stage a Stage (CS) Project (CP)
Design & appoint
PMT Prepare Risk Boundary Authorize Boundary Authorize Prepare
Work Work planned
Man. Strat. (MSB) Packages (MSB) Packages closure
Prepare Plan the next Plan the next
Prepare outline Receive Stage Receive Or, Prepare
Quality Stage completed completed
Business Case Man.Strat premature
Work Or, Produce Work closure
Or, Produce packages packages
Select the Project Prepare an exception an exception
Select& Pr.
approach Configuration plan Hand over
plan Review work Review work products
approach,
assemble the Project Man.Strat. package status package status
Management
Brief Update the Update the
Prepare Project Plan Evaluate the
Plan Initiation Communica- Project Plan Capture and Capture and
Stage examine examine project
tion Man.Strat Update the
Update the issues & risks issues & risks
Business Case Business Case Recommend
Set-up Project project closure
Controls Review Stage Review Stage
Report Stage Status Report Stage Status
Create project End End
plan Take Take
Corrective Corrective
Refine the action Highlight Report action
Business Case Work Package
Report End Stage Report Report
Highlights Exception Report Highlights
Assemble The Issue Report
PID Update Issue Register
Escalate Update Lessons Log Escalate
issues and Lessons Report issues and
risks Product Status account risks
pankajsh10@yahoo.com
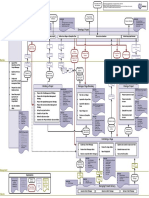
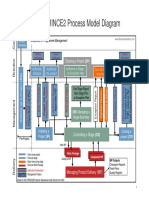
Business Case Project Initiation Document
Manage Product Delivery (MP)
Delivery
Exec Summary
Reasons
Extracts from P.Brief
Risk Man. Strategy Manage Product Delivery (MP)
Project Mandate Expected Benefits Quality Man. Strategy
Project Brief
Expected dis-benefits Config Man. Strategy Accept Work Execute Work Deliver Work Accept Work Execute Work Deliver Work
Project Definition Timescale Communication Package Package Package Package Package Package
Costs Man.Strategy
Four Management levels ->
Outline Business Case Proj Man Team structure
Proj. Product. Description Investment appraisal
Major Risks Role descriptions
Proj. Approach Detailed Business Case Highlight Report
Plan (Stage, Project, Team)
PMT Structure Date Additional work estimates
Plan description Project Plan Update / close
Role descriptions Reporting Period
Prerequisites Project Controls Checkpoint Report Project Plan
References Status Summary Acceptance Records
Dependencies Date, period Configuration item records
Assumptions Next Stage Plan Products & work packages Follow-ups (See Project Product Benefits review plan
Initiation Stage Plan Benefits Review Plan This reporting period Description)
Lessons This/next reporting period Registers:
Monitoring & control Next reporting period Work Package tolerance Issue Register,
Daily Log Configuration Item Records Project & Stage tolerances End Project Report
Budgets status Quality Register,
Tolerances Issue Register Requests for Change Issues & risks Follow-on actions rec’s Risk Register,
Lessons Log Quality Register Lessons report
Prod. Descriptions Key issues & risks Daily Log
Schedule Risk Register Lessons Report
PRINCE2® is a Registered Trademark of AXELOS LTD
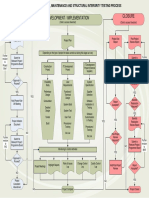
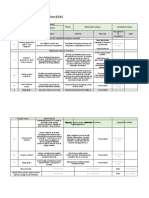
The four integrated elements of PRINCE2 Tolerances: Project assurance is responsibility of
project board; Checking on all aspects of
Tolerances on the 6 project objectives Time
Seven Principles help delegate authority - Management project performance
Seven Themes Seven Processes Tailoring PRINCE2 to
1. Continued business justification 1. Business Case (Why?) 1. Starting Up A Project (SU)
by Exception. Benefit Cost
2. Learn from experience create fit with project Quality assurance is responsibility of
2. Organization (Who?) 2. Directing A Project (DP) environment and Tolerance Area/Management Prod.: Corporate or Programme management
3. Defined roles and responsibilities Business Case (B) Risk Quality (Quality policies outside the project). It
3. Quality (What?) 3. Initiating a Project (IP) context of the project.
4. Manage by stages 4. Plans (How? How Much? When?) 4. Controlling A Stage (CS) Project Plan (T,C,S) Risk.strat.(R) provides stakeholders with confidence
5. Manage by exception Scope that quality requirements can be fulfilled
5. Risk (What if? ) 5. Managing Product Delivery (MP) PRINCE2 can be Stage Plan (T,C.S.R)
6. Focus on products Work Package (T,C,S,R) Quality assurance should not be confused
6. Change (What’s the impact?) 6. Managing Stage Boundaries (MSB) tailored to any type or
7. Tailor to suit the project 7. Progress (On Target? Tolerance?) 7. Closing a Project (CP) (Project) Product Description (Q) with Project Assurance. Project assurance
environment. size of project. refers to the Project Board’s accountability pankajsh10@yahoo.com
(Scope tol.of plans defined by products)
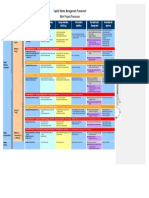
Business Case Quality The Quality Audit Trail Quality planning: to control quality, there must be a plan
Risk Threat Opportunity
Purpose is to judge if project is/remains desirable, Purpose of Risk theme is to identify, assess and Responses Responses
From Customer Project defining the products required of the project, with their
viable, achievable. Projects products enable business respective quality criteria, quality methods (including effort control uncertainty and, as a result, improve the
to acheive benefits: Project Customer’s Quality Response ability of the project to succeed. In the context of a Avoid Exploit
required for quality control and product acceptance) and the
Outputs expectations quality responsibilities of those involved. project, it is the project’s objectives that are at risk.
Output: project’s specialist products Reduce
Quality Expectations in broad terms (Robust, fast, etc.). These will include completing the project to a (probability and/or
Outcome: derived from using project’s outputs Acceptance Acceptance Criteria are Measurable; Rated: MoSCoW number of targets, covering time, cost, quality,
Quality Planning
Enable Criteria impact)
Benefit: measurable improvement perceived by Expectations & Criteria are in Project Product Description scope, benefits and risk. Enhance
stakeholders. Quality Quality assurance : Fallback
Business Project Product Quality Managem. Establishes and maintains a Risk Appetite: an organisations attitude to risk (reduces impact only)
Objectives depend on project type:
Changes Create Description Strategy Components quality management system taking. Risk tolerance: amount of risk that is
Reviews a projects acceptable Transfer
Feasibility study Product Quality Criteria organization, processes, (reduces impact only,
Compulsory project Descriptions and Tolerances products to assess if quality and often only the
Also Cause Desired PRINCE2 will be met. Risk Management procedure: financial impact
Not-for-profit project Outcomes Product Based Quality assurance is independent Identify context; obtain information on
Quality Methods Share
Evolving project Planning of the Project Management project to understand specific
Technique Team,it is a corporate objectives at risk and formulate Risk
Customer/supplier project Measured in responsibility, but quality Accept Reject
Side effects Quality Management Strategy.
Multi-organization project. Responsibilities planning and control are done by
and the project. The project is Identify risks; recognize the threats and Risk Owner: responsible for management,
consequences Realize opportunities that may affect the monitoring, control of all aspects of a risk,
responsible that quality
Communicate
further Benefits Quality Register including implementation of responses.
BC lifecycle: assurance is arranged. project’s objectives.
Risk Actionee: caries out actions
Develop: get information to make Quality control focuses on the Assess threats and opportunities to the
decisions (SU & IP) Result in
operational techniques and activities project in terms of probability and Summary risk profile
Product used by those involved in the project to:
Verify: assess if project is (still) Helps acheive PRINCE2 quality impact. Risk proximity describes how Very high Num
1 3
one or more Quality Fulfil the requirements for quality quickly risk can materialize . be
worthwhile (CS) Dis-
review (for example, by quality High 2 Risk rs from
Regis
4
technique Quality Approval Control inspections or testing) Plan; prepare management responses to Medium 8 ter
6
Maintain: Update costs, benefits and benefits Records Identify ways of eliminating causes threats and opportunities;remove/ Low 10
forecasts (MSB) 7
Strategic
of unsatisfactory performance (for reduce threats, maximize opportunities.
Confirm: if benefits are/will be Acceptance example, by introducing process Very Low 9 5
Objectives improvements as a result of
Implement; action risk responses,
Realized, mostly post-project. (MSB, Records monitor effectiveness, take corrective Prob Very Very
CP, post project) lessons learned). Low Medium High
action Impact Low high
Organization Plans Corporate or The purpose of Plans is to facilitate communication Progress Corporate or programme
Business Executive: looks after business interests; products to meet programme plan management
and control by defining means of delivering products; Progress describes mechanisms to: monitor and compare
business needs, value for money. the where and how, by whom, and estimating the achievements against plans, forecast project’s objectives and
Senior User: represents users requirements on project’s outputs; who: Project Plan viability, control deviations within tolerances, escalate Project Project Progress/
when and how much). tolerances exceptions
- Will use the project outputs to realize benefits after the project deviations outside tolerances.
- Will operate, maintain or support the project’s outputs (Initiation) (Delivery) It contributes to the principles “Managing by stages”,
- Will be impacted by project outputs Exception Plans (As nescessary) Project Board
Stage Plan Stage Plans “Continued business justification”, “Manage by exception”. It
Senior User specifies outputs and ensures delivery. can be monitored at Work Package, Stage and Project level.
Supplier represents those who will provide skills and produce project Team Plans Three levels of plan for three different levels of Each level of the PMT can check the next level: Stage Stage progress/
product. (Optional, free structure) management; Project, Stage and Team. The Initiation Monitor progress Tolerances exceptions
Corporate or program management Change Authority: Board Stage Plan is created (with the Project Brief) by Compare level of achievement with plan
can delegate authority for Design the plan Review plans and options against future situations
(during Plan the Project) Starting up a Project (influenced by corporate or
Project RFC’s or off-spec’s. Detect problems and identify risks Project Manager
programme plans). The Project Plan is created during
Manage- Project Board Severity ratings in Initiation (in the PID). Following Stage Plans created Initiate corrective action
Define & analyse Work Package
ment Senior Business Senior Configuration Man. products by Managing a Stage Boundary. Team Plans created Authorize further work. Work Package
Team User Executive Supplier Strategy list who handles progress/
Team Plan (optional)
Proj.prod.descr. (proj plan)
by Managing Product Delivery(Accept Workpackage). Tolerances are permissible deviations above and below a Tolerances
Issues
(PMT) requests : Prod. Breakdown plan’s target for time and cost without escalating to the next
Corporate/programme Prod. Descriptions Benefits Review Plan covers activities during and after level. There may also be tolerance for quality, scope, benefit
Change Prod. Fow Diagr.
the project that check if Business Case benefits have Team Manager
Analyse Risks
Project and risk. Exception is when it can be forecast that there will be
Project Plan
Project Authority management
Stage Plan
Manager been acheived. It may be part of a corporate or a deviation beyond the agreed tolerance levels.
Assurance Project Board Identify Activities and
Repeated for
dependencies programme plan. The Benefits Review Plan covers
Project Change Authority corporate, project and stage levels. Created during Specialist work aligned to management stages
Team Support Project Manager. Initiation, updated during Managing a Stage Management Stage 1 Management Stage 2 Management Stage 3 Management Stage 4
Prepare Estimates Boundary
Manager Delegated authorities are Specification
Peripheral
written into role An Exception Plan is a plan prepared for the Over all design
Detailed Design Commissioned
Team Members descriptions. Prepare the schedule appropriate management level to show the actions design Built facility Facility
Project Assurance: Project Board Checks all aspects of the project’s required to recover from the effect of a tolerance Training
performance independent of Project Manager. PB members are responsible Syllabus
Document the plan
deviation. If approved, the Exception Plan will replace Trained Staff
for aspects of Project Assurance from their respective areas: business, user the plan that is in exception(Stage or project).
or supplier. If they have no time or skills they appoint separate individuals
Project Manager: responsible for day-to-day management of project within
constraints set by Project Board. Project Manager ensures that project Change
produces required products within set tolerances. To identify, assess and control any potential changes to the baseline and get Configuration management is the administrative activity concerned Steps: Establish Controls, Set-up a
Project Support: Responsibility of Project Manager. He can delegate work them approved or dis-approved. Issue and change control is the continual with maintaining a controlled configuration throughout the life of a product. Configuration Management procedure and set-
to Project Support: administrative services, they advice on project activity throughout the project that identifies possible changes. Without Baselines are management products, once approved they are subject to up a Change Control procedure, ( Also see
management tools, configuration management, provide specialists for ongoing effective issue and change control, a project will become Change control (Benefits review plan, Business Case, All Strategies in the Change Authority in the PMT descriptions).
planning or risk management. unresponsive to stakeholders or drift out of control. Issues cover all relevant PID, plans, (Project) product description, Brief, PID and Workpackage) A change budget prevents that Project’s or
Team Manager: ensures cration of products in workpackage. Role may be events; Concern, Request for Change, or Off-Specifications Procedure: Planning, Identification, Control, Status acc., Verification & Audit Stage tolerances are “eaten” by changes.
combined with PM
PRINCE2® is a Registered Trademark of AXELOS LTD
You might also like
- Manage Product Delivery (MP) Manage Product Delivery (MP) : Project MandateDocument3 pagesManage Product Delivery (MP) Manage Product Delivery (MP) : Project Mandate007 009No ratings yet
- PRINCE2 Directing A ProjectDocument1 pagePRINCE2 Directing A ProjectWycliffe KadimaNo ratings yet
- PRINCE2 Process Flow DiagramDocument1 pagePRINCE2 Process Flow Diagrambabitasaini6402No ratings yet
- Prince2: ©2005, Pinkroccade Educational Services BV Slide 1Document30 pagesPrince2: ©2005, Pinkroccade Educational Services BV Slide 1MohamadTahseenNo ratings yet
- Product Map Diagram PRINCE2 2017Document2 pagesProduct Map Diagram PRINCE2 2017Shruti GuptaNo ratings yet
- Raline PMODocument4 pagesRaline PMOraline mncNo ratings yet
- PRINCE2 2017 Update Process ModelDocument1 pagePRINCE2 2017 Update Process ModelpvpramodNo ratings yet
- Project Initiation To CompletionDocument4 pagesProject Initiation To CompletionjesusgameboyNo ratings yet
- PMI Process TipsDocument13 pagesPMI Process Tipsparth_sarathyNo ratings yet
- Steps in The Process Group: Initial StartDocument1 pageSteps in The Process Group: Initial StartProsenjitNo ratings yet
- Sample Project Flow ChartDocument4 pagesSample Project Flow Chartiswkim100% (7)
- Project Delivery MatrixDocument2 pagesProject Delivery Matrixjohn_hollow_10% (1)
- Design Development Process.2Document1 pageDesign Development Process.2aezacsNo ratings yet
- PM Swimlaneposter Print 10.01.2018 PDFDocument1 pagePM Swimlaneposter Print 10.01.2018 PDFMarco PomaNo ratings yet
- Visio-PMPP-DIA-001 - Rev0 - Tank Project Delivery Process - FinalDocument1 pageVisio-PMPP-DIA-001 - Rev0 - Tank Project Delivery Process - Final15142442No ratings yet
- PRINCE2 Process Model - NoDocument2 pagesPRINCE2 Process Model - NoLayar KayarNo ratings yet
- Product Map Timeline 2 Slides V1.9aDocument2 pagesProduct Map Timeline 2 Slides V1.9aFaisNo ratings yet
- PMP Process Flow ChartDocument1 pagePMP Process Flow ChartGrisel Vargas50% (2)
- Prince2 2017 Product MapDocument2 pagesPrince2 2017 Product MapVijay JainNo ratings yet
- PMBOK ProcessesDocument47 pagesPMBOK ProcessesLuciana MoreiraNo ratings yet
- PMG Operations Guide (Draft)Document5 pagesPMG Operations Guide (Draft)deny prasetiaNo ratings yet
- Work Flow - Project Road MapDocument1 pageWork Flow - Project Road MapAhmed Turky100% (1)
- Flowchart of Project Management Process As Applied To PDPDocument2 pagesFlowchart of Project Management Process As Applied To PDPsamerric100% (1)
- Unit 5: Managing Requirements Backlog: Week 2: Explore Phase (Process Expert/Analyst)Document10 pagesUnit 5: Managing Requirements Backlog: Week 2: Explore Phase (Process Expert/Analyst)Oralia RomeroNo ratings yet
- D1 Lifecycle Processes 0.3Document1 pageD1 Lifecycle Processes 0.3Ronit KambojNo ratings yet
- Project Integration Management in MotionDocument1 pageProject Integration Management in MotionSAlman KhanNo ratings yet
- IC Kickoff Presentation 11167 - PowerPointDocument11 pagesIC Kickoff Presentation 11167 - PowerPointLOGAN_70No ratings yet
- Lecture 11 - Project Development & OIMSDocument12 pagesLecture 11 - Project Development & OIMSxjaf01No ratings yet
- Japan's ODA Loan Project Cycle ProceduresDocument5 pagesJapan's ODA Loan Project Cycle Proceduresdunghanoi10No ratings yet
- Prince2 Foundation Module 4 Process ModelDocument5 pagesPrince2 Foundation Module 4 Process Modelbob martinNo ratings yet
- FB - Solution Readiness Dashboard - L2 - SP06Document34 pagesFB - Solution Readiness Dashboard - L2 - SP06Alison MartinsNo ratings yet
- PM Presentation by Messi NisarDocument35 pagesPM Presentation by Messi NisarMesi NisarNo ratings yet
- 02 Inputs Outputs and Tools 6th Edition v.3Document21 pages02 Inputs Outputs and Tools 6th Edition v.3jill henderson100% (1)
- Project and Cost Management PaperDocument51 pagesProject and Cost Management PaperGabriela NunesNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Area Initiating: PlanningDocument1 pageKnowledge Area Initiating: PlanningBhattt ANo ratings yet
- Project Life Cycle: Manajemen Proyek Sistem KelistrikanDocument8 pagesProject Life Cycle: Manajemen Proyek Sistem Kelistrikanulya salmiyaNo ratings yet
- Project SystemsDocument126 pagesProject Systemsgauravjain21888% (8)
- PRINCE2 Process DiagramDocument5 pagesPRINCE2 Process DiagramWycliffe KadimaNo ratings yet
- Erp Transition - Pmo Retrospect 20200122Document3 pagesErp Transition - Pmo Retrospect 20200122ackarinNo ratings yet
- Playbook Mobilisation Phase ChecklistDocument2 pagesPlaybook Mobilisation Phase Checkliststimayo010809No ratings yet
- Workshop 1Document3 pagesWorkshop 1Jade Neri SultanNo ratings yet
- ILX PRINCE2 Process Map - Glyn DaviesDocument2 pagesILX PRINCE2 Process Map - Glyn DaviesnmoncefNo ratings yet
- Cataly PDM For Website PDFDocument1 pageCataly PDM For Website PDFrameshkarthik810No ratings yet
- Taking A Decision: 5 Steps of ProjectmanagementDocument1 pageTaking A Decision: 5 Steps of ProjectmanagementDaniel Oliveira OLiveiraNo ratings yet
- PRINCE2 Process Model - SimplifiedDocument1 pagePRINCE2 Process Model - Simplifiedyoel christopherNo ratings yet
- 4 - Project Budget Tracking DocumentDocument2 pages4 - Project Budget Tracking DocumentAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- Prince2 Process ModelDocument1 pagePrince2 Process Modelian mckinleyNo ratings yet
- PROJECT TIMELINE TEMPLATEDocument33 pagesPROJECT TIMELINE TEMPLATEJr BasalNo ratings yet
- Road To I PT Final PosterDocument1 pageRoad To I PT Final PosterChristian Trésor KandoNo ratings yet
- FInal Exam ITPMDR - Irwan AlfiansyahDocument12 pagesFInal Exam ITPMDR - Irwan Alfiansyahkota tangerangNo ratings yet
- Ov 7Document33 pagesOv 7demolaojaomoNo ratings yet
- Just Enough Project Management: The Indispensable Four-step Process for Managing Any Project, Better, Faster, CheaperFrom EverandJust Enough Project Management: The Indispensable Four-step Process for Managing Any Project, Better, Faster, CheaperRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Project Management Fundamentals: Key Concepts and MethodologyFrom EverandProject Management Fundamentals: Key Concepts and MethodologyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Keynote - SIGOS - Product - Portfolio-Global RoamerDocument82 pagesKeynote - SIGOS - Product - Portfolio-Global RoamerAnonymous SmYjg7gNo ratings yet
- GGSN Charging White Paper SummaryDocument54 pagesGGSN Charging White Paper SummaryAnonymous SmYjg7gNo ratings yet
- S13 Key2roam Data Roaming Implementation GuidelineDocument17 pagesS13 Key2roam Data Roaming Implementation GuidelineAnonymous SmYjg7g100% (1)
- GGSN Release 9.2 Command Reference: Draft - Cisco ConfidentialDocument752 pagesGGSN Release 9.2 Command Reference: Draft - Cisco ConfidentialAnonymous SmYjg7gNo ratings yet
- Sami IcgDocument318 pagesSami IcgAnonymous SmYjg7gNo ratings yet
- Deployment Plans Behind Larger Ipv6 Allocations: Jordi Palet (Jordi - Palet@Consulintel - Es)Document18 pagesDeployment Plans Behind Larger Ipv6 Allocations: Jordi Palet (Jordi - Palet@Consulintel - Es)Anonymous SmYjg7gNo ratings yet
- White Paper: CSG2 Key Performance Indicators CSG2 Release 3.5Document15 pagesWhite Paper: CSG2 Key Performance Indicators CSG2 Release 3.5Anonymous SmYjg7gNo ratings yet
- Configuring Load Balancing On The GGSNDocument28 pagesConfiguring Load Balancing On The GGSNAnonymous SmYjg7gNo ratings yet
- Configuring Charging On The GGSNDocument32 pagesConfiguring Charging On The GGSNAnonymous SmYjg7gNo ratings yet
- Configuring Security Features on the GGSNDocument52 pagesConfiguring Security Features on the GGSNAnonymous SmYjg7gNo ratings yet
- Monitoring Notifications: SNMP OverviewDocument26 pagesMonitoring Notifications: SNMP OverviewAnonymous SmYjg7gNo ratings yet
- Configuring Enhanced Service-Aware BillingDocument32 pagesConfiguring Enhanced Service-Aware BillingAnonymous SmYjg7gNo ratings yet
- Overview of Qos Support On The GGSNDocument26 pagesOverview of Qos Support On The GGSNAnonymous SmYjg7gNo ratings yet
- Configuring Dynamic IP Addressing on the GGSNDocument16 pagesConfiguring Dynamic IP Addressing on the GGSNAnonymous SmYjg7gNo ratings yet
- Overview of PPP Support On The GGSNDocument26 pagesOverview of PPP Support On The GGSNAnonymous SmYjg7gNo ratings yet
- GgsnoverDocument18 pagesGgsnoverlakshman_haldarNo ratings yet
- Configuring Network Access To The GGSNDocument58 pagesConfiguring Network Access To The GGSNAnonymous SmYjg7gNo ratings yet
- Configuring GGSN GTP Session RedundancyDocument28 pagesConfiguring GGSN GTP Session RedundancyAnonymous SmYjg7gNo ratings yet
- Content Services Gateway 2nd Generation (CSG2) : Technical OverviewDocument55 pagesContent Services Gateway 2nd Generation (CSG2) : Technical OverviewAnonymous SmYjg7gNo ratings yet
- Configuring IPv6 PDP Support on the GGSNDocument14 pagesConfiguring IPv6 PDP Support on the GGSNAnonymous SmYjg7gNo ratings yet
- Configuring GTP Services On The GGSNDocument34 pagesConfiguring GTP Services On The GGSNAnonymous SmYjg7gNo ratings yet
- White Paper: CSG2 Key Performance Indicators CSG2 Release 3.5Document15 pagesWhite Paper: CSG2 Key Performance Indicators CSG2 Release 3.5Anonymous SmYjg7gNo ratings yet
- A Technical Whitepaper: Diametercreditcontrol Application On GGSNDocument46 pagesA Technical Whitepaper: Diametercreditcontrol Application On GGSNAnonymous SmYjg7gNo ratings yet
- Planning To Configure The GGSN: PrerequisitesDocument12 pagesPlanning To Configure The GGSN: PrerequisitesAnonymous SmYjg7gNo ratings yet
- About This Book: Document Revision HistoryDocument4 pagesAbout This Book: Document Revision HistoryAnonymous SmYjg7gNo ratings yet
- Configuring Security Features on the GGSNDocument52 pagesConfiguring Security Features on the GGSNAnonymous SmYjg7gNo ratings yet
- Cisco Content Service Gateway CSG1 To CSG2 MigrationDocument16 pagesCisco Content Service Gateway CSG1 To CSG2 MigrationAnonymous SmYjg7gNo ratings yet
- Radiusinterface On Cisco GGSN: Modification HistoryDocument15 pagesRadiusinterface On Cisco GGSN: Modification HistoryAnonymous SmYjg7gNo ratings yet
- GGSN Charging White Paper SummaryDocument54 pagesGGSN Charging White Paper SummaryAnonymous SmYjg7gNo ratings yet
- Internet Gateway Router Design Using Cisco ASR 1000 Series RoutersDocument8 pagesInternet Gateway Router Design Using Cisco ASR 1000 Series RoutersAnonymous SmYjg7gNo ratings yet
- Tiểu luận đã chỉnhDocument28 pagesTiểu luận đã chỉnhĐức HoàngNo ratings yet
- Indiana's Creative Economy Report 2016 OverviewDocument1 pageIndiana's Creative Economy Report 2016 OverviewposnirohaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Research: Methodological Foundations, 9e: by Churchill and IacobucciDocument21 pagesMarketing Research: Methodological Foundations, 9e: by Churchill and IacobucciYazan GhanemNo ratings yet
- Job VacanciesDocument48 pagesJob VacanciesHijo del DuqueNo ratings yet
- Fed Rate Cut N ImplicationsDocument8 pagesFed Rate Cut N Implicationssplusk100% (1)
- International Public Sector Accounting StandardsDocument4 pagesInternational Public Sector Accounting Standardsdiana perez100% (1)
- Commission Fines Ajinomoto Cheil and Daesang in Food Flavour Enhancers Nucleotides CartelDocument1 pageCommission Fines Ajinomoto Cheil and Daesang in Food Flavour Enhancers Nucleotides CartelRohit JangidNo ratings yet
- PitchBook GuideDocument28 pagesPitchBook GuidePei ZiyanNo ratings yet
- Empire Jute CoDocument14 pagesEmpire Jute CoarmsarivuNo ratings yet
- Brand Audit CoeDocument10 pagesBrand Audit CoeMohammad ZubairNo ratings yet
- Invitation To Attend COSH Seminar WorkshopDocument1 pageInvitation To Attend COSH Seminar WorkshopOliver Sumbrana100% (1)
- CFAS - Prelims Exam With AnsDocument12 pagesCFAS - Prelims Exam With AnsAbarilles, Sherinah Mae P.No ratings yet
- Rental Quotation (Template)Document2 pagesRental Quotation (Template)I CNo ratings yet
- Discussion Papers in EconomicsDocument41 pagesDiscussion Papers in EconomicsdebasishNo ratings yet
- Customer Satisfaction Towards Honda Two Wheeler: Presented By: Somil Modi (20152002) BBA-MBA 2015Document9 pagesCustomer Satisfaction Towards Honda Two Wheeler: Presented By: Somil Modi (20152002) BBA-MBA 2015Inayat BaktooNo ratings yet
- Bluescope Steel 2016Document48 pagesBluescope Steel 2016Romulo AlvesNo ratings yet
- Average Down StrategyDocument11 pagesAverage Down StrategyThines KumarNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of DerivativesDocument5 pagesCharacteristics of Derivativesdhirendra shuklaNo ratings yet
- GST Filing & Invoicing Made Easy with ClearTaxDocument19 pagesGST Filing & Invoicing Made Easy with ClearTaxSudhir KumarNo ratings yet
- Alternative DevelopmentDocument13 pagesAlternative Developmentemana710% (1)
- Two Methods To Find Out The Profit or Loss From Incomplete RecordsDocument5 pagesTwo Methods To Find Out The Profit or Loss From Incomplete RecordsayyazmNo ratings yet
- Cooperatives (Republic Act No. 9520 A.k, A. Philippine Cooperative Code of 2008)Document14 pagesCooperatives (Republic Act No. 9520 A.k, A. Philippine Cooperative Code of 2008)xinfamousxNo ratings yet
- Pre104: Auditing and Assurance: Specialized Industries 1. Overview of Auditing in Specialized IndustriesDocument2 pagesPre104: Auditing and Assurance: Specialized Industries 1. Overview of Auditing in Specialized IndustriesCristina ElizaldeNo ratings yet
- Growthink - 8 Figure FormulaDocument41 pagesGrowthink - 8 Figure FormulaKlark KentNo ratings yet
- KU Internship Report on Nepal Investment BankDocument39 pagesKU Internship Report on Nepal Investment Bankitsmrcoolpb100% (1)
- Exercises and Case Study - Financial ManagementDocument1 pageExercises and Case Study - Financial ManagementJohn Verlie EMpsNo ratings yet
- Yu Chen-2023Document8 pagesYu Chen-2023jennyNo ratings yet
- Not Payable in Case Subsidized Canteen Facilities Are ProvidedDocument1 pageNot Payable in Case Subsidized Canteen Facilities Are Providedsurabhiarora1No ratings yet
- Entrepre Module 2Document10 pagesEntrepre Module 2Joshua Enriquez VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- 007.MTL-NSS-AB-2023-007 - Quotation For SS Fabrication & Coating - MR-SS-0145Document1 page007.MTL-NSS-AB-2023-007 - Quotation For SS Fabrication & Coating - MR-SS-0145abasithamNo ratings yet