Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Microbio Strep
Uploaded by
Rica Marquez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageOriginal Title
Microbio_Strep.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageMicrobio Strep
Uploaded by
Rica MarquezCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
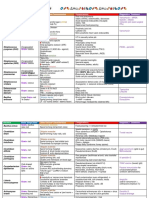
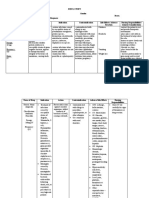
Lancefield
Hemolysin Rep. Species Characteristics Major Clinical Syndromes
Classification
Local Invasion and/or eotoxin release
Pus producing
1. Streptoccocal Pharyngitis
Anti- phagocytic & anti- immunogenic 2. Strep Skin Infections
Susceptible to Bacitracin a. Cellulitis
M protein (major virulence factor; weakest point) b. Impetigo
Pili (partly M protein covered by lipoteichoic acid) c. Necrotizing fascitis
Treatment: Penicillin & clindamycin
Group A PATHOGENIC ENZYMES 3. Scarlet Fever
(rhamnose – N- S. pyogenes Streptolysin O (O2 labile; antigenic) 4. Streptococcal Toxic Shock Syndrome
acetylglucose- amine) Streptolysin S (O2 stabile; not antigenic) Delayed Antibody- Mediated Disease
β Pyrogenic Exotoxin ( causes scarlet fever & streptococcal 1. Acute Rheumatic Fever
toxic shock syndrome) With prior Strep pharygitis without skin infection
Streptokinase (activates plasmin) Myocarditis to rheumatic valvular heart disease
Hyaluronidase ( splits hyaluronic acid to penetrate and infect) Prophylactic Penicillin theraphy
DNAses (degrade DNA -> produce pus) 2. Acute Glomerulonephritis
Anti-C5a peptidase (inactivates c5)
1 week after strep pharygitis with skin infection
Part of normal flora in vagina, urethral mucous membrane, Neonatal Meningitis
Group B
and lower GIT Neonatal pneumonia
(rhamnose- S. agalactitiae
Fever, vomiting, poor feeding, and irritability (NO nuchal Neonatal sepais
glucoseamine)
rigidity) Treatment: Penicillin + Ampicillin
Viridans Group S. mutans Bind to teeth and ferment sugar Dental Carries
Opportunistic
Microaerophilic
pathogens of S. intermedius Abscess in the brain or abdominal organs
low virulence Normal GIT flora
UTI
Normal Bowel Flora Biliary Tract Infection
Enterococci
Group D Grow well in 40% bile and 6.5% NaCl Bacteremia
(glycerol theicoic acid SBE
with d-alanine & UTI
S. bovis & S.
glucose) Grows in 40% bile but not in 6.5% NaCl Biliary Tract Infection
equinus
Epidemiologically associated with colon cancer Bacteremia
(nonenterococci)
α SBE (Subacute Bacterial Endocarditis
C polysaccharide (not associated with Lancefield antigen Pneumonia
Gram stain: Gram (+) cocci in pairs (diplococci) Otitis Media in Children
Virulence Factor: Polysaccharide capsule Meningitis
Cell Associated Enzymes Vaccines
Autolysin: hydrolyze CM to activate Lyt A, B, C -> release Pneumovax (25 common capsular polysaccharide antigens)
S. pneumoniae pneumolysin o For asplenic, immunocompromised, and elderly patients
Pneumolysin: intracellular virulence factor loacted in the o Low immunogenicity and efficacy
cytosol -> attack CM Heptavalent Conjugate Vaccine (7 capsular polysacc. Antigens)
o Pneumolysin binds to cholesterol -> stimulates o 4, 6B, 9V, 14, 18C, 19F, 23F conjugated with nontoxic
proinflammatory cytokines -> inhibit leukocytes and diphtheria-toxin
activate complement pathway o 100% efficacy in prevention in children
Reduce cases of otitis media in children
You might also like
- Infectious-Disease Tables PDFDocument81 pagesInfectious-Disease Tables PDFMiguel CuevasNo ratings yet
- BZZ BZZ BZZ: Sketchy MicroDocument18 pagesBZZ BZZ BZZ: Sketchy Microkissandtell88% (8)
- Bacteria ChartsDocument11 pagesBacteria ChartsFlowerNo ratings yet
- Vaccine Dose Route Site of Admministration Ageof1 Dose Interv AL Betwee N Doses Temperatu RE PurposeDocument3 pagesVaccine Dose Route Site of Admministration Ageof1 Dose Interv AL Betwee N Doses Temperatu RE PurposeCamilogs100% (1)
- Adult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookFrom EverandAdult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Staphylococcus: Mssa Mrsa Endocarditis Nafcilin VancomycinDocument2 pagesStaphylococcus: Mssa Mrsa Endocarditis Nafcilin VancomycinSijo SunnyNo ratings yet
- Microbiology NotesDocument13 pagesMicrobiology NotesMalekNo ratings yet
- S. Aureus, Cons: S.Epidermidis, Cons: S.SaprophyticusDocument14 pagesS. Aureus, Cons: S.Epidermidis, Cons: S.SaprophyticusMugiNo ratings yet
- Organism Description Drug of ChoiceDocument14 pagesOrganism Description Drug of ChoiceMary YongcoNo ratings yet
- Bacteria List Exam 1 PDFDocument16 pagesBacteria List Exam 1 PDFJamesHowsonNo ratings yet
- Module Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesModule Skeletal SystemRica Marquez100% (1)
- Sexually Transmitted Infections Basics in DiagnosisDocument95 pagesSexually Transmitted Infections Basics in Diagnosistummalapalli venkateswara raoNo ratings yet
- BacteriologyDocument20 pagesBacteriologyOj Alimbuyuguen100% (2)
- IMUNOLOGIEpentruFarmacisti Mihele Pop Onl PDFDocument245 pagesIMUNOLOGIEpentruFarmacisti Mihele Pop Onl PDFAnonymous xtsFkU2100% (1)
- Polio PowerpointDocument10 pagesPolio PowerpointQzmp1No ratings yet
- Pance Prep Pearls Antibiotics PDFDocument14 pagesPance Prep Pearls Antibiotics PDFkatNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive: CoccusDocument8 pagesGram Positive: CoccusLM MysNo ratings yet
- Medical WardDocument15 pagesMedical WardMon Revez LiNo ratings yet
- Micro paraDocument2 pagesMicro parafeminaNo ratings yet
- TigecyclineDocument2 pagesTigecyclineVanessa Egao100% (1)
- January 14, 2011 Pharmacology 2: Clinical Management TargetsDocument15 pagesJanuary 14, 2011 Pharmacology 2: Clinical Management Targetsrichardmd2No ratings yet
- BACTERIADocument1 pageBACTERIAKumkum MahajanNo ratings yet
- ملخص بكتريا PDFDocument27 pagesملخص بكتريا PDFDjdjjd SiisusNo ratings yet
- Bacteria PDFDocument13 pagesBacteria PDFJohn Christopher LucesNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Class Summary TableDocument2 pagesAntibiotic Class Summary TableuserherwwweNo ratings yet
- BenadrylDocument2 pagesBenadrylsamfandood10No ratings yet
- Antibiotic Class Summary TableDocument6 pagesAntibiotic Class Summary TableuserherwwweNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: BudesonideDocument8 pagesGeneric Name: BudesonidemeangelmeNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation Station 3B Drug Study AzithromycinDocument4 pagesCase Presentation Station 3B Drug Study AzithromycinhahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Every Drug EverDocument72 pagesEvery Drug EverMalNo ratings yet
- 2 Antibacterial DrugDocument7 pages2 Antibacterial DrugGeneto RosarioNo ratings yet
- تَـلـخـيـص شَـابـتـر ٢٥?Document12 pagesتَـلـخـيـص شَـابـتـر ٢٥?سلطان محمد فوزي سلمانNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument5 pagesAntibioticsgitama9904No ratings yet
- Staphylococcus: Skin Infections Osteomyelitis Bloodstream Infection Food Poisoning Foreign Body Infections MRSADocument7 pagesStaphylococcus: Skin Infections Osteomyelitis Bloodstream Infection Food Poisoning Foreign Body Infections MRSAnour achkarNo ratings yet
- Anti-Fungal DrugsDocument2 pagesAnti-Fungal Drugssarguss14No ratings yet
- CeftriaxoneDocument1 pageCeftriaxoneJayson Almario Aranas100% (2)
- Drug Name Indications Actions Contraindications and Cautions Adverse Effects Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities BeforeDocument3 pagesDrug Name Indications Actions Contraindications and Cautions Adverse Effects Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities BeforeArdel LabadaNo ratings yet
- Streptococci ReviewDocument5 pagesStreptococci ReviewEl-rohyKalongoNo ratings yet
- Gram NegativeDocument42 pagesGram NegativefernandoNo ratings yet
- G M Bacteria2Document42 pagesG M Bacteria2fernandoNo ratings yet
- Summary of MicroDocument25 pagesSummary of MicroAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Applied Pharmacotherapy: By: First GroupDocument13 pagesApplied Pharmacotherapy: By: First GroupMUHAMMAD ISLAMINo ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument1 pageCefuroximeAbijah Leris SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Olkimmilo - Protein Synthesis InhibitorsDocument2 pagesOlkimmilo - Protein Synthesis InhibitorsTricia Kaye IblanNo ratings yet
- Olkimmilo - Protein Synthesis Inhibitors - BWDocument2 pagesOlkimmilo - Protein Synthesis Inhibitors - BWhediyeNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial IIDocument11 pagesAntimicrobial IIFrances Lau Yee ChinNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Diphteria, Pertussis and Staphylococcal Infections-1Document15 pagesDiphteria, Pertussis and Staphylococcal Infections-1Nwosu Ogbonna GabrielNo ratings yet
- Typhoid FeverDocument63 pagesTyphoid FeverAggiFitiyaningsihNo ratings yet
- Isah Drug StudyDocument2 pagesIsah Drug StudyJames AbendanNo ratings yet
- StaphylococcusDocument13 pagesStaphylococcusZeth MoturiNo ratings yet
- Bibliography: Life Span - Philadelphia, PA 19103: F.A. Davis CompanyDocument5 pagesBibliography: Life Span - Philadelphia, PA 19103: F.A. Davis CompanyCarlos LleverNo ratings yet
- Drug Index: Generic/ Brand Name Dosage Mode of Action Indications Contraindications Adverse Effects Co AmoxiclavDocument3 pagesDrug Index: Generic/ Brand Name Dosage Mode of Action Indications Contraindications Adverse Effects Co AmoxiclavSheinna BarcelonaNo ratings yet
- 2023.pedia - Trans24.-Bacterial-Infections - Gram Postitive (Part 1)Document6 pages2023.pedia - Trans24.-Bacterial-Infections - Gram Postitive (Part 1)Adrian CaballesNo ratings yet
- MOA Antimicrobial Activity Resistance Adme Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsDocument2 pagesMOA Antimicrobial Activity Resistance Adme Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsFreakyRustlee LeoragNo ratings yet
- DRUGSTUDYDocument8 pagesDRUGSTUDYWinnie Salazar AriolaNo ratings yet
- Sa CelulitisDocument19 pagesSa CelulitisJulio Ramos EliasNo ratings yet
- StreptococciDocument40 pagesStreptococciGjfyigyivNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MugnaDocument7 pagesDrug Study Mugnakint manlangitNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy 20Document9 pagesDrugstudy 20MahledJoy EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug: Ceftazidime Therapeutic Class: Pharmacologic Class: CephalosporinsDocument20 pagesName of Drug: Ceftazidime Therapeutic Class: Pharmacologic Class: CephalosporinsianNo ratings yet
- Chart - Gram Positive BacteriaDocument2 pagesChart - Gram Positive BacteriaRedNo ratings yet
- Lipid MediatorsFrom EverandLipid MediatorsFiona M. CunninghamNo ratings yet
- Small Molecular Immunomodifiers of Microbial Origin: Fundamental and Clinical Studies of BestatinFrom EverandSmall Molecular Immunomodifiers of Microbial Origin: Fundamental and Clinical Studies of BestatinHamao UmezawaNo ratings yet
- Types of Burns: ST NDDocument2 pagesTypes of Burns: ST NDRica MarquezNo ratings yet
- NutitionDocument2 pagesNutitionRica MarquezNo ratings yet
- Friction IntroductionDocument2 pagesFriction IntroductionRica MarquezNo ratings yet
- Critique Paper Botany 109Document7 pagesCritique Paper Botany 109Rica MarquezNo ratings yet
- Determination of Aspirin by Indirect TitrationDocument3 pagesDetermination of Aspirin by Indirect TitrationRica Marquez100% (2)
- Rafa Guia Final 23 1 10 08Document82 pagesRafa Guia Final 23 1 10 08Johanna Nayely lópez GuerraNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris Makalah Corona - Ima Amalia Juliyantiara - 14201.12.20015 - S1 KeperawatanDocument15 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris Makalah Corona - Ima Amalia Juliyantiara - 14201.12.20015 - S1 KeperawatanImaliaNo ratings yet
- ENT Diseases of Paranasal SinusesDocument3 pagesENT Diseases of Paranasal SinusesLucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- DV - Dr. Sri AwaliaDocument30 pagesDV - Dr. Sri AwaliaTimothy supitNo ratings yet
- Marigold Phase-1 Co-Operative Housing Society LTD: Kalyani Nagar, Pune 411 014Document2 pagesMarigold Phase-1 Co-Operative Housing Society LTD: Kalyani Nagar, Pune 411 014ARCHANNAANo ratings yet
- Etiologic Agent Means A Disease-Causing Agent. Hepatitis A - o - o o - o - oDocument5 pagesEtiologic Agent Means A Disease-Causing Agent. Hepatitis A - o - o o - o - ojin0meNo ratings yet
- Purpura Fulminans: Mechanism and Management of Dysregulated HemostasisDocument21 pagesPurpura Fulminans: Mechanism and Management of Dysregulated HemostasisntnquynhproNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis A LetterDocument1 pageHepatitis A Letter10News WTSPNo ratings yet
- Tatsumi 1997Document9 pagesTatsumi 1997dad dzd adaNo ratings yet
- Rajesh Singh M. Pharm 1 Year: Made byDocument17 pagesRajesh Singh M. Pharm 1 Year: Made byNaman SharmaNo ratings yet
- Stages of AidsDocument10 pagesStages of AidsHarshitha Gowda HarshiNo ratings yet
- Acute Otitis Media: Jama Patient PageDocument1 pageAcute Otitis Media: Jama Patient PageS. JohnNo ratings yet
- DR TB Treatment Guideline of Timor Leste - REVISED 3 March 2021Document13 pagesDR TB Treatment Guideline of Timor Leste - REVISED 3 March 2021Yoan Manuel Ruiz ArencibiaNo ratings yet
- Size: 137 X 218 MM: Rapid Test For The Detection of Dengue NS 1 Antigen in Human Serum/plasma DeviceDocument4 pagesSize: 137 X 218 MM: Rapid Test For The Detection of Dengue NS 1 Antigen in Human Serum/plasma DeviceMatibar RahmanNo ratings yet
- Immuno Multi Therapy and Prophylaxis Efficacy Against COVID 19Document9 pagesImmuno Multi Therapy and Prophylaxis Efficacy Against COVID 19Athenaeum Scientific PublishersNo ratings yet
- National EPI Policy & Strategic Guidelines Pakistan 2015Document64 pagesNational EPI Policy & Strategic Guidelines Pakistan 2015Salman MinhasNo ratings yet
- Pathology MCQ - Liver and Biliary Tract PDFDocument5 pagesPathology MCQ - Liver and Biliary Tract PDFCHRISTOPHER OWUSU ASARENo ratings yet
- Bullous Pemphigoid: Clinical Practice Guidelines: ReviewDocument19 pagesBullous Pemphigoid: Clinical Practice Guidelines: Reviewsri karuniaNo ratings yet
- Vaccination CertificateDocument1 pageVaccination CertificateZiya SaifiNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument4 pagesCase StudyAbdurRahmanShafiNo ratings yet
- Garp-Nepal - Sa (Global Antibiotic Resistance Partnership)Document90 pagesGarp-Nepal - Sa (Global Antibiotic Resistance Partnership)Nivea VazNo ratings yet
- ModernaDocument22 pagesModernagoslugs12No ratings yet
- Quiz navigation: Home Courses 2018 يوﯾطﻌﻟا ﻲﻧﯾﺳﺣﻟا دوﻣﺣﻣ ﮫﻣﺣر "Document31 pagesQuiz navigation: Home Courses 2018 يوﯾطﻌﻟا ﻲﻧﯾﺳﺣﻟا دوﻣﺣﻣ ﮫﻣﺣر "Rahma MahmouuddNo ratings yet
- Rabbits: Diseases and Their ControlDocument4 pagesRabbits: Diseases and Their Controlaleks3No ratings yet
- Materi MIMBAR 20 - BPK HadiDocument20 pagesMateri MIMBAR 20 - BPK HadiYoga RivaldiNo ratings yet
- 87% of Animals Does Not Have Anti-Rabies Injection: GoalDocument3 pages87% of Animals Does Not Have Anti-Rabies Injection: GoalDan HizonNo ratings yet