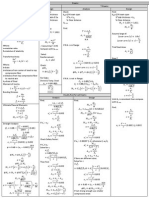
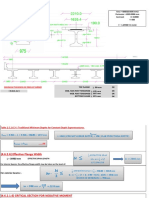
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Concrete-Steel Composite Structures - Designing Buildings Wiki
Uploaded by
Lucas AntonioOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Concrete-Steel Composite Structures - Designing Buildings Wiki
Uploaded by
Lucas AntonioCopyright:
Available Formats
By continuing to use this site you are agreeing to our use of cookies.
Read our Privacy Policy (/wiki/Privacy_policy#Cookies) to find out more. Close.
(http://www.rsh-
(http://www.uandiplc.com/)
(http://www.ciob.org) (https://www.bsria.co.uk/) (https://ciat.org.uk/)
(https://www.ice.org.uk/)(http://www.bre.co.uk/bretrust) (/wiki/Conservation_wiki) p.com)
esigning Buildings Wiki
Newsletter (http://designingbuildings.us4.list-manage.com/subscribe?u=d574d9ea2afa87f3015d176f3&id=b0e8c9e30b)
Register (/w/index.php?title=Special:UserLogin&type=signup&returnto=Home) Sign in (/w/index.php?title=Special:UserLogin&returnto=Home)
Share your construction industry knowledge Search
(/)
Subjects (/) Tools / info
Last edited 07 Feb 2018
See full history (/w/index.php?title=Concrete-steel%20composite%20structures&action=history) Create an article
(/w/index.php?title=Special:CreateArticle)
Concrete-steel composite structures Share Follow(http://www.facebook.com/pages/D
(https://twitter.com/#!/DesigningB)
(http://www.linkedin.com/company
(http://www.youtube.com/user/des
Buildings-
buildings)
Wiki/349836558377133)
Related articles
Architectural concrete
(/wiki/Architectural_concrete).
Braced frame (/wiki/Braced_frame).
Composites (/wiki/Composites).
Concrete (/wiki/Concrete).
Concrete vs. steel (/wiki/Concrete_vs._steel).
Design of durable concrete structures
(/wiki/Design_of_durable_concrete_structures).
Galvanised steel (/wiki/Galvanised_steel).
(/wiki/File:Composite_decking.jpg)
CEAGESP -
COMPANHIA DE EN
R$142.80
Contents
MÊTRO/SP -
1 Introduction COMPANHIA DO M
2 Composite slabs
R$238.80
3 Composite beams
3.1 Downstand beam CEAGESP -
3.2 Shallow floors COMPANHIA DE EN
4 Composite columns R$130.80
5 Standards
6 Find out more
Gran Cursos Online - Cursos para Concursos
6.1 Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
6.2 External sources
Introduction
Structural members that are made up of two or more different materials (/wiki/Materials) are
known as composite elements. The main benefit of composite elements is that the properties
of each material can be combined to form a single unit that performs better overall than its
separate constituent parts. The most common form of composite element in construction is a
steel (/wiki/Steel)-concrete (/wiki/Concrete) composite, however, other types of composites
(/wiki/Composites) include; steel (/wiki/Steel)-timber (/wiki/Timber), timber (/wiki/Timber)-
(https://www.designingbuildings.co.uk/adserver/www/delivery/ck.php?
concrete (/wiki/Concrete), plastic-concrete (/wiki/Concrete), and so on. oaparams=2__bannerid=40__zoneid=1__cb=1f68a59bf1__oadest=https%
As a material, concrete (/wiki/Concrete) works well in compression, but it has less resistance in
tension. Steel (/wiki/Steel), however, is very strong in tension, even when used only in relatively
Featured articles and news
small amounts. Steel (/wiki/Steel)-concrete (/wiki/Concrete) composite elements use concrete
(/wiki/Concrete)'s compressive strength alongside steel (/wiki/Steel)'s resistance to tension,
Strip foundations (/wiki/Strip_foundation)
and when tied together this results in a highly efficient and lightweight unit that is commonly
used for structures (/wiki/Structure) such as multi-storey buildings (/wiki/Multi-storey_building)
and bridges (/wiki/Bridges).
Composite slabs (/wiki/Composite_slab)
Composite slabs (/wiki/Composite_slab) are typically constructed from reinforced concrete
(/wiki/Reinforced_concrete) cast on top of profiled steel (/wiki/Steel) decking, (re-entrant or
trapezoidal). (/wiki/Strip_foundation)
The decking is capable of acting as formwork (/wiki/Formwork) and a working platform Strip foundations are used to provide a
(/wiki/Working_platform) during the construction stage, as well as acting as external continuous, level strip of support to a linear
reinforcement (/wiki/Reinforcement) at the composite stage. Decking is lifted (/wiki/Lift) into structure. Read more here.
place in bundles (/wiki/Bund) and distributed across the floor area (/wiki/Floor_area) by hand.
Slab depths range from 130 mm upwards. Slabs are most commonly made of concrete Management of time in major projects
(/wiki/Concrete) because of its mass and stiffness which can be used to reduce the floor (/wiki/Guide_to_good_practice_in_the_manageme
(/wiki/Floor)'s deflections and vibrations (/wiki/Vibrations), and achieve the necessary fire
(/wiki/Fire) protection and thermal storage (/wiki/Thermal_storage). Steel (/wiki/Steel) is often
used as the supporting system underneath the slab due to its superior strength-weight and
stiffness-weight ratio and ease of handling.
Re-entrant or trapezoidal decking (/wiki/Trapezoidal_decking) is usually 50-60 mm deep and
can span around 3 m unsupported. Trapezoidal profiles of 80 mm deep can span around 4.5 m
unsupported. Deep decking is trapezoidal decking (/wiki/Trapezoidal_decking) that is over 200
mm deep, and if required, additional reinforcement (/wiki/Reinforcement) may be placed in the
decking troughs. Deep decking can span around 6 m unsupported.
Galvanised steel (/wiki/Galvanised_steel) is used for the decking and is usually around 1 mm
thick. To avoid local buckling, stiffeners may be used to stiffen the upper flange (/wiki/Flange)
and support hangers for relatively lightweight items to be suspended from the soffit
(/wiki/Soffit). Dimples known as embossments are rolled onto the decking profile which trap the (/wiki/Guide_to_good_practice_in_the_manageme
concrete (/wiki/Concrete) around the re-entrant parts of the profile and allow for interlocking.
Management of time is critical for big project
Where openings are required in composite slabs (/wiki/Composite_slab) these are best formed success, reveals the CIOB in new good practice
at the construction stage as opposed to having to cut out sections of concrete (/wiki/Concrete). guide.
Up to 300 sq. mm openings do not need additional provisions, but up to 700 sq. mm require
additional local reinforcement (/wiki/Reinforcement) around the opening. If openings are in
excess of 700 sq. mm, trimming steel (/wiki/Steel) can be used as support. Inspiring future engineers
(/wiki/Inspiring_young_civil_engineers)
Composite beams (/wiki/Composite_beam)
Downstand beam (/wiki/Downstand_beam)
A downstand beam (/wiki/Downstand_beam) is connected to a composite slab
(/wiki/Composite_slab) by the use of through-deck welded shear studs (/wiki/Stud).
Alternatively, a precast concrete (/wiki/Precast_concrete) slab sits on top of the steel
(/wiki/Steel) beam (/wiki/Beam)'s top flange (/wiki/Flange). The effective span range is around
6-12 m. Other variations (/wiki/Variations) on downstand beams (/wiki/Downstand_beam) can
(/wiki/Inspiring_young_civil_engineers)
reach spans of 20 m or more.
Why we need to bridge the lack of civil
Shallow floors (/wiki/Shallow_floor) engineers, and suggestions for how to do it.
Shallow floors (/wiki/Shallow_floor) are where the main part of the steel (/wiki/Steel) section is
within the concrete (/wiki/Concrete) slab depth, and can be used for a span range of around 4- Minimum energy efficiency standard
9 m. As opposed to downstand beams (/wiki/Downstand_beam), the slab sits on the upper (/wiki/Minimum_energy_efficiency_standard_(MEE
surface of the bottom flange (/wiki/Flange) instead of the upper surface of the top flange
(/wiki/Flange), with a key consideration being the torsion that is applied to the beam
(/wiki/Beam). The slab may be either in situ concrete (/wiki/Concrete) on deep steel
(/wiki/Steel) decking, usually around 225 mm, or precast concrete (/wiki/Precast_concrete).
The benefits of shallow floors (/wiki/Shallow_floor) are that since the slabs and beams
(/wiki/Beam) are placed within the same zone, there are none of the interruptions found with
downstand beams (/wiki/Downstand_beam), and there is often no need for additional fire
(/wiki/Fire) protection.
(/wiki/Minimum_energy_efficiency_standard_(MEE
Composite columns (/wiki/Composite_column)
The government's proposed cap on landlords'
financial contribution is flawed, according to
Composite columns (/wiki/Composite_column) can have high strength for a relatively small
sustainability expert.
cross-sectional area, meaning that useable floor (/wiki/Floor) space can be maximised. There
are several different types of composite column (/wiki/Composite_column); the most common
being a hollow section steel (/wiki/Steel) tube which is filled with concrete (/wiki/Concrete); or Carillion (/wiki/Carillion#Jobs)
an open steel (/wiki/Steel) section encased in concrete (/wiki/Concrete). The concrete
(/wiki/Concrete) infill adds to the compression resistance of the steel (/wiki/Steel) section,
preventing the steel (/wiki/Steel) from buckling. Its fire (/wiki/Fire) resistant properties can
permit the column (/wiki/Column) to be left unprotected or only lightly protected.
Rectangular and circular hollow sections are most commonly used, although rectangular
sections are beneficial for being having flat faces suitable for end plate beam (/wiki/Beam)-to-
column (/wiki/Column) connections. However, fin plates can be used for rectangular and
circular shapes. (/wiki/Carillion#Jobs)
A further 230 redundancies takes the total
Standards number of job losses to 1,371.
The design of composite beams (/wiki/Composite_beam) and composite slabs Sir Vince Cable interview
(/wiki/Composite_slab) (for buildings) are covered by BS EN 1994-1-1. Composite slabs (/wiki/Vince_Cable_interview)
(/wiki/Composite_slab) with profiled steel (/wiki/Steel) sheeting are designed to BS 5950-4,
while the profiled decking used for those slabs is designed to BS EN 1993-1-3.
Find out more (/wiki/Find_out_more)
Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki (/wiki/Designing_Buildings_Wiki)
Architectural concrete (/wiki/Architectural_concrete).
Braced frame (/wiki/Braced_frame).
Composites (/wiki/Composites). (/wiki/Vince_Cable_interview)
Concrete (/wiki/Concrete).
Concrete vs. steel (/wiki/Concrete_vs._steel).
The housing market is made "much worse by
Design of durable concrete structures (/wiki/Design_of_durable_concrete_structures).
Galvanised steel (/wiki/Galvanised_steel). Help to Buy ... it was an absolutely terrible idea".
Precast concrete (/wiki/Precast_concrete). Watch our interview with Sir Vince Cable here.
Prestressed concrete (/wiki/Prestressed_concrete).
Rebar (/wiki/Rebar).
Reinforced concrete (/wiki/Reinforced_concrete).
Smart concrete (/wiki/Smart_concrete). Planning Delivery Fund
Steel frame (/wiki/Steel_frame). (/wiki/Planning_Delivery_Fund)
Structural steelwork (/wiki/Structural_steelwork).
Superstructure (/wiki/Superstructure).
Tube structural system (/wiki/Tube_structural_system).
Types of steel (/wiki/Types_of_steel).
Weathering steel (/wiki/Weathering_steel).
External sources
'Building Construction Handbook' (6th ed.), CHUDLEY, R., GREENO, R., Butterworth-
Heinemann (2007)
Steelconstruction (/wiki/Steel) - Composite construction
(http://www.steelconstruction.info/Composite_construction)
(/wiki/Planning_Delivery_Fund)
Share (http://www.sharethis.com/share?publisher=832c94fd-9945-4b2b-b15f-
Housing Minister announces new funding to
599ff8a8df60&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.designingbuildings.co.uk%2Fwiki%2FConcrete-
steel_composite_structures&title=Designing+Buildings+Wiki+-+Concrete- help speed up planning decisions and deliver
steel+composite+structures&img=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.designingbuildings.co.uk%2Fskins%2Fdesigningbuildings%2Fdesigning-
new homes.
buildings-logo-square.png)
Add a comment (/w/index.php?title=Talk:Concrete-
steel_composite_structures&action=edit#commentStart) Preston Barracks
Send us feedback (/wiki/Special:Contact? (/wiki/Preston_Barracks,_Brighton)
request_uri=%2Fwiki%2FConcrete-steel_composite_structures)
(/wiki/Preston_Barracks,_Brighton)
Deal between U and I Group and Brighton
Council paves the way for this significant
regeneration project.
Conservation of transport infrastructure
(/wiki/The_conservation_of_historic_transport_infra
(/wiki/The_conservation_of_historic_transport_infra
A tapestry of continued use, new use,
preservation, dismantlement, dereliction and
abandonment.
Whole-life costs (/wiki/Whole-
life_costs_for_buildings_WLC)
(/wiki/Whole-life_costs_for_buildings_WLC)
Whole-life costs consider all costs associated
with the life of a building, from inception to
disposal. Find out more here.
Click here to see more Featured articles and
news. (/wiki/Featured_articles_and_news)
© Designing Buildings Ltd. 2018
You might also like
- Lajes Mistas Steel Deck 5Document14 pagesLajes Mistas Steel Deck 5Lucas AntonioNo ratings yet
- Lajes Mistas 1Document15 pagesLajes Mistas 1Lucas AntonioNo ratings yet
- Jornal Construção Burj KhalifaDocument36 pagesJornal Construção Burj KhalifaLucas AntonioNo ratings yet
- Sap StartDocument75 pagesSap StartvbdeantoniNo ratings yet
- SEO STEEL DECK TABLEDocument8 pagesSEO STEEL DECK TABLEEvanio MirandaNo ratings yet
- Bang Na ExpresswayDocument13 pagesBang Na ExpresswayLucas AntonioNo ratings yet
- Non Linear Analysis of Reinforced Concrete ChimneyDocument10 pagesNon Linear Analysis of Reinforced Concrete ChimneyLucas AntonioNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design of Tall ChimneysDocument10 pagesSeismic Design of Tall Chimneyssrikanth.iitkgpNo ratings yet
- Distance: You Created This PDF From An Application That Is Not Licensed To Print To Novapdf PrinterDocument2 pagesDistance: You Created This PDF From An Application That Is Not Licensed To Print To Novapdf PrinterLucas AntonioNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- TJ 4000 PDFDocument32 pagesTJ 4000 PDFkirubaNo ratings yet
- Concrete Cheat SheatDocument2 pagesConcrete Cheat SheatTom Curry86% (7)
- StructuralDocument11 pagesStructuralMary Ann FiguerasNo ratings yet
- Plate ElementsDocument23 pagesPlate ElementsEhsan WasimNo ratings yet
- SandwichStructures PDFDocument447 pagesSandwichStructures PDFRammohan YS100% (1)
- NSC1701 Feature 9Document3 pagesNSC1701 Feature 9MoonzeNo ratings yet
- Crane BeamDocument8 pagesCrane BeamastorNo ratings yet
- IS808 2021 Smx1mhtgqfgnyculmeemie1srmsd20230207103407Document60 pagesIS808 2021 Smx1mhtgqfgnyculmeemie1srmsd20230207103407baubleNo ratings yet
- Design Preboard Exam NOV 2021Document17 pagesDesign Preboard Exam NOV 2021Glaiza Marie100% (1)
- Warping Constant of Open Sections With Arbitrary Profile Geometry Rev 1 2011Document24 pagesWarping Constant of Open Sections With Arbitrary Profile Geometry Rev 1 2011hoojzteNo ratings yet
- Gantry Girder DesignDocument7 pagesGantry Girder DesignsatydevsinghnegiNo ratings yet
- Torsion, Bending and Buckling of Steel Beams by Trahair 1997Document6 pagesTorsion, Bending and Buckling of Steel Beams by Trahair 1997fahmi aballiNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Get SP Grade 8 Technology Term 3 Week 3Document4 pagesLesson Plan Get SP Grade 8 Technology Term 3 Week 3Kutlwano TemaNo ratings yet
- Short Proposal Finite ElementDocument9 pagesShort Proposal Finite ElementMuhammad Ilham ZulkipllyNo ratings yet
- Example 2 To Start ExplainationDocument8 pagesExample 2 To Start ExplainationsamehNo ratings yet
- RST Instruments: Vibrating Wire Strain Gauge Model VWSG-S Instruction ManualDocument32 pagesRST Instruments: Vibrating Wire Strain Gauge Model VWSG-S Instruction ManualSyed Aqib AliNo ratings yet
- Design of I-BeamDocument28 pagesDesign of I-BeamngNo ratings yet
- A.Boudjemia and L.Dahmani: Keywords: Steel Beam, Lateral Torsional Buckling, Eurocode 3, Finite Element Method, ANSYSDocument4 pagesA.Boudjemia and L.Dahmani: Keywords: Steel Beam, Lateral Torsional Buckling, Eurocode 3, Finite Element Method, ANSYSBAMOUROU SANOGONo ratings yet
- RC Beam Design QuestionsDocument22 pagesRC Beam Design QuestionsVenkatesanNo ratings yet
- Possible Use of T-Section Columns in RC Frame: Indian Concrete Journal December 2003Document6 pagesPossible Use of T-Section Columns in RC Frame: Indian Concrete Journal December 2003Clemente RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Burj KhalifaDocument2 pagesBurj KhalifaWalter Eduardo Loayza ChambillaNo ratings yet
- 24 MasterSeries-Revit Integrated LinkDocument13 pages24 MasterSeries-Revit Integrated Linksegun ajibolaNo ratings yet
- Seismic Performance of Steel Structures With Slit DampersDocument12 pagesSeismic Performance of Steel Structures With Slit DampersMohsen MNo ratings yet
- Jib Cranes: Ree StandingDocument6 pagesJib Cranes: Ree Standingprad.bal123No ratings yet
- Design of Spandrel Beams - PCI JOURNALDocument49 pagesDesign of Spandrel Beams - PCI JOURNALtrabajosicNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials: Pure BendingDocument42 pagesMechanics of Materials: Pure BendingmaycollNo ratings yet
- STAAD Pro Plates and Solids FAQ: Top 15 Questions AnsweredDocument15 pagesSTAAD Pro Plates and Solids FAQ: Top 15 Questions AnsweredKamal RaoNo ratings yet
- Design, Analysis and Optimization of Thin Walled Semi-Monocoque Wing Structures Using Different Structural Idealizations in The Preliminary Design PhaseDocument319 pagesDesign, Analysis and Optimization of Thin Walled Semi-Monocoque Wing Structures Using Different Structural Idealizations in The Preliminary Design Phaserokhgireh_hojjatNo ratings yet
- Mac Des Legit Complete1'Document962 pagesMac Des Legit Complete1'Archie LaranangNo ratings yet