Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Design Flow & Parameter Calculation of Operational Amplifier
Uploaded by
Vincent BaltazarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Design Flow & Parameter Calculation of Operational Amplifier
Uploaded by
Vincent BaltazarCopyright:
Available Formats
Design Flow of Operational Amplifier
Hong-Yi Huang
Department of Electronic Engineering
Fu-Jen Catholic University
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Outline
Op Amp Specification
Op Amp Parameter Calculation
Op Amp Simulation Method
Comparison of Calculation and Simulation
Op Amp Measurement
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Outline
Op Amp Specification
Op Amp Parameter Calculation
Op Amp Simulation Method
Comparison of Calculation and Simulation
Op Amp Measurement
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Op Amp Specification
Ideal Op. Amp. Practical Op. Amp.
Voltage control voltage source Finite gain
Infinite voltage gain Finite linear region
Infinite input impedance Offset voltage
Zero output impedance CMRR
It is free of frequency and Frequency response
temperature dependence, distortion,
Slew rate
and noise
Nonzero output resistance
Noise
Dynamic range
PSRR
DC power dissipation
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Op Amp Specification
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Outline
Op Amp Specification
Op Amp Parameter Calculation
Op Amp Simulation Method
Comparison of Calculation and Simulation
Op Amp Measurement
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Two Stage Op Amp
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Expect Specification
Low-frequency gain A0=75dB
Unity-gain frequency GBW=10MHz
Slew rate SR=10 V/us
Common mode rejection ratio CMRR=80dB
Phase margin PM=60o
Load impedance CL=10pF
DC supply voltages 0~3.3V
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Two Stage Op Amp Parameters
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Device Parameter
u n = 0.05m 2 /V ⋅ s
Device
NMOS PMOS up = 0.02m 2 /V ⋅ s
Parameter
K ox ε 0
µCox 2 2 Cox =
74 µA V 24 µA V t ox
2
K ox ≅ 3.9, ε 0 = 8.854 × 10 −12 F/m
Vt0 0 .6 − 0.8
tox and Vt0 can be found in spice
model
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Hand Calculation
1
1.choose CC = CL = 3.3pF
3
2. According to the spec. of G.B.
gm2
10M =
2πCc
gm2 = 209.44 uA
V
3. Determined current bias by slew rate
I5 I
SR = = ref = 10V/us
Cc Cc
IREF = I5 = SR × CC ≥ 10 × 10 6 × (3.3 × 10 −12 ) = 33.33uA
I7 I7
SR- = = = 10 V
CL 3CC us
⎛W⎞ ⎛W⎞
I7 = 100uA It means ⎜ ⎟ = 3 × ⎜ ⎟
⎝ L ⎠7 ⎝ L ⎠5
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Hand Calculation (con’t)
O
4. Because of PM=60
−1 ⎛ G.B ⎞ −1 ⎛ G.B ⎞ −1 ⎛ G.B ⎞
PM= 180° − tan ⎜ ⎟ − tan ⎜ ⎟ + tan ⎜ ⎟
⎝ P1 ⎠ ⎝ P2 ⎠ ⎝ Z ⎠
⎛ G.B ⎞ −1 ⎛ G.B ⎞
∴ 30° = tan −1 ⎜ ⎟ − tan ⎜ ⎟
⎝ P2 ⎠ ⎝ Z ⎠
By the small signal analysis
−1 1
Pole1= ωp1 ≅ where R1 =
gm6R 2R1Cc g ds,4 + g ds2
− gm6 1
Pole2= ωp2 ≅ R2 =
C2 gds6 + gds7
−1 C1 = Cb
Pole3= ωp3 =
R c C1
C 2 = CL
1
Zero= ωZ =
⎛ 1 ⎞
Cc ⎜⎜ − R c ⎟⎟
⎝ gm6 ⎠
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Hand Calculation (con’t)
1
set Rc=
gm6
⎛ G.B ⎞
30° = tan −1 ⎜ ⎟
⎝ P2 ⎠
⎛ 10M × 10p ⎞
30° = tan −1⎜⎜ ⎟⎟
⎝ g m6 ⎠
gm6=1.088m
RC=0.919kΩ
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Hand Calculation (con’t)
5. Determined the gm of Mp3,Mp4
I5 100
(W/L )3 = (W/L )4 = 2 = 6=1
(W/L )6 (W/L )6 I7 100 6
up C ox ⎛ W ⎞ I5
gm3 = gm4 = 2 ⎜ ⎟
2 ⎝ L ⎠3 2
up C ox ⎛ W ⎞
gm6 = 2 ⎜ ⎟ I7
2 ⎝ L ⎠6
⎛ W ⎞ I5
⎜ ⎟ ×
⎝ L ⎠3 2 1 1 1
gm3 = gm4 = × gm6 = gm6 × × = × 1.088m = 181.3 uA
⎛W⎞ 6 6 6 V
⎜ ⎟ × I7
⎝ L ⎠8
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Hand Calculation (con’t)
6. Calculate the A0 and CMRR
gm1gm6 gm1gm6
A0 = =
(gds2 + gds4 )(gds6 + gds7 ) (λI5 )(2 ⋅ λI7 )
209.44 × 10 −6 × 1.088 × 10 −3
≅ ≅ 79.53dB ≥ 75dB
(0.06 × 33.33 × 10 −6 ) × (2 × 0.06 × 100 × 10 −6 )
λ = 0.06V −1 for L = 1um
2gm2 gm4 2 × 209.44u × 125.6u
CMRR = ≈
gds5 gds2 λI
λI5 × 5
2
2 × 209.44u × 125.6u
= ≈ 85.53dB ≥ 80dB
33.33u
(0.06 × 33.33u) × (0.06 × )
2
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Hand Calculation (con’t)
7. Determined the dimension of M5 and M7
It depends on the current mirror M10.
⎛W⎞ ⎛W⎞ 1 ⎛W⎞
⎜ ⎟ = ⎜ ⎟ = ×⎜ ⎟
⎝ L ⎠10 ⎝ L ⎠5 3 ⎝ L ⎠ 7
⎛W⎞
If set ⎜ ⎟ = 10
⎝ L ⎠10
⎛W⎞
⎜ ⎟ = 10
⎝ L ⎠5
⎛W⎞
⎜ ⎟ = 30
⎝ L ⎠7
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Hand Calculation (con’t)
8.Determined the dimension of M1~M4 and M6
unCox ⎛ W ⎞ I5
gm2 = 2 ⎜ ⎟ = 209.44 uA
2 ⎝ L ⎠2 2 V
⎛ W ⎞ 33.33
209.44 = 2 74 × ⎜ ⎟ ×
⎝ L ⎠2 2
⎛W⎞
⎜ ⎟ = 8.89
⎝ L ⎠2
L = 1um, W1 = W2 = 8.89um
2
⎛W⎞ ⎛W⎞ gm4 (181.3u)2
⎜ ⎟ =⎜ ⎟ = = = 20.55
⎝ L ⎠3 ⎝ L ⎠ 4 4 upCox I5 4 × 24 × 33.33u
2 2 2
⎛W⎞ ⎛W⎞
gm6 = 6 × gm3 ⎜ ⎟ = 6 × ⎜ ⎟ = 123.3
⎝ L ⎠6 ⎝ L ⎠3
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Hand Calculation (con’t)
9. Determined the dimension of M8
1 1
RC = 0.919kΩ = =
⎛W⎞ ⎛W⎞
upCox ⎜ ⎟ × Vt 48 × ⎜ ⎟ × 0.8
⎝ L ⎠8 ⎝ L ⎠8
⎛W⎞
⎜ ⎟ = 28.3
⎝ L ⎠8
L = 1um W8 = 28.3um
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Hand Calculation (con’t)
Device W L Device W L
Mn1 8.89 Mp5 10
Mn2 8.89 Mp6 123.3
Mp3 20.55 Mn7 30
Mp4 20.55 Mp8 28.3
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Outline
Op Amp Specification
Op Amp Parameter Calculation
Op Amp Simulation Method
Comparison of Calculation and Simulation
Op Amp Measurement
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Two Stage Op Amp
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Operational Point
.op
Determine the operation region
of MOS
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Frequency Response
vinp vinp 0 dc 1v ac 1v
vinn vinn 0 dc 1v ac 0v
.ac dec 10 100 100000MEG
.print vdb(vout)
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Frequency Response
Because of stray capacitance, finite
Large Signal carrier mobilities, and so on, the
Voltage Gain
gain A decrease at high frequencies.
Gain
Large Signal Voltage Gain(A0) : The
Phase
gain at dc and low frequency.
PM 3dB Frequency (f3dB) : The maximum
f3dB
bandwidth of dc gain.
Phase Margin (PM) :the stability of
Op Amp.
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Frequency Response
Vout vinp vinp 0 dc 1v ac 1v
vinn vinn 0 dc 1v ac 0v
Vinp
Vout vinp vinp 0 dc 1v ac 0.1v
vinn vinn 0 dc 1v ac 0v
Vinp
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Transient Operation
Input Signal Vp-p = 25mV
Frequency
=1Mhz
Frequency Frequency
=10Mhz =50Mhz
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Input Voltage Noise Density
Noise: because of shot noise,
thermal noise ,and so on, the MOS
generates noise.
.noise v(Y) X Z
Y: the point wanted to analysis
X: reference point
Z: frequency resolution
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Input Common Mode Range (ICMR)
Input Common Mode Range
(ICMR): the range of input
common mode voltage
.dc Vin 0 3.3 0.1
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Input Common Mode Range (ICMR)
Unity gain Response
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Input Common Mode Range (ICMR)
Vcm < ICMR-
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Output Voltage Swing
Output Voltage Swing:
The range of output voltage which can operate normally.
10R
VOUT = − VIN = −10VIN
R
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Output Voltage Swing
Transient response, Output saturated
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Output Voltage Swing
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Output Voltage Swing
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Common Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR)
Common Mode Rejection Ratio
(CMRR): the ability of rejecting
common mode signal.
vinp vinp 0 dc 1v ac 1v
vinn vinn 0 dc 1v ac 0v
.ac dec 10 100 100000MEG
.print vdb(vout)
Common mode gain
.alter
vinn vinn 0 dc 1v ac 1v
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Common Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR)
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Power Supply Rejection Ratio (PSRR)
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
(PSRR): the ability of rejecting noise
from power supply.
.alter
vdd vdd 0 dc 3.3v ac 1v
vinn vinn 0 dc 1v ac 1v
.alter
vss vss 0 dc 0v ac 1v
vinn vinn 0 dc 1v ac 1v
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Power Supply Rejection Ratio (PSRR)
PSRR+ PSRR-
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Slew Rate & Settling Time
Slew Rate: the maximum rate of
change dvo/dt is called slew rate.
Settling Time: the time during
output signal be stable shown as
right figure.
vinp vinp 0 pulse(1v 2v 0n 0.5n 0.6n
150n 300n)
.meas tran t when v(vout)=1.9v rise=1
.meas SR param='0.9/t'
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Slew Rate & Settling Time
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Total Harmonic Distortion
vinp vinp 0 sin(1.65 0.1m 1k 0)
DC:1.65V
Amplitude: 0.1mV
Frequency: 1kHz
Delay time: 0
.four 1k v(vout)
Fouriur analysis for 1kHz signal
Fouriur analysis for vout
.fft v(vout) np=1024 start=1u stop=56u freq=1x
Resolution: np
Simulation time: stop-start
Fouriur analysis for 1MHz signal
Fouriur analysis for vout
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Operation point
.op
DC power dissipation
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Outline
Op Amp Specification
Op Amp Parameter Calculation
Op Amp Simulation Method
Comparison of Calculation and Simulation
Op Amp Measurement
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Comparison of Calculation and Simulation
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Frequency Response
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Slew Rate & Settling Time
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Common Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR)
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Input Common Mode Range (ICMR)
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Output Voltage Swing
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Power Supply Rejection Ratio (PSRR)
PSRR+ PSRR-
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Outline
Op Amp Specification
Op Amp Parameter Calculation
Op Amp Simulation Method
Comparison of Calculation and Simulation
Op Amp Measurement
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Input Offset Voltage
The offset voltage is the
difference of Vin+ and Vout
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Open Loop Gain and Frequency Response
R=10MΩ At lower frequency, this Op Amp
is unity gain configuration.
C=100uF
At higher frequency, this Op
RL=1MΩ
Amp is open loop configuration.
CL=8pF for Probe
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Common Mode Gain
Eliminate the effect of offset
voltage, and import the same
input signal to the Vin+ and Vin-.
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Common Mode Rejection Ratio
Vo = A d (V+ − V− ) ± A c Vcm
Ac
= A d (Vcm − Vo − Vcm ) ± (2Vcm + Vo )
2
Vo ± Ac Ac 1
= ≅ =
1 + A d − ⎛⎜ ± ⎞
Vcm Ac Ad CMRR
⎝ 2 ⎟⎠
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Power Supply Rejection Ratio (PSRR)
Vo = A d (V+ − V- ) + A dd Vdd
Vo = A d (Vo ) + A dd Vdd
A dd A 1
Vo = Vdd ≅ dd Vdd = Vdd
1+ A d Ad PSRR+
Vo = A d (V+ − V- ) + A ss Vss
Vo = A d (Vo ) + A ss Vss
A ss A 1
Vo = Vss ≅ ss Vss = Vss
1+ A d Ad PSRR−
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Input Common Mode Range
Unity gain configuration
The method of measurement is
the same as the one of
simulation.
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Output Voltage Swing
VO= -10Vi
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Output Resistance
R∞
Vo1 = iout ×
Rout + R ∞
RL
Vo2 = iout ×
RL + Rout
RL
Vo2 = Vo1
Rout + RL
⎛V ⎞
R out = R L ⎜⎜ o1 − 1⎟⎟
⎝ Vo2 ⎠
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
Slew Rate and Settling Time
Unity gain configuration
The method of measurement is
the same as the one of
simulation.
Analog ICs;Hong-Yi Huang
You might also like
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsFrom EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- h-PARAMETER BJT MODEL: Two Port NetworksDocument6 pagesh-PARAMETER BJT MODEL: Two Port NetworksArmor BatsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. Single-Transistor Primitives An Intuitive Approach (Analog IC Design An Intuitive Approach)Document26 pagesChapter 3. Single-Transistor Primitives An Intuitive Approach (Analog IC Design An Intuitive Approach)Minh Hai RungNo ratings yet
- Allen and Holberg Homework SolutionDocument121 pagesAllen and Holberg Homework SolutionNihit Varshney100% (1)
- High Frequency VCO Design for mm-Wave ApplicationsDocument70 pagesHigh Frequency VCO Design for mm-Wave Applicationstoto byNo ratings yet
- Opamp ReportDocument38 pagesOpamp ReportMuhammad SaperNo ratings yet
- Analog IC Design: Chủ đề 6: Amplifiers Differential AmplifiersDocument80 pagesAnalog IC Design: Chủ đề 6: Amplifiers Differential AmplifiersQuang Nhật TrầnNo ratings yet
- Amplifiers Frequency Response Examples: Pole-Splitting EquationsDocument7 pagesAmplifiers Frequency Response Examples: Pole-Splitting EquationsDušan KrčumNo ratings yet
- Eetop - CN - A Low Power Two Stages CMOS OpAmpDocument6 pagesEetop - CN - A Low Power Two Stages CMOS OpAmp王威棟No ratings yet
- Microelectronic Circuits -10EC63Document10 pagesMicroelectronic Circuits -10EC63Noorullah ShariffNo ratings yet
- Design Problem:: Design A Fully Differential Version of Two Stage CMOS Op-Amp With The Following SpecificationsDocument37 pagesDesign Problem:: Design A Fully Differential Version of Two Stage CMOS Op-Amp With The Following Specificationslearn simplyNo ratings yet
- Study of R-C Phase Shift OscillatorDocument6 pagesStudy of R-C Phase Shift OscillatorTawsiful AlamNo ratings yet
- High Frequency VCO Design OptimizationDocument67 pagesHigh Frequency VCO Design OptimizationEnricoLiaNo ratings yet
- LNADocument54 pagesLNAkavyashree_pNo ratings yet
- AmplifierDocument20 pagesAmplifierHua-Chien ChangNo ratings yet
- Mos CS LnaDocument11 pagesMos CS LnaDajana DanilovicNo ratings yet
- chapter 7Document22 pageschapter 7louischen1228No ratings yet
- Frequency ResponseDocument53 pagesFrequency ResponseRithwik Reddy AavulaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 01 ReportDocument13 pagesAssignment 01 ReportSalaudeen IlyasNo ratings yet
- Fault Location DetectrorDocument20 pagesFault Location DetectrorAung MyatNo ratings yet
- Microelectronic Circuits Frequency Response AnalysisDocument134 pagesMicroelectronic Circuits Frequency Response AnalysisAniruddh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 MidDocument49 pagesModule 1 MidZylah NorberteNo ratings yet
- Frequency ResponseDocument30 pagesFrequency ResponseAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Amplificador de Potencia de Baja Frecuencia Cd8227gpDocument8 pagesAmplificador de Potencia de Baja Frecuencia Cd8227gplaboratorio fercorNo ratings yet
- CD8227GPDocument8 pagesCD8227GPAlfredo Valencia RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Ex - No 7 RC Phase Shift and Wien BridgeDocument9 pagesEx - No 7 RC Phase Shift and Wien BridgeBharath kNo ratings yet
- Freq Response of BJT AmplifierDocument6 pagesFreq Response of BJT AmplifierAnonymous jiembdNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor ExercisesDocument2 pagesInduction Motor ExercisesOscar Ardila67% (3)
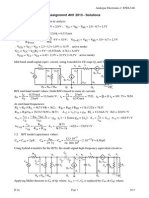
- 3AE Assignment AN1 2013 SolnsDocument2 pages3AE Assignment AN1 2013 SolnsAluwani KhomolaNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Fault LevelDocument23 pages2.0 Fault Levelrathaurs100% (2)
- 665 LNA-Design-2005Document78 pages665 LNA-Design-2005Faizan MasoodNo ratings yet
- Analog & Digital (Microp)Document3 pagesAnalog & Digital (Microp)Bharath ChNo ratings yet
- Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook: Try Yourself QuestionsDocument10 pagesWorkbook Workbook Workbook Workbook Workbook: Try Yourself QuestionsarunNo ratings yet
- Common Drain Frequency Response: PART 1: Sizing ChartDocument9 pagesCommon Drain Frequency Response: PART 1: Sizing ChartAhmad KamalNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 6 Op-Amp As Comparator & Schmitt Trigger: Analog Circuits LAB ManualDocument14 pagesExperiment No. 6 Op-Amp As Comparator & Schmitt Trigger: Analog Circuits LAB ManualchaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Control SystemDocument36 pagesControl SystemARVINDNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Summer Session 2009 10Document5 pagesAssignment 1 Summer Session 2009 10asdf2121No ratings yet
- Solucionario CAP 5 RAZAVIDocument112 pagesSolucionario CAP 5 RAZAVIBenjaminJimenezNo ratings yet
- Final Project Report Sachin Basavarajappa KenchammanagathihalliDocument14 pagesFinal Project Report Sachin Basavarajappa KenchammanagathihalliSachin BkNo ratings yet
- Problem 22Document11 pagesProblem 22f20212698No ratings yet
- SOLUTIONS to ELE22EMI 2004 NOVEMBER ExamDocument12 pagesSOLUTIONS to ELE22EMI 2004 NOVEMBER Examسعيد ابوسريعNo ratings yet
- List of Linear IC ExperimentsDocument26 pagesList of Linear IC ExperimentsVenkatGollaNo ratings yet
- EE 2257-Control Systems Lab ManualDocument66 pagesEE 2257-Control Systems Lab ManualRam KumarNo ratings yet
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1From EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Audio IC Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesFrom EverandAudio IC Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Newnes Radio and Electronics Engineer's Pocket Book: Revised by the Editorial Staff of Electronics Today InternationalFrom EverandNewnes Radio and Electronics Engineer's Pocket Book: Revised by the Editorial Staff of Electronics Today InternationalNo ratings yet
- Combinatorial Algorithms: For Computers and CalculatorsFrom EverandCombinatorial Algorithms: For Computers and CalculatorsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Product Datasheet for PK-G021 PCB KEYBOARD GDS101 ColourDocument2 pagesProduct Datasheet for PK-G021 PCB KEYBOARD GDS101 ColourSiva RamanNo ratings yet
- Intraoral X-Ray UnitsDocument1 pageIntraoral X-Ray UnitsxrayserviceNo ratings yet
- RTCU AX9 Turbo Technical Manual 1.03Document45 pagesRTCU AX9 Turbo Technical Manual 1.03Manuel Alejandro Espinosa FarfanNo ratings yet
- Geh 6808Document642 pagesGeh 6808Kolade BakareNo ratings yet
- QXDM Logs On HTC DesireDocument1 pageQXDM Logs On HTC Desiretech_geekNo ratings yet
- Automation of Rotogravure Printing MachineDocument12 pagesAutomation of Rotogravure Printing MachineshraddhaNo ratings yet
- FI01 en Kap03Document118 pagesFI01 en Kap03pvalverdea2014No ratings yet
- Esabfeed 30-2 Yardfeed 200: M11 Origot M13YDocument30 pagesEsabfeed 30-2 Yardfeed 200: M11 Origot M13YPascu AurelNo ratings yet
- IVR-1200MPPT/IVR-2400MPPT User ManualDocument17 pagesIVR-1200MPPT/IVR-2400MPPT User ManualTesla Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- Bloxx A101: Key FeaturesDocument4 pagesBloxx A101: Key FeaturesHammad HussainNo ratings yet
- Liquid Rheostat Operation and MaintenanceDocument20 pagesLiquid Rheostat Operation and MaintenanceMaheshwar Kumar100% (1)
- Hakko FR-300 Teardown and Mod: 13 CapturesDocument8 pagesHakko FR-300 Teardown and Mod: 13 CapturesAaronNo ratings yet
- TV repair manual diagrams TDA9381ps flyback LGDocument1 pageTV repair manual diagrams TDA9381ps flyback LGprasadwijeNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual for MillivoltmeterDocument51 pagesInstruction Manual for MillivoltmeterRoxana Aldea-CiaciruNo ratings yet
- CONVO User Manual of SY5000 Series AC DrivesDocument115 pagesCONVO User Manual of SY5000 Series AC DrivesRavshan SaidahmetovNo ratings yet
- Ammeter, Voltmeter Testing Not Applicable For This PanelDocument3 pagesAmmeter, Voltmeter Testing Not Applicable For This Paneleswaran005No ratings yet
- XA9221 X AudioDocument19 pagesXA9221 X Audioha haihaNo ratings yet
- ANSI NEMA WC 51-2009 ICEA P-54-440-2009 Ampacities of Cables Installed in Cable TraysDocument38 pagesANSI NEMA WC 51-2009 ICEA P-54-440-2009 Ampacities of Cables Installed in Cable TraysGlenn Adalia Bonita100% (2)
- Report on Industrial Attachment at ECG in TakoradiDocument41 pagesReport on Industrial Attachment at ECG in TakoradiDerrick BaidooNo ratings yet
- C2250 D5 SubmittalDocument28 pagesC2250 D5 SubmittalZoka AhmadNo ratings yet
- Eplan Power1 17 Eplan Software & Service GMBH & Co. KGDocument11 pagesEplan Power1 17 Eplan Software & Service GMBH & Co. KGTinto TenNo ratings yet
- Altium Designer Platform Manual - BKMKDDocument45 pagesAltium Designer Platform Manual - BKMKDMelliaa AmelNo ratings yet
- M002-012-9 NVGate TechSpecDocument27 pagesM002-012-9 NVGate TechSpecОлег ЗахарийNo ratings yet
- Battery Charging 1Document21 pagesBattery Charging 1Bilal QasimNo ratings yet
- Programmable Electronic Current Burden: Features and BenefitsDocument3 pagesProgrammable Electronic Current Burden: Features and BenefitsEdgar JimenezNo ratings yet
- ZMP 4058117 Ot DX 110 220 240 1a0 Dima LT2 eDocument9 pagesZMP 4058117 Ot DX 110 220 240 1a0 Dima LT2 eionelg834549No ratings yet
- 980F 3HK, 8CJ, 5XJ1-587Document2 pages980F 3HK, 8CJ, 5XJ1-587Rafa GarciaNo ratings yet
- Directory of Accredited Testing LaboratoriesDocument645 pagesDirectory of Accredited Testing LaboratoriesSharafat AliNo ratings yet
- LGMV Total EngDocument69 pagesLGMV Total EngAlejandro SianNo ratings yet
- Yamaha Su-200 Manual (En)Document62 pagesYamaha Su-200 Manual (En)xxxNo ratings yet