Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transient Voltage Protection of Mosfets
Uploaded by
Varun NarisettyOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Transient Voltage Protection of Mosfets
Uploaded by
Varun NarisettyCopyright:
Available Formats
S196-13
Surging Ideas
TVS Diode Application Note
PROTECTION PRODUCTS
Transient Protection of MOSFETS
One of the most common causes of failure in MOSFET • For switching inductive oads and power supply
devices results from exceeding the maximum drain - applications, a 1500W (tp = 10/1000µs) TVS is
source voltage (VDS). Inductive load switching for recommended.
example can cause transients which can force VDS to
exceed the maximum breakdown voltage of the Gate-Source Protection
MOSFET. If the transient contains enough energy, the Transient on the input of the MOSFET can puncture
MOSFET will be destroyed if it begins to avalanche. the thin gate oxide of the device and melt the silicon.
Transients at the gate of the device are often due to
Drain-Source Protection electrostatic discharge (ESD). Connecting a TVS diode
One method of protecting the MOSFET is to connect a from gate to source can protect the MOSFET from
TVS diode from drain to source. To choose the correct input transients. Choose a suppressor with a working
TVS diode, use the following guidelines: voltage which exceeds the MOSFET input voltage. For
• The working voltage of the TVS diode (Vrwm) must suppression of ESD, a device rated at 300W (tp = 8/
exceed the worst case supply voltage. 20µs) will suffice.
• The TVS diode clamping voltage (Vc) must be less A schematic diagram illustrating these protection
than the minimum breakdown voltage of the techniques is shown in Figure 1.
MOSFET under peak pulse current conditions.
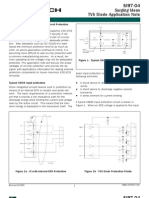
SUPPLY/LOAD
DRAIN
INPUT GATE
SOURCE
Figure 1 - MOSFET Protection
Revision 9/2000 1 www.semtech.com
You might also like
- Transient Voltage Protection of MosfetsDocument1 pageTransient Voltage Protection of MosfetsAnand AbhishekNo ratings yet
- TVS Diode Application Note: Surging IdeasDocument1 pageTVS Diode Application Note: Surging IdeasGrimmjow JaegerjaquezNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsFrom EverandSemiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsNo ratings yet
- Slva 680 ADocument11 pagesSlva 680 Achuku7No ratings yet
- Automotive SBR Battery Reverse ProtectionDocument7 pagesAutomotive SBR Battery Reverse Protectionab_s5036No ratings yet
- ESD ClampsDocument30 pagesESD ClampsKishore RoyNo ratings yet
- Railclamp Low Capacitance Tvs Diode Array: Protection Products Protection Products Description FeaturesDocument9 pagesRailclamp Low Capacitance Tvs Diode Array: Protection Products Protection Products Description Featuressiev29No ratings yet
- Infineon-MOSFETs OptiMOS Selection For DC-DC converters-AN-v01 00-ENDocument6 pagesInfineon-MOSFETs OptiMOS Selection For DC-DC converters-AN-v01 00-ENLûtwàmä JôëNo ratings yet
- For Operating Voltage of 5V and Below Ultra Low Capacitance: 0.5pF TypicalDocument10 pagesFor Operating Voltage of 5V and Below Ultra Low Capacitance: 0.5pF TypicalTri Nguyen Real EstateNo ratings yet
- Transistor - 10n100 EDocument8 pagesTransistor - 10n100 Eivanaldo tavaresNo ratings yet
- Faq Esd ProtectionDocument11 pagesFaq Esd ProtectionSaumyaranjan M BeheraNo ratings yet
- T3055el Motorola Mosfet de InyectoresDocument10 pagesT3055el Motorola Mosfet de InyectoresDaniel Arturo PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Lectura 3 M PDFDocument12 pagesLectura 3 M PDFFlakita S MelcOchitaNo ratings yet
- TVS PDFDocument2 pagesTVS PDFjosbullNo ratings yet
- Vishay Tvs AnDocument2 pagesVishay Tvs AnthewaywewereNo ratings yet
- No - EE331-Lab-3 - 2023-05-23T103126.278Document9 pagesNo - EE331-Lab-3 - 2023-05-23T103126.278Def AbcNo ratings yet
- JFET and MOSFET Characterization: Experiment-3Document23 pagesJFET and MOSFET Characterization: Experiment-3James JohnsonNo ratings yet
- MTP3055Document9 pagesMTP3055lisandroantonNo ratings yet
- Jfet and Mosfet Characterization 5aae458a1723dd235e70b7d9Document23 pagesJfet and Mosfet Characterization 5aae458a1723dd235e70b7d9hasan mubinNo ratings yet
- Application Note: Ethernet Protection - A Whole SolutionDocument4 pagesApplication Note: Ethernet Protection - A Whole SolutionАндрей НовиковNo ratings yet
- Disadvantage of On-Chip Transient Voltage ProtectionDocument2 pagesDisadvantage of On-Chip Transient Voltage ProtectionnonyannNo ratings yet
- For Operating Voltage of 3.3V and Below Ultra Low Capacitance: 0.45pF TypicalDocument9 pagesFor Operating Voltage of 3.3V and Below Ultra Low Capacitance: 0.45pF TypicalFábio MenezesNo ratings yet
- TVS SMCJ Series Datasheets2Document7 pagesTVS SMCJ Series Datasheets2drxyzNo ratings yet
- What Are TVS DiodesDocument1 pageWhat Are TVS Diodesrajat nimjeNo ratings yet
- Wolfspeed CPM3-1200-0016A Data Sheet ExternalDocument7 pagesWolfspeed CPM3-1200-0016A Data Sheet ExternalSonia ElouedNo ratings yet
- Circuit Design Concepts For Esd Protection 2008 PDFDocument32 pagesCircuit Design Concepts For Esd Protection 2008 PDFNguyen Van ToanNo ratings yet
- Surface Mount Transient Voltage Suppressors (TVS) : SMF Series 5.0 To 190 V 200WDocument6 pagesSurface Mount Transient Voltage Suppressors (TVS) : SMF Series 5.0 To 190 V 200WdrxyzNo ratings yet
- Why Mosfets FailDocument2 pagesWhy Mosfets FailkholshNo ratings yet
- EE Times Asia White Paper AmazingDocument6 pagesEE Times Asia White Paper AmazingJeremy ChiangNo ratings yet
- MEV3 Series: 3kVDC Isolated 3W Single Output DC/DC ConvertersDocument5 pagesMEV3 Series: 3kVDC Isolated 3W Single Output DC/DC Convertersmklimesh2600No ratings yet
- Stacking Power MOSFETs For Use in High Speed InstrumentationDocument3 pagesStacking Power MOSFETs For Use in High Speed InstrumentationTomas MullerNo ratings yet
- JFET and MOSFET Characterization: Experiment-3Document23 pagesJFET and MOSFET Characterization: Experiment-3engineer_3No ratings yet
- N-Channel Enhancement-Mode Silicon Gate: Semiconductor Technical DataDocument10 pagesN-Channel Enhancement-Mode Silicon Gate: Semiconductor Technical DataHAROL ALEXIS VALENCIA OSPINANo ratings yet
- DatasheetDocument7 pagesDatasheetabdelmoumene djafer beyNo ratings yet
- IRFD9120: 1.0A, 100V, 0.6 Ohm, P-Channel Power Mosfet FeaturesDocument6 pagesIRFD9120: 1.0A, 100V, 0.6 Ohm, P-Channel Power Mosfet FeaturesJaime Enrique ValbuenaNo ratings yet
- VaristorDocument19 pagesVaristorDan AndreiNo ratings yet
- Ecler Pam1400 1000 600 300Document183 pagesEcler Pam1400 1000 600 300Lluis Reparacion ElectronicaNo ratings yet
- Surge Protection With Jaydeep ShahDocument18 pagesSurge Protection With Jaydeep ShahJAYDEEP SHAHNo ratings yet
- ESD Protection (EETimes India)Document2 pagesESD Protection (EETimes India)abhineet sharmaNo ratings yet
- Medium Power Surface Mount Products: Semiconductor Technical DataDocument10 pagesMedium Power Surface Mount Products: Semiconductor Technical DataStuxnetNo ratings yet
- Irsf3010s DatDocument11 pagesIrsf3010s DatNoelNo ratings yet
- Ds 0026Document10 pagesDs 0026dcastrelos2000No ratings yet
- Description: 1A LDO Linear Voltage RegulatorDocument8 pagesDescription: 1A LDO Linear Voltage RegulatorMateus souzaNo ratings yet
- LM12CLKDocument14 pagesLM12CLKGheorghe DanielNo ratings yet
- Surge Protective Device Types - Type 1, Type 2, Type 3, Type 4Document3 pagesSurge Protective Device Types - Type 1, Type 2, Type 3, Type 4anuragpugaliaNo ratings yet
- Pet Essentials 2013Document29 pagesPet Essentials 2013Silvester MacakNo ratings yet
- 2020 16 How To Select Silicon TVS DevicesDocument3 pages2020 16 How To Select Silicon TVS DevicesSateesh TalisettyNo ratings yet
- Using The Power MOSFET As A SwitchDocument5 pagesUsing The Power MOSFET As A SwitchNgoc Nguyen HaNo ratings yet
- Surge Diverters Type VSD: Response TimeDocument2 pagesSurge Diverters Type VSD: Response TimevetsasNo ratings yet
- IRF9520Document7 pagesIRF9520Emilio QuijanoNo ratings yet
- 6A, 100V, 0.600 Ohm, P-Channel Power Mosfet Features: File Number 2281.3 Data Sheet July 1999Document8 pages6A, 100V, 0.600 Ohm, P-Channel Power Mosfet Features: File Number 2281.3 Data Sheet July 1999rex999No ratings yet
- Transient-Voltage Aspects of GroundingDocument9 pagesTransient-Voltage Aspects of Groundingee_rahulyadavNo ratings yet
- MT7812 Lamp ParsDocument9 pagesMT7812 Lamp ParsEb INo ratings yet
- 1N8149US MicrosemiDocument6 pages1N8149US Microsemithuco.18No ratings yet
- Module 7: I/O Pads Lecture 33: I/O Pads: ObjectivesDocument7 pagesModule 7: I/O Pads Lecture 33: I/O Pads: ObjectivespriyanklaadNo ratings yet
- Lightinig Protection AircraftDocument20 pagesLightinig Protection AircraftelectworldNo ratings yet
- Surge Protection Circuit Thyristor TIC126 - Electronics Projects CircuitsDocument4 pagesSurge Protection Circuit Thyristor TIC126 - Electronics Projects Circuitssisay bitewNo ratings yet
- Deepak John S1 M. Tech Power System: Presented byDocument36 pagesDeepak John S1 M. Tech Power System: Presented byVarun NarisettyNo ratings yet
- Notification Vii Convocation: WWW - Jntuh.ac - inDocument1 pageNotification Vii Convocation: WWW - Jntuh.ac - inVarun NarisettyNo ratings yet
- Power Dist NetworkDocument62 pagesPower Dist NetworkVarun NarisettyNo ratings yet
- Annexure - I: VH-W (Open) - 1 HH (Local) - 1 OH (Local) - 1Document1 pageAnnexure - I: VH-W (Open) - 1 HH (Local) - 1 OH (Local) - 1Varun NarisettyNo ratings yet
- Automatic Transfer SwitchDocument18 pagesAutomatic Transfer SwitchVarun Narisetty100% (1)
- Circuit Breakers Lecture Notes 3Document124 pagesCircuit Breakers Lecture Notes 3Varun NarisettyNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Symbols List (+,-,X, - , , - , - ,..Document13 pagesMathematical Symbols List (+,-,X, - , , - , - ,..Varun NarisettyNo ratings yet
- 3tf ContactorDocument25 pages3tf Contactorpadminitt100% (1)
- Quick Exhaust Solenoid Valves: NC NODocument4 pagesQuick Exhaust Solenoid Valves: NC NOMuhammad AsadNo ratings yet
- Npcil PDFDocument15 pagesNpcil PDFAmit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Abdul Rasheed (2019-Me-34) Thermodynamic AssignmentDocument6 pagesAbdul Rasheed (2019-Me-34) Thermodynamic AssignmentAbdul Rasheed GhaziNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: The First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument54 pagesChapter 5: The First Law of ThermodynamicsRishabh VaraiyaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Propulsion SystemDocument15 pagesElectrical Propulsion SystemAngelito AndaNo ratings yet
- A C M V: PsychrometryDocument31 pagesA C M V: PsychrometryMessi CakeNo ratings yet
- How To Read PWHTchartDocument10 pagesHow To Read PWHTchartAkhilesh Kumar100% (3)
- Transformer Interview Questions & Answers: Search For Jobs..Document29 pagesTransformer Interview Questions & Answers: Search For Jobs..shamshadNo ratings yet
- Mass BalanceDocument8 pagesMass BalanceShiraz NajatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Chemical EquilibriumDocument52 pagesChapter 13 - Chemical EquilibriummukhlishNo ratings yet
- Pix CarsDocument149 pagesPix CarsRicardo AssunçãoNo ratings yet
- Como Sobreviver A Um Apocalipse ZumbiDocument30 pagesComo Sobreviver A Um Apocalipse ZumbirejaneNo ratings yet
- Max Seal Fluid Loss Control AdditiveDocument2 pagesMax Seal Fluid Loss Control AdditiveadrianitoalaNo ratings yet
- LPG Blackmer PumpsDocument16 pagesLPG Blackmer Pumpssizweh100% (1)
- Green Building PBLDocument11 pagesGreen Building PBLsofea1121No ratings yet
- Group Practice GP 34-00 Machinery: Use and Interpretation of This DocumentDocument40 pagesGroup Practice GP 34-00 Machinery: Use and Interpretation of This DocumentSuresh Kumar A P80% (5)
- EGY D 22 06311 - R1 - ReviewerDocument101 pagesEGY D 22 06311 - R1 - ReviewerWEIWEI YANGNo ratings yet
- Bombardier¿ and Challenger¿ Are Trademarks of Bombardier, IncDocument5 pagesBombardier¿ and Challenger¿ Are Trademarks of Bombardier, IncMiguel Andres Esparragoza CeballosNo ratings yet
- True Charge 20 Amp 3 Stage Charger ManualDocument78 pagesTrue Charge 20 Amp 3 Stage Charger ManualElliot Capson100% (1)
- 4 - AppendicesDocument27 pages4 - AppendicesDin Flores MacawiliNo ratings yet
- SMPS PPT Summer Traning by VijayDocument60 pagesSMPS PPT Summer Traning by VijayVijay Kaplsya86% (7)
- Rigo 2012Document11 pagesRigo 2012saeedNo ratings yet
- Recovered Fiber Pulping NoteDocument28 pagesRecovered Fiber Pulping Noteteewee_cuteNo ratings yet
- Brochure Ball Mills enDocument16 pagesBrochure Ball Mills enmarviNo ratings yet
- Electrical Design CriteriaDocument533 pagesElectrical Design CriteriaHimdad Bahri100% (3)
- Smart Energy Coordination of Autonomous ResidentiaDocument13 pagesSmart Energy Coordination of Autonomous ResidentiaAhmed SabriNo ratings yet
- Commissioning NotesDocument13 pagesCommissioning NotesÇınar İnalNo ratings yet
- Module No 3: Liquefied Natural Gas Markets, Consumption, Measurement & CalculationDocument30 pagesModule No 3: Liquefied Natural Gas Markets, Consumption, Measurement & CalculationAndreiNo ratings yet
- Fallsem2016-17 1286 RM001 27-Jul-2016 Mee1003 THDocument74 pagesFallsem2016-17 1286 RM001 27-Jul-2016 Mee1003 THaman agarwalNo ratings yet