Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DISEASES Kawasaki, RHD, Is HPN)
Uploaded by
jenn212Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DISEASES Kawasaki, RHD, Is HPN)
Uploaded by
jenn212Copyright:
Available Formats
KAWASAKI DISEASE
a.k.a. Mucocutaneous Lymph node syndrome
Infantile polyarteritis
Definition: An acute febrile illness of young children that causes
widespread vasculitis.
Principal finding:
Vasculitis - inflammation of blood vessels
- can lead to formation of aneurysms, platelet
accumulation, formation of thrombi
Causes: - unknown
- possible genetic role after exposure to a virus, bacteria or
other pathogen
S/S: - fever for five (5) days or more, unresponsive to antipyretics
- lethargy
- irritability
- reddened, swollen hands and feet
- conjunctivitis
- “strawberry” tongue č red cracked lips
- rash in trunk area
- enlarged cervical lymph nodes
- reddened, swollen joints
- abdominal pain, anorexia, diarrhea
Assessment Findings: - fever for five (5) days or more, unresponsive to
antipyretics
- occurrence of s/s
- increase WBC
- increase platelet count
Therapeutic Management: - IV gamma globulin
- Aspirin
- Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery (CAD)
Nursing Interventions: - keep clothing from constructing or irritating rash
- moisten lips with lip balm to prevent from
cracking
- offer frequent fluids
- observe for signs of GI upset
- avoid pressure on extremities č edema
- monitor I and O
- give prescribed drugs
Health Teachings: - Aspirin therapy after hospitalization
- report exposure to viral illness
- possibility of long-term management
- need to delay immunization
- encourage to schedule a follow up exam in two
(2) to three (3) weeks
RHEUMATIC HEART DISEASE
Definition: Systemic inflammatory disease of childhood that occurs
two (2) to six (6) weeks following an inadequately
treated URTI č group A beta-hemolytic streptococci.
Most common symptom: Arthritis
S/S: (Revised Jones Criteria):
Major: Arthritis
Carditis
Erythema Marginatum
Subcutaneous Nodules
Chonea
Minor: previous Hx of Rheumatic Fever
Arthralgia
Increase levels of acute phase reactants
Prolonged PR interval on ECG
Fever
Other s/s: chest pain
SOB
Tachycardia
Bradycardia
Complain of sore throat
Cough
Dx Test: chest x-ray
Echocardiography
Cardiac catheterization
Assessment Findings: - recurrent streptococcal infection
- recent Hx of low-grade fever č unexplained
epistaxis
and abdominal pain
- occurrence of s/s
- increase WBC count
- anemia
Therapeutic Management: - antibiotics
- corticosteroids
- Phenobarbital
- heart valve replacement
Nursing Interventions: - give prescribed antibiotics on time
- stress importance of bed rest
- provide analgesics as needed
- allow patient to express feelings and
concerns
Health Teachings: - disorder, Dx, treatment
- scheduling frequent rest periods
- report early s/s of left sided heart failure
and recurrent strep. Infection
- avoid people č resp. infections
- compliance č prolonged antibiotic therapy
- prophylaxis before invasive procedures
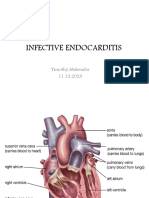
ENDOCARDITIS
Definition: Inflammation and infection of the endocardium or valves
of the heart.
Causes: - complication of congenital heart diseases:
Tetralogy of fallot, VSD, coarotation of aorta
- streptococci infection, possible: staphylococcal or
fungal
S/S: - pale
- anorexia
- weight loss
- arthralgia
- malaise
- chills
- periods of sweating
- heart murmurs
- petechiae of conjunctiva/oral mucosa
- hemorrhages
- left upper quadrant pain from spleen infraction
Dx Tests: Echocardiogram
Blood Cultures
CBC
U/A
Assessment Findings: - occurrence of s/s
- increase WBC
- anemia
- proteinuria
- hematuria
- vegetative growths on heart valves based on ECG
Therapeutic Management: IV antibiotic therapy
Corrective surgery
Bed rest
Sufficient fluid intake
Nursing Intervention: - stress importance of bed rest
- allow patient to express his concerns
- obtain Hx of allergies
- administer antibiotics on time
Health Teaching: - disorder, Dx, treatment
- compliance of medication therapy
- watch for early s/s of reoccurrence of disease and
notify physician immediately
- prophylaxis before invasive procedures
HYPERTENSION
Definition: A systolic pressure reading above the 95th percentile for a
given age.
2 types:
Essential - no known cause
Secondary - results from renal disease or
another identifiable cause
Risk Factor: - Family History
- Stress
- Obesity
- High Sodium, High saturated Fat Diet
- use of tobacco
- use of hormonal contraceptives
- excess alcohol intake
- sedentary lifestyle
- aging
Signs and Symptoms: - headache in occipital region
- dizziness
- fatigue
- confusion
- palpitations
- chest pain
- hematuria
- dyspnea
- epistaxis
- blurred vision
Assessment Findings: - elevated BP on at least two (2) consecutive
occasions after initial screening
- peripheral edema
- hemorrhages
- papilledema of the exe
- pulsating abdominal mass
- bruits over abdominal aorta and femoval arteries
Therapeutic Management: - lifestyle modification
- reduction of weight in cases of obesity
- ACE inhibitor
- diuretic
- vasodilator
Nursing Intervention: - give prescribed drugs
- encourage dietary changes as appropriate
- help; identify risk factors and modify lifestyle as
appropriate
- monitor v/s especially BP
Health Teaching: - disorder, Dx, treatment
- antihypertensive therapy compliance
- examining and modifying lifestyle, including diet
- importance of follow up care
WRITTEN OUTPUT ON KAWASAKI
DISEASE, RHEUMATIC HEART DISEASE,
ENDOCARDITIS, AND HYPERTENSION
SUBMITTED BY:
SARINES, JENNYCEL MAE C.
SUBMITTED TO:
MS. DAISY COLLEEN YOUNG-MERCADO
You might also like
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDocument37 pagesRheumatic Heart Diseasesalman hNo ratings yet
- 0002 Infectious Diseases of The HeartDocument35 pages0002 Infectious Diseases of The Heartmblanco.dchNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Fever and Heart DiseaseDocument37 pagesRheumatic Fever and Heart Diseasejiregna eticha dakoNo ratings yet
- Week 5 LectureDocument16 pagesWeek 5 LectureMorgan LongworthNo ratings yet
- WK1 - Inflammatory Heart Failure Infectious DiseaseDocument4 pagesWK1 - Inflammatory Heart Failure Infectious DiseaseJhaji Mei Margarete CasiNo ratings yet
- Dengue: History Physical Examination InvestigationDocument4 pagesDengue: History Physical Examination InvestigationNik Hanisah Zuraidi AfandiNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Assessment FormatDocument20 pagesCardiac Assessment FormatSalman Habeeb75% (4)
- Pediatric Cardiac DisordersDocument5 pagesPediatric Cardiac DisordersJerome DazNo ratings yet
- Cardiopericarditis BienDocument8 pagesCardiopericarditis Bienlanilyn bienNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic - Fever - Internal Medicine 15 MarchDocument35 pagesRheumatic - Fever - Internal Medicine 15 MarchLedia EssamNo ratings yet
- CD CompleteDocument19 pagesCD CompletebhibhiNo ratings yet
- Anak 3.1 Infective Endocarditis DRTLTDocument21 pagesAnak 3.1 Infective Endocarditis DRTLTAnastasia PinkyNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Cardiovascular Disorders GuideDocument4 pagesPediatric Cardiovascular Disorders GuideWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- C. Lymphatic DisordersDocument18 pagesC. Lymphatic DisordersaileenmarjlimNo ratings yet
- Infective Endocarditis: Uaepong Limpapanasit July 5, 2010Document45 pagesInfective Endocarditis: Uaepong Limpapanasit July 5, 2010Rapid MedicineNo ratings yet
- Sepsis 23-24 (1)Document45 pagesSepsis 23-24 (1)mcmillanb2No ratings yet
- Lecture 9Document10 pagesLecture 9Grafu Andreea AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Management of Dengue FeverDocument31 pagesManagement of Dengue FeverDaniel RajNo ratings yet
- Cardio - InfectiveDocument13 pagesCardio - InfectiveHgiel100% (1)
- Cardiology-2 IEDocument7 pagesCardiology-2 IEMahmoud RamadanNo ratings yet
- Problems in Systemic Circulation Diagnostic ProceduresDocument4 pagesProblems in Systemic Circulation Diagnostic ProceduresryubomiNo ratings yet
- Dengue FeverDocument5 pagesDengue FeverRayana UbasNo ratings yet
- Microbiology of CVSDocument44 pagesMicrobiology of CVSsultan khabeebNo ratings yet
- Infective Endocarditis.... MshembaDocument39 pagesInfective Endocarditis.... MshembaTimothy Casmiry MshembaNo ratings yet
- R. P. Vashist, Consultant Public HealthDocument26 pagesR. P. Vashist, Consultant Public Healthmaharshi mNo ratings yet
- BSC Nursing: Medical Surgical Nursing Unit V - Disorders of The Cardio Vascular SystemDocument34 pagesBSC Nursing: Medical Surgical Nursing Unit V - Disorders of The Cardio Vascular SystemPoova Ragavan100% (1)
- Seminar On Rhuematic Heart DiseaseDocument16 pagesSeminar On Rhuematic Heart Diseasenaga maniNo ratings yet
- Cardio DiseasesDocument77 pagesCardio Diseasesrea bentayaoNo ratings yet
- Acute Rheumatic Fever and Valvular Heart DiseaseDocument8 pagesAcute Rheumatic Fever and Valvular Heart DiseaseHASNIZZAM BIN AHMAD AMIN -No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Disorders in Children - StudentDocument53 pagesCardiovascular Disorders in Children - StudentKeanu Win CatipayNo ratings yet
- Acute Chest PainDocument45 pagesAcute Chest PainJonathan DavidNo ratings yet
- Test 37 Qid: 2223: Medicine - Renal, Urinary Systems & ElectrolytesDocument7 pagesTest 37 Qid: 2223: Medicine - Renal, Urinary Systems & Electrolyteskabal321No ratings yet
- Meq PJPDocument19 pagesMeq PJPAtiqah ShahNo ratings yet
- Test 33: Surgery - Rheumatology/Orthopedics & SportsDocument8 pagesTest 33: Surgery - Rheumatology/Orthopedics & Sportskabal321No ratings yet
- VS SYNDROME: AN OVERVIEW OF VASCULITIS CONDITIONSDocument45 pagesVS SYNDROME: AN OVERVIEW OF VASCULITIS CONDITIONSDavid ChristianNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic FeverDocument39 pagesRheumatic FeverDharaneedhar AdepuNo ratings yet
- PEDIA - Acquired Heart DiseaseDocument5 pagesPEDIA - Acquired Heart DiseaseStephen Pilar PortilloNo ratings yet
- (Nelson Hour) Acquired Heart DiseasesDocument26 pages(Nelson Hour) Acquired Heart DiseasesJustin Ng SincoNo ratings yet
- Pericardial DiseaseDocument59 pagesPericardial DiseaseGunawan Yoga100% (1)
- Infection - Dr. Allam 2021Document16 pagesInfection - Dr. Allam 2021MohammedNo ratings yet
- New-Infective EndocarditisDocument30 pagesNew-Infective Endocarditisزياد سعيدNo ratings yet
- Systemic Diseases: Learning ObjectivesDocument29 pagesSystemic Diseases: Learning ObjectivesYuusuf MubarikNo ratings yet
- Lecture Infective Endocarditis (2)Document37 pagesLecture Infective Endocarditis (2)Johnson OlawaleNo ratings yet
- Hta - Angor - AtheromeDocument14 pagesHta - Angor - AtheromeAsma LOTFINo ratings yet
- Lecture 01 Hemorrh-Diat KaplanDocument53 pagesLecture 01 Hemorrh-Diat KaplanАбдул Насер МохаммадізмаелNo ratings yet
- Acquired Cardiac Disorders ExplainedDocument40 pagesAcquired Cardiac Disorders ExplainedRajaNo ratings yet
- Dengue Management in Primary CareDocument61 pagesDengue Management in Primary CareDaniel RajNo ratings yet
- 2 - RH Fev, Inf EndoDocument37 pages2 - RH Fev, Inf EndoLobna ElkilanyNo ratings yet
- 14.1. Chest Pain-朱悫Document108 pages14.1. Chest Pain-朱悫mirabel IvanaliNo ratings yet
- Quiz LetDocument45 pagesQuiz LetA FishNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic FeverDocument19 pagesRheumatic FeverKanwal SafeerNo ratings yet
- D.D. in PediatricsDocument16 pagesD.D. in PediatricsOm El ShohadaaNo ratings yet
- 07 The Valvular PatientDocument83 pages07 The Valvular PatientDanielaNo ratings yet
- AV Block Types, Causes, EKG Findings & TreatmentDocument59 pagesAV Block Types, Causes, EKG Findings & Treatmentmmmmz100% (1)
- CARDIOVASCULAR INFECTION GUIDEDocument32 pagesCARDIOVASCULAR INFECTION GUIDERaisa Louise Gamiao TattaoNo ratings yet
- Infectiveendocarditis 180301061044Document27 pagesInfectiveendocarditis 180301061044jiregna eticha dakoNo ratings yet
- CARDIO - Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDocument3 pagesCARDIO - Rheumatic Heart DiseaseMoon KillerNo ratings yet
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtFrom EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- JITPDocument3 pagesJITPjenn212No ratings yet
- A Failed Search For The Answers To Questions About One's Self (And Life, of Course)Document4 pagesA Failed Search For The Answers To Questions About One's Self (And Life, of Course)jenn212No ratings yet
- Appendectomy: Emergency Surgery to Remove AppendixDocument3 pagesAppendectomy: Emergency Surgery to Remove Appendixjenn212No ratings yet
- Isolation TechniqueDocument19 pagesIsolation Techniquejenn21283% (6)
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Respiratory Infection DepressionDocument6 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Respiratory Infection Depressionjenn212No ratings yet
- The Generic Pharmacy (Powerpoint)Document7 pagesThe Generic Pharmacy (Powerpoint)Ronelyn BritoNo ratings yet
- Abdominal UltrasoundDocument6 pagesAbdominal Ultrasounds0800841739100% (1)
- Local Anesthetic Systemic Toxicity AlgorithmDocument1 pageLocal Anesthetic Systemic Toxicity AlgorithmSydney JenningsNo ratings yet
- Mandibular Molar Protraction With Temporary Anchorage DevicesDocument5 pagesMandibular Molar Protraction With Temporary Anchorage Devicescarlosasd15No ratings yet
- Poster ROICAM 2018Document1 pagePoster ROICAM 2018ibrahimNo ratings yet
- 7 Day Free Guide PDFDocument14 pages7 Day Free Guide PDFGuille RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Resume 101: Write A Resume That Gets You NoticedDocument16 pagesResume 101: Write A Resume That Gets You Noticedgqu3No ratings yet
- ICU HandoverDocument2 pagesICU HandoverMark 'Mark Douglas' DouglasNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Nursing (1) 2007Document14 pagesPerioperative Nursing (1) 2007Lorraine BuelvaNo ratings yet
- How To Make Your Own Starecta (Gelb Splint)Document18 pagesHow To Make Your Own Starecta (Gelb Splint)Martín T.No ratings yet
- Eucalyptus The Genus Eucalyptus PDFDocument433 pagesEucalyptus The Genus Eucalyptus PDFPeter Wilhelmsen100% (5)
- Chapter 6 DiscussionDocument3 pagesChapter 6 DiscussionyughaNo ratings yet
- Kumara Reiki 2013 Attunement NotesDocument17 pagesKumara Reiki 2013 Attunement NotesHaryadi Yadi100% (2)
- Disectie AnatomieDocument908 pagesDisectie AnatomieMircea SimionNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Approach To Discounting Patient ShareDocument11 pagesDynamic Approach To Discounting Patient SharemaleticjNo ratings yet
- 4 Levels of Perio DZDocument2 pages4 Levels of Perio DZKIH 20162017No ratings yet
- Care for Neonatal PatientsDocument5 pagesCare for Neonatal PatientsJonette Castro HermidaNo ratings yet
- Lab Test Results 7 2015Document3 pagesLab Test Results 7 2015Antzee Dancee0% (1)
- Coating of Pellets With Micronized Ethylcellulose Particles by A Dry Powder Coating TechniqueDocument11 pagesCoating of Pellets With Micronized Ethylcellulose Particles by A Dry Powder Coating TechniqueFaizNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of RabiesDocument5 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of RabiesDavid CalaloNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Imaging: A Practical Approach: Adam Greenspan 6th EditionDocument11 pagesOrthopedic Imaging: A Practical Approach: Adam Greenspan 6th EditionNovien WilindaNo ratings yet
- Influence of Anthropometric Parameters On Aerobic Capacity Among DancersDocument7 pagesInfluence of Anthropometric Parameters On Aerobic Capacity Among DancersAnonymous izrFWiQNo ratings yet
- Ozone Therapy in DentistryDocument16 pagesOzone Therapy in Dentistryshreya das100% (1)
- PCI-DPharm Syllabus Guidelines 2020Document30 pagesPCI-DPharm Syllabus Guidelines 2020Chander PrakashNo ratings yet
- Broadline Epar Public Assessment Report enDocument25 pagesBroadline Epar Public Assessment Report enPablo OrricoNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Ultrasil® VN 3 (Insilco)Document6 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Ultrasil® VN 3 (Insilco)Bharat ChatrathNo ratings yet
- Vaginitis: Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument9 pagesVaginitis: Diagnosis and TreatmentAbigail MargarethaNo ratings yet
- The Ethics of Medical Marijuana Government Restrictions vs. Medical Necessity - An UpdateDocument12 pagesThe Ethics of Medical Marijuana Government Restrictions vs. Medical Necessity - An UpdateAle PicadoNo ratings yet
- Life Calling Map Fillable FormDocument2 pagesLife Calling Map Fillable Formapi-300853489No ratings yet
- Student study on family health and pregnancy in rural ZimbabweDocument3 pagesStudent study on family health and pregnancy in rural ZimbabweTubocurareNo ratings yet