Professional Documents
Culture Documents
45 PDF
Uploaded by
Camelia Moise0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageOriginal Title
45.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 page45 PDF
Uploaded by
Camelia MoiseCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Basic Chemistry of Polystyrene
45
necessary to add a chain transfer agent. Generally aliphatic
mercaptans are used for this purpose in the manufacture of
synthetic rubber from styrene and butadiene.
When polymerization is complete the polymer particles
have a diameter of 0.02 to 0.2 microns. The beads in a sus-
pension polymerization system have a diameter of 50 to 1000
microns; thus the particle and bead volumes differ consider-
ably. There may be more than one polymer radical in each
droplet or bead in suspension polymerization; there is usually
only one in each emulsion particle.
Since polymerization in each emulsion particle is inde-
pendent of that in other particles the over-all rate of poly-
merization will depend on the number of particles present.
This in turn depends on the quantity of soap used. As the
temperature is increased in a particular system the rate of
chain propagation increases and, consequently, that of poly-
merization. An increase in initiator concentration frequently
does not cause an increase in the rate of polymerization since
the number of particles remains constant and only half are
active at any time. There have been instances in which in-
creased initiator concentration has increased the rate of poly-
merization. It is believed that either the number of particles
was also increased or the free radical concentration was so
high that there was more than one free radical per particle.
Generated for camelia_moise@yahoo.com on 2013-04-10 16:37 GMT / http://hdl.handle.net/2027/mdp.39015016511761
Molecular weight is decreased as the rate of free radical
formation is increased (either by an increase in temperature
or initiator concentration) since free radicals enter the par-
ticles more often and cause more frequent interruptions of
chain growth. Thus the frequency of alternation between ac-
tivity and inactivity in each particle is increased.
In emulsion polymerization it is possible to obtain a much
higSerjiter7)FpdTy^ the bulk and sus-
pension processes which produce polymers having the same
moiecula^weight. In suspension and in bulk polymerization
Public Domain, Google-digitized / http://www.hathitrust.org/access_use#pd-google
You might also like
- DATA Space ReplaimDocument3 pagesDATA Space ReplaimCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 44 PDFDocument1 page44 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 43 PDFDocument1 page43 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 55 PDFDocument1 page55 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 53 PDFDocument1 page53 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 40 PDFDocument1 page40 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 41 PDFDocument1 page41 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 51 PDFDocument1 page51 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 42 PDFDocument1 page42 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 46 PDFDocument1 page46 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 54 PDFDocument1 page54 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 52 PDFDocument1 page52 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 60 PDFDocument1 page60 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 49 PDFDocument1 page49 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 50 PDFDocument1 page50 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 62 PDFDocument1 page62 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 48 PDFDocument1 page48 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 57 PDFDocument1 page57 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- Manufacture of Polystyrene Process DetailsDocument1 pageManufacture of Polystyrene Process DetailsCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 56 PDFDocument1 page56 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 59 PDFDocument1 page59 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 47 PDFDocument1 page47 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 58 PDFDocument1 page58 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 64 PDFDocument1 page64 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- Polystyrene Production via Suspension PolymerizationDocument1 pagePolystyrene Production via Suspension PolymerizationCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 102 PDFDocument1 page102 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 65 PDFDocument1 page65 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 99 PDFDocument1 page99 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- 104 PDFDocument1 page104 PDFCamelia MoiseNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Journal Publication Details of VIT For November 2021Document41 pagesJournal Publication Details of VIT For November 2021Selvaraji MuthuNo ratings yet
- SPE 121182 Selective Water Shutoff in Gas Well Turns A Liability Into An Asset: A Successful Case History From East Kalimantan, IndonesiaDocument7 pagesSPE 121182 Selective Water Shutoff in Gas Well Turns A Liability Into An Asset: A Successful Case History From East Kalimantan, Indonesiahade wantoNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument11 pagesNCERT Solutions For Chemical Reactions and EquationsSuman LataNo ratings yet
- Solution Stoichiometry PDFDocument6 pagesSolution Stoichiometry PDFJulio100% (1)
- Donaldson DC 20-450 ABDocument36 pagesDonaldson DC 20-450 ABSerwis SprężarekNo ratings yet
- Kerosene: Kerosene (Kerosine, Paraffin Oil Approximately Boiling Range: 205 ToDocument17 pagesKerosene: Kerosene (Kerosine, Paraffin Oil Approximately Boiling Range: 205 Toapi-3774614100% (1)
- Chapter 1 5Document114 pagesChapter 1 5Dosirt VisdaNo ratings yet
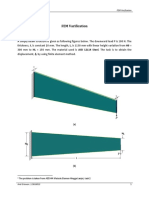
- FEM Varification: ProblemDocument11 pagesFEM Varification: Problemandi0610bNo ratings yet
- Komatsu Coolant High Performance Long Life Coolant With Low Impact On Global EnvironmentDocument7 pagesKomatsu Coolant High Performance Long Life Coolant With Low Impact On Global EnvironmentDian Wahyu AlfatahNo ratings yet
- Properties of Iron AlloysDocument2 pagesProperties of Iron AlloysAmber ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Office of The Municipal Engineer: Municipality of Governor GenerosoDocument2 pagesOffice of The Municipal Engineer: Municipality of Governor GenerosoMEO GGDONo ratings yet
- Gating ManualDocument84 pagesGating Manualmr.nguyenk100% (4)
- The First-Principles Phase Diagram of Monolayer Nanoconfined WaterDocument33 pagesThe First-Principles Phase Diagram of Monolayer Nanoconfined WaterNiNo ratings yet
- Melt Rheology and Its Role in Plastics Processing by Dealy PDFDocument684 pagesMelt Rheology and Its Role in Plastics Processing by Dealy PDFBakshi Ashok Kumar100% (4)
- Iso TS 04949-2016Document15 pagesIso TS 04949-2016Laukik FegdeNo ratings yet
- BoilerDocument3 pagesBoilerTerry YongNo ratings yet
- " Work Experience in Ishan Equipments Pvt. LTD.": Internship Presentation OnDocument20 pages" Work Experience in Ishan Equipments Pvt. LTD.": Internship Presentation OnrajivNo ratings yet
- Frontiers e ManufacturingDocument9 pagesFrontiers e ManufacturingmartinsandovalandresNo ratings yet
- GraphiteDocument13 pagesGraphiteFrederic WustNo ratings yet
- BLOCK DATA AlloycraftDocument104 pagesBLOCK DATA Alloycraftv2vcoderNo ratings yet
- A500A500M-13 Standard Specification For Cold-Formed Welded and Seamless Carbon Steel Structural Tubing in Rounds and ShapesDocument9 pagesA500A500M-13 Standard Specification For Cold-Formed Welded and Seamless Carbon Steel Structural Tubing in Rounds and ShapesChuthaNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument15 pagesRedox ReactionsAdarsh YadavNo ratings yet
- Food Processing Ncii W L: Orkshop AyoutDocument9 pagesFood Processing Ncii W L: Orkshop AyoutAbraham BojosNo ratings yet
- Technical Data SheetDocument3 pagesTechnical Data SheetkmasanNo ratings yet
- Comparative study of concrete mix design by adding various types of admixturesDocument6 pagesComparative study of concrete mix design by adding various types of admixturesSagarNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Process-Ii: Lab Manual 01Document8 pagesManufacturing Process-Ii: Lab Manual 01Abdul Rehman FaisalNo ratings yet
- VTU SyllabusDocument164 pagesVTU SyllabusChethan KSNo ratings yet
- QCP Barangonbong RevisedDocument44 pagesQCP Barangonbong Revisedruzsi07No ratings yet
- Experiment 7: Determination of AshDocument7 pagesExperiment 7: Determination of AshhasifahNo ratings yet