Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Stages of heart failure prevention and treatment
Uploaded by
diany astutiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Stages of heart failure prevention and treatment
Uploaded by
diany astutiCopyright:
Available Formats
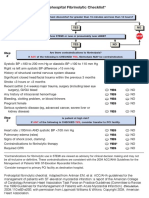
AT RISK FOR HEART FAILURE HEART FAILURE
STAGE A STAGE B STAGE C STAGE D
At high risk for HF but without Structural heart disease but Structural heart disease with Refractory HF
structural heart disease or without signs or symptoms prior or current symptoms
symptoms of HF of HF of HF
e.g., Patients with:
e.g., Patients with: e.g., Patients with: • Marked HF symptoms at
e.g., Patients with: Refractory rest
• HTN • Previous MI
• Atherosclerotic disease • LV remodeling including LV • Known structural heart symptoms • Recurrent hospitalizations
• DM Hand low EF disease and of HF at rest, despite GDMT
• Obesity • Asymptomatic valvular • HF signs and symptoms despite GDMT
• Metabolic syndrome disease
OR
HFpEF HFr EF THERAPY
Patients Development
Goals
• Using cardiotoxins of symptoms
• With family history of of HF • Control symptoms
cardiomyopathy • Improve HRQOL
THERAPY THERAPY
• Reduce hospital
Goals Goals readmissions
THERAPY
• Control symptoms • Control symptoms • Establish patient’s end-of-
Goals • Improve HRQOL • Patient education life goals
Structural • Prevent HF symptoms • Prevent hospitalization • Prevent hospitalization
heart disease • Prevent further cardiac • Prevent mortality • Prevent mortality Options
remodeling • Advanced care measures
Strategies Drugs for routine use • Heart transplant
THERAPY Drugs • Identification of comorbidities • Chronic inotropes
• Diuretics for fluid retention
Goals • ACEI or ARB as appropriate • ACEI or ARB • Temporary or permanent
• Heart healthy lifestyle • Beta blockers as Treatment • Beta blockers MCS
• Prevent vascular, coronary appropriate • Diuresis to relieve symptoms • Aldosterone antagonists • Experimental surgery or
disease of congestion drugs
• Prevent LV structural In selected patients • Follow guideline driven • Palliative care and hospice
Drugs for use in selected
abnormalities • ICD indications for comorbidities, • ICD deactivation
patients
• Revascularization or e.g., HTN, AF, CAD, DM
• Hydralazine/isosorbide dinitrate
Drugs valvular surgery as • Revascularization or valvular
• ACEI and ARB
• ACEI or ARB in appropriate appropriate surgery as appropriate
• Digitalis
patients for vascular
disease or DM Inselected patients
• Statins as appropriate Stages in the development of HF and recommended therapy by stage. ACEI indicates angiotensin-converting
enzyme inhibitor; AF, atrial fibrillation; ARB, angiotensin-receptor blocker; CAD, coronary artery disease; • CRT
CRT, cardiac resynchronization therapy; DM, diabetes mellitus; EF, ejection fraction; GDMT, guideline-
directed medical therapy; HF, heart failure; HFpEF, heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; HFrEF,
• ICD
heart failure with reduced ejection fraction; HRQOL, health-related quality of life; HTN, hypertension; ICD, • Revascularization or valvular
implantable cardioverter-defibrillator; LV, left ventricular; LVH, left ventricular hypertrophy; MCS, mechanical
circulatory support; and MI, myocardial infarction. Adapted from Hunt et al.3
surgery as appropriate
Yancy CW et al., ACCF/AHA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure, Circulation, 10/15/13.
You might also like
- Best Practice ProtocolsDocument46 pagesBest Practice ProtocolsRaigheil LayNo ratings yet
- Stroke: AHA/ASA Guidelines For The Early Management of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke (2019)Document14 pagesStroke: AHA/ASA Guidelines For The Early Management of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke (2019)Natalia OrtizNo ratings yet
- ACC/AHA STEMI GuidelinesDocument94 pagesACC/AHA STEMI GuidelinesDika DekokNo ratings yet
- IV PO Conversion CAPDocument3 pagesIV PO Conversion CAPdamondouglasNo ratings yet
- STEMI Guidline 23.11.2022Document60 pagesSTEMI Guidline 23.11.2022NATARAJAN RAJENDRANNo ratings yet
- Challenges in Hypertension ManagementDocument86 pagesChallenges in Hypertension ManagementAdel SALLAMNo ratings yet
- Blood Flow Q: The Transmembrane Pressure (TMP) GradientDocument1 pageBlood Flow Q: The Transmembrane Pressure (TMP) GradientNicholas HelmstetterNo ratings yet
- Acute Stroke ProtocolDocument3 pagesAcute Stroke ProtocolKarissaNo ratings yet
- VTE Risk AssessmentDocument2 pagesVTE Risk AssessmentpriyopanjiNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhytmics Treatable Antiarrhytmics: Atrial Fibrillation, Atrial Flutter, Vtach and PSVT Drugs MOA Indication S/E NotesDocument1 pageAntiarrhytmics Treatable Antiarrhytmics: Atrial Fibrillation, Atrial Flutter, Vtach and PSVT Drugs MOA Indication S/E Notesmonica leeNo ratings yet
- ADH & Potassium Sparing Diuretics BDSDocument18 pagesADH & Potassium Sparing Diuretics BDSDr.U.P.Rathnakar.MD.DIH.PGDHMNo ratings yet
- Role of New 3rd Generation of Beta-Blocker in The ... Dr. Elfiani, SPPD., FINASIMDocument55 pagesRole of New 3rd Generation of Beta-Blocker in The ... Dr. Elfiani, SPPD., FINASIMZikri HakimNo ratings yet
- IvabradineDocument33 pagesIvabradinepashaNo ratings yet
- Acs Nstemi PathwayDocument3 pagesAcs Nstemi PathwayAliey's SKeplek NgeNersNo ratings yet
- Acute Decompensated Heart FailureDocument31 pagesAcute Decompensated Heart Failure568563No ratings yet
- Adrenal Insufficiency and Addison's DiseaseDocument8 pagesAdrenal Insufficiency and Addison's DiseaseyancefinceNo ratings yet
- Radio PharmaceuticalsDocument48 pagesRadio PharmaceuticalsKris Joy EbonNo ratings yet
- CHFDocument45 pagesCHFAry 01No ratings yet
- Maste Med SheetDocument78 pagesMaste Med SheetBarbie Wiggers100% (1)
- Guide To Diabetes MedicationsDocument2 pagesGuide To Diabetes MedicationsJianhua ShiNo ratings yet
- Labs 1.19 ABG AnalysisDocument1 pageLabs 1.19 ABG AnalysisMonica GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Drugs in Cardiac EnmergenciesDocument94 pagesDrugs in Cardiac EnmergenciesVijayan VelayudhanNo ratings yet
- Anxiolytic and Hypnotic AgentsDocument50 pagesAnxiolytic and Hypnotic AgentsMoxie Macado100% (1)
- NHS DIABETESUNDERGOING Surgery Adults Full PDFDocument72 pagesNHS DIABETESUNDERGOING Surgery Adults Full PDFekyNo ratings yet
- The New Rapid ResponderDocument3 pagesThe New Rapid RespondersarahNo ratings yet
- ADULT CRITICAL CARE SEDATION GUIDELINESDocument12 pagesADULT CRITICAL CARE SEDATION GUIDELINESBeatriz Maria Espinosa HernandezNo ratings yet
- Outcomes of Ebp Process 2017Document3 pagesOutcomes of Ebp Process 2017api-272725467100% (1)
- Are You at Risk for DVT? Take This Assessment to Find OutDocument2 pagesAre You at Risk for DVT? Take This Assessment to Find OutAnonymous PjQxbsJQaNo ratings yet
- Profil Farmakikinetik Pantoprazole InjeksiDocument17 pagesProfil Farmakikinetik Pantoprazole InjeksitikaNo ratings yet
- 24 CFP Clinical Guideline 10 - Chemical RestraintDocument20 pages24 CFP Clinical Guideline 10 - Chemical RestraintFernando Feliz ChristianNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Hypothermia ChillOutDocument38 pagesTherapeutic Hypothermia ChillOutJason RodmanNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Case StudyDocument44 pagesCardiac Case StudyNatalia Bernard100% (1)
- Vancomycin Protocol RQHRDocument15 pagesVancomycin Protocol RQHRl1o2stNo ratings yet
- Abbreviations ListDocument6 pagesAbbreviations ListolivedaisychainNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINEDocument3 pagesPharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINEMitu Miressa تNo ratings yet
- Adults With Suspected Epiglottitis - Supraglottitis Guidelines For The Management ofDocument2 pagesAdults With Suspected Epiglottitis - Supraglottitis Guidelines For The Management ofAlexandros MegasNo ratings yet
- Chemo Stability Chart - LtoZDocument41 pagesChemo Stability Chart - LtoZOcy EmailNo ratings yet
- Milrinone Can ONLY Be Mixed With NS!: Alpha 1 Beta 1 & Alpha 1Document1 pageMilrinone Can ONLY Be Mixed With NS!: Alpha 1 Beta 1 & Alpha 1njones33No ratings yet
- 1183 - The Global Burden of Heart Failure. - Martin COWIE (London, United Kingdom)Document21 pages1183 - The Global Burden of Heart Failure. - Martin COWIE (London, United Kingdom)Mulyani EdwarNo ratings yet
- Common Drug Stems Cheat Sheet: Drug Stem Drug Class And/or Stem Explanation ExamplesDocument2 pagesCommon Drug Stems Cheat Sheet: Drug Stem Drug Class And/or Stem Explanation ExamplesjthsNo ratings yet
- Medication Adherence Scale PDFDocument13 pagesMedication Adherence Scale PDFRommel G. SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Woman With DysuriaDocument26 pagesWoman With DysuriaAlFi KamaliaNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Drugs OverviewDocument23 pagesCritical Care Drugs OverviewAsri Ernadi100% (1)
- Kathrine O Neal PP PDFDocument92 pagesKathrine O Neal PP PDFrezqNo ratings yet
- JNC 6 Vs 7Document2 pagesJNC 6 Vs 7zhen33No ratings yet
- RX Cheat Sheet Pharmacy CrackDocument1 pageRX Cheat Sheet Pharmacy Crackramesh kumar100% (1)
- Pharm - Chapter - 13 - Central Nervous System StimulantsDocument42 pagesPharm - Chapter - 13 - Central Nervous System StimulantsFeliciaDorghamNo ratings yet
- Cardiac MedicationsDocument8 pagesCardiac Medicationsangeline totaram100% (2)
- 2010 Integrated - Updated Circulation ACLS Prehospital Fibrinolytic Checklist PDFDocument1 page2010 Integrated - Updated Circulation ACLS Prehospital Fibrinolytic Checklist PDFms_lezahNo ratings yet
- RN Case ManagerDocument2 pagesRN Case Managerapi-79243469No ratings yet
- Acute Wheeze Flow-Chart for Children 2-16Document2 pagesAcute Wheeze Flow-Chart for Children 2-16geonMMNo ratings yet
- Clinical Case Aki Presentation EportfolioDocument32 pagesClinical Case Aki Presentation Eportfolioapi-463444835No ratings yet
- Neutropenic Fever Empiric TherapyDocument5 pagesNeutropenic Fever Empiric TherapyRominaPulvermüllerSalvatierraNo ratings yet
- Standard 2.1: The Governing Body Leads The Organisation in Its Commitment To Improving Performance and Ensures The Effective Management of Corporate and Clinical RisksDocument17 pagesStandard 2.1: The Governing Body Leads The Organisation in Its Commitment To Improving Performance and Ensures The Effective Management of Corporate and Clinical RisksIntan PermataNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Regimens in HIVDocument36 pagesTherapeutic Regimens in HIVGail HoadNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument19 pagesOsteoporosisLasa SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Using Consumer Medicine Information (CMI)Document15 pagesUsing Consumer Medicine Information (CMI)Joseph OchoaNo ratings yet
- Standard Precautions Hand Hygiene Gloves GownsDocument4 pagesStandard Precautions Hand Hygiene Gloves GownsAjeesh GopidasanNo ratings yet
- NCP-S/P AppendectomyDocument6 pagesNCP-S/P Appendectomytinatin989100% (7)
- 3500 ObDocument8 pages3500 ObkimgodfreyNo ratings yet
- Parkinson in Adult NICE Guideline 2017Document30 pagesParkinson in Adult NICE Guideline 2017yustikaNo ratings yet
- Kheir 31st Anniversary Dinner Sponsorship Packet 20171012Document5 pagesKheir 31st Anniversary Dinner Sponsorship Packet 20171012Anonymous wnCXWd3No ratings yet
- Newport, D.J. and Nemeroff, C.B. Neurobiology of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Cognitive Neuroscience JAARTALDocument8 pagesNewport, D.J. and Nemeroff, C.B. Neurobiology of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Cognitive Neuroscience JAARTALg10564433No ratings yet
- Diseases of The Immune System: OBC 231 General PathologyDocument91 pagesDiseases of The Immune System: OBC 231 General PathologyRana MohammadNo ratings yet
- Facts and Definition of EclampsiaDocument5 pagesFacts and Definition of EclampsiaChoi Gong JuNo ratings yet
- Physical Health Assessment PreparationDocument3 pagesPhysical Health Assessment PreparationaliNo ratings yet
- Menieres DiseaseDocument43 pagesMenieres DiseaseChlodette Eizl M. Laurente100% (4)
- Schenke in 2006Document17 pagesSchenke in 2006Rest0No ratings yet
- Courier WedgeDocument19 pagesCourier WedgesurfnewmediaNo ratings yet
- Tech MagDocument44 pagesTech Magcarambola88No ratings yet
- Ma 11sem. TMP Perio2Document2 pagesMa 11sem. TMP Perio2Karen RosalesNo ratings yet
- MCQ Pink BookDocument7 pagesMCQ Pink BookpaediatricaNo ratings yet
- Recavery After Anasthesia PDFDocument3 pagesRecavery After Anasthesia PDFYudionoNo ratings yet
- Literatur Pasien SafetyDocument11 pagesLiteratur Pasien SafetyRisky SetyoNo ratings yet
- 2017 Bethesda System of Reporting Thyroid CytopathologyDocument6 pages2017 Bethesda System of Reporting Thyroid CytopathologyLuisNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Important QuestionsDocument9 pagesOphthalmology Important QuestionsGhaidaa SadeqNo ratings yet
- GoitreDocument6 pagesGoitreJohn Vladimir A. BulagsayNo ratings yet
- Coarctation of The Aorta 1Document3 pagesCoarctation of The Aorta 1Zig OngNo ratings yet
- The Radiology Assistant: Ankle Fracture - Weber and Lauge-Hansen ClassificationDocument16 pagesThe Radiology Assistant: Ankle Fracture - Weber and Lauge-Hansen ClassificationAnonymous V5xDcrNo ratings yet
- TB and HIVDocument62 pagesTB and HIVNational Press FoundationNo ratings yet
- Yemisi Chapter ThreeDocument10 pagesYemisi Chapter ThreeAbimbola OyarinuNo ratings yet
- Ichthyosis Vulgaris: A Case Report and Review of LiteratureDocument3 pagesIchthyosis Vulgaris: A Case Report and Review of LiteratureJames Czar Fontanilla IlaganNo ratings yet
- Citizens Response and Arguments Against Closing Muhlenberg HospitalDocument15 pagesCitizens Response and Arguments Against Closing Muhlenberg HospitalDeborah Joyce DoweNo ratings yet
- Brain TumorDocument1 pageBrain TumorMortaza AhmadNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Body and Health ProblemDocument13 pagesParts of The Body and Health ProblemSonia Tri AgustinaNo ratings yet
- GLOVINGDocument4 pagesGLOVINGAngelene CalivaNo ratings yet
- 256 CircumcisionDocument5 pages256 CircumcisionMD Luthfy LubisNo ratings yet