Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PLATE TECTONICS (Continued) Divergent Boundaries More Evidence For Plate Tectonics
Uploaded by
Jasmine Bianca Castillo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageDivergent boundaries occur where tectonic plates pull apart, like at mid-ocean ridges. There are three types of spreading centers: oceanic rises with fast or slow spreading, and ultra-slow spreading with deep valleys and scattered volcanoes. Transform boundaries are where plates slide past each other, like the San Andreas Fault. More evidence for plate tectonics includes hotspots that cause volcanism as plates move over thermal plumes, and the global positioning system allows monitoring of plate movement. Convection currents and the gravitational pull and push of cooling oceanic crust drive the motions of tectonic plates.
Original Description:
sdasda
Original Title
sdasd
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDivergent boundaries occur where tectonic plates pull apart, like at mid-ocean ridges. There are three types of spreading centers: oceanic rises with fast or slow spreading, and ultra-slow spreading with deep valleys and scattered volcanoes. Transform boundaries are where plates slide past each other, like the San Andreas Fault. More evidence for plate tectonics includes hotspots that cause volcanism as plates move over thermal plumes, and the global positioning system allows monitoring of plate movement. Convection currents and the gravitational pull and push of cooling oceanic crust drive the motions of tectonic plates.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pagePLATE TECTONICS (Continued) Divergent Boundaries More Evidence For Plate Tectonics
Uploaded by
Jasmine Bianca CastilloDivergent boundaries occur where tectonic plates pull apart, like at mid-ocean ridges. There are three types of spreading centers: oceanic rises with fast or slow spreading, and ultra-slow spreading with deep valleys and scattered volcanoes. Transform boundaries are where plates slide past each other, like the San Andreas Fault. More evidence for plate tectonics includes hotspots that cause volcanism as plates move over thermal plumes, and the global positioning system allows monitoring of plate movement. Convection currents and the gravitational pull and push of cooling oceanic crust drive the motions of tectonic plates.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
PLATE TECTONICS (Continued)
Divergent Boundaries MORE EVIDENCE FOR PLATE
TECTONICS
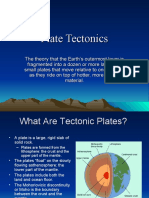
• Places where plates are being
pulled away from each other 1. Hotspots
• Example: East African Rift, Mid- • Relatively small, long-
Atlantic Ridge lasting, and exceptionally
hot regions which exist
Types of Spreading Centers: below the plates
• Oceanic rise • Thermal plumes sustain
• Fast spreading volcanism
• Gentle slopes • Traces the direction of
• Ex. East Pacific plate motion
rise, 16 cm per year • e.g. Hawaiian Emperor
• Oceanic ridge Seamount Chain
• Slow spreading
• Steep slopes 2. Global Positioning System
• Ex. Mid-Atlantic • Allows us to monitor
ridge, 2.5 cm per plate movement
year
• Ultra-slow
• Deep rift valley
• Widely scattered
volcanoes
• Ex. Southwest
Indian and Arctic
oceans
Transform Boundaries
• Places where plates slide past
each other
• Shallow but strong earthquakes
• Example: San Andreas Fault
DRIVING MECHANISMS
1. Convection Currents
a. Two-layer convection –
separated at depth of
660 kilometers
b. Whole-mantle convection
– entire 2900-km mantle
2. Slab Pull and Ridge Push –
gravitational sliding of dense,
cooling mafic rocks.
You might also like
- Junior Cycle Geography Revision NotesDocument55 pagesJunior Cycle Geography Revision NotesГлеб КиктенкоNo ratings yet
- How the Mountains Grew: A New Geological History of North AmericaFrom EverandHow the Mountains Grew: A New Geological History of North AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics and The Ocean FloorDocument34 pagesChapter 2: Plate Tectonics and The Ocean FloorCarol GirottoNo ratings yet
- Lecture #6 Rift BasinDocument29 pagesLecture #6 Rift BasinMeerra100% (1)
- Plate TectonicsDocument38 pagesPlate TectonicsKhanett DagohoyNo ratings yet
- What Is Tectonic PlatesDocument4 pagesWhat Is Tectonic PlatesElgen EniloNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Boundaries and EvidenceDocument34 pagesPlate Tectonics Boundaries and EvidenceEzzadin BabanNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument7 pagesPlate TectonicsMarycorNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic Theory Is Powerful. - It Provides A Unified Mechanism ExplainingDocument43 pagesPlate Tectonic Theory Is Powerful. - It Provides A Unified Mechanism ExplainingParas PatelNo ratings yet
- Geog!!Document11 pagesGeog!!diandra.yanuar2017No ratings yet
- Week 3 Plate TectonicsDocument74 pagesWeek 3 Plate TectonicsmuhammadNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument84 pagesPlate Tectonicsg.hi45.jklNo ratings yet
- Sea Floor Spreading ExplainedDocument15 pagesSea Floor Spreading ExplainedRolando DumlaoNo ratings yet
- Normal Faults and Extensional TectonicsDocument40 pagesNormal Faults and Extensional TectonicsAzman AzmanNo ratings yet
- Lec-04 - Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift (Part-3)Document46 pagesLec-04 - Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift (Part-3)BIPL REPORTNo ratings yet
- Tectonofisik 8Document78 pagesTectonofisik 8Harlen MuntheNo ratings yet
- Mkp1213 Chapter 2 NoteDocument38 pagesMkp1213 Chapter 2 NoteHaziq YussofNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument9 pagesScience ReviewerJasmine CatanaNo ratings yet
- Earth's Materials and Processes: A Guide to Endogenic ForcesDocument57 pagesEarth's Materials and Processes: A Guide to Endogenic ForcesSheyah Villanueva100% (1)
- Basin Analysis PDFDocument31 pagesBasin Analysis PDFlory30100% (1)
- Plate BoundariesDocument48 pagesPlate BoundariesBhea Marie Songcuya100% (1)
- Mkp1213 Chapter 2 NoteDocument38 pagesMkp1213 Chapter 2 NoteHaziq YussofNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Notes Pt-IIDocument9 pagesPlate Tectonics Notes Pt-II19rikenNo ratings yet
- JC Geography Revision BookletDocument55 pagesJC Geography Revision Booklet13593678No ratings yet
- Sedimentary BasinDocument34 pagesSedimentary BasinDivya Dsk100% (2)
- Plate Tectonics: Physical Geology 13, Chapter 19Document22 pagesPlate Tectonics: Physical Geology 13, Chapter 19Pravin KhartadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Marine ProvincesDocument30 pagesChapter 3: Marine ProvincesCarol GirottoNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Power PointDocument22 pagesPlate Tectonics Power PointGuia GoopioNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes Types Structure and EffectsDocument41 pagesVolcanoes Types Structure and Effectstcshs.antoque.sheinnadayneNo ratings yet
- Tectonic and Structural Geomorphology ExplainedDocument94 pagesTectonic and Structural Geomorphology Explainedreuben kwotaNo ratings yet
- Extensional Tectonics: Jan Kees Blom December 2011Document58 pagesExtensional Tectonics: Jan Kees Blom December 2011Melissa2305No ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument38 pagesPlate TectonicsAlfVera RectoNo ratings yet
- Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide Deposits Part 1: Classification and ModelDocument48 pagesVolcanogenic Massive Sulfide Deposits Part 1: Classification and ModelAgus BudiluhurNo ratings yet
- Sed Basin Lecture3Document62 pagesSed Basin Lecture3janlayaNo ratings yet
- Geotectonic-4Document58 pagesGeotectonic-4Arieq ClasherNo ratings yet
- Plate BoundariesDocument65 pagesPlate Boundariesajbrjsny blpNo ratings yet
- Paleomagnetism and HotspotsDocument22 pagesPaleomagnetism and HotspotsRodel Odper BravoNo ratings yet
- GG101 Lecture11Document31 pagesGG101 Lecture11Jhon Manuel PorcinculaNo ratings yet
- GEO L2 Geomorphology Plate Tect 0.1Document112 pagesGEO L2 Geomorphology Plate Tect 0.1AjeetNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Kenneth Cabahug Karla Clarisse R. CallejaDocument23 pagesPresented By: Kenneth Cabahug Karla Clarisse R. Callejakarla callejaNo ratings yet
- Layers of The Earth Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics TheoryDocument37 pagesLayers of The Earth Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics TheoryJunai AlontoNo ratings yet
- Types of Plate Boundaries Divergent and TransformDocument1 pageTypes of Plate Boundaries Divergent and TransformGeorcelle CarcillarNo ratings yet
- Global PlatecDocument59 pagesGlobal PlatecAlaNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics TheoryDocument43 pagesPlate Tectonics TheoryKirfan 123No ratings yet
- Proseso EndogeniqueDocument57 pagesProseso EndogeniqueRETLAWNo ratings yet
- Tectonics:: Tecton"Document25 pagesTectonics:: Tecton"api-25965024No ratings yet
- Science 10 - Reviewer - Quarter 1Document6 pagesScience 10 - Reviewer - Quarter 1LiraNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic Theory and Plate BoundariesDocument32 pagesPlate Tectonic Theory and Plate BoundariesMarben Apostol MelencionNo ratings yet
- Science 1st PeriodicalDocument2 pagesScience 1st PeriodicalAgatha AquinoNo ratings yet
- 2 SeafloorDocument16 pages2 Seafloorjohnkirbyfamorcan928No ratings yet
- ISNS 4359 Earthquakes and Volcanoes (Aka Shake and Bake) : Lecture 4: Plate TectonicsDocument37 pagesISNS 4359 Earthquakes and Volcanoes (Aka Shake and Bake) : Lecture 4: Plate TectonicsAgeologistNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Endogenic ProcessDocument27 pagesChapter 6 Endogenic ProcessRutchie Quillo TuandoNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics TheoryDocument24 pagesPlate Tectonics TheoryBernice CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Paleomagnetism reveals evidence for seafloor spreading and plate tectonicsDocument28 pagesPaleomagnetism reveals evidence for seafloor spreading and plate tectonicsMartinez 100No ratings yet
- Analysis of Sedimentary BasinsDocument30 pagesAnalysis of Sedimentary BasinsFrancisco RojasNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics: How the Earth's Plates Move and Interact in <40Document7 pagesPlate Tectonics: How the Earth's Plates Move and Interact in <40CypherNo ratings yet
- Plate BoundariesDocument24 pagesPlate Boundariesnanno manoban100% (1)
- Convergent Plate Boundaries NOTESDocument15 pagesConvergent Plate Boundaries NOTESTracy NewKirkNo ratings yet
- The Sutter Buttes of California: A Study of Plio-Pleistocene VolcanismFrom EverandThe Sutter Buttes of California: A Study of Plio-Pleistocene VolcanismNo ratings yet
- Essay 1Document2 pagesEssay 1Jasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Essay 16Document2 pagesEssay 16Jasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Essay 7Document1 pageEssay 7Jasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Essay 6Document1 pageEssay 6Jasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Essay 17Document1 pageEssay 17Jasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- QuadDocument7 pagesQuadJasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- 3 Wdaw 234Document1 page3 Wdaw 234Jasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Essay 15Document2 pagesEssay 15Jasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Essay 18Document1 pageEssay 18Jasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Essay 12Document2 pagesEssay 12Jasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Essay 11Document2 pagesEssay 11Jasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Dasd 24214Document2 pagesDasd 24214Jasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Electric and Magnetic FieldDocument2 pagesElectric and Magnetic FieldJasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Das 214Document1 pageDas 214Jasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- SSD SSD 1.47 Ut+ UDocument1 pageSSD SSD 1.47 Ut+ UJasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Potential Energy DerivativeDocument1 pagePotential Energy DerivativeJasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Elastic PotentialDocument1 pageElastic PotentialJasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Calculator DensityDocument1 pageCalculator DensityJasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Angle B Is in Quadrant 1 (+X and +y Axis) - Therefore, The Angle B Must Lie BetweenDocument1 pageAngle B Is in Quadrant 1 (+X and +y Axis) - Therefore, The Angle B Must Lie BetweenJasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Regression SdasdDocument4 pagesRegression SdasdJasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Heating Curve of Water: Temperature (C°)Document2 pagesHeating Curve of Water: Temperature (C°)Jasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Dispersion EquationDocument3 pagesDispersion EquationJasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Rotational MotionDocument2 pagesRotational MotionJasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document3 pagesBook 1Jasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Frac SubmergedDocument2 pagesFrac SubmergedJasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Rotational MotionDocument2 pagesRotational MotionJasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- HeighttDocument2 pagesHeighttJasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Verifying Coulombs ConstantDocument1 pageVerifying Coulombs ConstantJasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Verifying Coulombs ConstantDocument1 pageVerifying Coulombs ConstantJasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Frac SubmergedDocument2 pagesFrac SubmergedJasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet