Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Groundwater reservoirs contain most water
Uploaded by
Anonymous EvbW4o1U7Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Groundwater reservoirs contain most water
Uploaded by
Anonymous EvbW4o1U7Copyright:
Available Formats
Which of the following reservoirs contains the most water?
atmosphere
biosphere
groundwater***
lakes and rivers
How much of the Earth's water is stored in underground aquifers?
less than 1%***
about 5%
about 10%
about 20%
What is the process by which water enters the small pore spaces between particles in soil or rocks
transpiration
inflitration***
precipation
sublimation
Which of the following terms is a measure of the amount of water vapor in the air as a proportion of the
maximum amount the air could hold at the same temperature?
dew point
sublimation point
evaporation rate
relative humidity***
The percentage of a rock's total volume that is taken up by pore space is called the _______ .
permeability
recharge
aquifer
porosity***
Permeability is __________ .
the ability of a solid to allow fluids to pass through***
the process by which plants release water vapor to the atmosphere
the amount of water vapor in the air relative to the maximum amount of water vapor the air can hold.
the percentage of pore space in the rock
The best groundwater reservoirs have __________ .?
low permeability and low porosity
low permeability and high porosity
high permeability and low porosity
high permeability and high porosity***
The ability of an Earth material to transmit water is a measure of its:
porosity
aquifer characteristics
chemical cement
permeability***
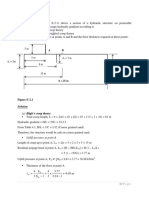
The lowering effect on the water table about the base of the well stem is called a(n):
aquiclude
artesian surface
cone of depression***
speleothem
A local water table positioned above the regional water table is said to be:
stranded
perched***
displaced
depressed
Which of the following statements about the water table is false:
the water table changes when discharge is not balanced by recharge
the water table is generally flat***
the water table is above the land surface in lakes
the water table is depressed near high volume pumping wells
The boundary between the saturated zone and the unsaturated zone is called the______ .
water table***
aquifer
aquiclude
porosity
The infiltration of water into the subsurface is the __________ .
influent
effluent
discharge
recharge***
What is the term for a relatively impermeable geologic unit?
an artesian
an aquiclude***
an aquifer
none of these
Excessive pumping in relation to recharge can cause ________ .
the water table to decline
a cone of depression to form
the well to go dry
all of these***
The most abundant, natural acid is:
nitric
hyrdochloric
carbonic***
citric
Most groundwater withdrawn in the United States is used for ________ .
industry
irrigation***
drinking water
swimming pools
In what types of rock do most caves form?
granite
shale
limestone***
sandstone
Stalactites and stalagmites in caves are composed of ________ .
quartz
alkali feldspar
halite
calcite***
Hard water contains large amounts of __________ .
lead
sodium
calcium***
silicon
Most of the water coming out of continental hot springs is ________ .
meteoric water***
magmatic water
seawater
metamorphic water
Which of the following can contaminate an aquifer?
landfills
agricultural regions
gas stations
all of these***
Water that is good enough to drink is called ________.
potable water***
groundwater
surface water
artesian water
Sinkholes are a possible danger in regions underlain by what type of bedrock?
granite
sandstone
shale
limestone***
In what type of rock do most caves form?
granite
shale
limestone***
sandstone
Excessive pumping in relation to recharge can cause_______
the water table to decline
a cone of depression
the well to go dry
all of these***
Influent streams are _______
more common in arid regions***
more common in humid regions
only found in areas of permafrost
sinkhole
In the diagram above region A is the _______ .
discharge zone
recharge zone
saturated zone
unsaturated zone***
In the diagram above region B is the _______ .
discharge zone
recharge zone
saturated zone***
unsaturated zone
The boundary between the saturated zone and the unsaturated zone is called the _____.
water table***
aquifer
aquilude
porosity
What is the difference between the saturated and the unsaturated zones of ground water?
the saturated zone has a higher porosity than the unsaturated zone
the saturated zone has a lower porosity than the unsaturated zone
the pore spaces in the saturated zone are completely full of water; the pore spaces in the unsaturated
zone are not completely full of water. ***
the pore spaces in the saturated zone are not completely full of water; the pore spaces in the
unsaturated zone are completely full of water
Which of the following materials has the lowest porosity?
shale
gravel
granite***
sandstone
Which of the following rocks has the highest permeability?
an unfractured shale
a cemented sandstones
an uncemented sandstone***
all of these rocks have approximately the same permeability
Groundwater represents how much of the world's fresh water supply?
A) About 1%
B) About 5%
C) About 20%***
D) About 50%
What river carries the most water _______?
A) Amazon in South America***
B) Mississippi in US
C) Amazon in Africa
D) Ganges in Asia
The diagram above represents a cross section through a coastal mountain range. Which of the following
statements is correct?
Region A would receive the most precipitation***
Region B would receive the most precipitation
Regions C would receive the most precipitation
Regions A, B, and C would receive about the same amount of precipitation
Which one of the following features is a sure sign of karst?
Sinkholes***
artesian wells
cones of depression
speleothems
Karst is a special type of landscape that is formed by the dissolution of soluble rocks, including limestone
and dolomite. Karst regions contain aquifers that are capable of providing large supplies of water.
Which of the following statements is true?
cool air can hold more water vapor than warm air
warm air can hold more water than cool air***
cool air and warm air always hold the same amount of water vapor
air cannot contain water vapor
Sub-irrigation is used in areas with:
a) Low water table
b) High water table***
c) Sloping terrain
d) Flat terrain
The field water efficiency of trickle irrigation is:
a) 50-55%
b) 55-85%
c) 80-90%***
d) 60-70%
The sources of water for irrigation can be ground water, surface water and non-conventional sources.
The non-conventional sources are treated wastewater, drainage water, fog collection, etc.
You might also like
- Final Exam Dam Engineering 18-12-2020 PDFDocument11 pagesFinal Exam Dam Engineering 18-12-2020 PDFBaba ArslanNo ratings yet
- Chapter-One Quantity of Water: Arbaminch Institute of TechnologyDocument41 pagesChapter-One Quantity of Water: Arbaminch Institute of Technologytsegaw tesfaye100% (1)
- Hydrology Multiple ChoiceDocument7 pagesHydrology Multiple ChoiceNarayanan RmNo ratings yet
- Two Dimensional Flow of Water Through SoilDocument28 pagesTwo Dimensional Flow of Water Through SoilMinilik Tikur SewNo ratings yet
- Bahirdar Model Exam CIVILEngEXIT - 230710 - 040757Document21 pagesBahirdar Model Exam CIVILEngEXIT - 230710 - 040757Tadesse MegersaNo ratings yet
- HW II - Chapter 3 - Traffic Volume and LoadingDocument29 pagesHW II - Chapter 3 - Traffic Volume and LoadingbulchaNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Engineering Questions and Answers PDFDocument63 pagesIrrigation Engineering Questions and Answers PDFabhishek100% (1)
- Ch. 5 - Stream Gauging PDFDocument38 pagesCh. 5 - Stream Gauging PDFviedos liker100% (1)
- DISTANCE MEASUREMENT - Problem Solving With Theory and Objective Type QuestionsDocument40 pagesDISTANCE MEASUREMENT - Problem Solving With Theory and Objective Type QuestionsSakuntala Uteebrirova100% (2)
- 8 1 EvaporationDocument11 pages8 1 EvaporationChadColeman100% (1)
- Earthwork Quantity and Mass Haul DiagramDocument59 pagesEarthwork Quantity and Mass Haul DiagramHaile GuebreMariamNo ratings yet
- 4-Computation of Average RainfallDocument15 pages4-Computation of Average RainfallDarya Memon100% (9)
- Darcy's Law Exercise and ProblemsDocument23 pagesDarcy's Law Exercise and ProblemsWandy Gunawan100% (7)
- Surface Water Hydrology and Hydrological Cycle GuideDocument14 pagesSurface Water Hydrology and Hydrological Cycle GuideAafaque HussainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 WcuDocument29 pagesChapter 4 WcuKuba100% (3)
- What Is The Difference Between Hydraulic Mean Depth and Hydraulic RadiusDocument1 pageWhat Is The Difference Between Hydraulic Mean Depth and Hydraulic RadiusDeep Debnath0% (1)
- Irrigation Water Resources Engineering Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument2 pagesIrrigation Water Resources Engineering Multiple Choice Questionsengineeringmcqs67% (3)
- Irrigation Engineering Worksheet-One: A) Porosity (45.06%) ) )Document1 pageIrrigation Engineering Worksheet-One: A) Porosity (45.06%) ) )Reffisa Jiru100% (2)
- Hydraulic Structures II ExamplesDocument4 pagesHydraulic Structures II ExamplesBona HirkoNo ratings yet
- Embankment Dam Design & AnalysisDocument280 pagesEmbankment Dam Design & AnalysisOtoma OrkaidoNo ratings yet
- Water Work ch-2Document100 pagesWater Work ch-2Zekarias TadeleNo ratings yet
- Surface Irrigation Methods ExplainedDocument28 pagesSurface Irrigation Methods ExplainedMūssā Mūhābā ZēĒthiopiāNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8. InflitrationDocument36 pagesChapter 8. InflitrationkamagaraNo ratings yet
- Weather and HydrologyDocument20 pagesWeather and HydrologyIamKish Tipono ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3: Crop Water Requirements: 3.1 Evapotranspiration ProcessDocument27 pagesChapter-3: Crop Water Requirements: 3.1 Evapotranspiration ProcessKubaNo ratings yet
- Course Outline - CEng 3204 - Foundation Engineering I - 2020 PDFDocument1 pageCourse Outline - CEng 3204 - Foundation Engineering I - 2020 PDFNatty TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Water Losses: Evaporation From Water Surfaces (Lake Evaporation)Document14 pagesChapter Three Water Losses: Evaporation From Water Surfaces (Lake Evaporation)به شدار ازاد عبدالرحمن عليNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions on Geotechnical EngineeringDocument16 pagesMultiple Choice Questions on Geotechnical EngineeringMahesh RamtekeNo ratings yet
- It is the process of calculating water levels in reservoir, the storage quantaties and outflow rates corresponding to a particular inflow hydrograph at various instantsDocument7 pagesIt is the process of calculating water levels in reservoir, the storage quantaties and outflow rates corresponding to a particular inflow hydrograph at various instantsامين الزريقي100% (1)
- Water Treatment Exam PDFDocument1 pageWater Treatment Exam PDFGebrewahid Adhana100% (1)
- Hydraulic Structure Chapter3,4 PDFDocument47 pagesHydraulic Structure Chapter3,4 PDFBahirDarKetema100% (17)
- Chapter 3 (CWR)Document37 pagesChapter 3 (CWR)Mūssā Mūhābā ZēĒthiopiāNo ratings yet
- Ce353 CH2Document22 pagesCe353 CH2Bishwajit ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 RunoffDocument27 pagesChapter 5 RunoffnimcanNo ratings yet
- INFILTRATION Lecture PDFDocument5 pagesINFILTRATION Lecture PDFsammy lopez0% (1)
- Chapter 5 SEWAGE EFFLUENT DISPOSAL TECHNIQUES Jen 2019 MtuDocument21 pagesChapter 5 SEWAGE EFFLUENT DISPOSAL TECHNIQUES Jen 2019 MtuANDLENATU0% (1)
- Hydrology Problem in Thiessen Polygon MethodDocument3 pagesHydrology Problem in Thiessen Polygon MethodJoseph Oraño0% (2)
- Chapter 2 B 1 Arch ButressDocument19 pagesChapter 2 B 1 Arch ButressYasin Mohamed BulqaazNo ratings yet
- Bligh's creep theory and modificationsDocument1 pageBligh's creep theory and modificationsLo0oVve50% (8)
- Worksheet - 143760187HS-II, TUTORIAL ON CH-5Document14 pagesWorksheet - 143760187HS-II, TUTORIAL ON CH-5A MusaverNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 02Document1 pageAssignment - 02kirubel zewde100% (2)
- CEng2142 REG 2014 FinalExam SolutionSetDocument10 pagesCEng2142 REG 2014 FinalExam SolutionSetDarek HaileNo ratings yet
- Sewer Appurtenances Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument2 pagesSewer Appurtenances Multiple Choice QuestionsJaire100% (1)
- Final Exam Engineering GeologyDocument7 pagesFinal Exam Engineering GeologyBoos yousufNo ratings yet
- Radial Groundwater Flow of Confined and Unconfined Aquifer: By: Jake Nathaniel R. AbadDocument24 pagesRadial Groundwater Flow of Confined and Unconfined Aquifer: By: Jake Nathaniel R. AbadJake Nathaniel AbadNo ratings yet
- Problems On Bearing CapacityDocument82 pagesProblems On Bearing CapacityEngineer fozeb ali85% (20)
- Connect Intersecting Gradients in The Vertical PlaneDocument8 pagesConnect Intersecting Gradients in The Vertical PlaneuipohlklgfNo ratings yet
- Groundwater Introduction and ImportanceDocument45 pagesGroundwater Introduction and ImportanceAsjad UllahNo ratings yet
- 2 Hydrologic Equation Example Lec 1Document12 pages2 Hydrologic Equation Example Lec 1Saif ullahNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5-PermeabilityDocument2 pagesAssignment 5-Permeabilitytushar gautamNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument1 pageSoil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering Multiple Choice Questionsengineeringmcqs100% (2)
- Hydraulics-I IntroductionDocument16 pagesHydraulics-I IntroductionJôssŷ Fkr100% (2)
- Radial Flow For Unconfined AquiferDocument4 pagesRadial Flow For Unconfined Aquifertom meeteiNo ratings yet
- Water Supply and Sewarage Handout PDFDocument99 pagesWater Supply and Sewarage Handout PDFmsea100% (1)
- Ethiopian river basins assignmentDocument6 pagesEthiopian river basins assignmentmasre1742100% (1)
- HS Chapter 4Document28 pagesHS Chapter 4Akli Ale Man100% (3)
- 6 Precipitation 2Document45 pages6 Precipitation 2Kashif IqbalNo ratings yet
- Ground Water2Document11 pagesGround Water2Geo CUKNo ratings yet
- Unit-IV 1. Ground WaterDocument14 pagesUnit-IV 1. Ground WaterRohan RohithNo ratings yet
- Lecturenote 1288194012chapter 1-2Document61 pagesLecturenote 1288194012chapter 1-2Baysa CamadNo ratings yet
- BLGF SRE Manual 2015 PDFDocument120 pagesBLGF SRE Manual 2015 PDFBench Bayan100% (1)
- Boat andDocument7 pagesBoat andAnonymous EvbW4o1U7No ratings yet
- Tupad Project Proposal I. Project Profile: (Name of Brgy Captain or Mayor of ACP)Document2 pagesTupad Project Proposal I. Project Profile: (Name of Brgy Captain or Mayor of ACP)Anonymous EvbW4o1U7No ratings yet
- Part I, Ii, Iii - Answer Key PDFDocument1 pagePart I, Ii, Iii - Answer Key PDFAnonymous EvbW4o1U7No ratings yet
- Contract of Service VsDocument3 pagesContract of Service VsAnonymous EvbW4o1U7No ratings yet
- 13 Full CSE Reviewer With AnswersDocument72 pages13 Full CSE Reviewer With AnswersAnonymous EvbW4o1U7No ratings yet
- Central Tendency Measures Statistics Test ReviewDocument5 pagesCentral Tendency Measures Statistics Test ReviewAnonymous EvbW4o1U7No ratings yet
- NOR - SSS Personal - Record - 3476382113 PDFDocument1 pageNOR - SSS Personal - Record - 3476382113 PDFAnonymous EvbW4o1U7No ratings yet
- The Philippine National HeroesDocument4 pagesThe Philippine National HeroesAnonymous EvbW4o1U7No ratings yet
- Sangka organization planning guideDocument2 pagesSangka organization planning guideAnonymous EvbW4o1U7No ratings yet
- Ic Contract of Service - AcpDocument5 pagesIc Contract of Service - AcpAnonymous EvbW4o1U7No ratings yet
- Functions and Responsibilities / Key Projects and ActivitiesDocument4 pagesFunctions and Responsibilities / Key Projects and ActivitiesAnonymous EvbW4o1U7No ratings yet
- Licensure Examination For Teachers Set 1 Part 1 - Answer KeysDocument1 pageLicensure Examination For Teachers Set 1 Part 1 - Answer KeysNelsonPontipedraSunicoNo ratings yet
- Duty of Mayors To Enforce Laws and OrdinancesDocument2 pagesDuty of Mayors To Enforce Laws and OrdinancesAnonymous EvbW4o1U7No ratings yet
- Exit Interview FormDocument2 pagesExit Interview FormAnonymous EvbW4o1U7No ratings yet
- A QuasiDocument9 pagesA QuasiAnonymous EvbW4o1U7No ratings yet
- Dearest Union Raffle May 18, 2017: Control Number Name SignatureDocument5 pagesDearest Union Raffle May 18, 2017: Control Number Name SignatureAnonymous EvbW4o1U7No ratings yet
- Train ProblemdocDocument2 pagesTrain ProblemdocAnonymous EvbW4o1U7No ratings yet
- DO 123-12 - SAWP Coconut As Feedstock PDFDocument11 pagesDO 123-12 - SAWP Coconut As Feedstock PDFAnonymous EvbW4o1U7No ratings yet
- Rosales Street Property in Butuan Sold for P11MDocument3 pagesRosales Street Property in Butuan Sold for P11MAnonymous EvbW4o1U7No ratings yet
- Ethics in Government and Understanding Sexual HarassmentDocument11 pagesEthics in Government and Understanding Sexual Harassmentcrazzy foryouNo ratings yet
- LGU Best PracticesDocument170 pagesLGU Best PracticesBang Ohh Brokie Duday100% (2)
- Department of Labor and EmploymentDocument1 pageDepartment of Labor and EmploymentAnonymous EvbW4o1U7100% (1)
- Dept Order No. 161-16 (1) SAWP CoconutDocument14 pagesDept Order No. 161-16 (1) SAWP CoconutAnonymous EvbW4o1U7No ratings yet
- Sapad Contract of Service - AcpDocument5 pagesSapad Contract of Service - AcpAnonymous EvbW4o1U7No ratings yet
- Social Amelioration and Welfare Program (SAWP) Presentation - 21 July 2017Document38 pagesSocial Amelioration and Welfare Program (SAWP) Presentation - 21 July 2017Anonymous EvbW4o1U7100% (1)
- Program 174Document1 pageProgram 174Anonymous EvbW4o1U7No ratings yet
- Gip Accomplishment Report FormDocument1 pageGip Accomplishment Report FormAnonymous EvbW4o1U767% (3)
- Gip Accomplishment Report FormDocument1 pageGip Accomplishment Report FormAnonymous EvbW4o1U70% (1)
- DOLE-GIP Form A ApplicationDocument2 pagesDOLE-GIP Form A ApplicationAnonymous EvbW4o1U7No ratings yet
- Tecnam P2006T Standard ProceduresDocument56 pagesTecnam P2006T Standard ProceduresTony Paco100% (2)
- Taking The Offensive, October 1966 To October 1967Document512 pagesTaking The Offensive, October 1966 To October 1967Bob Andrepont100% (10)
- Broadcast Radar Brochure - 04 2022Document8 pagesBroadcast Radar Brochure - 04 2022Arie SuryantokoNo ratings yet
- ART 1999 NiemczynowiczDocument14 pagesART 1999 NiemczynowiczAnita MarquezNo ratings yet
- Water Balance Analysis For Determination of Time Shift in Rice (Oryza Sativa L.)Document13 pagesWater Balance Analysis For Determination of Time Shift in Rice (Oryza Sativa L.)Mamta AgarwalNo ratings yet
- BCME StressCorrosion enDocument14 pagesBCME StressCorrosion enmichael_george291616100% (1)
- Masonry: Building Weather-Resistant Masonry WallsDocument4 pagesMasonry: Building Weather-Resistant Masonry WallsghchgNo ratings yet
- EF - English IdiomsDocument24 pagesEF - English IdiomsEdson Ribeiro100% (1)
- En 15239 Inspection of Ventilation SystemsDocument47 pagesEn 15239 Inspection of Ventilation SystemsWilfrid DutruelNo ratings yet
- Assignment IIDocument2 pagesAssignment IIhabtamu100% (2)
- Magnetic Refrigeration Seminar ReportDocument49 pagesMagnetic Refrigeration Seminar ReportAman agrawal94% (17)
- FormulaeDocument33 pagesFormulaeLcm TnlNo ratings yet
- Khitai PDFDocument125 pagesKhitai PDFNatalie Daniel100% (1)
- 5 Grade Science: Forces and Motion Life Science Earth Science Weather Parts of A CellDocument53 pages5 Grade Science: Forces and Motion Life Science Earth Science Weather Parts of A Cellapi-306929216No ratings yet
- Transcripts and Questions - 1000 Words - Part IDocument109 pagesTranscripts and Questions - 1000 Words - Part IPat Viet NamNo ratings yet
- DP 3766 20130128 PDFDocument16 pagesDP 3766 20130128 PDFtradingpostNo ratings yet
- Laxmipur District - Ramgati UpazilaDocument15 pagesLaxmipur District - Ramgati UpazilaCDMP BangladeshNo ratings yet
- Scie 4Document3 pagesScie 4Mira PepinoNo ratings yet
- Urashima the Fisherman: A Fisherman Rescues a TortoiseDocument7 pagesUrashima the Fisherman: A Fisherman Rescues a TortoiseMónica Pabón MéndezNo ratings yet
- PE Notes MidtermDocument6 pagesPE Notes MidtermHannah OmegaNo ratings yet
- Issued For Use: Offshore Terminal HandbookDocument124 pagesIssued For Use: Offshore Terminal Handbookarvinth mNo ratings yet
- CombatFlight Simulator 3 ReviewDocument14 pagesCombatFlight Simulator 3 ReviewtumbNo ratings yet
- Operating Instructions - VEGASON 65-4-20 Ma - HART - Four-WireDocument64 pagesOperating Instructions - VEGASON 65-4-20 Ma - HART - Four-WireSantiago Eliú Castillo BarreraNo ratings yet
- Fabrication Erection and Installation Procedure For PipingDocument60 pagesFabrication Erection and Installation Procedure For Pipinghasan_676489616No ratings yet
- Llanrwst Flooding Case StudyDocument3 pagesLlanrwst Flooding Case StudyLola YunNo ratings yet
- Nokia 7705 SAR Conformal Coating Application Note enDocument13 pagesNokia 7705 SAR Conformal Coating Application Note enPeng HaoNo ratings yet
- Importance of Marine Geospatial Data InfrastructureDocument7 pagesImportance of Marine Geospatial Data InfrastructureAdila IshakNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Negative WorksheetDocument1 pagePresent Simple Negative WorksheetRaquel Sánchez De LahozNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Heat Pumps A Guide For Planning and Installing PDFDocument167 pagesGeothermal Heat Pumps A Guide For Planning and Installing PDFfranteslaNo ratings yet
- Monograph - Design Seminar - AthiraDocument6 pagesMonograph - Design Seminar - AthiraAthira NairNo ratings yet
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastFrom EverandThe Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- The Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterFrom EverandThe Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterNo ratings yet
- The Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorFrom EverandThe Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (137)
- Why Fish Don't Exist: A Story of Loss, Love, and the Hidden Order of LifeFrom EverandWhy Fish Don't Exist: A Story of Loss, Love, and the Hidden Order of LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (699)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- Water to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesFrom EverandWater to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (21)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsFrom EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (221)
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsFrom EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (63)
- The Mind of Plants: Narratives of Vegetal IntelligenceFrom EverandThe Mind of Plants: Narratives of Vegetal IntelligenceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- Smokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersFrom EverandSmokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersNo ratings yet
- The Secret Life of Lobsters: How Fishermen and Scientists Are Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Favorite CrustaceanFrom EverandThe Secret Life of Lobsters: How Fishermen and Scientists Are Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Favorite CrustaceanNo ratings yet
- Gathering Moss: A Natural and Cultural History of MossesFrom EverandGathering Moss: A Natural and Cultural History of MossesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (347)
- Come Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogFrom EverandCome Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (10)
- Spoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeFrom EverandSpoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (19)
- Survival Mom: How to Prepare Your Family for Everyday Disasters and Worst-Case ScenariosFrom EverandSurvival Mom: How to Prepare Your Family for Everyday Disasters and Worst-Case ScenariosRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Soil: The Story of a Black Mother's GardenFrom EverandSoil: The Story of a Black Mother's GardenRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (16)
- The Hummingbirds' Gift: Wonder, Beauty, and Renewal on WingsFrom EverandThe Hummingbirds' Gift: Wonder, Beauty, and Renewal on WingsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (60)