Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pat Atlas e Muscle Pain
Uploaded by
Velinska Helfriza PurbaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pat Atlas e Muscle Pain
Uploaded by
Velinska Helfriza PurbaCopyright:
Available Formats
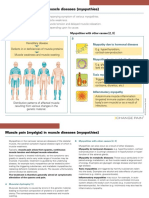
Muscle pain (myalgia) in muscle diseases (myopathies)
Myalgia develops as a cardinal or accompanying symptom of various myopathies.
All myopathies are associated with muscle weakness.
Pain arises from spasms, persistent muscle tension and delayed muscle relaxation.
Each myopathy is treated individually depending upon its cause.
Muscular dystrophy [1] Myopathies with other causes [2, 3]
A B
Hereditary disease O
Myopathy due to hormonal diseases
OH
Defects in or deficiencies of muscle proteins E.g. hyperthyroidism,
HO O
cortisol over-production
Muscle weakness and muscle wasting
Myopathy due to metabolic diseases
E.g. glycogen storage disease,
lipid storage disease
Toxic myopathy
Triggered for example by alcohol
or particular medicines (statins,
cortisone, diuretics, etc.)
Inflammatory myopathy
Autoimmune muscle inflammation
(impaired immune system attacks the
© 2013 Grünenthal GmbH
Distribution patterns of affected muscle body’s own muscle) or as a result of
resulting from various changes in the infections.
genetic material.
Muscle pain (myalgia) in muscle diseases (myopathies)
Myopathies in the narrower sense are diseases of the skeletal B Myopathies with other causes [2, 3]
muscle, the cardinal symptom (typical disease sign) of which is
muscle weakness. Myopathies can also occur as a result of other diseases.
Typically, muscle pain arises from spasms, continuous Myopathy in hormonal diseases: e.g. hyperthyroidism, cortisol
muscle tension and delayed muscle relaxation. over-production in Cushing’s disease or in hypofunction or hyper-
function of the adrenal glands.
Each myopathy is treated individually, as the symptoms vary
greatly in severity and a very wide range of muscles may be Myopathy in metabolic diseases: These occur particularly in im-
involved. If possible, treatment is guided by the underlying paired energy metabolism, as the muscle needs a large amount
disease, for example toxic myopathies can be treated by elim- of energy. Examples are glycogen storage disease and lipid stor-
inating the triggering substances, and metabolic myopathies by age disease.
replacing deficient metabolic products. The causes unfortunately Toxic myopathies are triggered by harmful substances taken
cannot always be addressed. into the body. Examples are alcohol and side effects of particular
The treatment is therefore generally aimed at symptomatic medicines (e.g. statins, glucocorticoids).
alleviation of the spasms and pain. Inflammatory myopathies may occur: for example, in auto-
immune diseases, in which an incorrectly controlled immune
system attacks the body’s own muscles (e.g. in polymyositis or
A Muscular dystrophy [1]
dermatomyositis). An infection (e.g. trichinosis) may also lead to
Muscular dystrophy is caused by errors in the genetic material, inflammatory myopathy.
leading to incorrect composition of proteins or a protein defi-
ciency. The consequences are muscle weakness and muscle
wasting.
Depending on the particular change in the genetic material,
there are numerous different muscular dystrophies, with typ-
ical distribution patterns of the affected muscles. The most
common types include Duchenne, Becker-Kiener, limb-girdle
dystrophy (shoulder and pelvic girdles), facioscapulohumeral
dystrophy (muscles of the face, shoulder girdle and upper arm)
and distal dystrophy (hands and feet).
© 2013 Grünenthal GmbH
[1] Lovering RM et al. Phys Ther (2005) 85(12): 1372 - 1388.
[2] Chawla J. Front Neurol (2011) 2: 49.
[3] Ozen H. World J Gastoroenterol (2007) 13(18): 2541 - 2553.
34 Muscle pain (myalgia) in muscle diseases (myopathies)
You might also like
- Tabel 8 Poa SD Setelah IntervensiDocument3 pagesTabel 8 Poa SD Setelah IntervensiVelinska Helfriza PurbaNo ratings yet
- Pat Atlas e Muscle Pain PDFDocument2 pagesPat Atlas e Muscle Pain PDFVelinska Helfriza PurbaNo ratings yet
- Crisp DMDocument76 pagesCrisp DMyeibiNo ratings yet
- Vitamin D and Diabetes Mellitus: ReviewDocument19 pagesVitamin D and Diabetes Mellitus: ReviewVelinska Helfriza PurbaNo ratings yet
- 4592 8834 1 SM PDFDocument6 pages4592 8834 1 SM PDFHillary LopezNo ratings yet
- Islet TransplantationDocument4 pagesIslet Transplantationnawalahmed101No ratings yet
- Islet TransplantationDocument4 pagesIslet Transplantationnawalahmed101No ratings yet
- Pat Atlas e Muscle Pain PDFDocument2 pagesPat Atlas e Muscle Pain PDFVelinska Helfriza PurbaNo ratings yet
- Get Me Off Your Fucking Mailing ListDocument10 pagesGet Me Off Your Fucking Mailing ListboTT1ENo ratings yet
- InTech-Application of Ftir Spectroscopy in Environmental StudiesDocument36 pagesInTech-Application of Ftir Spectroscopy in Environmental StudiesVelinska Helfriza PurbaNo ratings yet
- Features of Gastritis Predisposing To Gastric Adenoma and Early Gastric CancerDocument19 pagesFeatures of Gastritis Predisposing To Gastric Adenoma and Early Gastric CancerVelinska Helfriza PurbaNo ratings yet
- Liver Disease in Canada E 3Document72 pagesLiver Disease in Canada E 3Velinska Helfriza PurbaNo ratings yet
- EK-VK100-In-002 GIGI Terminal Installation and Owners Manual Apr81Document116 pagesEK-VK100-In-002 GIGI Terminal Installation and Owners Manual Apr81Velinska Helfriza PurbaNo ratings yet
- The Liver: HST.035 Spring 2003Document35 pagesThe Liver: HST.035 Spring 2003miss illaNo ratings yet
- Emulsi 1Document6 pagesEmulsi 1Velinska Helfriza PurbaNo ratings yet
- Performance Characteristics of Argentometric Method of Cyanide DeterminationDocument6 pagesPerformance Characteristics of Argentometric Method of Cyanide DeterminationVelinska Helfriza PurbaNo ratings yet
- 975 1925 1 SM PDFDocument8 pages975 1925 1 SM PDFVelinska Helfriza PurbaNo ratings yet
- Performance Characteristics of Argentometric Method of Cyanide DeterminationDocument6 pagesPerformance Characteristics of Argentometric Method of Cyanide DeterminationVelinska Helfriza PurbaNo ratings yet
- EnzimDocument7 pagesEnzimVelinska Helfriza PurbaNo ratings yet
- Antimalarial Activity of Papaya Leaf ExtractsDocument5 pagesAntimalarial Activity of Papaya Leaf ExtractsFaris AgazaliNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5782)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- BPAC 11.22.19 Meeting Issue Summary Topic 1 Considerations For Cold Stored Platelets Intended For TransfusionDocument11 pagesBPAC 11.22.19 Meeting Issue Summary Topic 1 Considerations For Cold Stored Platelets Intended For Transfusionmy accountNo ratings yet
- Genetic code and protein synthesis flashcardsDocument15 pagesGenetic code and protein synthesis flashcardsnfnf otupyooorefnNo ratings yet
- Antenatal Care PPT EchyDocument14 pagesAntenatal Care PPT EchyYuliana alensi falloNo ratings yet
- Terapi LintahDocument3 pagesTerapi LintahDevi FitriNo ratings yet
- Ken AlibekDocument8 pagesKen AlibekHenry Escobar0% (1)
- Death Watch Beetle: in CultureDocument2 pagesDeath Watch Beetle: in Culturewinofvin9No ratings yet
- Land Use in UP by DistrictDocument7 pagesLand Use in UP by DistrictFaisal AnsariNo ratings yet
- M.Sc. ZoologyDocument21 pagesM.Sc. ZoologySabyasachi DasNo ratings yet
- NBME 27 AnswersDocument198 pagesNBME 27 Answershaneen gf100% (3)
- Question Bank For The Final Biology Exam PDFDocument72 pagesQuestion Bank For The Final Biology Exam PDFmrgamer9923No ratings yet
- Flow Chart Analysis & ElementsDocument11 pagesFlow Chart Analysis & ElementsSergio SmithNo ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Biol3v20.001.07s Taught by Ernest Hannig (Hannig)Document8 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Biol3v20.001.07s Taught by Ernest Hannig (Hannig)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- Brinas Julie Science9 Exodus Las5Document3 pagesBrinas Julie Science9 Exodus Las5Julie Angel BriñasNo ratings yet
- Soft Tissues PathologyDocument53 pagesSoft Tissues PathologyWz bel DfNo ratings yet
- Soal Bahasa Inggris SIMAK UI 2013 PDFDocument20 pagesSoal Bahasa Inggris SIMAK UI 2013 PDFTiara Rahmadianti AlawiNo ratings yet
- Phytostabilization of Nickel by The Zinc and Cadmium Hyperaccumulator SolanumDocument7 pagesPhytostabilization of Nickel by The Zinc and Cadmium Hyperaccumulator SolanumYogi PernandaNo ratings yet
- Dragon Fruit Growth on BAP Concentration and Germination Age In VitroDocument7 pagesDragon Fruit Growth on BAP Concentration and Germination Age In VitroAzmi NadhifNo ratings yet
- Protein Function Prediction IntroductionDocument20 pagesProtein Function Prediction IntroductionEndah Sekar PalupiNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Tissue Practice TestDocument15 pagesCH 4 Tissue Practice TestMelody B. MiguelNo ratings yet
- As ISO 10993.5-2002 Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices Tests For in Vitro CytotoxicityDocument8 pagesAs ISO 10993.5-2002 Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices Tests For in Vitro CytotoxicitySAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- NEET Jan 2020 PaperDocument385 pagesNEET Jan 2020 PaperDivya RagavanNo ratings yet
- Course EvaluationDocument14 pagesCourse EvaluationKimberly IgbalicNo ratings yet
- Extended Essay NorhanDocument23 pagesExtended Essay NorhanAbed ZaghalNo ratings yet
- NBME Samples Qs - PathologyDocument7 pagesNBME Samples Qs - PathologyAli AlshehhiNo ratings yet
- English Project About ZoosDocument11 pagesEnglish Project About ZoosYehya YasserNo ratings yet
- P H A R M A C o G e N e T I C A N D Pharmacokinetic Assays From Saliva Samples Can Guarantee Personalized Drug PrescriptionDocument6 pagesP H A R M A C o G e N e T I C A N D Pharmacokinetic Assays From Saliva Samples Can Guarantee Personalized Drug PrescriptionjavelezhNo ratings yet
- 370 Labs 1 4 - 2013v1Document39 pages370 Labs 1 4 - 2013v1MercyNo ratings yet
- Practice Test Questions Downloaded From FILIPINO NURSES CENTRALDocument26 pagesPractice Test Questions Downloaded From FILIPINO NURSES CENTRALFilipino Nurses CentralNo ratings yet
- Antoniou 2015 - Physicochemical - ChitosanDocument10 pagesAntoniou 2015 - Physicochemical - ChitosanJéssica FonsecaNo ratings yet