Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Resp Examination
Uploaded by
phreakyfilOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Resp Examination
Uploaded by
phreakyfilCopyright:
Available Formats
Examination of the Respiratory Examination
Introduce yourself. Clubbing:
Explain procedure Thoracic Tumours: Interstitial:
Obtain consent Bronchial Carcinoma Fibrosing Alveolitis
Position patient supine and inclined at Mesothelioma Asbestosis
45 degrees Pleural Fibroma AV Shunt:
Expose the chest to the waist Atrial Myxoma AV malformations
Thymoma Cyanotic CHD
Inspect: Oesophageal Cancer
General appearance Sepsis: Non-Thoracic:
Hands: colour, nails, CO2 Flap Bronchiectasis (+CF) Hepatic Cirrhosis
Face Lung Abcess IBD
Tongue Infective Endocarditis Coeliac Disease
Neck - JVP TB
Front of chest: deformity, scars, Empyema
Chest movement and accessory muscle
activity
Chest Wall Deformities
Respiratory rate Barrel Chest: COPD
Kyphoscoliosis
Pectus Carinatum: Severe
Tracheal Deviation: childhood asthma / osteomalacia
Towards Lesion: Pectus Excavatum
Upper lobe/lung collapse Palpate:
Upper lobe Fibrosis Trachea
Pneumonectomy Lymph nodes: neck and axilla
Away from Lesion: Chest tenderness or lumps
Tension Pneumothorax Depth and symmetry of breathing
Massive PE Tactile vocal fremitus: four sites from top to bottom
Upper Mediastinal Mass
Retrosternal Goitre
Lymphoma Decreased Chest Expansion:
Lung Cancer Unilateral:
Pleural Effusion
Lung/lobe collapse
Pneumohthorax
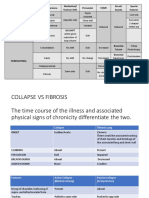
Percussion: Unilateral Fibrosis
Resonant: Bilateral
Normal Lung Percuss: Advanced COPD
Hyperresonant: Clavicles Diffuse Fibrosis
Pneumothorax Upper zone
Dull: Mid zone
Consolidation Lower zone
Lung/lobe collapse
Laterally - comparing right and left at each stage
Severe Fibrosis
‘Stoney’ Dull:
Pleural Effusion Tactile Vocal Fremitus:
Haemothorax Trasmission of Vibration from
mouth to chest wall
Over areas of Dull Percussion:
↑TVF: Consolidation/Fibrosis
↓TVF: Fluid/Collapse
Auscultate: Diminished Vesicular Breathing:
Upper zone Decreased Conduction:
Mid zone Obesity
Lower zones Pleural Effusion
Laterally -comparing right and left at each stage Pheumothorax
Check vocal resonance at same sites Decreased Airflow
Sit patient forward and repeat inspection, palpation, Generalised: COPD
percussion and auscultation on the back of the chest. Localised: collapse
Look for Sacral/Ankle Oedema
Breath Sounds:
Normal = Vesicular – rustling quality Cause: uniformly conducting tissue
Bronchial Breathing: Common:
High Pitched Consolidation (pneumonia)
Blowing Quality Uncommon:
Insp/Exp Similar length and intensity Local Fibrosis
Characteristic Pause Top of Pleural Effusion
Collapsed lung with major
bronchus patent
Crackles Musical
Wheeze: (inspiratory):
Quality
Opening of collapsed
Osscilating small airways
narrowed Airway
Interrupted,
Usually Loudestnon musical sounds
Expiration
Early:
Inspiratory = Severe Airway disease Mediastinal
DDx
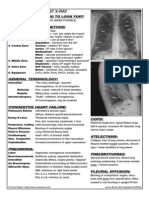
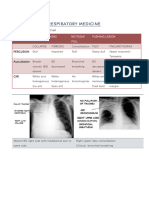
Small airway disease (bronchiolitis) Expansion Percussion Tactile Vocal Auscultation
Middle: Shift Fremitus/
Friction rub: grating sound ‘creaking leather’ Vocal
Pulmonary
pleural Oedema
inflammation and thickening.
Late: Resonance
Stridor: on inspiration
Fine: Pulmonary Pleural Effusion no/away
Fibrosis ↓ Stoney Dull ↓ ↓ Breath Sounds
narrowing of the upper airways
Medium: Pulmonary Oedema Occasional Rub
Coarse: BronchialConsolidation No
Secretions (COPD, Normal/↓ Dull ↑ Bronchial Breathing +
Pneumonia) (pneumonia) Crackles (coarse)
Lobar Collapse
Biphasic: Bronchiectasis - Coarse Towards ↓ Dull ↓ ↓ Breath Sounds
Pneumothorax No (simple) Normal/ ↓ Hyper- ↓ ↓ Breath Sounds
Away (Tension) resonant
Pleural No ↓ Dull ↓ ↓ Breath Sounds
Thickening
Asthma/COPD No ↓ Polyphonic wheeze
COPD: Coarse Crackles
You might also like
- Notes SC RSDocument5 pagesNotes SC RS202213No ratings yet
- AMTEC Revision Resp-ExaminationDocument2 pagesAMTEC Revision Resp-ExaminationjevonyapNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts in Lung DiseaseDocument38 pagesBasic Concepts in Lung DiseaselecturioNo ratings yet
- Chest ExaminationDocument25 pagesChest ExaminationYuvraj soniNo ratings yet
- Respiratory ExamDocument6 pagesRespiratory Exam95kscbyqxmNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System SummaryDocument6 pagesRespiratory System SummaryKiara GovenderNo ratings yet
- Abdomen 2Document9 pagesAbdomen 2Ar-em BautistaNo ratings yet
- NCM 112-Mod3Document19 pagesNCM 112-Mod3Samantha BolanteNo ratings yet
- Lungs and Thorax Assessment - PPTX RAHEEM KHANDocument60 pagesLungs and Thorax Assessment - PPTX RAHEEM KHANRabia IsrafilNo ratings yet
- Rev Widya Physical Examination of Respiratory SystemDocument72 pagesRev Widya Physical Examination of Respiratory SystemYuliaNo ratings yet
- An Approach To A Patient With BreathlessnessDocument35 pagesAn Approach To A Patient With Breathlessnessgl tousifNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Fisik ThoraxDocument16 pagesPemeriksaan Fisik ThoraxYudiWatanabeNo ratings yet
- Thorax MedDocument3 pagesThorax Medangela mamauagNo ratings yet
- Physical Exam - Chest 2006Document84 pagesPhysical Exam - Chest 2006api-19916399No ratings yet
- Lung Examination: AbnormalDocument56 pagesLung Examination: AbnormalBECAREFUL89ANo ratings yet
- Chest Examination New SsDocument16 pagesChest Examination New SsNAINo ratings yet
- Approach To Respiratory Disorders: Kurniyanto Department of Internal Medicine FK UkiDocument35 pagesApproach To Respiratory Disorders: Kurniyanto Department of Internal Medicine FK UkiDaud ParluhutanNo ratings yet
- Wk4 Restrictive Lung DisordersDocument38 pagesWk4 Restrictive Lung DisordersPotato PceeNo ratings yet
- STUDY GUIDE 2 OXYGENATION Operaña EllayzaDocument5 pagesSTUDY GUIDE 2 OXYGENATION Operaña EllayzaOPERAñA ELLAYZA RB DECANONo ratings yet
- What To Ask:: Infection (LRTI)Document11 pagesWhat To Ask:: Infection (LRTI)habbouraNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Conditions ChartDocument1 pageRespiratory Conditions ChartAmanda MuchaNo ratings yet
- Final Death Note - Compre NotesDocument1,550 pagesFinal Death Note - Compre NotesSteph TabasaNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Child With Cough and Difficulty in BreathingDocument23 pagesApproach To A Child With Cough and Difficulty in BreathingKashif Burki100% (2)
- Med SurgDocument3 pagesMed SurgShaira Mae GordoraNo ratings yet
- Dyspnoea Ddx/Associated Features Body System/key Qs AcuteDocument4 pagesDyspnoea Ddx/Associated Features Body System/key Qs Acutedragtoss2No ratings yet
- Chest X Ray BasicsDocument99 pagesChest X Ray BasicsHarshaWakodkarNo ratings yet
- Examination of Respiratory SystemDocument78 pagesExamination of Respiratory Systemwidya sri hastutiNo ratings yet
- Respi 2Document11 pagesRespi 2Jeno SigamaniNo ratings yet
- Introduksi Chest X RayDocument64 pagesIntroduksi Chest X RaySanyuki KhoirunnisaNo ratings yet
- RespiratoryDocument7 pagesRespiratoryThomas KearneyNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination in Respiratory SystemDocument58 pagesPhysical Examination in Respiratory SystemMarian0% (1)
- RespiDocument22 pagesRespifatima chrystelle nuñalNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Symptoms and Signs of Respiratory DiseasesDocument52 pagesInterpretation of Symptoms and Signs of Respiratory DiseasesAbdul JalilNo ratings yet
- Chest AuscultationDocument24 pagesChest AuscultationAtu KaushalNo ratings yet
- Patho RevDocument21 pagesPatho RevJo CastilloNo ratings yet
- Physical Examinations Respiratory System: InspectionDocument5 pagesPhysical Examinations Respiratory System: InspectionAzizan HannyNo ratings yet
- Cough SummaryDocument2 pagesCough SummarydwNo ratings yet
- 4 Respiratory System ExaminationDocument26 pages4 Respiratory System ExaminationLiew John KhengNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Case of Respiratoey SystemDocument105 pagesApproach To A Case of Respiratoey SystemprashuNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Sounds: by Oluwaseun OlaiyaDocument16 pagesRespiratory Sounds: by Oluwaseun OlaiyaOlaiya OluwaseunNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - THORAX AND LUNGSDocument2 pagesLesson 6 - THORAX AND LUNGSKuldip GillNo ratings yet
- DR Marcel Blok 18Document39 pagesDR Marcel Blok 18vaiyenNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Examination - Knowledge at AMBOSSDocument1 pagePulmonary Examination - Knowledge at AMBOSSKC Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Chest Tubes: From Indication To RemovalDocument49 pagesChest Tubes: From Indication To Removaldara octavianiNo ratings yet
- CoughDocument30 pagesCoughAnil NarayanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory ExaminationDocument19 pagesRespiratory ExaminationMohini33% (3)
- DR Marcel Blok 18Document39 pagesDR Marcel Blok 18vaiyenNo ratings yet
- NCM103 - 2016 - Lecture2 - Response To Altered Respiratory FunctionDocument128 pagesNCM103 - 2016 - Lecture2 - Response To Altered Respiratory FunctionrimeoznekNo ratings yet
- Chest X-Ray - CVS: 1/3 Cardiac On Right, 2/3 On Left SideDocument2 pagesChest X-Ray - CVS: 1/3 Cardiac On Right, 2/3 On Left SideJennyu YuNo ratings yet
- Thorax PatologisDocument72 pagesThorax PatologisAida Fitriyane HamdaniNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Tract RadiologyDocument106 pagesRespiratory Tract RadiologyKalemNo ratings yet
- Scut Report: Chest X-RayDocument1 pageScut Report: Chest X-RayJames Booth100% (4)
- Examination of The Respiratory SystemDocument35 pagesExamination of The Respiratory SystemRashhmi Karthodi100% (1)
- Symptoms and Signs of Respiratory DiseasesDocument35 pagesSymptoms and Signs of Respiratory DiseasesEmereole FrancesNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORY MEDICINE Rama Medical CollegeDocument5 pagesRESPIRATORY MEDICINE Rama Medical Collegeshrishti tyagiNo ratings yet
- Lung SoundsDocument35 pagesLung SoundsRaluca AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary ConditionsDocument42 pagesPulmonary ConditionsMinetteNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Chest and LungsDocument46 pagesAssessment of The Chest and LungsSumathi GopinathNo ratings yet
- Pleurisy, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandPleurisy, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- GlucomaDocument14 pagesGlucomametalheavy9993No ratings yet
- Medicine Disease in The Elizabethan EraDocument5 pagesMedicine Disease in The Elizabethan Eraapi-553556825No ratings yet
- 4TH YEAR BCQS MbbsDocument9 pages4TH YEAR BCQS MbbsHira PanhwerNo ratings yet
- QNST3R Manual IntroDocument8 pagesQNST3R Manual IntroANDREA ESQUIVEL QUINTERONo ratings yet
- 3 Interview Transcripts From The Leaky Brain SummitDocument39 pages3 Interview Transcripts From The Leaky Brain SummitJimmy SchibelloNo ratings yet
- Seminar REPORTDocument24 pagesSeminar REPORTMICHEALNo ratings yet
- Lic Health Plus FormDocument27 pagesLic Health Plus FormKuldeep Chakerwarti100% (1)
- Reading LeonDocument4 pagesReading LeonMarién Mateos FernándezNo ratings yet
- Abg Analysis NotesDocument32 pagesAbg Analysis Notesakheel ahammedNo ratings yet
- School Clinic Policies, VMGODocument6 pagesSchool Clinic Policies, VMGOGissele AbolucionNo ratings yet
- Vedavaani-A Gurukulam ProjectDocument98 pagesVedavaani-A Gurukulam ProjectDr Suvarna NalapatNo ratings yet
- Basal Metabollic Rate (BMR)Document16 pagesBasal Metabollic Rate (BMR)ibnu affanNo ratings yet
- Measuring Outcomes After Critical Illness: Nathan E. BrummelDocument12 pagesMeasuring Outcomes After Critical Illness: Nathan E. BrummelVlady78No ratings yet
- CROSSWORD PUZZLE - Health ProblemsDocument4 pagesCROSSWORD PUZZLE - Health ProblemsVeZ xNo ratings yet
- Wine Spectator Jan. 31 - Feb. 29, 2016 Issue (M.J)Document126 pagesWine Spectator Jan. 31 - Feb. 29, 2016 Issue (M.J)Anonymous hbmZEVFrCNo ratings yet
- Menstrual Disorders 2Document39 pagesMenstrual Disorders 2Nanang HidayatullohNo ratings yet
- Case AnaDocument12 pagesCase AnaBiel DelcanoNo ratings yet
- Eating Disorders: BY: Pavithini Gopalan Priya Tharsini Shanaaz KhanDocument55 pagesEating Disorders: BY: Pavithini Gopalan Priya Tharsini Shanaaz KhanNabighah ZukriNo ratings yet
- Stroke Statistics 2018Document46 pagesStroke Statistics 2018Aghnia PutriNo ratings yet
- The Growing FetusDocument68 pagesThe Growing Fetusjean thereseNo ratings yet
- PsychiatryDocument12 pagesPsychiatrySurya BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Mark Anthony A. Tom, M.D. First Year Internal Medicine Resident Davao Doctors HospitalDocument55 pagesMark Anthony A. Tom, M.D. First Year Internal Medicine Resident Davao Doctors HospitalMark Anthony TomNo ratings yet
- Fibromyalgia Syndrome Clinical Picture, Diagnosis, TreatmentDocument6 pagesFibromyalgia Syndrome Clinical Picture, Diagnosis, TreatmentCentral Asian StudiesNo ratings yet
- Categorize The Treatment Options For Patients With Existing Medical ConditionDocument3 pagesCategorize The Treatment Options For Patients With Existing Medical ConditionMicah LatosaNo ratings yet
- Phosphate BinderDocument51 pagesPhosphate BinderbedestySNo ratings yet
- 3806 Disease Prediction by Using Machine Learning PDFDocument6 pages3806 Disease Prediction by Using Machine Learning PDFJhon tNo ratings yet
- Acute ComaDocument16 pagesAcute ComaDean AccountNo ratings yet
- Ending Therapy - Terry KupersDocument222 pagesEnding Therapy - Terry KupersIleana Balaci100% (1)
- MSN I 25.06 .2020 AN Unit IV. Small Intestinal Malabsorption & ObstructionDocument92 pagesMSN I 25.06 .2020 AN Unit IV. Small Intestinal Malabsorption & ObstructionYAMINIPRIYAN0% (1)
- Pathology AIIMSDocument26 pagesPathology AIIMSvkNo ratings yet