Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is STD Cells? How You Will Decide The Height of STD Cells? What Is Mean by Track What Is Mean by A Pitch?
Uploaded by
Analog Layout0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
97 views2 pagesThis document discusses topics related to MOSFETs and CMOS integrated circuit design including:
1. It defines MOSFETs and compares their advantages over BJTs.
2. It covers the operation of MOSFETs as switches and the differences between PMOS and NMOS transistors.
3. It discusses CMOS inverters, including their cross-sectional view and operation, and why CMOS gates dissipate close to zero static power.
4. It addresses various aspects of IC layout design such as design rules, standard cells, and poly routing as well as differences between process technologies.
Original Description:
xncbjd
Original Title
What is Mosfet
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses topics related to MOSFETs and CMOS integrated circuit design including:
1. It defines MOSFETs and compares their advantages over BJTs.
2. It covers the operation of MOSFETs as switches and the differences between PMOS and NMOS transistors.
3. It discusses CMOS inverters, including their cross-sectional view and operation, and why CMOS gates dissipate close to zero static power.
4. It addresses various aspects of IC layout design such as design rules, standard cells, and poly routing as well as differences between process technologies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
97 views2 pagesWhat Is STD Cells? How You Will Decide The Height of STD Cells? What Is Mean by Track What Is Mean by A Pitch?
Uploaded by
Analog LayoutThis document discusses topics related to MOSFETs and CMOS integrated circuit design including:
1. It defines MOSFETs and compares their advantages over BJTs.
2. It covers the operation of MOSFETs as switches and the differences between PMOS and NMOS transistors.
3. It discusses CMOS inverters, including their cross-sectional view and operation, and why CMOS gates dissipate close to zero static power.
4. It addresses various aspects of IC layout design such as design rules, standard cells, and poly routing as well as differences between process technologies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
1. What is Mosfet ,Why we called it Mosfet ?
2. What are advantages of using mosfet over bjts ?
3. Draw the crossectional view of any mosfet ?explain layers .
4. Explain operation of Mosfet ? why it act as a switch and how ?
5. What is pmos and nmos explain ? difference , which one is fast among them ?
6. Cmos ? why ? explain cmos inverter operation and charateristics
7. Draw crossectional view of cmos inverter ?
8. Why are PMOS transistor networks generally used to produce high (i.e. 1) signals, while
NMOS networks are used to product low (0) signals?
9. On IC schematics, transistors are usually labeled with one, or sometimes two numbers.
What do each of those numbers mean?
10. Why is the number of gate inputs to CMOS gates (e.g. NAND or NOR gates) usually limited
to four?
11. What is meant by static and dynamic power with respect to the operation of a CMOS gate?
Why do CMOS gates dissipate close to zero static power? Why is the static power not
exactly zero?
12. What is a transmission gate, and what is it used for typically? Why are transmission gates
made with both PMOS and NMOS transistors?
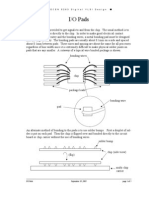
13. In an IC layout, what is a polygon and what is a path? What are the advantages and
disadvantages of each?
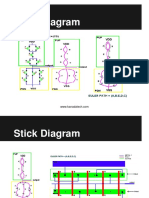
14. Draw the stick diagram of basic logic gates
15. Why is it that NMOS transistors can be created directly in a P-type substrate, whereas PMOS
transistors must be created in an N-type well?
16. Why must transistors be provided with "bulk" connections? What voltage levels are
connected to a p-type substrate and an n-type well through these connections, and why?
17. What are process design rules? What is their major purpose? How are design rules created?
18. What are width rules, space rules, and overlap rules?
19. What are the major advantages of hierarchical IC design?
20. Define what is meant by the terms design rules checking, layout versus schematic, and
electrical rules check? Are all three procedures required in every chip design?
21. What is the purpose of end overlap rules?
22. Explain threshold voltage ? body effect ?
23. what is STD cells? How you will decide the height of STD cells?
what is mean by Track
What is mean by a pitch?
24. What are the advantages of standard cells ? any dis advantages ?
25. How do you choose height of the STD cells ?
26. What are the constraints you will fallow while doing STD cells
27. How will you take power routing in standard cells ?
28. What is ploy ? what is poly pitch ?
29. Which poly routing is minimized in your layout ?
30. what is the difference between 130nm and 45 nm ?
You might also like
- VLSI Design Related Good QuestionsDocument2 pagesVLSI Design Related Good QuestionsGaurav PatelNo ratings yet
- Antenna Diode Vlsi Operation Positive ChargeDocument21 pagesAntenna Diode Vlsi Operation Positive ChargeNegin HashemiNo ratings yet
- Questions Are Related To Comparison (What Is The Difference Betweem ... )Document21 pagesQuestions Are Related To Comparison (What Is The Difference Betweem ... )palakNo ratings yet
- Layout Proximity Effect 1Document4 pagesLayout Proximity Effect 1Sindhu100% (1)
- IO Design, ESDDocument18 pagesIO Design, ESDashishmanyanNo ratings yet
- VLSI Placement - CMOS Interview Question - Part 1 (MOSFET)Document3 pagesVLSI Placement - CMOS Interview Question - Part 1 (MOSFET)shivanand_shettennavNo ratings yet
- Analog Layout EngineerDocument4 pagesAnalog Layout EngineerAjay Kumar MattupalliNo ratings yet
- Interview Questions - VLSI - Physical Design For FreshersDocument5 pagesInterview Questions - VLSI - Physical Design For FreshersSri ShandilyaNo ratings yet
- Texas Instruments Placement Paper May 2011Document5 pagesTexas Instruments Placement Paper May 2011Shayendra RajuNo ratings yet
- Cross Talk Effect and Shielding: RSK DesignDocument8 pagesCross Talk Effect and Shielding: RSK DesignVamsi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Physical DesignDocument52 pagesPhysical Designsandyp21No ratings yet
- 4101 - PowerGridVerif - WP - IR em XT Good PDFDocument14 pages4101 - PowerGridVerif - WP - IR em XT Good PDFKhadar BashaNo ratings yet
- DRAM Lecture2Document32 pagesDRAM Lecture2santanu_sinha87No ratings yet
- Crosstalk AnalysisDocument26 pagesCrosstalk AnalysisVinit PatelNo ratings yet
- Interconnect Noise Optimization in Nanometer TechnologiesDocument145 pagesInterconnect Noise Optimization in Nanometer TechnologiesSmile NagsNo ratings yet
- General Digital 1. General Digital Design Questions Design QuestionsDocument44 pagesGeneral Digital 1. General Digital Design Questions Design QuestionsAbdul KhaliqNo ratings yet
- InterconnectDocument32 pagesInterconnectLouisNo ratings yet
- Anil Resume NewDocument5 pagesAnil Resume NewVishnuGundaNo ratings yet
- VLSI Physical Design - Physical Design Interview Question Part 2Document2 pagesVLSI Physical Design - Physical Design Interview Question Part 2srinathNo ratings yet
- VLSI Interview Questions and AnswersDocument5 pagesVLSI Interview Questions and AnswersMahesh S GourNo ratings yet
- 28Nm and Below, New Path and Beyond: Danny Rittman PHDDocument15 pages28Nm and Below, New Path and Beyond: Danny Rittman PHDAbhesh Kumar TripathiNo ratings yet
- Vector-Based Peak Current Analysis During Wafer Test of Flip-Chip DesignsDocument206 pagesVector-Based Peak Current Analysis During Wafer Test of Flip-Chip DesignsLakshman YandapalliNo ratings yet
- Product How To Fully Utilize TSMC S 28HPC ProcessDocument8 pagesProduct How To Fully Utilize TSMC S 28HPC ProcessvpsampathNo ratings yet
- Basic of Timing Analysis in Physical Design - VLSI ConceptsDocument5 pagesBasic of Timing Analysis in Physical Design - VLSI ConceptsIlaiyaveni IyanduraiNo ratings yet
- Io PadsDocument5 pagesIo PadsKislay AnandNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Voltage DropDocument7 pagesDynamic Voltage DropBaluvu JagadishNo ratings yet
- Antenna EffectDocument12 pagesAntenna EffectrevanuNo ratings yet
- Analog Layout TipsDocument4 pagesAnalog Layout TipsmouneshskNo ratings yet
- Lesson8 CMOS GatesDocument33 pagesLesson8 CMOS GatestienchuanNo ratings yet
- VLSI Physical Design - STA Interview Questions Part 1Document2 pagesVLSI Physical Design - STA Interview Questions Part 1srinathNo ratings yet
- VLSI Physical Design - Physical Design (Power Planning) Interview Question Part 5Document2 pagesVLSI Physical Design - Physical Design (Power Planning) Interview Question Part 5srinath100% (1)
- Introduction To Liberty - CCS, ECSM and NDLMDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Liberty - CCS, ECSM and NDLMStudentNo ratings yet
- Low Power Vlsi Design1Document23 pagesLow Power Vlsi Design1Shruthi GourishettiNo ratings yet
- Placement Issues and Fixes - NishanthDocument15 pagesPlacement Issues and Fixes - NishanthNishanth GowdaNo ratings yet
- Vlsi DesignDocument31 pagesVlsi Designajas777BNo ratings yet
- Net Delay Is Calculated Using Rs and CsDocument12 pagesNet Delay Is Calculated Using Rs and CsemaNo ratings yet
- Congestion Driven PlacementDocument25 pagesCongestion Driven PlacementJayanth bemesettyNo ratings yet
- An Efficient RDL Routing For Flip Chip DesignsDocument10 pagesAn Efficient RDL Routing For Flip Chip DesignsAparna TiwariNo ratings yet
- LVF Variation ModellingDocument5 pagesLVF Variation ModellingKishore RoyNo ratings yet
- VLSI Interview QuestionsDocument19 pagesVLSI Interview QuestionssamNo ratings yet
- PD FlowDocument6 pagesPD FlowUTtNo ratings yet
- (Selected) LVS Is That Simple (Digital Backend Physical Verification) - Lvs Verification-CSDN BlogDocument9 pages(Selected) LVS Is That Simple (Digital Backend Physical Verification) - Lvs Verification-CSDN BlogAgnathavasiNo ratings yet
- CMOS Interview QuestionsDocument52 pagesCMOS Interview QuestionsKAMARUDHEEN KP100% (1)
- VLSI Routing InformationDocument23 pagesVLSI Routing InformationSwathi KambleNo ratings yet
- ARM ArchitectureDocument6 pagesARM ArchitectureCarlos AraujoNo ratings yet
- Tips For Macro PlacementDocument1 pageTips For Macro Placementrashmi sNo ratings yet
- Primetime: Golden Timing Signoff Solution and EnvironmentDocument7 pagesPrimetime: Golden Timing Signoff Solution and Environmentsubrahmanya_rao_1No ratings yet
- Standard Cell LibraryDocument46 pagesStandard Cell LibraryAjay G BellamNo ratings yet
- Migration in Solid State MaterialsDocument15 pagesMigration in Solid State MaterialsNitin PatelNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Design AutomationDocument31 pagesVlsi Design AutomationNischita KeerthiNo ratings yet
- Ec1401 Vlsi DesignDocument18 pagesEc1401 Vlsi DesignChaitanya PrabhuNo ratings yet
- AOCVDocument9 pagesAOCVcherry987100% (1)
- Synthesis QuestionsDocument4 pagesSynthesis QuestionsSupraja VedulaNo ratings yet
- Static vs. Dynamic Timing AnalysisDocument8 pagesStatic vs. Dynamic Timing Analysisd-fbuser-61705927No ratings yet
- ASIC-System On Chip-VLSI Design - Clock GatingDocument4 pagesASIC-System On Chip-VLSI Design - Clock Gatinguni_saraNo ratings yet
- Physical Design Objective Type of Questions and AnswersDocument7 pagesPhysical Design Objective Type of Questions and AnswersDivya Jiya0% (1)
- Vlsi Mitra DefinitionsDocument5 pagesVlsi Mitra DefinitionsVamsi Krishna100% (1)
- Electronics TXT Book - I PUCDocument356 pagesElectronics TXT Book - I PUCAnalog LayoutNo ratings yet
- Ph.D. Entrance Test Syllabus For Electronics and Communication EngineeringDocument2 pagesPh.D. Entrance Test Syllabus For Electronics and Communication EngineeringAnalog LayoutNo ratings yet
- Lecture8 PDFDocument24 pagesLecture8 PDFAnalog LayoutNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument6 pagesAssignmentAnalog LayoutNo ratings yet
- Proven Perimeter Protection: Single-Platform SimplicityDocument6 pagesProven Perimeter Protection: Single-Platform SimplicitytecksanNo ratings yet
- LC-3 Assembly LanguageDocument18 pagesLC-3 Assembly LanguageElad TalicNo ratings yet
- Seminar On: Hadoop TechnologyDocument13 pagesSeminar On: Hadoop TechnologySAV SportsNo ratings yet
- COP User Manual 2.0 PDFDocument5 pagesCOP User Manual 2.0 PDFخالدعبدالله100% (1)
- Email Security PolicyDocument3 pagesEmail Security PolicycroslutNo ratings yet
- Ip Profiling SytemDocument72 pagesIp Profiling Sytemjohnraymart colasitoNo ratings yet
- Andy CrowDocument37 pagesAndy CrowJobin JohnNo ratings yet
- 100 Watts OTL Amplifier Circuit Using Transistor MJ15003Document7 pages100 Watts OTL Amplifier Circuit Using Transistor MJ15003metinprivat01No ratings yet
- Entity Properties and Parameters 7 1 5Document623 pagesEntity Properties and Parameters 7 1 5Anonymous GtBrT1No ratings yet
- Philips FWC170Document54 pagesPhilips FWC170Luis Nava CastilloNo ratings yet
- Pascal Ehimare,: Popm, AsmDocument2 pagesPascal Ehimare,: Popm, AsmharshNo ratings yet
- L5 L6 L7 L8 L9 - Project ManagementDocument94 pagesL5 L6 L7 L8 L9 - Project Managementapi-19922408No ratings yet
- BS-240Pro&240E New Service Manual V3.0 enDocument419 pagesBS-240Pro&240E New Service Manual V3.0 enXavieltNo ratings yet
- Cable Design User GuideDocument84 pagesCable Design User GuidelumagbasNo ratings yet
- Huawei HG630 QSGDocument18 pagesHuawei HG630 QSGAmer EzahirNo ratings yet
- Ninjaadvancedsurgeryaox (Marked)Document4 pagesNinjaadvancedsurgeryaox (Marked)rersrsr0% (1)
- What Is Github Actions?: Benefits and ExamplesDocument13 pagesWhat Is Github Actions?: Benefits and Examplesniraj kulhariNo ratings yet
- BSNL VMC AN1020-21 (Detailed Visual Guide)Document14 pagesBSNL VMC AN1020-21 (Detailed Visual Guide)Nagaraju Gunturu100% (1)
- Grade 10 Computer Appications Project PDFDocument45 pagesGrade 10 Computer Appications Project PDFkarthikeya kakarlapudi100% (1)
- PDF Dis StandardsDocument35 pagesPDF Dis StandardsEdén PastoraNo ratings yet
- Sentiment Analysis of Stock News Using NLTKDocument6 pagesSentiment Analysis of Stock News Using NLTKVIVA-TECH IJRINo ratings yet
- Display TechnologyDocument63 pagesDisplay Technologyanalog changeNo ratings yet
- Mackie 802VLZ3 HookupsDocument5 pagesMackie 802VLZ3 HookupsDavid BenkoNo ratings yet
- CG PDFDocument63 pagesCG PDFVarnakeepcreating Varna100% (1)
- Understand JSPDocument30 pagesUnderstand JSPMohdAsyrafZNo ratings yet
- Why Implements AmDocument23 pagesWhy Implements Amdayanx2014No ratings yet
- Integral Cycle Speed Control of Single Phase Induction Motor Using At89c51 Microcontroller PDFDocument47 pagesIntegral Cycle Speed Control of Single Phase Induction Motor Using At89c51 Microcontroller PDFrijilpoothadiNo ratings yet
- Cover Letter Examples For Every Type of Job Seeker - The MuseDocument14 pagesCover Letter Examples For Every Type of Job Seeker - The MuseJimmyNo ratings yet
- Cinimamachine TuteDocument7 pagesCinimamachine TutegregoryNo ratings yet
- Retrostar (Quick Play)Document42 pagesRetrostar (Quick Play)Stephen SandersNo ratings yet