Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mass Culturing of Stem and Bulb Nematode (Ditylenchus Dipsaci) For Use in Screeni̇ng and İmpression Training On Carrot Discs
Uploaded by
IJEAB JournalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mass Culturing of Stem and Bulb Nematode (Ditylenchus Dipsaci) For Use in Screeni̇ng and İmpression Training On Carrot Discs
Uploaded by
IJEAB JournalCopyright:
Available Formats
International Journal of Environment, Agriculture and Biotechnology (IJEAB) Vol-2, Issue-6, Nov-Dec- 2017
http://dx.doi.org/10.22161/ijeab/2.6.48 ISSN: 2456-1878
Mass Culturing of Stem and Bulb Nematode
(Ditylenchus dipsaci) for use in screenİng and
İmpression Training on Carrot Discs
Tohid Behmand1, Lerzan Ozturk2, İbrahim Halil Elekcioğlu1
1
Çukurova University, Faculty of Agriculture, Department of Plant Protection, 01360, Balcalı, Adana, Turkey,
2
Viticulture Research Institute ,Tekirdag, Turkey
Abstract— Stem and bulb nematode, Ditylenchus dipsaci, is carrot discs was used for grown nematodes. This technique
a very important plant parasitic nematode, has a very wide is workable to migratory nematodes (Ditylenchusspp) for
host range and causes economic yield losses in many serial manufacture of nematode for experimental aim, direct
cultural plants in worldwide. Its races are very diverse and studies of nematodes, screening trial and increase
found in most temperate areas of the world. D. dipsaci is a nematodes. The most advantage this method to save
migratory endoparasite, has the ability to enter into a timethat,allow a quick mass production of nematode. Plant
dormancy stage. Genetic resistance offers one of the best parasitic nematode can only develop in fresh root tissue this
control methods within the integrated pest management method help Ditylenchusdipsaci nematode to be produce on
strategies for D. dipsaci. However mass rearing of stem and sterilised carrot discs in petri dishes in an incubator more
bulb nematode requires for the resistant studies including than in root plant under laboratory condition. Nematodes
screening for this nematode species. The aim of study is feeding two the type of plant tissue that necessary for their
focused on alternative rearing methods using carrot discs culture their can feed as migratory endoparasites and
as a food source, culturing medium and provide a clearly ectoparasites.Sedentary endoparasites nematode need
outlined and visually informative guide. Carrot discs enable individuate tissue for reproduction but it is the opposite
the rearing of high numbers of individuals of D. dipsaci for about migratory endoparasites nematodes like
timely use in experiments and for screening purposes in Ditylenchusdipsaci that do not require for it and reproduce
under sterile conditions to provide a clean, same and pure easily on undifferentiated tissue like as carrot disk and it has
source of inoculum. The carrot disc method has been shown been indicated to be suitable tissue for their
to be suitable for stem and bulb nematode multiplication. multiplication.This technique provides a basic facility for
Keyword—Resistant,stem and bulb migratory endoparasites nematodes to be reared carrot discs
nematode,culture,Technique. in petri dishes inside an incubator more than in root of plant
under greenhouse condition (8).Also, This study provides a
I. SUMMARY protocol for the use carrot to produce and extract stem and
Nematologists have a long time were looking to find the bulb nematodes from carrot disk culture.
best methods for culture and increase population density of
plant parasitic nematodes (5)., but these techniques II. MATERIAL AND METHOD
generally has not easy. Although,the three most commenly We choose infected roots or soil with Ditylenchusdipsaci
used techniques for culturing migratory endoparasitic for extraction of the nematode to be culture.Nematodes
nematodes, including alfa alfa callus (1,3,6),root expland were inoculated on the carrot disc.The suggested
(4),and carrot discs (5) have been published. We present in temperature for rapid multiplication between 19°c and 23°c
this study tried to use carrot cultur method to increase depending on nematode reproduction population must be
population density of nematodes. Ditylenchus dipsaci or sub culture every 4-6 weeks, the development rate
stem nematode, attacks more than 1200 type of wild and decreased when Temperatureincreased up to 30° or
cultivated plants.many agriculture plants are hosts for this decrease down to 18 °c.The first to start a carrot culture,
species of nematode.D.dipsaci live mostly as a migratory weselected clean carrots without overly thick and cracks,
endoparasite in different parts of plants like stem,leaves and Washes selected carrots under distilled water, sterilise all of
flowers.In vitro rearing of Ditylenchusdipsaci nematodes on equipment and materials by autoclaving at 121°c for 20
www.ijeab.com Page | 3148
International Journal of Environment, Agriculture and Biotechnology (IJEAB) Vol-2, Issue-6, Nov-Dec- 2017
http://dx.doi.org/10.22161/ijeab/2.6.48 ISSN: 2456-1878
minutes and sterilise the workingand tools surface with 96% remain viable for up to 1-2 week. For a more completed
ethanol and hold the carrot with 96% ethanol and flame collection, the first cut carrot disc to small pieces and placed
over spirit lamp repeat this for three times.Also, in the petri dishes with sterile water and let the nematodes
westerilised all of the equipment including: forceps,peeler migrate freely into the petri, thenextracted nematodes
and knife with ethanol and flaming eachbefore used them counted under binocular microscope and placed in the flask.
every time. We peeled the carrot with the sterilised peeler
and Cut the peeled carrot into 5 mm thick section of 3-4 cm III. RESULT
diameter and transfer the cut carrot disc into sterilise petri The number of nematodes extracted from the 45,60,90 and
dishes by using the sterilised forceps. Disk must not be less 120 days callus culture are listed (Table 1). 2 or 3 thousands
than 3 cm diameter, then transfer the carrot discs into of nematodes can be extracted out of one carrot discs after
sterilise glass petri dishes (5-6 cm diameter). We stored 45-60 days of culture. However, the number of nematode is
them in the dark incubator to keep underground condition different use of nematode species and geographical
for 3-4 weeks at 19-23°c.Also,it was necessary control population The greatest number of nematodes was recoverd
carrot discs best signal of healthy cultures during incubation from the 45 old day with temperature of 19 °c to 23°c,which
every week. After 3-4 weeks nematodes were started to exit yielded a greater than 1,2 and 3 fold in number of
the carrot and when nutrient in carrots go to become empty nematodes that was observed from the 60, 90 and 120 days
it was indicator for harvesting the nematodes .The other with same temperature.The lowest number of nematodes
words, incubation time and the initial inoculum effected recovery was from the 120 days with 25°c to 30°c in the
how soon the nutrients become empty. For selection of carrot disk taht was only slightly increased from the initial
nematodes we placed a concentrated of the nematode inoculum levels.The number of nematodes extracted from
extract into a small (3-5 cm diam.) andaccounted under callus after 45 days with 19°c to 23°c showed potential
light microscope.The number of nematode for inoculation yields using this technique for us (Table 1).The other
depends how many carrots are to be required. However,it word,extracted of more than 3400 nematodes were observed
was suggested to inoculate at least 100-150 nematodes on formthe 45 days with 19°c to 23°c. Therfore, temperature
one carrot disc and not inoculate less than 100 of them.It between 19 °c to 23°c could increase the cultivation
was recommended to inoculate at least five replicates from potential of Ditylenchus dipsaci nematode.Also,These result
petri dishes .For mass multiplication we increasednumber of indicated that, when as the number of days increased and
inoculated nematode on one carrot disc and selected female the temperature dropped under 19°c or increased up to
and male of the Ditylenchusdipsaci nematode and placed 23°c, the number of nematodes decreased.Becuace of that
them in a glass petri including sterile distilled water.The we observedthat The stem and bulb (ditylenchus dipsaci)
aim was to deliver 50-80 nematodes per disc in a maximum nematode was suited for culture carrot disk and the yield of
of two 50 microliter smaller drops of nematode suspension eggs and increased population density of this migratory
transfer the nematodes.The number of nematodes in the endoparasite nematode was much better by this technique
suspension were determined the number to transfer. It was than other extraction and culture methodes
suggested use about 80-150 nematodes for mass (2,5,7,8,9).Therfore, the carrot callus method was suitable
multiplication. After that, we placed the carrot disk in an and easy to use and produce high number of Ditylenchus
incubator for 5-6 week, after thanthe nematodes were dipsaci(Fig 1).
harvested and stored in the fridge at 5°c,the nematode can
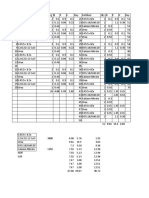
Table.1: The effect of different days and temperature on the development of the Ditylenchus dipsaci nematode.
Nematode number 15-18°c 19-23°c 25-30°c
45 day-old cultur 2200 3400 1400
60 day-old culture 2000 3000 1100
90 day-old culture 1100 1400 900
120 day-old culture 600 800 500
www.ijeab.com Page | 3149
International Journal of Environment, Agriculture and Biotechnology (IJEAB) Vol-2, Issue-6, Nov-Dec- 2017
http://dx.doi.org/10.22161/ijeab/2.6.48 ISSN: 2456-1878
3500
3000
2500
Nematode. No 15-18°c
2000
Nematode. No 19-23°c
1500
Nematode. No 25-30°c
1000
500
0
45 day 60 day 90 day 120 day
Fig.1: Mixed life stage and eggs number ofDitylenchus dipsaci nematode from 45,60,90 and 120 days old carrot callus culture.
IV. DISCUSSION [5] Lawn, D. A., and G. R. Noel. 1984. Monoxenic
This protocol presented is now routinly used in our culture of Pratylenchus scribneri on carrot disks.
laboratory.The condition of carrots was importent, work (7) Proceedings of the First International Congress of
has shown that carrots used in carrot disk culture must be Nematology. P. 47 (Abstr.)
freshly harvested from the field and greenery intact before [6] Myers, R. J., W. A. Feder, and P. C. Hutchens. 1965.
use.Also, carrots that are badly cut must be avoided.Culture The rearing ofRadopholus similis (Cobb) Thorne on
can remain available for up to 2 months and are easly grapefruit, okra, and alfalfa root callus tissues.
generated.Once the nematode are established on the callus Proceedings of the Helminthological Society of
can be divided to small infested piece and transferred Washington 32:94-95
directly to make a new carrot culture.The yield of eggs and [7] Moody, E. H., B. F. Lownsbery, and J. M. Ahmed.
increased population density of this migratory endoparasite 1973. Culture of the root-lesion nematode
nematode was much better by this technique than other Pratylenchus vulnus on carrot disks. Journal of
extraction and culture methodes (2,5,7,8,9). Nematology 5:225-226.
[8] O'Bannon,J. H., and A. L. Taylor. 1968. Migratory
REFERENCES endoparasitic nematodes reared on carrot discs.
[1] Bingefors, S., and K. B. Eriksson. 1963. Rearing stem Phytopathology 58:385.
nematode inoculum on tissue culture: Preliminary [9] Young, T. W. 1954. An incubation method for
report. Landbrukshogskolan Annaler 29: 107-118. collecting migratory endo-parasitic nematodes. Plant
[2] Huettel, R. N. 1985. Carrot disc culture. Pp. 212 in B. Disease Reporter 38:794-795
M. Zuckerman, W. F. Mai, and M. B. Harrison, eds.
Plant nematology, laboratory manual. University of
Massachusetts Agricultural Experiment Station,
University of Massachusetts, Amherst.
[3] Krusberg, L. R. 1961. Studies on the culturing and
parasitism of plant-parasitic nematodes, in particular
Ditylenchus dipsaci and Aphelenchoides ritzemabosi
on alfalfa tissues. Nematologica 6:181-200.
[4] Lauritis, J. A., R. V. Rebois, and L. I. Graney. 1982.
Gnotobiotic cultivation of Heterodera glycines
Ichinohe on Glycine max (L.) Merr. Journal of
Nematology 14:422-424..
www.ijeab.com Page | 3150
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Labor Production TableDocument6 pagesLabor Production TableMelgaszarGerry80% (5)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument3 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogEG Bitong-Alamani100% (2)
- Environmental Factors and Reactor Configurations in Biogas Production From Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Fruit WastesDocument14 pagesEnvironmental Factors and Reactor Configurations in Biogas Production From Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Fruit WastesIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- A Review On Feed Additives Used in Fish DietDocument7 pagesA Review On Feed Additives Used in Fish DietIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- Growth, Yield and Yield Components of Sesame (Sesamumindicum L.) As Influenced by Crop Variety and Different Rates of Herbicides in Mubi, Adamawa State, Nigeria.Document11 pagesGrowth, Yield and Yield Components of Sesame (Sesamumindicum L.) As Influenced by Crop Variety and Different Rates of Herbicides in Mubi, Adamawa State, Nigeria.IJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- The Value Connotation of Evidence Evaluation On Forensic ConclusionsDocument4 pagesThe Value Connotation of Evidence Evaluation On Forensic ConclusionsIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- Flood Modeling and Vulnerability Analysis of Abia State Using Remote Sensing and Flood ModelerDocument5 pagesFlood Modeling and Vulnerability Analysis of Abia State Using Remote Sensing and Flood ModelerIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain of Fish Performance and Analysis Fisherman Share in Paotere Landing Fish, Makassar CityDocument5 pagesSupply Chain of Fish Performance and Analysis Fisherman Share in Paotere Landing Fish, Makassar CityIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- Optimized Recombinant Bacillus Subtilis 168 Whole-Cell Catalyzes One-Step Biosynthesis of High Fructose SyrupDocument9 pagesOptimized Recombinant Bacillus Subtilis 168 Whole-Cell Catalyzes One-Step Biosynthesis of High Fructose SyrupIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- The Impact of China's Fertilizer Industry De-Capacity On Agricultural Production CostsDocument10 pagesThe Impact of China's Fertilizer Industry De-Capacity On Agricultural Production CostsIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- Effect of The Marination Time & Marinade Ingredients On Sensory Evaluation of TawoukDocument5 pagesEffect of The Marination Time & Marinade Ingredients On Sensory Evaluation of TawoukIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- Observation of El Niño and La Niña Phenomena, On The Island of Sulawesi - Indonesia, Based On The Global Positioning System (GPS)Document7 pagesObservation of El Niño and La Niña Phenomena, On The Island of Sulawesi - Indonesia, Based On The Global Positioning System (GPS)IJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- Gender Involvement in Crop Production and Livestock Related Activities in Chitwan and Lamjung District of NepalDocument4 pagesGender Involvement in Crop Production and Livestock Related Activities in Chitwan and Lamjung District of NepalIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- 37IJEAB 102202130 MetabolicDocument12 pages37IJEAB 102202130 MetabolicIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- Nexus Between Climate Change and Agricultural Production in Odisha, India: An ARDL ApproachDocument9 pagesNexus Between Climate Change and Agricultural Production in Odisha, India: An ARDL ApproachIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- Development and Quality Evaluation of Ragi Supplemented CupcakesDocument4 pagesDevelopment and Quality Evaluation of Ragi Supplemented CupcakesIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- 37IJEAB 102202130 MetabolicDocument12 pages37IJEAB 102202130 MetabolicIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- Effect of Polysaccharides (Pectins) On Postprandial GlucoseDocument7 pagesEffect of Polysaccharides (Pectins) On Postprandial GlucoseIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- Current Biotechnological Applications of L-Amino Acid Deaminases For Keto Acids ProductionDocument11 pagesCurrent Biotechnological Applications of L-Amino Acid Deaminases For Keto Acids ProductionIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- Effect of Estrus Synchronization with Prostaglandins (PGF2Α) and Gonadothropin Realising Hormone (GNRH) on the Hematological Profile of Pasundan Heifers during PregnancyDocument6 pagesEffect of Estrus Synchronization with Prostaglandins (PGF2Α) and Gonadothropin Realising Hormone (GNRH) on the Hematological Profile of Pasundan Heifers during PregnancyIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- Prediction of High-Risk Probability Areas Under Current and Future Climate Scenarios in India For The Establishment of Fall ArmywormDocument30 pagesPrediction of High-Risk Probability Areas Under Current and Future Climate Scenarios in India For The Establishment of Fall ArmywormIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- Effect of Poultry Manure Amendment On The Distribution and Mobility of Heavy Metals in Naturally Contaminated Dump SoilDocument8 pagesEffect of Poultry Manure Amendment On The Distribution and Mobility of Heavy Metals in Naturally Contaminated Dump SoilIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- 36IJEAB 102202117 PerformanceDocument5 pages36IJEAB 102202117 PerformanceIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- 35IJEAB 102202112 EffectofDocument8 pages35IJEAB 102202112 EffectofIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- 34IJEAB 102202123 ComparativeDocument12 pages34IJEAB 102202123 ComparativeIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- Induction of Genetic Variation and Variability of Saudi Arabian Cultivars of WheatDocument11 pagesInduction of Genetic Variation and Variability of Saudi Arabian Cultivars of WheatIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- 38IJEAB 102202125 IsolationDocument9 pages38IJEAB 102202125 IsolationIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- 36IJEAB 102202117 PerformanceDocument5 pages36IJEAB 102202117 PerformanceIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- 38IJEAB 102202125 IsolationDocument9 pages38IJEAB 102202125 IsolationIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- Transfusion Transmissible Infections Among Voluntary Blood Donors in Port-Harcourt Metropolis, Rivers State, NigeriaDocument5 pagesTransfusion Transmissible Infections Among Voluntary Blood Donors in Port-Harcourt Metropolis, Rivers State, NigeriaIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- Contribution of Traditional Date Palm (Phoenix Sylvestris) Agroforestry in Income Generation and Livelihood Improvements: A Case of Jashore District, BangladeshDocument9 pagesContribution of Traditional Date Palm (Phoenix Sylvestris) Agroforestry in Income Generation and Livelihood Improvements: A Case of Jashore District, BangladeshIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- 35IJEAB 102202112 EffectofDocument8 pages35IJEAB 102202112 EffectofIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- Liste Des Pesticides Usage Agricole Commercialises Par Membres CropLife MarocDocument252 pagesListe Des Pesticides Usage Agricole Commercialises Par Membres CropLife MarocMohamed El AlamiNo ratings yet
- usefulPlantsOfIranIraq PDFDocument180 pagesusefulPlantsOfIranIraq PDFSarwat Naim SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- A) Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) - Also Known Simply As Portland Cement orDocument7 pagesA) Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) - Also Known Simply As Portland Cement orRoberto AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Vicia Pannonica - Hungarian VetchDocument4 pagesVicia Pannonica - Hungarian VetchennescribeNo ratings yet
- ICL Daily FertigationDocument7 pagesICL Daily FertigationVijay Varma RNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Soil in India and Their Specific Crops: Made ByDocument20 pagesDifferent Types of Soil in India and Their Specific Crops: Made ByriddhisnewworldNo ratings yet
- The Status of Temporary Immersion SystemDocument11 pagesThe Status of Temporary Immersion SystemaguilaquecaeNo ratings yet
- Stabilisation of Soft Clay Using Ground Granulated Blastfurnace Slag and LimeDocument7 pagesStabilisation of Soft Clay Using Ground Granulated Blastfurnace Slag and LimeVivek SvkNo ratings yet
- Basement Wall SPR NewDocument12 pagesBasement Wall SPR NewAnonymous O404LiV4CNo ratings yet
- African Tulip Tree PP64Document2 pagesAfrican Tulip Tree PP64Andry HarmonyNo ratings yet
- Atlas Brick PDFDocument1 pageAtlas Brick PDFBobNo ratings yet
- Aac BlocksDocument14 pagesAac Blocksanurag singhNo ratings yet
- Cactus and SucculentsDocument4 pagesCactus and Succulentsvandv printsNo ratings yet
- Science Tech Grade 4Document4 pagesScience Tech Grade 4Dennis Onchieku OnyandoNo ratings yet
- AAC Vs CLCDocument23 pagesAAC Vs CLCsandipgargNo ratings yet
- Science - Life Cycle of A PlantDocument31 pagesScience - Life Cycle of A PlantSetyo NugrohoNo ratings yet
- 8 Worksheet Reproduce FloweringDocument2 pages8 Worksheet Reproduce Floweringelsa khairunnisa100% (3)
- Straw Bale Gardening, Soiless Gardening Texas, Ellis CountyDocument13 pagesStraw Bale Gardening, Soiless Gardening Texas, Ellis CountyStrawbale100% (1)
- Humic Acid and Cultivar Effects On Growth, Yield, Vase Life, and Corm CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesHumic Acid and Cultivar Effects On Growth, Yield, Vase Life, and Corm Characteristicsyasir majeedNo ratings yet
- L8Document27 pagesL8Jose100% (1)
- Physical Properties of Sugarcane Pertaining To The Design of A Whole Stalk Sugarcane HarvesterDocument6 pagesPhysical Properties of Sugarcane Pertaining To The Design of A Whole Stalk Sugarcane HarvesterKen MaglinteNo ratings yet
- Plant Propagation For Successful Hydroponic Production PDFDocument23 pagesPlant Propagation For Successful Hydroponic Production PDFasdfNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam 1 - 2015 BOT 101Document12 pagesPractice Exam 1 - 2015 BOT 101Daniel GohNo ratings yet
- Influence of Curing On The Properties of High Volume Fly Ash ConcreteDocument8 pagesInfluence of Curing On The Properties of High Volume Fly Ash ConcreteGlobal Research and Development ServicesNo ratings yet
- New Hosts of Aeginetia PedunculataDocument3 pagesNew Hosts of Aeginetia PedunculataBikash Ranjan RayNo ratings yet
- Crop Training ReportDocument50 pagesCrop Training ReportByakatonda Jimmy100% (3)
- Civil Engineering MCQ'S: Ans. (D) Ans. (D)Document4 pagesCivil Engineering MCQ'S: Ans. (D) Ans. (D)NISHIKANTA MONDALNo ratings yet
- Management of Insect Pests of TobaccoDocument5 pagesManagement of Insect Pests of TobaccoStaidCasperNo ratings yet