Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Detailed Table of Contents Norton
Uploaded by
jeyaselvanm0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views8 pagesvibration
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentvibration
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views8 pagesDetailed Table of Contents Norton
Uploaded by
jeyaselvanmvibration
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
CONTENTS
Preface ................................................................................................................ xv
Part I Kinematics of Mechanisms .................................................................. 1
Chapter 1 Introduction .................................................................................. 3
1.0 Purpose .............................................................................................................. 3
1.1 Kinematics and Kinetics .................................................................................. 3
1.2 Mechanisms and Machines ........................................................................... 4
1.3 A Brief History of Kinematics ........................................................................... 5
1.4 Applications of Kinematics ............................................................................. 6
1.5 The Design Process ........................................................................................... 7
Design, Invention, Creativity ....................................................................... 7
Identification of Need ................................................................................. 8
Background Research ................................................................................ 9
Goal Statement ......................................................................................... 10
Performance Specifications ..................................................................... 10
Ideation and Invention ............................................................................. 10
Analysis ....................................................................................................... 12
Selection ..................................................................................................... 13
Detailed Design ......................................................................................... 13
Prototyping and Testing ............................................................................ 13
Production .................................................................................................. 14
1.6 Other Approaches to Design ....................................................................... 15
Axiomatic Design ....................................................................................... 15
1.7 Multiple Solutions ............................................................................................ 16
1.8 Human Factors Engineering ......................................................................... 16
1.9 The Engineering Report ................................................................................. 17
1.10 Units ................................................................................................................... 17
1.11 A Design Case Study ..................................................................................... 18
Educating for Creativity in Engineering ................................................... 18
1.12 Whats to Come ............................................................................................. 24
1.13 References ....................................................................................................... 24
1.14 Bibliography .................................................................................................... 25
Chapter 2 Kinematics Fundamentals ........................................................ 28
2.0 Introduction ..................................................................................................... 28
2.1 Degrees of Freedom (DOF) or Mobility ...................................................... 28
2.2 Types of Motion ............................................................................................... 29
2.3 Links, Joints, and Kinematic Chains ............................................................ 30
2.4 Drawing Kinematic Diagrams ...................................................................... 34
2.5 Determining Degree of Freedom or Mobility ............................................ 35
Degree of Freedom (Mobility) in Planar Mechanisms ........................... 36
Degree of Freedom (Mobility) in Spatial Mechanisms .......................... 38
2.6 Mechanisms and Structures ......................................................................... 38
2.7 Number Synthesis ........................................................................................... 40
2.8 Paradoxes ........................................................................................................ 44
viii KINEMATICS AND DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY CONTENTS
2.9 Isomers .............................................................................................................. 45
2.10 Linkage Transformation ................................................................................. 46
2.11 Intermittent Motion ........................................................................................ 51
2.12 Inversion ........................................................................................................... 51
2.13 The Grashof Condition .................................................................................. 53
Classification of the Fourbar Linkage ...................................................... 58
2.14 Linkages of More Than Four Bars ................................................................. 60
Geared Fivebar Linkages ......................................................................... 60
Sixbar Linkages ........................................................................................... 61
Grashof-Type Rotatability Criteria for Higher-Order Linkages ............... 61
2.15 Springs as Links ................................................................................................ 63
2.16 Compliant Mechanisms ................................................................................ 63
2.17 Micro Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) ............................................... 65
2.18 Practical Considerations ............................................................................... 67
Pin Joints versus Sliders and Half Joints .................................................... 67
Cantilever or Straddle Mount? ................................................................. 69
Short Links ................................................................................................ 70
Bearing Ratio .............................................................................................. 70
Commercial Slides ..................................................................................... 71
Linkages versus Cams ............................................................................... 71
2.19 Motors and Drivers ......................................................................................... 72
Electric Motors ........................................................................................... 72
Air and Hydraulic Motors .......................................................................... 77
Air ad Hydraulic Cylinders ......................................................................... 77
Solenoids ................................................................................................. 78
2.20 References ....................................................................................................... 78
2.21 Problems ........................................................................................................... 79
Chapter 3 Graphical Linkage Synthesis ................................................... 92
3.0 Introduction ..................................................................................................... 92
3.1 Synthesis ........................................................................................................... 92
3.2 Function, Path, and Motion Generation .................................................... 94
3.3 Limiting Conditions ......................................................................................... 96
3.4 Dimensional Synthesis .................................................................................... 98
Two-Position Synthesis ................................................................................ 99
Three-Position Synthesis with Specified Moving Pivots ......................... 105
Three-Position Synthesis with Alternate Moving Pivots ......................... 106
Three-Position Synthesis with Specified Fixed Pivots ............................. 109
Position Synthesis for More Than Three Positions ................................... 113
3.5 Quick-Return Mechanisms .......................................................................... 113
Fourbar Quick-Return .............................................................................. 114
Sixbar Quick-Return ................................................................................. 116
3.6 Coupler Curves ............................................................................................. 119
3.7 Cognates ....................................................................................................... 128
Parallel Motion ......................................................................................... 133
Geared Fivebar Cognates of the Fourbar ............................................ 135
3.8 Straight-Line Mechanisms ........................................................................... 136
Designing Optimum Straight-Line Fourbar Linkages ............................ 139
3.9 Dwell Mechanisms ........................................................................................ 143
Single-Dwell Linkages .............................................................................. 143
Double-Dwell Linkages ............................................................................ 146
3.10 Other Useful Linkages* ................................................................................. 148
Constant Velocity Piston Motion ............................................................ 148
Large Angular Excursion Rocker Motion ............................................... 149
Remote Center Circular Motion ............................................................ 151
3.11 References ..................................................................................................... 152
CONTENTS ix
3.12 Bibliography .................................................................................................. 153
3.13 Problems ......................................................................................................... 154
3.14 Projects ........................................................................................................... 164
Chapter 4 Position Analysis ....................................................................... 168
4.0 Introduction ................................................................................................... 168
4.1 Coordinate systems ..................................................................................... 170
4.2 Position and Displacement ......................................................................... 170
Position ...................................................................................................... 170
Coordinate Transformation .................................................................... 171
Displacement ........................................................................................... 171
4.3 Translation, Rotation, and Complex Motion ............................................ 173
Translation ................................................................................................ 173
Rotation .................................................................................................... 173
Complex Motion ...................................................................................... 174
Theorems .................................................................................................. 175
4.4 Graphical Position Analysis of Linkages ................................................... 175
4.5 Algebraic Position Analysis of Linkages .................................................... 177
Vector Loop Representation of Linkages ............................................. 178
Complex Numbers as Vectors ............................................................... 178
The Vector Loop Equation for a Fourbar Linkage ................................ 180
4.6 The Fourbar Slider-Crank Position Solution ............................................... 184
4.7 An Inverted Slider-Crank Position Solution ............................................... 186
4.8 Linkages of More Than Four Bars ............................................................... 188
The Geared Fivebar Linkage .................................................................. 188
Sixbar Linkages ......................................................................................... 191
4.9 Position of any Point on a Linkage ............................................................ 192
4.10 Transmission Angles ...................................................................................... 193
Extreme Values of the Transmission Angle ............................................ 194
4.11 Toggle Positions ............................................................................................. 196
4.12 Circuits and Branches in Linkages ............................................................. 197
4.13 Newton-Raphson Solution Method ........................................................... 198
One-Dimensional Root-Finding (Newtons Method) ............................ 199
Multidimensional Root-Finding (Newton-Raphson Method) ............... 200
Newton-Raphson Solution for the Fourbar Linkage ............................. 201
Equation Solvers ....................................................................................... 202
4.14 References ..................................................................................................... 202
4.15 Problems ......................................................................................................... 203
Chapter 5 Analytical Linkage Synthesis ................................................. 214
5.0 Introduction ................................................................................................... 214
5.1 Types of Kinematic Synthesis ...................................................................... 214
5.2 Two-Position Synthesis for Rocker Output ................................................. 215
5.3 Precision Points .............................................................................................. 217
5.4 Two-Position Motion Generation by Analytical Synthesis ..................... 217
5.5 Comparison of Analytical and Graphical Two-Position Synthesis ....... 224
5.6 Simultaneous Equation Solution ................................................................. 226
5.7 Three-Position Motion Generation by Analytical Synthesis ................... 229
5.8 Comparison of Analytical and Graphical Three-Position Synthesis .... 234
5.9 Synthesis for a Specified Fixed Pivot Location* ....................................... 238
5.10 Center-Point and Circle-Point Circles ....................................................... 244
5.11 Four- and Five-Position Analytical Synthesis ............................................ 247
5.12 Analytical Synthesis of a Path Generator with Prescribed Timing ....... 248
5.13 Analytical Synthesis of a Fourbar Function Generator .......................... 248
x KINEMATICS AND DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY CONTENTS
5.14 Other Linkage Synthesis Methods .............................................................. 251
Precision Point Methods .......................................................................... 252
Coupler Curve Equation Methods ......................................................... 254
Optimization Methods ............................................................................. 255
5.15 References ..................................................................................................... 258
5.16 Problems ......................................................................................................... 260
Chapter 6 Velocity Analysis ...................................................................... 269
6.0 Introduction ................................................................................................... 269
6.1 Definition of Velocity .................................................................................... 269
6.2 Graphical Velocity Analysis ........................................................................ 272
6.3 Instant Centers of Velocity .......................................................................... 277
6.4 Velocity Analysis with Instant Centers ....................................................... 284
Angular Velocity Ratio ............................................................................ 285
Mechanical Advantage ......................................................................... 287
Using Instant Centers in Linkage Design ................................................ 289
6.5 Centrodes ...................................................................................................... 291
A Linkless Linkage ................................................................................. 294
Cusps ........................................................................................................ 295
6.6 Velocity of Slip ............................................................................................... 295
6.7 Analytical Solutions for Velocity Analysis .................................................. 299
The Fourbar Pin-Jointed Linkage ............................................................ 299
The Fourbar Slider-Crank ......................................................................... 302
The Fourbar Inverted Slider-Crank ......................................................... 303
6.8 Velocity Analysis of the Geared Fivebar Linkage ................................... 306
6.9 Velocity of any Point on a Linkage ........................................................... 307
6.10 References ..................................................................................................... 308
6.11 Problems ......................................................................................................... 308
Chapter 7 Acceleration Analysis ............................................................. 330
7.0 Introduction ................................................................................................... 330
7.1 Definition of Acceleration .......................................................................... 330
7.2 Graphical Acceleration Analysis ............................................................... 333
7.3 Analytical Solutions for Acceleration Analysis ........................................ 338
The Fourbar Pin-Jointed Linkage ............................................................ 338
The Fourbar Slider-Crank ......................................................................... 341
Coriolis Acceleration ............................................................................... 343
The Fourbar Inverted Slider-Crank ......................................................... 345
7.4 Acceleration Analysis of the Geared Fivebar Linkage ......................... 349
7.5 Acceleration of any Point on a Linkage .................................................. 350
7.6 Human Tolerance of Acceleration ............................................................ 352
7.7 Jerk .................................................................................................................. 355
7.8 Linkages of n Bars ......................................................................................... 357
7.9 References ..................................................................................................... 357
7.10 Problems ......................................................................................................... 357
Chapter 8 Cam Design .............................................................................. 377
8.0 Introduction ................................................................................................... 377
8.1 Cam Terminology ......................................................................................... 378
Type of Follower Motion .......................................................................... 379
Type of Joint Closure ............................................................................... 380
Type of Follower ....................................................................................... 380
Type of Cam ............................................................................................ 380
CONTENTS xi
Type of Motion Constraints ..................................................................... 383
Type of Motion Program ......................................................................... 383
8.2 S V A J Diagrams ......................................................................................... 384
8.3 Double-Dwell Cam DesignChoosing S V A J Functions ..................... 385
The Fundamental Law of Cam Design .................................................. 388
Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) ............................................................. 389
Cycloidal Displacement ......................................................................... 391
Combined Functions ............................................................................... 394
The SCCA Family of Double-Dwell Functions ........................................ 397
Polynomial Functions ............................................................................... 407
Double-Dwell Applications of Polynomials ........................................... 408
8.4 Single-Dwell Cam DesignChoosing S V A J Functions ........................ 411
Single-Dwell Applications of Polynomials .............................................. 414
Effect of Asymmetry on the Rise-Fall Polynomial Solution ................... 417
8.5 Critical Path Motion (CPM) ........................................................................ 420
Polynomials Used for Critical Path Motion ............................................ 421
8.6 Sizing the CamPressure Angle and Radius of Curvature ................... 429
Pressure AngleTranslating Roller Followers ......................................... 429
Choosing a Prime Circle Radius ............................................................. 433
Overturning MomentTranslating Flat-Faced Follower ...................... 434
Radius of CurvatureTranslating Roller Follower ................................. 434
Radius of CurvatureTranslating Flat-Faced Follower ........................ 439
8.7 Practical Design Considerations ................................................................ 443
Translating or Oscillating Follower? ........................................................ 443
Force- or Form-Closed? .......................................................................... 444
Radial or Axial Cam? .............................................................................. 445
Roller or Flat-Faced Follower? ................................................................ 445
To Dwell or Not to Dwell? ........................................................................ 446
To Grind or Not to Grind? ........................................................................ 446
To Lubricate or Not to Lubricate? .......................................................... 447
8.8 References ..................................................................................................... 447
8.9 Problems ......................................................................................................... 448
8.10 Projects ........................................................................................................... 451
Chapter 9 Gear Trains ................................................................................ 454
9.0 Introduction ................................................................................................... 454
9.1 Rolling Cylinders ............................................................................................ 455
9.2 The Fundamental Law of Gearing ............................................................ 456
The Involute Tooth Form .......................................................................... 457
Pressure Angle .......................................................................................... 459
Changing Center Distance .................................................................... 459
Backlash ................................................................................................... 460
9.3 Gear Tooth Nomenclature ......................................................................... 461
9.4 Interference and Undercutting ................................................................. 464
Unequal-Addendum Tooth Forms ......................................................... 465
9.5 Contact Ratio ............................................................................................... 466
9.6 Gear Types ..................................................................................................... 468
Spur, Helical, and Herringbone Gears ................................................... 468
Worms and Worm Gears ........................................................................ 470
Rack and Pinion ....................................................................................... 470
Bevel and Hypoid Gears ......................................................................... 471
Noncircular Gears ................................................................................... 472
Belt and Chain Drives .............................................................................. 473
9.7 Simple Gear Trains ........................................................................................ 475
9.8 Compound Gear Trains ............................................................................... 475
Design of Compound Trains ................................................................... 476
xii KINEMATICS AND DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY CONTENTS
Design of Reverted Compound Trains .................................................. 477
An Algorithm for the Design of Compound Gear Trains ..................... 480
9.9 Epicyclic or Planetary Gear Trains ............................................................. 484
The Tabular Method ................................................................................ 486
The Formula Method ............................................................................... 491
9.10 Efficiency of Gear Trains .............................................................................. 493
9.11 Transmissions .................................................................................................. 496
9.12 Differentials .................................................................................................... 500
9.13 References ..................................................................................................... 502
9.14 Bibliography .................................................................................................. 503
9.15 Problems ......................................................................................................... 503
Part II Dynamics of Machinery .................................................................. 511
Chapter 10 Dynamics Fundamentals ...................................................... 513
10.0 Introduction ................................................................................................... 513
10.1 Newtons Laws of Motion ............................................................................ 513
10.2 Dynamic Models ........................................................................................... 514
10.3 Mass ................................................................................................................ 514
10.4 Mass Moment and Center of Gravity ....................................................... 515
10.5 Mass Moment of Inertia (Second Moment of Mass) ............................. 517
10.6 Parallel Axis Theorem (Transfer Theorem) ................................................. 519
10.7 Determining Mass Moment of Inertia ....................................................... 519
Analytical Methods ................................................................................. 520
Experimental Methods ............................................................................ 520
10.8 Radius of Gyration ........................................................................................ 521
10.9 Modeling Rotating Links .............................................................................. 522
10.10 Center of Percussion .................................................................................... 523
10.11 Lumped Parameter Dynamic Models ...................................................... 525
Spring Constant ....................................................................................... 525
Damping .................................................................................................. 526
10.12 Equivalent Systems ....................................................................................... 528
Combining Dampers ............................................................................... 529
Combining Springs .................................................................................. 530
Combining Masses .................................................................................. 531
Lever and Gear Ratios ............................................................................ 531
10.13 Solution Methods .......................................................................................... 537
10.14 The Principle of dAlembert ........................................................................ 538
10.15 Energy MethodsVirtual Work ................................................................... 539
10.16 References ..................................................................................................... 542
10.17 Problems ......................................................................................................... 542
Chapter 11 Dynamic Force Analysis ....................................................... 545
11.0 Introduction ................................................................................................... 545
11.1 Newtonian Solution Method ...................................................................... 545
11.2 Single Link in Pure Rotation ......................................................................... 546
11.3 Force Analysis of A Threebar Crank-Slide Linkage ................................. 549
11.4 Force Analysis of a Fourbar Linkage ......................................................... 555
11.5 Force Analysis of a Fourbar Slider-Crank Linkage .................................. 562
11.6 Force Analysis of the Inverted Slider-Crank ............................................. 564
11.7 Force AnalysisLinkages with More Than Four Bars .............................. 567
11.8 Shaking Force and Shaking Moment ........................................................ 568
CONTENTS xiii
11.9 Linkage Force Analysis by Energy Methods ............................................ 569
11.10 Controlling Input TorqueFlywheels ......................................................... 572
11.11 A Linkage Force Transmission Index .......................................................... 578
11.12 Practical Considerations ............................................................................. 579
11.13 References ..................................................................................................... 581
11.14 Problems ......................................................................................................... 581
11.15 Projects ........................................................................................................... 592
Chapter 12 Balancing ................................................................................ 594
12.0 Introduction ................................................................................................... 594
12.1 Static Balance ............................................................................................... 595
12.2 Dynamic Balance ......................................................................................... 598
12.3 Balancing Linkages ...................................................................................... 603
Complete Force Balance of Linkages .................................................. 604
12.4 Effect of Balancing on Shaking and Pin Forces ...................................... 607
12.5 Effect of Balancing on Input Torque ......................................................... 609
12.6 Balancing the Shaking Moment in Linkages ........................................... 610
12.7 Measuring and Correcting Imbalance .................................................... 614
12.8 References ..................................................................................................... 616
12.9 Problems ......................................................................................................... 616
Chapter 13 Engine Dynamics ................................................................... 622
13.0 Introduction ................................................................................................... 622
13.1 Engine Design ............................................................................................... 624
13.2 Slider-Crank Kinematics ............................................................................... 629
13.3 Gas Force and Gas Torque ........................................................................ 635
13.4 Equivalent Masses ........................................................................................ 637
13.5 Inertia and Shaking Forces ......................................................................... 641
13.6 Inertia and Shaking Torques ....................................................................... 644
13.7 Total Engine Torque ...................................................................................... 645
13.8 Flywheels ........................................................................................................ 646
13.9 Pin Forces in the Single-Cylinder Engine .................................................. 647
13.10 Balancing the Single-Cylinder Engine ...................................................... 655
Effect of Crankshaft Balancing on Pin Forces ...................................... 659
13.11 Design Trade-offs and Ratios ...................................................................... 660
Conrod/Crank Ratio ................................................................................ 660
Bore/Stroke Ratio ..................................................................................... 660
Materials ................................................................................................... 661
13.12 Bibliography .................................................................................................. 661
13.13 Problems ......................................................................................................... 661
13.14 Projects ........................................................................................................... 664
Chapter 14 Multicylinder Engines ............................................................ 665
14.0 Introduction ................................................................................................... 665
14.1 Multicylinder Engine Designs ...................................................................... 667
14.2 The Crank Phase Diagram .......................................................................... 670
14.3 Shaking Forces in Inline Engines ................................................................. 671
14.4 Inertia Torque in Inline Engines ................................................................... 675
14.5 Shaking Moment in Inline Engines ............................................................. 676
14.6 Even Firing ...................................................................................................... 678
Two-Stroke Cycle Engine ........................................................................ 679
Four-Stroke Cycle Engine ........................................................................ 681
xiv KINEMATICS AND DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY CONTENTS
14.7 Vee Engine Configurations ......................................................................... 687
14.8 Opposed Engine Configurations ............................................................... 699
14.9 Balancing Multicylinder Engines ................................................................ 700
Secondary Balance in the Four-Cylinder Inline Engine ....................... 704
A Perfectly Balanced Two-Cylinder Engine .......................................... 706
14.10 References ..................................................................................................... 707
14.11 Bibliography .................................................................................................. 707
14.12 Problems ......................................................................................................... 708
14.13 Projects ........................................................................................................... 709
Chapter 15 Cam Dynamics ...................................................................... 711
15.0 Introduction ................................................................................................... 711
15.1 Dynamic Force Analysis of the Force-Closed Cam-Follower ............... 712
Undamped Response ............................................................................. 712
Damped Response ................................................................................. 715
15.2 Resonance .................................................................................................... 721
15.3 Kinetostatic Force Analysis of the Force-closed Cam-Follower ........... 723
15.4 Kinetostatic Force Analysis of the Form-Closed Cam-Follower ........... 727
15.5 Kinetostatic Camshaft Torque .................................................................... 731
15.6 Measuring Dynamic Forces and Accelerations ..................................... 733
15.7 Practical Considerations ............................................................................. 736
15.8 References ..................................................................................................... 738
15.9 Bibliography .................................................................................................. 738
15.10 Problems ......................................................................................................... 738
Appendix A Material Properties ................................................................. 741
Appendix B Geometric Properties ............................................................ 745
Appendix C Spring Data .............................................................................. 747
Appendix D Equations for Overbalanced Multicylinder Engines .......... 749
Appendix E Answers to Selected Problems ............................................. 753
Index ................................................................................................................ 769
You might also like
- Influence of Tensioner Dry Friction On The Vibration of Belt Drives With Belt Bending Stiffness PDFDocument9 pagesInfluence of Tensioner Dry Friction On The Vibration of Belt Drives With Belt Bending Stiffness PDFjeyaselvanmNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Modelling of Belt Drives PDFDocument76 pagesDynamic Modelling of Belt Drives PDFjeyaselvanmNo ratings yet
- SIAT - First Announcement 2021 - Final PDFDocument4 pagesSIAT - First Announcement 2021 - Final PDFjeyaselvanmNo ratings yet
- SIAT - First Announcement 2021 - Final PDFDocument4 pagesSIAT - First Announcement 2021 - Final PDFjeyaselvanmNo ratings yet
- Belt Study1 PDFDocument6 pagesBelt Study1 PDFjvaldebe82No ratings yet
- Four-Fold Method of Noise and Vibration ControlDocument8 pagesFour-Fold Method of Noise and Vibration ControlasdmoomNo ratings yet
- A SHORT TERM COURSE ON ADVANCES IN VIBRATION ENGINEERINGDocument2 pagesA SHORT TERM COURSE ON ADVANCES IN VIBRATION ENGINEERINGjeyaselvanmNo ratings yet
- Influence of Tensioner Dry Friction On The Vibration of Belt Drives With Belt Bending Stiffness PDFDocument9 pagesInfluence of Tensioner Dry Friction On The Vibration of Belt Drives With Belt Bending Stiffness PDFjeyaselvanmNo ratings yet
- 3-day introductory course on acoustic engineering in Pune, IndiaDocument1 page3-day introductory course on acoustic engineering in Pune, IndiajeyaselvanmNo ratings yet
- Applications of Triaxial AccelerometersDocument14 pagesApplications of Triaxial AccelerometersjeyaselvanmNo ratings yet
- One-Dimensional Flows of Fluid and Gas in PipelinesDocument30 pagesOne-Dimensional Flows of Fluid and Gas in PipelinesjeyaselvanmNo ratings yet
- Digital Audio - Creating A WAV (RIFF) FileDocument3 pagesDigital Audio - Creating A WAV (RIFF) FilejeyaselvanmNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Interior Acoustics BasicsDocument12 pagesAircraft Interior Acoustics BasicsjeyaselvanmNo ratings yet
- TVC Input Data Form Page 7Document17 pagesTVC Input Data Form Page 7jeyaselvanmNo ratings yet
- V Belt FailureDocument10 pagesV Belt Failuremuki10No ratings yet
- Changing CoordinatesDocument13 pagesChanging CoordinatesjeyaselvanmNo ratings yet
- The Story of Allan D. Pierce Jerry H. GinsbergDocument7 pagesThe Story of Allan D. Pierce Jerry H. GinsbergjeyaselvanmNo ratings yet
- The Story of Allan D. Pierce Jerry H. GinsbergDocument7 pagesThe Story of Allan D. Pierce Jerry H. GinsbergjeyaselvanmNo ratings yet
- Arku LevelingDocument20 pagesArku Levelingjeyaselvanm0% (1)
- A Model For Analyzing The Startup Dynamics of A Belt-Transmission Driven by A DC MotorDocument6 pagesA Model For Analyzing The Startup Dynamics of A Belt-Transmission Driven by A DC MotorjeyaselvanmNo ratings yet
- Helling Katalog NDTDocument43 pagesHelling Katalog NDTjeyaselvanmNo ratings yet
- Top 8 Vibration Analysis Software PackagesDocument7 pagesTop 8 Vibration Analysis Software PackagesjeyaselvanmNo ratings yet
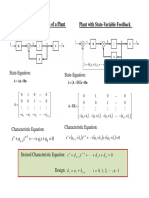
- State-Space Representation of A Plant Plant With State-Variable FeedbackDocument1 pageState-Space Representation of A Plant Plant With State-Variable FeedbackjeyaselvanmNo ratings yet
- 950 3-3 P5ZR 30 Pag 650-100Document8 pages950 3-3 P5ZR 30 Pag 650-100jeyaselvanmNo ratings yet
- Understanding Noise Radiation From A Hermetic CompressorDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Noise Radiation From A Hermetic CompressorjeyaselvanmNo ratings yet
- Pipeline NetworksDocument15 pagesPipeline NetworksjeyaselvanmNo ratings yet
- Suppression PassiveDocument2 pagesSuppression PassivejeyaselvanmNo ratings yet
- Smartphone SensorsDocument14 pagesSmartphone SensorsjeyaselvanmNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
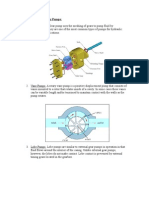
- Classification of Rotary PumpsDocument3 pagesClassification of Rotary Pumpsapi-26349602100% (2)
- PARKER PS1-E11 Technical Datasheet PDFDocument1 pagePARKER PS1-E11 Technical Datasheet PDFCardoso MalacaoNo ratings yet
- Abs VSCDocument15 pagesAbs VSCDayro GeneyNo ratings yet
- Full bore brass ball valveDocument1 pageFull bore brass ball valveMF CHOONGNo ratings yet
- Gate ValveDocument222 pagesGate ValveMetoo ChyNo ratings yet
- Automotive Brake SystemDocument39 pagesAutomotive Brake Systemjubaer ahmed50% (4)
- Kinematics of Machinery Anna University Question Papers CompiledDocument77 pagesKinematics of Machinery Anna University Question Papers CompiledNatesha SundharanNo ratings yet
- Technical data on dimension tolerances for fittingsDocument1 pageTechnical data on dimension tolerances for fittingsHien Bui XuanNo ratings yet
- FWD 6 Speed: Ganzeboom Transmission Parts & Torque ConvertersDocument2 pagesFWD 6 Speed: Ganzeboom Transmission Parts & Torque ConvertersAlli YantiNo ratings yet
- T12000 Series: MODEL NO. - Part NoDocument29 pagesT12000 Series: MODEL NO. - Part Nocesar100% (1)
- Baelz 373-E07 Electric ActuatorDocument3 pagesBaelz 373-E07 Electric ActuatorAbdulSattarNo ratings yet
- Optra Solenoid PDFDocument16 pagesOptra Solenoid PDFjosue100% (3)
- ME8694 Hydraulics and Pneumatics MCQDocument19 pagesME8694 Hydraulics and Pneumatics MCQaNo ratings yet
- 272c HidraulioDocument4 pages272c Hidraulioarmando vara chavez100% (1)
- Undercarriage: Hydraulic System 6060 BH Hydraulic Mining ShovelDocument6 pagesUndercarriage: Hydraulic System 6060 BH Hydraulic Mining Shoveladriano smithNo ratings yet
- Heavy Construction Equipment Seal SolutionsDocument69 pagesHeavy Construction Equipment Seal SolutionsSaif0% (1)
- Catalogo Bucyrus 295bii y Stock FiltrosDocument57 pagesCatalogo Bucyrus 295bii y Stock Filtrosjaime_perez_lopezNo ratings yet
- Train epicycloid calcul torque gear teethDocument3 pagesTrain epicycloid calcul torque gear teethmohammedNo ratings yet
- 330B Excavators Hydraulic Systems: 3YR1-UP 5LR1-UP 4RS1-UP 5LS1-UPDocument2 pages330B Excavators Hydraulic Systems: 3YR1-UP 5LR1-UP 4RS1-UP 5LS1-UPJim LiebNo ratings yet
- F21 Hyundai Vera CruzDocument338 pagesF21 Hyundai Vera CruzMiguel ApazaNo ratings yet
- th103 HydrDocument2 pagesth103 Hydrvic13rNo ratings yet
- Fail Position PDFDocument4 pagesFail Position PDFSergio IvánNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Centrifugal PumpsDocument27 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Centrifugal PumpsNischal LgNo ratings yet
- 793D SERV1817-01 - SLIDE - Aug2006Document233 pages793D SERV1817-01 - SLIDE - Aug2006Ishan IqbalNo ratings yet
- Manual HandgludsDocument11 pagesManual HandgludsBruno Peterson de PauliNo ratings yet
- 0310-Vsa-0020 0310-Vsa-0023 0310-Vsa-0021 0310-Vsa-0022: 3/4"-0310-Ho-01601-Spe0qDocument1 page0310-Vsa-0020 0310-Vsa-0023 0310-Vsa-0021 0310-Vsa-0022: 3/4"-0310-Ho-01601-Spe0qnestor159357No ratings yet
- 008 Cat-6060 Attachment Functions FSDocument37 pages008 Cat-6060 Attachment Functions FSenrico100% (3)
- Maintenance Manual of LHB Coaches Air Brake SystemDocument4 pagesMaintenance Manual of LHB Coaches Air Brake SystemLove TodkarNo ratings yet
- d8r II Serp3245 AkaDocument0 pagesd8r II Serp3245 Akamacross13100% (4)
- PumpsDocument1 pagePumpsDexter ContaweNo ratings yet