Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Roles of Manager
Uploaded by
Punit KumarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Roles of Manager
Uploaded by
Punit KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
Roles of Manager
Discuss Henry Mintzberg’s classification of basic role performed by manager in modern
organization.
The job of a modern manager is very complex and multi-dimensional. Therefore, a
manager has to play several roles to perform his job effectively and efficiently.
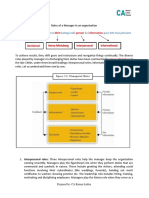
Mintzberg has identified ten roles of a manager which are grouped into three categories.
There is some arbitrariness in this classification but it is a useful framework for analyzing
and understanding the managerial job. These jobs are inseparable and should, therefore,
be viewed as an integrated whole. For example, status as manifested in the interpersonal
roles, brings information to the manager and it is this information that enables him to
perform the decision-making role effectively.
Ten Managerial Work Roles
INTERPERSONAL ROLES
1. Figurehead- In this role a manager performs symbolic duties required by the status
of his office. Making speeches, bestowing honours, welcoming official visitors,
distributing gifts to retiring employees are of such ceremonial and social duties.
2. Leader-This role defines the manager’s relationship with his own subordinates. The
manager sets an example, legitimizes the power of subordinates and brings their needs in
accord with those of his organization.
3. Liaison-It describes a manager’s relationships with the outsiders. A manager maintains
mutually beneficial relation with other organization, government, industry groups, etc.
INFORMATIONAL ROLES
4. Monitor-It implies seeking and receiving information about his organization and
external events. An example is picking up a rumour about his organization.
5. Disseminator-It involves transmitting information and judgments to the member of the
organization. The information relates to internal operations and the external environment.
A manager calling a staff meeting after a business trip is an example of such a role.
6. Spokesman- In this role, a manager speaks for his organization. He lobbies and
defends his enterprise. A manager addressing the trade union is an example.
DECISIONAL ROLES
7. Entrepreneur-It involves initiating change or acting as a change agent. For example, a
manager decides to launch a feasibility study for setting up a new plant.
8. Disturbance handler-This refers to taking charge when a organization face a problem
or crisis, e.g., a strike, feud between subordinates, loss of an important customer. A
manager handles conflicts, complaints and competitive actions.
9. Resource allocator- In this role a manager approves budgets and schedules, sets
priorities and distributes resources.
10. Negotiator-As a negotiator, a manager bargains with suppliers, dealers, trade union,
agents, etc.
You might also like
- MODULE 2 - LESSON 2 10 ROLES OF A MANAGERDocument17 pagesMODULE 2 - LESSON 2 10 ROLES OF A MANAGERDaphne YapNo ratings yet
- Functions of ManagerDocument4 pagesFunctions of ManagerapolNo ratings yet
- Bormgt L1Document3 pagesBormgt L1Maricris CaldozaNo ratings yet
- What Are Managerial RolesDocument2 pagesWhat Are Managerial RolesBuddhi PahiNo ratings yet
- Student Name - C.Buddhika Pahindra Student ID - Yet To Be Received Submission Date - 01/14/2021Document2 pagesStudent Name - C.Buddhika Pahindra Student ID - Yet To Be Received Submission Date - 01/14/2021Buddhi PahiNo ratings yet
- 1 What Are ManagersDocument7 pages1 What Are ManagersTeodoraMariaGhitaNo ratings yet
- Leadership 2Document30 pagesLeadership 2Miko Paolo SanchezNo ratings yet
- Management Levels and Skills: Henry Fayol Identified Three Basic SkillsDocument15 pagesManagement Levels and Skills: Henry Fayol Identified Three Basic SkillsVanessa GardnerNo ratings yet
- Strategic Decision-Making Chapter II ReactionDocument2 pagesStrategic Decision-Making Chapter II ReactionXyliene EngañoNo ratings yet
- OrgMngt Notes 1st GradingDocument37 pagesOrgMngt Notes 1st GradingKhassie B. GrandeNo ratings yet
- Roles Skills of A ManagerDocument8 pagesRoles Skills of A ManagerDelina TedrosNo ratings yet
- Key Differences Between Entrepreneur and Manager: Managerial Roles and Managerial SkillsDocument3 pagesKey Differences Between Entrepreneur and Manager: Managerial Roles and Managerial SkillsvijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Organizational ManagementDocument5 pagesOrganizational Managementmae ledesmaNo ratings yet
- Index Roles of Managers: Interpersonal Roles: Informational Roles: Decisional Roles: Conclusion: ReferenceDocument9 pagesIndex Roles of Managers: Interpersonal Roles: Informational Roles: Decisional Roles: Conclusion: ReferenceVenkatesh GajulaNo ratings yet
- Roles of ManagerDocument7 pagesRoles of ManagerShubham KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Management of Small FirmsDocument3 pagesManagement of Small FirmsSurvi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 MGMT 1Document5 pagesLesson 1 MGMT 1ninoangelodulayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1editedDocument13 pagesChapter 1editedMuktar jiboNo ratings yet
- 10 Managerial Roles by Henry MintzbergDocument5 pages10 Managerial Roles by Henry MintzbergLheiAmorCariño100% (5)
- MN SCDocument15 pagesMN SCmagicalsouvenirNo ratings yet
- Organizational BehaviourDocument130 pagesOrganizational BehaviourPawan Kumar Prajapat100% (1)
- What Is The Role of A ManagerDocument2 pagesWhat Is The Role of A ManagerMayank JhaNo ratings yet
- Int To MGT 01Document34 pagesInt To MGT 01dine62611No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Managers in The WorkplaceDocument8 pagesChapter 1 - Managers in The WorkplaceMy KiềuNo ratings yet
- The Role of Management Has Been Changing With Time. Justify This StatDocument2 pagesThe Role of Management Has Been Changing With Time. Justify This StatHassan Mohamed EgehNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Management FundamentalsDocument34 pagesIntroduction to Management FundamentalsYinebeb GifachewNo ratings yet
- Lec2 Note Ch1Document5 pagesLec2 Note Ch1Moktasid HossainNo ratings yet
- Ob - Ass-1Document8 pagesOb - Ass-1siddhigundecha16No ratings yet
- There Are Three Specific Categorization Schemes To Explain What Managers DoDocument5 pagesThere Are Three Specific Categorization Schemes To Explain What Managers DoMona Sharma DudhaleNo ratings yet
- Role of A ManagerDocument2 pagesRole of A ManagerTanishka GuptaNo ratings yet
- Managment RolesDocument3 pagesManagment RolesMubashir MustafaNo ratings yet
- Business ManagementDocument8 pagesBusiness ManagementAvadhut PaymalleNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document30 pagesLesson 2Thea Jeonieesa GarayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Principles of ManagementDocument26 pagesChapter 1 - Principles of ManagementLisa GalinaNo ratings yet
- (Management and Operations) : Assignment Title: (Document6 pages(Management and Operations) : Assignment Title: (Randy KyawNo ratings yet
- 10 Managerial Roles by Henry MintzbergDocument5 pages10 Managerial Roles by Henry MintzbergShadaab FarooqNo ratings yet
- Management Roles & Responsibilities at Different LevelsDocument2 pagesManagement Roles & Responsibilities at Different LevelsMary JhoyNo ratings yet
- CH 01 GEDocument13 pagesCH 01 GEShariful ShishirNo ratings yet
- Mintzberg's Management Roles: Identifying The Roles Managers PlayDocument4 pagesMintzberg's Management Roles: Identifying The Roles Managers Playjulie roseNo ratings yet
- MANAGEMENT NewDocument7 pagesMANAGEMENT NewThenmozhi ArunNo ratings yet
- Name: Fierryl Shaine Menis 12-EncarnacionDocument4 pagesName: Fierryl Shaine Menis 12-EncarnacionFIERRYL SHAINE MENISNo ratings yet
- Name: Dhiraj Kumar Gupta Rollno.: 1976137 Section: A Mintzberg Managerial RolesDocument3 pagesName: Dhiraj Kumar Gupta Rollno.: 1976137 Section: A Mintzberg Managerial RolesDhiraj GuptaNo ratings yet
- MANAGERIAL ROLES AND SKILLS FOR SUCCESSDocument6 pagesMANAGERIAL ROLES AND SKILLS FOR SUCCESSCielo PetilNo ratings yet
- Chief Executive Officer, President, or General Manager: Roles and ResponsibilitiesDocument8 pagesChief Executive Officer, President, or General Manager: Roles and ResponsibilitiesRoger Brewington BeyNo ratings yet
- AssignmentsDocument16 pagesAssignmentsTeena SharmaNo ratings yet
- MBA - Unit 1 - MB20107 - Managerial Skills and CommunicationDocument21 pagesMBA - Unit 1 - MB20107 - Managerial Skills and CommunicationBalaji DNo ratings yet
- QuranDocument4 pagesQuranTahir AlyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1,2,3 Word Document Notes Managerial SkillsDocument44 pagesUnit 1,2,3 Word Document Notes Managerial SkillsVintageNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ManagementDocument14 pagesIntroduction To ManagementFloRhyda DahinoNo ratings yet
- My Report For LeadershipDocument23 pagesMy Report For LeadershipNewgleer WengNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Management and OrganizationsDocument12 pagesChapter 1 Management and OrganizationsBo Zydarin100% (1)
- You Should Spend About 20 Minutes On Questions 1-13, Which Are Based On Reading Passage 1 BelowDocument12 pagesYou Should Spend About 20 Minutes On Questions 1-13, Which Are Based On Reading Passage 1 Below王小妞No ratings yet
- qweqweqDocument2 pagesqweqweqvevosod753No ratings yet
- Functions of Manager: Planning, Organizing, Staffing, Directing & ControllingDocument9 pagesFunctions of Manager: Planning, Organizing, Staffing, Directing & ControllingMlyn100% (1)
- Top 10 Roles of A Manager in OrganizationDocument5 pagesTop 10 Roles of A Manager in OrganizationANUPAM KAPTINo ratings yet
- The 10 managerial roles explainedDocument2 pagesThe 10 managerial roles explainedShimelis Tesema100% (1)
- Basic Managerial Roles and Skills: InterpersonalroleDocument22 pagesBasic Managerial Roles and Skills: InterpersonalroleKartik AroraNo ratings yet
- Administrative Procedures and ManagementFrom EverandAdministrative Procedures and ManagementRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A Pragmatic Introduction to Middle Manager Fundamentals: Part 1 - Role and FunctionFrom EverandA Pragmatic Introduction to Middle Manager Fundamentals: Part 1 - Role and FunctionNo ratings yet
- Scope of BusinessDocument3 pagesScope of BusinessPunit KumarNo ratings yet
- Managerial SkillsDocument2 pagesManagerial SkillsPunit KumarNo ratings yet
- Scientific ManagementDocument1 pageScientific ManagementPunit KumarNo ratings yet
- PlanningDocument3 pagesPlanningPunit KumarNo ratings yet
- Give The Difference Between Scientific Management and Administrative ManagementDocument1 pageGive The Difference Between Scientific Management and Administrative ManagementPunit KumarNo ratings yet
- Nature of ManagementDocument2 pagesNature of ManagementPunit KumarNo ratings yet
- Henry FayolDocument3 pagesHenry FayolPunit KumarNo ratings yet
- Forms of Business OrganisationDocument15 pagesForms of Business OrganisationPunit KumarNo ratings yet
- Four Pillars of EducationDocument4 pagesFour Pillars of EducationJeffren P. Miguel100% (2)
- Assessment Brief For Assessment Point 2Document11 pagesAssessment Brief For Assessment Point 2Israel AlabiNo ratings yet
- Reluctant Workers Project TeamDocument1 pageReluctant Workers Project TeamSagun P. PokharelNo ratings yet
- Disabilities in SchoolsDocument8 pagesDisabilities in Schoolsapi-286330212No ratings yet
- TemperamentDocument2 pagesTemperamentBatka BekNo ratings yet
- Deep WaterDocument10 pagesDeep WaterRomil Shah0% (1)
- Final Baby ThesisDocument43 pagesFinal Baby ThesisCrystal Fabriga AquinoNo ratings yet
- The Saturn ReturnDocument2 pagesThe Saturn Returnwhackz100% (3)
- NegotiationDocument43 pagesNegotiationmatthewmackelly75% (4)
- GDSSDocument8 pagesGDSSsadiakureshiNo ratings yet
- The Flight From ConversationDocument2 pagesThe Flight From ConversationAllyra MendozaNo ratings yet
- Patient Safety and Quality Care MovementDocument9 pagesPatient Safety and Quality Care Movementapi-300362983No ratings yet
- Q3 English Summative TestDocument4 pagesQ3 English Summative TestBanda Sa CcnhsNo ratings yet
- Communication & Emotional IntelligenceDocument22 pagesCommunication & Emotional IntelligenceRaghuram Bhandari100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Understanding Management Context Constraints and ChallengesDocument7 pagesChapter 3 Understanding Management Context Constraints and ChallengesChristian SawayaNo ratings yet
- Sample Hip-Hop Course SyllabusDocument5 pagesSample Hip-Hop Course SyllabusTech_HIp_Ed0% (1)
- Brayton Polka Rethinking Philosophy in Light of The Bible From Kant To Schopenhauer PDFDocument186 pagesBrayton Polka Rethinking Philosophy in Light of The Bible From Kant To Schopenhauer PDFNegru CorneliuNo ratings yet
- Mgt162 Fundamentals of Management Topic 5: Motivation (Assignment 5)Document4 pagesMgt162 Fundamentals of Management Topic 5: Motivation (Assignment 5)Valerie ColeNo ratings yet
- History MadnessDocument41 pagesHistory MadnessWinston LuizNo ratings yet
- Nat Cat 10 FullDocument15 pagesNat Cat 10 FullMbatutesNo ratings yet
- Bibliography: Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 50, 772-781Document13 pagesBibliography: Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 50, 772-781Micaella LalamoroNo ratings yet
- Amina NazirDocument2 pagesAmina NazirMuhammad NazirNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Theories Explained in 6 SituationsDocument2 pagesBehavioral Theories Explained in 6 SituationsHyun Woo LeeNo ratings yet
- Industrial Supervisor Evaluation (ISE)Document3 pagesIndustrial Supervisor Evaluation (ISE)Khairul IkhwanNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 - Shear Box PDFDocument2 pagesLab 5 - Shear Box PDFdixn__No ratings yet
- Literacy Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesLiteracy Lesson Planapi-437974951No ratings yet
- Clegg 1982 Simple Statistics A Course Book For The Social SciencesDocument105 pagesClegg 1982 Simple Statistics A Course Book For The Social SciencesMihaela Alina TiticaNo ratings yet
- AP Psychology Mnomonic DevicesDocument7 pagesAP Psychology Mnomonic DevicesBellony SandersNo ratings yet
- Herbert Gans On LevittownDocument2 pagesHerbert Gans On LevittownAnastasiia Sin'kovaNo ratings yet
- Gioia 2020 A Systematic Methodology For Doing Qualitative ResearchDocument10 pagesGioia 2020 A Systematic Methodology For Doing Qualitative ResearchJack WaltonNo ratings yet