Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial 1
Uploaded by
Syakirin SpearsCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial 1
Uploaded by
Syakirin SpearsCopyright:
Available Formats
NKB30503 JULY-2017
PROBLEMS
9.3-1 The air in a room is at 37.8 C and a total pressure of 101.3 kPa abs containing water vapor
with a partial pressure pA = 3.59 kPa. Calculate
a) Humidity
b) Saturation humidity and percentage humidity
c) Percentage relative humidity
9.3-2 The air in a room has a humidity H = 0.021 kg H2O/kg DA at 32.2 C and 101.3 kPa abs
pressure. Calculate
a) Percentage humidity, HP
b) Percentage relative humidity, HR
9.3-3 The air entering a dryer has a temperature of 65.6 C and dew point of 15.6 C. By using
the humidity chart, determine the actual humidity and percentage humidity. Calculate the
humid volume of this mixture and also calculate cs using SI and English units.
9.3-4 An air-water vapor mixture going to a drying process has a dry bulb temperature of 57.2
C and a humidity of 0.030 kg H2O/kg DA. Determine the percentage humidity, saturation
humidity at 57.2 C, dew point, humid heat and humid volume.
9.3-5 Air at 82.2 C having a humidity H = 0.0655 kg H2O/kg DA is contacted in an adiabatic
saturator with water. It leaves the saturator 80% saturated. What are the final values of H
and T C. For 100% saturation, what are the values of H and T.?
9.3-6 Air enters an adiabatic saturator having a temperature of 76.7 C and a dew-point
temperature of 40.6 C. It leaves the saturator 90% saturated. What are the finals values of
H and T C.
9.3-9 Air having a dry bulb temperature of 37.8 C and a wet bulb temperature of 26.7 C is to
be dried first by cooling to 15.6 C to condense water-vapor and then heating to 23.9 C.
a) Calculate initial humidity and percentage humidity.
b) Calculate the final humidity and percentage humidity.
NKB30503 JULY-2017
9.6-1 A batch of wet solid was dried on a tray dryer using constant drying conditions and
thickness of material on the tray of 25.4 mm. Only the top surface was exposed. The
drying rate during the constant-rate period was R = 2.05 kg H2O/h.m2. The ratio Ls/A used
was 24.4 kg dry solid/m2 exposed surface. The initial free moisture was X1 = 0.55 and the
critical moisture content Xc= 0.22 kg free moisture/kg dry solid. Calculate the time
required to dry a batch of this material from X1 = 0.45 to X2 = 0.30 using the same drying
condition but a thickness of 50.8 mm, with drying from top and bottom surfaces.
9.6-2 An insoluble wet granular material is dried in a pan 0.457 x 0.457m and 25.4 mm deep.
The material is 25.4 mm deep in the pan, amd the sides and bottom can be considered to
be insulated. Heat transfer is by convection from an air stream flowing parallel to the
surface at a velocity of 6.1 m/s. The air is at 65.6 C and has a humidity of 0.010 kg
H2O/kg dry air.
a) Predict the effect on Rc if the air velocity is only 3.05 m/s.
b) Predict the effect of the gas temperature is raised to 76.7 C and H remains the
same.
You might also like
- Psychrometrics Drying Problems SEODocument5 pagesPsychrometrics Drying Problems SEOStephanie Torrecampo Delima100% (2)
- Tutorial 2 - DryingDocument3 pagesTutorial 2 - DryingDinesh Kumar VijeyanNo ratings yet
- DryingDocument2 pagesDryingZhi ChaoNo ratings yet
- Drying PSDocument10 pagesDrying PSVan Vesper DulliyaoNo ratings yet
- Hydrodynamics of Packed ColomnDocument6 pagesHydrodynamics of Packed ColomnDhananjay KadamNo ratings yet
- Extracting soybean oil from beansDocument27 pagesExtracting soybean oil from beans3lks0y0% (1)
- CHE 312 Problem Set #2Document4 pagesCHE 312 Problem Set #2rkz93No ratings yet
- Crystallizations QuestionsDocument4 pagesCrystallizations Questionsengr2021No ratings yet
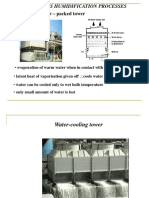
- Continuous Humidification Processes Cooling Tower DesignDocument30 pagesContinuous Humidification Processes Cooling Tower DesignNur AishaNo ratings yet
- Checal2 LauritoDocument1 pageChecal2 LauritoGarcia RaphNo ratings yet
- Unit OperationDocument17 pagesUnit OperationMohamed KilanyNo ratings yet
- Solid Fuels Problem SetDocument1 pageSolid Fuels Problem SetCaseyJaneAguilarNo ratings yet
- BAB 9 Rajiv DuttaDocument86 pagesBAB 9 Rajiv DuttaYuhin meidina ocsaNo ratings yet
- Batch Drying Rate CalculationsDocument35 pagesBatch Drying Rate CalculationshNo ratings yet
- Crystallization PrdasddaoblemsDocument4 pagesCrystallization PrdasddaoblemsJim Laab100% (1)
- Ps1-Che171 Chemical Reaction Engineering 1Document2 pagesPs1-Che171 Chemical Reaction Engineering 1Cha CanceranNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument88 pagesPDFMuralidharanNo ratings yet
- AssigDocument2 pagesAssigZakwan0% (1)
- CycloneDocument25 pagesCycloneAna Marie AllamNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument71 pagesHeat TransferZeus OlympusNo ratings yet
- Humidification and Air Conditioning: Lecture No. 8Document6 pagesHumidification and Air Conditioning: Lecture No. 8Anonymous UFa1z9XUANo ratings yet
- CHE 511A Compilation 2 3 M F PDFDocument164 pagesCHE 511A Compilation 2 3 M F PDFMaame Efua NeizerNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 7 Measurement of Reaction ConversionDocument8 pagesExperiment No. 7 Measurement of Reaction ConversionHoneylet Recaña TayactacNo ratings yet
- Volume 6 Solns ManualDocument8 pagesVolume 6 Solns ManualshaaaaaaaaareeeeeeeNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesThermodynamicsRachita Prakash Saraf0% (1)
- Heat TransferDocument3 pagesHeat TransferAlbert Junior EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Material Balance in Unit OperationsDocument25 pagesMaterial Balance in Unit OperationsStephen IpanNo ratings yet
- ICHEMDocument4 pagesICHEMAnthon ToledanoNo ratings yet
- A. Answer The Following Questions With Proper ExplanationsDocument1 pageA. Answer The Following Questions With Proper ExplanationsRohitNo ratings yet
- ChE 126 SEPARATION PROCESSES: ADSORPTION ISOTHERMS (39Document27 pagesChE 126 SEPARATION PROCESSES: ADSORPTION ISOTHERMS (39Anthony Justin EdmaNo ratings yet
- D D D D DDocument5 pagesD D D D Drazzee yuchengkoNo ratings yet
- Sedimentation ExperimentDocument10 pagesSedimentation ExperimentKen VenzonNo ratings yet
- BangbangDocument5 pagesBangbangAutumn JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Diffusion of HCl Through Water FilmDocument2 pagesDiffusion of HCl Through Water FilmJack SutherlandNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer Diffusion EquationsDocument79 pagesMass Transfer Diffusion EquationsPrakhar AggarwalNo ratings yet
- CHECALC Sample ProblemsDocument7 pagesCHECALC Sample ProblemshulyenNo ratings yet
- Liquid-Liquid Extraction - 17 Sept 2020 - 4 PDFDocument32 pagesLiquid-Liquid Extraction - 17 Sept 2020 - 4 PDFshubham100% (1)
- Problem SetDocument4 pagesProblem SetR SuyaoNo ratings yet
- Problems in Mass TransferDocument3 pagesProblems in Mass TransferAngelica Joyce BenitoNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document6 pagesProblem Set 1Emilee Noven RamirezNo ratings yet
- 3.ionic Equilibria and Biochemical ReactionsDocument4 pages3.ionic Equilibria and Biochemical ReactionsbackseeNo ratings yet
- CHE Thermodynamics Competency Exam 2013 2014 For Students1Document3 pagesCHE Thermodynamics Competency Exam 2013 2014 For Students1Inie DimaanoNo ratings yet
- Energy Balance Around The Conveyor WasherDocument5 pagesEnergy Balance Around The Conveyor WasherlucasNo ratings yet
- Latihan Uas CH 4-6Document16 pagesLatihan Uas CH 4-6rizkaNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Problems On Single Effect EvaporatorDocument2 pages3.3 Problems On Single Effect EvaporatorRobert JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Single effect evaporator problems and examplesDocument8 pagesSingle effect evaporator problems and examplesJosé Antonio AntemateNo ratings yet
- Learning Assessment Activity 1. QUESTIONS.: Name: Franzes Mar Eria Heat and Mass Transfer Bsche 3Document7 pagesLearning Assessment Activity 1. QUESTIONS.: Name: Franzes Mar Eria Heat and Mass Transfer Bsche 3Franzes Mar EriaNo ratings yet
- BIochem AssDocument5 pagesBIochem AssCheng PasionNo ratings yet
- Centeno, CRE PDFDocument10 pagesCenteno, CRE PDFrj centenoNo ratings yet
- Solid Fuels Group 7 & 8Document91 pagesSolid Fuels Group 7 & 8Jowel MercadoNo ratings yet
- Gas Absorption: Determining Drag and Flooding FlowsDocument5 pagesGas Absorption: Determining Drag and Flooding FlowsDean Joyce AlborotoNo ratings yet
- Experiment: Packed Distillation ColumnDocument4 pagesExperiment: Packed Distillation Columnnhalieza1067No ratings yet
- Review Key Concepts of Transport PhenomenaDocument7 pagesReview Key Concepts of Transport PhenomenaAdelaida CruzNo ratings yet
- Answers - Heat & Mass Transfer - IDocument8 pagesAnswers - Heat & Mass Transfer - IKTINE08No ratings yet
- AIRCONDITIONING ProblemsDocument28 pagesAIRCONDITIONING Problemsعبدالرحمن منصورNo ratings yet
- DryingDocument24 pagesDryingramnareshretneniNo ratings yet
- Short Answer QuestionsDocument7 pagesShort Answer Questionsvenky437No ratings yet
- Problem Set - MidtermDocument3 pagesProblem Set - MidtermJohn Paul JacalanNo ratings yet
- Problems 1 0100103304 2-59Document1 pageProblems 1 0100103304 2-59Jj LewandyNo ratings yet
- SH - No.1 ACDocument3 pagesSH - No.1 ACيوسف عبيد خليفةNo ratings yet
- C5 Occ Health Sept 2015 RevisedDocument117 pagesC5 Occ Health Sept 2015 RevisedSyakirin SpearsNo ratings yet
- C6 Biohazard Sept 2015 RevisedDocument49 pagesC6 Biohazard Sept 2015 RevisedSyakirin SpearsNo ratings yet
- Empty Fruit BunchDocument4 pagesEmpty Fruit BunchSyakirin SpearsNo ratings yet
- Challenges (Capacity of Carbon Sinks)Document5 pagesChallenges (Capacity of Carbon Sinks)Syakirin SpearsNo ratings yet
- DISCUSSIONDocument5 pagesDISCUSSIONSyakirin SpearsNo ratings yet
- Turbidity Test For Drinking Water TheoryDocument13 pagesTurbidity Test For Drinking Water TheorySyakirin SpearsNo ratings yet
- 5.3 Inverse FunctionsDocument43 pages5.3 Inverse FunctionsSyakirin SpearsNo ratings yet
- OSHA ReportDocument4 pagesOSHA ReportSyakirin SpearsNo ratings yet
- METHODOLOGYDocument3 pagesMETHODOLOGYSyakirin Spears100% (1)
- Engineers Commit SafetyDocument59 pagesEngineers Commit SafetySyakirin SpearsNo ratings yet
- Mini ProjectDocument7 pagesMini ProjectSyakirin SpearsNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument12 pagesOrganic ChemistrySyakirin SpearsNo ratings yet
- Open Ended Statement LabDocument1 pageOpen Ended Statement LabSyakirin SpearsNo ratings yet
- Petro ChemDocument2 pagesPetro ChemSyakirin SpearsNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document3 pagesTutorial 2Syakirin SpearsNo ratings yet
- Adsorption and Ion Exchange ProcessesDocument14 pagesAdsorption and Ion Exchange ProcessesSyakirin SpearsNo ratings yet
- Distillation Column Internal Components GuideDocument8 pagesDistillation Column Internal Components GuideSyakirin SpearsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 DistillationDocument110 pagesChapter 1 DistillationSiti Nurshahira80% (5)
- HUMIDIFICATION Industrial ApplicationDocument4 pagesHUMIDIFICATION Industrial ApplicationSyakirin SpearsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Drying ProcessDocument43 pagesChapter 2 Drying ProcessSyakirin SpearsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document27 pagesChapter 4Syakirin SpearsNo ratings yet
- Challenges (Capacity of Carbon Sinks)Document5 pagesChallenges (Capacity of Carbon Sinks)Syakirin SpearsNo ratings yet
- Extraction CHAPTER 7 UpdatesDocument22 pagesExtraction CHAPTER 7 UpdatesSyakirin SpearsNo ratings yet
- 41 D448Document2 pages41 D448dyah_inggitNo ratings yet
- Soil PollutionDocument21 pagesSoil PollutionSyakirin SpearsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Regression Analysis - 010810 (Compatibility Mode)Document57 pagesChapter 6 - Regression Analysis - 010810 (Compatibility Mode)Syakirin SpearsNo ratings yet
- Literature Review ExampleDocument5 pagesLiterature Review ExampleSyakirin SpearsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document28 pagesChapter 1Syakirin SpearsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3a Laminar Flow ContinuesDocument22 pagesLecture 3a Laminar Flow ContinuesSyakirin SpearsNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument11 pagesIntroductionImdad JalaliNo ratings yet
- Araldite FT CY205IN Aradur HY905IN DY040 DY061 Si02 Eur e PDFDocument8 pagesAraldite FT CY205IN Aradur HY905IN DY040 DY061 Si02 Eur e PDFneerajaNo ratings yet
- Data XRF ST14Document78 pagesData XRF ST14Achmad Nabil ZulfaqarNo ratings yet
- 08.solutions To ConceptsDocument16 pages08.solutions To ConceptsPallav Jyoti PalNo ratings yet
- Gotuj Z Oliverem Chomikuj GryphonDocument3 pagesGotuj Z Oliverem Chomikuj GryphonHajiNo ratings yet
- Science 9 exam questions on atomic structure and bondingDocument3 pagesScience 9 exam questions on atomic structure and bondingLimar Anasco Escaso67% (3)
- Annealing Process Explained in 40 CharactersDocument8 pagesAnnealing Process Explained in 40 CharactersRohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Definition: Origin of ChargesDocument5 pagesDefinition: Origin of ChargesDavies MasumbaNo ratings yet
- Titration CurveDocument12 pagesTitration Curveoguztop10No ratings yet
- Lehninger Biochem Ch 1-2 ReviewDocument13 pagesLehninger Biochem Ch 1-2 ReviewHugo DuarteNo ratings yet
- Improved Control Valve Sizing For Multiphase FlowDocument10 pagesImproved Control Valve Sizing For Multiphase FlowThitikorn WassanarpheernphongNo ratings yet
- Exp5 The Green Minded 3735Document16 pagesExp5 The Green Minded 3735CyberR.DomingoNo ratings yet
- MeteorologyDocument2 pagesMeteorologyIoniță AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Oxidation States of ManganeseDocument4 pagesOxidation States of ManganesexbokyxNo ratings yet
- EstañoDocument646 pagesEstañoJuan MartínezNo ratings yet
- Physics homework guideDocument3 pagesPhysics homework guideRahul ChandraNo ratings yet
- 1mrk507004-Uen B en Radhl User S GuideDocument40 pages1mrk507004-Uen B en Radhl User S Guideali surfNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Relative Masses and Mole CalculationsDocument9 pagesChapter 7 - Relative Masses and Mole CalculationsAdrawa NorwelNo ratings yet
- Realization Phase of Model in Terms of EcodesignDocument7 pagesRealization Phase of Model in Terms of EcodesignZvonimir MajićNo ratings yet
- Mechanical EngineeringDocument23 pagesMechanical EngineeringAditya ShindeNo ratings yet
- Industria1 C o M B U S T I o N Pollution and C o N T R o L PDFDocument890 pagesIndustria1 C o M B U S T I o N Pollution and C o N T R o L PDFAfzaal AshrafNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and of The Company/UndertakingDocument7 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and of The Company/Undertakingdaniel abiaNo ratings yet
- Co(III) Coordination Compounds Synthesis ReactionsDocument28 pagesCo(III) Coordination Compounds Synthesis ReactionsRahul GogiaNo ratings yet
- About Soda Ash - ANSACDocument2 pagesAbout Soda Ash - ANSAChabib1234No ratings yet
- RedoxDocument30 pagesRedoxMelanie perez cortezNo ratings yet
- Yyzzzz Fluidization - J.R. Van Ommen & N. Ellis - 2010Document25 pagesYyzzzz Fluidization - J.R. Van Ommen & N. Ellis - 2010José Pedro Casagrande TrentínNo ratings yet
- Fire Resistant Fluid Study on Deterioration of Physicochemical PropertiesDocument34 pagesFire Resistant Fluid Study on Deterioration of Physicochemical Propertiesgolden430No ratings yet
- CH 4 Separation TechniquesDocument16 pagesCH 4 Separation TechniquestanhuikuanNo ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument20 pagesClass Notesrockybhaighost97No ratings yet
- EMPC2015 - Wire Bonding of Au-Coated Ag Wire Bondwire Properties, Bondability andDocument4 pagesEMPC2015 - Wire Bonding of Au-Coated Ag Wire Bondwire Properties, Bondability andChong Leong GanNo ratings yet
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (33)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- The Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorFrom EverandThe Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (137)
- The Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterFrom EverandThe Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterNo ratings yet
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Smokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersFrom EverandSmokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersNo ratings yet
- Water to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesFrom EverandWater to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (21)
- The Secret Life of Lobsters: How Fishermen and Scientists Are Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Favorite CrustaceanFrom EverandThe Secret Life of Lobsters: How Fishermen and Scientists Are Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Favorite CrustaceanNo ratings yet
- The Mind of Plants: Narratives of Vegetal IntelligenceFrom EverandThe Mind of Plants: Narratives of Vegetal IntelligenceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsFrom EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (63)
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsFrom EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (221)
- Eels: An Exploration, from New Zealand to the Sargasso, of the World's Most Mysterious FishFrom EverandEels: An Exploration, from New Zealand to the Sargasso, of the World's Most Mysterious FishRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (30)
- Why Fish Don't Exist: A Story of Loss, Love, and the Hidden Order of LifeFrom EverandWhy Fish Don't Exist: A Story of Loss, Love, and the Hidden Order of LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (699)
- The Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastFrom EverandThe Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- Last Child in the Woods: Saving Our Children From Nature-Deficit DisorderFrom EverandLast Child in the Woods: Saving Our Children From Nature-Deficit DisorderRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (283)
- When You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsFrom EverandWhen You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (13)