Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 2 1 Notes Teacher CH 12 1
Uploaded by
api-3697067790 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
59 views10 pagesOriginal Title
1 2 1 notes teacher ch 12 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
59 views10 pages1 2 1 Notes Teacher CH 12 1
Uploaded by
api-369706779Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
1.2.1 & 1.2.2 Chapter 12.
1 Forces
Force - an interaction between two objects that
can change the motion of those two objects
Can cause a resting object to move
Can accelerate a moving object by changing
its speed or direction
For example: force of gravity, friction (a force
that opposes motion of objects that touch as
they move past one another)
Measured in newtons (N); i.e. weight of apples
Net force the overall force acting on an object
after all the forces are combined
Balanced forces-forces on an object that are equal
in size and opposite in direction
Net force equals zero
No change in objects motion
i.e. balanced sides in tug of war
------> <------
50N 50N
East West
Unbalanced forces -
A force that is not equal in size and opposite in
direction
Will result in a net force; object accelerates
(i.e. change in speed or change in direction or
change in both)
--------> <--
100N 10N
East West
Balanced forces = no movement
Unbalanced forces = movement in the direction of
the greater force
Friction - the force that opposes motion between
two surfaces that are touching each other
Depends on the kinds of surfaces and the force
pressing the surfaces together
Without friction, every surface would be more
slippery than a sheet of ice
So walking would be impossible; cars would
just slide around
Why does a rolling ball eventually stop? b/c of
friction! Friction occurs b/w any 2 surfaces in
contact
1) static friction: force required to overcome
inertia, to start moving something, its the hardest
(i.e. a book sitting on a table)
2) sliding friction: force required to keep an object
moving, less than static b/c the object is already
moving (i.e. a box pushed across the floor)
3) rolling friction: force required to keep an object
rolling, easiest to overcome (i.e. a ball rolling
across the floor
4) fluid: force required to keep moving in a fluid
(i.e. an object in free fall, swimming)
Air resistance fluid friction acting on an object
moving through the air or force air exerts on a
moving object.
Gravity causes objects to accelerate
downward, but air resistance acts in an upward
direction and reduces acceleration
i.e. flying squirrel uses air resistance to slow
his acceleration to the Earth; spreads his arms
and legs to achieve maximum surface area
Air resistance affects anything that moves in
Earths atmosphere.
This force acts in the opposite direction to that
of the objects motion.
In the case of a falling object, air resistance
pushes up as gravity pulls down.
The amount of air resistance on an object
depends on the speed, size, shape and density
of the object.
Larger surface area = greater the amount of
air resistance on it
Gravity - force that acts between any two masses
It is an attractive force (pulls objects together)
i.e. the force of gravity is what holds us on
Earth
The amount of gravitational force between
objects depends on: mass and distance
The greater the mass = the stronger the
gravitational force
The greater the distance = the less effect
gravity will play
Earths gravity keeps the moon in a nearly
circular orbit around Earth
Therefore, it a centripetal force.
A centripetal force is a center-directed force
that continuously changes direction of an
object to make it move in a circle.
This force has only causes a change in
direction
Examples: car going around a curve or a toy
plane spun in a circle by a string
Weight- measure of the force of gravity on an
object
Weight = mass x acceleration due to gravity
W = mg written on formula sheet as Fg = mg,
W = m (in kilograms) x g (9.8 m/s2)
Greater mass = greater gravitational force =
greater weight
Weight is measured in newtons (N)
A kilogram of mass on Earths surface weighs
9.8N.
Weight depends on where you are
Earth has more mass than the moon = more
gravitational pull
Therefore, objects weigh more here than on
the moon
Mass of objects doesnt change with changes
in gravity
Samples:
1. What causes a rolling object to stop moving?
A. an opposing force such as friction
b. the force of gravity
c. the weight of the object
d. the mass of the object
2. The mass of a kangaroo is 125 kg. What is the
weight of the kangaroo?
3. What is the resultant force of a 50N force in a
northerly direction and a 40N force in a southerly
direction?
4. A car works harder to accelerate from 0 to
10km/hr than it does to maintain a 10km/hr
speed. Why is this?
A. b/c static friction is harder to overcome than
kinetic or rolling friction.
B. b/c static friction is easier to overcome than
kinetic or rolling friction.
C. b/c static friction is harder to overcome than
potential energy.
D. b/c static friction is easier to overcome than
gravity.
5. Which of the following might be the effect of an
unbalanced force acting on an object?
A. An unbalanced force can only cause an object
to slow down.
B. An unbalanced force can cause an object to
speed up only.
C. An unbalanced force can cause on object to
speed up, slow down, or change direction.
D. An unbalanced force can only cause a change
in direction of motion.
6. A beach ball rests on the sand. When the wind
blows, the ball rolls away. Which statement
correctly assesses the reason for this change in
motion?
A. The ball moved b/c an unbalanced force acted upon
it.
B. The ball moved b/c a balance force acted upon
it.
C. The ball moved b/c the force of gravity was
overcome.
D. The ball moved b/c there was no friction to
overcome.
7. Aisha and Kaleb are playing tug of war. Aisha is
pulling with a force of 21N east. Kaleb is pulling
w/ a force of 18N west. What is the net force in
the contest?
A. 39N north B. 3N east C. 3N
west D. 3N south
8. Use the diagram to determine in which
direction the object will move.
A. left B. right C. up D. down
9. Gravity is the force of attraction b/w any two
objects that have mass. The gravitational force
that a body exerts depends, in part, on its mass.
Which of the following factors also affects the
amount of gravitational force experienced b/w two
bodies?
A. the distance b/w the bodies
b. the relative speed of the bodies
c. the altitude of the bodies
d. the angle of the bodies
10. Jared threw a softball up in the air to a height
of 10m. Rayquan threw a softball up 12m.
Rayquan threw the ball higher b/c
a. the pull of gravity on the ball was less
b. he threw with greater force
c. there was less air friction where he threw the
ball
d. gravity pulled the ball higher
11. A bowling ball with a mass of 5.44kg and a
soccer ball with a mass of 0.43kg are dropped
from a 15m platform. Identify the correct
description of the acceleration of the bowling ball
and the force with which it hits the ground, with
respect to the soccer ball.
A. The force of the bowling ball is greater and its
acceleration is greater.
B. The force of the bowling ball is greater and its
acceleration is the same.
C. The force of the bowling ball is the same and
its acceleration is greater.
D. The force of the bowling ball is the same, and
its acceleration is the same.
12. Select the situation that will result in the
greatest gravitational force b/w 2 bodies.
A. large combined mass and small distance apart
B. large combined mass and great distance apart.
C. small combined mass and great distance apart.
D. small combined mass and small distance
apart.
13. The weight of an object is less on the moon
b/c
A. objects on the moon experience a greater
acceleration due to gravity.
B. objects on the moon experience a lesser
acceleration due to gravity
C. there are fewer frictional forces on the moon.
D. there are more frictional forces on the moon.
14. Which statement describes an objects
velocity during freefall toward Earth?
A. an object travels at a constant velocity
throughout the fall
B. An objects velocity increases as it falls.
C. An objects velocity decreases as it falls.
D. An object during freefall does not have a
measurable velocity.
15. Which statement about the weight of an
object is correct?
A. The force of gravity determines an objects
weight.
B. Weight is an unchanging measure of an
objects mass.
C. The weight and mass of an object are the same.
D. An objects weight is not related to its mass.
16. Monisha planted pumpkin seeds in the spring.
The pumpkin she grew weighed 3920N. What was
its mass?
A. 3920kg B. 400kg C. 400N D. 1372 kg
17. Which statement is false?
A. Mass is the amount of matter in an object.
B. Kg are units of mass.
C. An objects mass does not change with location.
D. An objects mass increases in stronger gravity
fields.
18. What is the gravitational force acting on a 70-
kg person standing at sea level?
A. 79.8N B. 159.6N C. 602N D. 686N
19. Jupiters gravity is 254% as strong as the
gravity on Earth. What is the best explanation for
this?
A. Jupiters mass is less than the mass on Earth,
and the gravitational pull of Jupiter is therefore
greater.
B. Jupiter is closer to the Sun than Earth, and the
gravitational pull of Jupiter is therefore greater.
C. Earths distance from the Sun is less than the
distance of Jupiter to the Sun, and the
gravitational pull of Jupiter is therefore greater.
D. Jupiter is far more massive compared to Earth,
and the gravitational pull is therefore greater.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Mitosisnotes 170209212950 2Document17 pagesMitosisnotes 170209212950 2api-369706779No ratings yet
- 06 - Air Pressure and WindDocument12 pages06 - Air Pressure and Windapi-369706779No ratings yet
- Waves and Sound WebquestDocument2 pagesWaves and Sound Webquestapi-369706779No ratings yet
- Radioactivity Research ProjectDocument6 pagesRadioactivity Research Projectapi-369706779No ratings yet
- Classification of LifeDocument32 pagesClassification of Lifeapi-3697067790% (1)
- EvolutionDocument34 pagesEvolutionKim LukeNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Balancing Chemical Equations Web Quest 1Document5 pagesChemical Reactions and Balancing Chemical Equations Web Quest 1api-2625864460% (1)
- 02 - Atmospheric HeatDocument13 pages02 - Atmospheric Heatapi-369706779No ratings yet
- 1 1 1 Notes Teacher CH 11 1Document4 pages1 1 1 Notes Teacher CH 11 1api-369706779No ratings yet
- 1 2 3 Notes Teacher CH 12 2 and 12 3Document7 pages1 2 3 Notes Teacher CH 12 2 and 12 3api-369706779No ratings yet
- 1 1 2 Notes Teacher CH 11 2Document8 pages1 1 2 Notes Teacher CH 11 2api-369706779No ratings yet
- 01 - Composition and Structure of The AtmosphereDocument10 pages01 - Composition and Structure of The Atmosphereapi-369706779No ratings yet
- 12 TidesDocument19 pages12 Tidesapi-369706779No ratings yet
- Earth Science Water Test ReviewDocument17 pagesEarth Science Water Test Reviewapi-369706779No ratings yet
- 08-Ocean Life AquacultureDocument11 pages08-Ocean Life Aquacultureapi-369706779No ratings yet
- 3 2 4 Teacher Notes Wave BehaviorDocument6 pages3 2 4 Teacher Notes Wave Behaviorapi-369706779No ratings yet
- 09 - Temp Salinity Ocean AcidificationDocument12 pages09 - Temp Salinity Ocean Acidificationapi-369706779No ratings yet
- 11-Wave Shoreline Features 1Document26 pages11-Wave Shoreline Features 1api-332249032No ratings yet
- 10-Currents and ClimatesDocument15 pages10-Currents and Climatesapi-369706779No ratings yet
- 07-Continental MarginsDocument12 pages07-Continental Marginsapi-369706779No ratings yet
- Water Resources SWDocument34 pagesWater Resources SWapi-369706779No ratings yet
- 3 2 1 - 3 2 3 Teacher Notes CH 17 18Document9 pages3 2 1 - 3 2 3 Teacher Notes CH 17 18api-369706779No ratings yet
- 3 2 WavesDocument22 pages3 2 Wavesapi-369706779No ratings yet
- 2 2 4 2 2 5 NotesDocument6 pages2 2 4 2 2 5 Notesapi-369706779No ratings yet
- 2 2 1 NotesDocument7 pages2 2 1 Notesapi-369706779No ratings yet
- RadioactivityDocument49 pagesRadioactivityapi-369706779No ratings yet
- Nuclear Chemistry NotesDocument13 pagesNuclear Chemistry Notesapi-369706779No ratings yet
- Geohazards ProjectDocument2 pagesGeohazards Projectapi-369706779No ratings yet
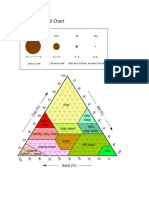
- Earth Science Soil ChartDocument1 pageEarth Science Soil Chartapi-369706779No ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Testing Cellular Glass Insulation Block: Standard Test Methods ofDocument4 pagesTesting Cellular Glass Insulation Block: Standard Test Methods ofArun UdayabhanuNo ratings yet
- Ibc 2003Document10 pagesIbc 2003MIKHA2014No ratings yet
- KV Sizer GuideDocument3 pagesKV Sizer GuideBasavaraj ManturNo ratings yet
- Guia SupacDocument44 pagesGuia SupacMario Vazquez BNo ratings yet
- Climbing Film EvaporatorDocument8 pagesClimbing Film Evaporatorsaz140% (1)
- Sowinkumar Namel A/l Nagarajan (Ee095367) Raneej A/l Sukumaran (Ee095356) Section 4 Bench 05Document2 pagesSowinkumar Namel A/l Nagarajan (Ee095367) Raneej A/l Sukumaran (Ee095356) Section 4 Bench 05Sowin HustleNo ratings yet
- Cooling by Underground Earth TubesDocument4 pagesCooling by Underground Earth TubesNaava BasiaNo ratings yet
- Travel Drive ExampleDocument10 pagesTravel Drive Examplep-nicoNo ratings yet
- The Undivided Universe, An Ontological Interpretation of Quantum PDFDocument418 pagesThe Undivided Universe, An Ontological Interpretation of Quantum PDFMagda Ali94% (16)
- CNG Gas Station GSPCDocument9 pagesCNG Gas Station GSPCMilan KothariNo ratings yet
- Master Cyilinder Actuation Package CO Pneumatic Release ActuatorDocument2 pagesMaster Cyilinder Actuation Package CO Pneumatic Release ActuatorEliud RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 2008 Product Catalogue PDFDocument255 pages2008 Product Catalogue PDFrenoyaboNo ratings yet
- Conclusion & ReferencesDocument4 pagesConclusion & ReferencesAlejandro GilNo ratings yet
- Assignment#1Document5 pagesAssignment#1Hennesey LouriceNo ratings yet
- Test-2 - Capacitor + Work + CurrentDocument7 pagesTest-2 - Capacitor + Work + CurrentSombir AhlawatNo ratings yet
- TechnetiumDocument3 pagesTechnetiumDavid JonesNo ratings yet
- Chemical Properties of AluminumDocument5 pagesChemical Properties of AluminumAnonymous cgcKzFtXNo ratings yet
- TC FLS Sihi Leh 1200 1500 1800 enDocument10 pagesTC FLS Sihi Leh 1200 1500 1800 enGustavo ZavalaNo ratings yet
- TLP 2355Document16 pagesTLP 2355teomondoNo ratings yet
- Hazards of Cell PhonesDocument17 pagesHazards of Cell PhonesNiri KshaNo ratings yet
- Subtle Biology - The Web of Life - John DavidsonDocument5 pagesSubtle Biology - The Web of Life - John DavidsonJohn Davidson100% (1)
- Inserto Clase 15KV 200a PDFDocument16 pagesInserto Clase 15KV 200a PDFjavier vargasNo ratings yet
- 4-LET - General Education - SCIENCE 82-109Document28 pages4-LET - General Education - SCIENCE 82-109Rogen Hemodo67% (6)
- Fault Code 195 Coolant Level Sensor Circuit - Voltage Above Normal or Shorted To High SourceDocument13 pagesFault Code 195 Coolant Level Sensor Circuit - Voltage Above Normal or Shorted To High SourceAhmedmah100% (1)
- Fuel, Lubricants and Fluids: en-GBDocument59 pagesFuel, Lubricants and Fluids: en-GBRuanNo ratings yet
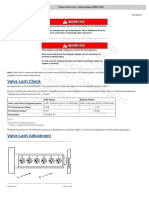
- Engine Valve Lash - Inspect AdjustDocument3 pagesEngine Valve Lash - Inspect AdjustRay CapriNo ratings yet
- Full Product Line Catalogue 2018 2270Document232 pagesFull Product Line Catalogue 2018 2270kingreadyNo ratings yet
- Definition of Terms - Plumbing2Document15 pagesDefinition of Terms - Plumbing2Gels GenovaNo ratings yet
- Heating Resistor LeafletDocument2 pagesHeating Resistor LeafletNaqi Min GilNo ratings yet
- Impressed Current Cathodic Protection Design For Eleme Petrochemical 6 and 8'' Pipeline PDFDocument16 pagesImpressed Current Cathodic Protection Design For Eleme Petrochemical 6 and 8'' Pipeline PDFobuseNo ratings yet