Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Cloud?: Unit 1: Introduction To Cloud Computing
Uploaded by
kashinath.kbOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Cloud?: Unit 1: Introduction To Cloud Computing
Uploaded by
kashinath.kbCopyright:
Available Formats
Cloud Computing
Unit 1 : Introduction to Cloud Computing
Evolution of cloud, Essentials, Cloud Computing definition, Benefits and Challenges, Limitations,
Usage and Applications, Business Models around Cloud Computing, Characteristics, Cloud Adoption
. 6 Hrs / 20 Marks
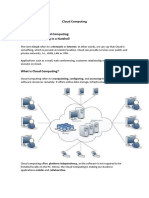
1.0 Introduction
Cloud Computing provides us a means by which we can access the applications as
utilities, over the Internet. It allows us to create, configure, and customize applications
online.
What is Cloud?
The term Cloud refers to a Network or Internet. In other words, we can say that
Cloud is something, which is present at remote location. Cloud can provide services over
network, i.e., on public networks or on private networks, i.e., WAN, LAN or VPN.
Applications such as e-mail, web conferencing, customer relationship management (CRM),
all run in cloud.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud Computing refers to manipulating, configuring, and accessing the
applications online. It offers online data storage, infrastructure and application. We need
not to install a piece of software on our local PC and this is how the cloud computing
overcomes platform dependency issues. Hence, the Cloud Computing is making our
business application mobile and collaborative.
Cloud computing is a computing paradigm, where a large pool of systems are
connected in private or public networks, to provide dynamically scalable infrastructure for
application, data and file storage. The idea of cloud computing is based on a very
fundamental principal of reusability of IT capabilities'.
15CS53B: Cloud Computing Unit 1: Introduction to Cloud computing Page 1
Cloud Computing
1.1 Evolution of Cloud
The concept of Cloud Computing came into existence in 1950 with implementation
of mainframe computers, accessible via thin/static clients. Since then, cloud computing
has been evolved from static clients to dynamic ones from software to services. The
following diagram explains the evolution of cloud computing.
15CS53B: Cloud Computing Unit 1: Introduction to Cloud Computing Page 2
Cloud Computing
15CS53B: Cloud Computing Unit 1: Introduction to Cloud Computing Page 3
Cloud Computing
15CS53B: Cloud Computing Unit 1: Introduction to Cloud Computing Page 4
Cloud Computing
Benefits of Cloud Computing
One can access applications as utilities, over the Internet.
Manipulate and configure the application online at any time.
It does not require installing a specific piece of software to access or
manipulating cloud application.
Cloud Computing offers online development and deployment tools,
programming runtime environment through Platform as a Service model.
Cloud resources are available over the network in a manner that provides
platform independent access to any type of clients.
Cloud Computing offers on-demand self-service. The resources can be used
without interaction with cloud service provider.
Cloud Computing is highly cost effective because it operates at higher
efficiencies with greater utilization. It just requires an Internet connection.
Cloud Computing offers load balancing that makes it more reliable.
15CS53B: Cloud Computing Unit 1: Introduction to Cloud Computing Page 5
Cloud Computing
Limitation of Cloud Computing
PUBLIC CLOUD PRIVATE CLOUD
Public clouds are based on shared physical A private cloud is infrastructure dedicated
hardware which is owned and operated by a entirely to your business thats hosted either on-
third-party provider. site or in a service providers data center.
Public clouds are ideal for small and medium Private clouds are ideal for large sized
sized businesses or businesses that have businesses or businesses that have fixed demands
fluctuating demands
A public cloud provides less or no control and A private cloud provides greater levels of control
security. and security
New application can be deploy very quick New application deployment takes more time
and The ability to pay only of the server and whether you use or not you have to pay for
resources you use. Servers.
It has advantage of a low-cost, pay-as-you-go Very high initial cost.
approach to IT provisioning.
Due to the sheer size of public clouds, you Since servers are solo owned or reserved, very
can scale compute power up and down as difficult to scale compute power up and down as
business demands, within a matter of minutes business demands and it takes lot of time.
The ability to customize the compute, storage One of key benefit of private cloud is the ability
and networking components to best suit your to customize the compute, storage and
specific IT requirements is very difficult. networking components to best suit your specific
IT requirements.
15CS53B: Cloud Computing Unit 1: Introduction to Cloud Computing Page 6
Cloud Computing
PRIVATE CLOUD PUBLIC CLOUD
ADVANTAGES
Private cloud infrastructure is a dedicated In public clouds the resources are shared
infrastructure provided to one single between multiple clients and all the services are
organization or client. controlled by services provider.
Controls: Better controls for data, users and Simple and easy: Public clouds are available as
information assets. a service in the internet, they are easy to deploy
Cost: Initial investment for hardware is very Cost: Initial investment is very low or nil
high in case of an on-premise infrastructure.
Security: The cloud belongs to a single Less time: The IT resources and services are
client. Hence, the infrastructure and systems available immediately saving time for the
can be configured to provide high levels of company
security
Superior Performance: Normally private No maintenance: The hardware and networks
clouds are deployed inside the firewall of the are maintained by the cloud services provider.
organizations intranet which ensures Internal IT staffs have no responsibility in
efficiency and good network performance maintaining the infrastructure
Easy Customization: The hardware and No contracts: No long term commitment with
other resources can be customized easily by service provider because public clouds are
the company usually pay-as-you-go models
Compliance: Compliance is achieved easily
in private clouds
DISADVANTAGES
Cost: Costs are substantial in the case of Lacks proper controls: The client has no
building an on-premise private cloud. The control of data or infrastructure. There are issues
running cost would include personnel cost of data privacy and integrity. The service level
and periodic hardware upgrade costs. In the policies and compliances are completely
case of outsourced private cloud, operating enforced by the service provider.
cost will include per resource usage and
subject to change at the discretion of the
service provider
Under-utilization: In some instances the Performance: The performance of the network
resources subscribed can be under-utilized. depends on the speed of the internet connectivity
Hence, optimizing the utilization of all
resources is a challenge
Capacity ceiling: Due to physical hardware Weak on Security: Since the hardware resource
limitations with the service provider, there is shared between multiple users, IT security
could be a capacity ceiling to handle only issues are more profound and data is vulnerable
certain amount of servers or storage to thefts
Vendor lock-in: This can be a major Customization: Customization of resources or
impediment in private cloud adoption services is not possible
especially when the hardware and
infrastructure is outsourced. This is a service
15CS53B: Cloud Computing Unit 1: Introduction to Cloud Computing Page 7
Cloud Computing
delivery technique where the client company
is forced to continue with the same service
provider, thus preventing the client to migrate
to another vendor
15CS53B: Cloud Computing Unit 1: Introduction to Cloud Computing Page 8
Cloud Computing
15CS53B: Cloud Computing Unit 1: Introduction to Cloud Computing Page 9
Cloud Computing
Advantages of Cloud Computing
Drive down costs: Avoid large capital expenditure on hardware and
upgrades. Cloud can also improve cost efficiency by more closely matching
your cost pattern to your revenue/demand pattern, moving your business from a
capital-intensive cost model to an Opex model.
Cope with demand: You know what infrastructure you need today, but what about
your future requirements? As your business grows, a cloud environment should
grow with you. And when demand is unpredictable or you need to test a new
application, you have the ability spin capacity up or down, while paying only for
what you use.
Run your business; dont worry about your IT: Monitoring your infrastructure
24/7 is time consuming and expensive when you have a business to run. A managed
cloud solution means that your hosting provider is doing this for you. In addition to
monitoring your infrastructure and keeping your data safe, they can provide creative
and practical solutions to your needs, as well as expert advice to keep your IT
infrastructure working efficiently as your needs evolve.
Innovate and lead: Ever-changing business requirements mean that your IT
infrastructure has to be flexible. With a cloud infrastructure, you can rapidly deploy
new projects and take them live quickly, keeping you at the vanguard of innovation
in your sector.
Improved security and compliance: You have to protect your business against loss
of revenue and brand damage. In addition, many organizations face strict regulatory
and compliance obligations. A cloud environment means that this responsibility no
longer rests entirely on your shoulders. Your cloud hosting provider will build
in resiliency and agility at an infrastructure-level to limit the risk of a security
breach, and will work with you to help address compliance and regulatory
requirements.
Reduce your carbon footprint: Hosting in a data center rather than onsite allows
you to take advantage of the latest energy-efficient technology. Additionally, as
cloud service providers host multiple customers on shared infrastructure, they can
drive higher and more efficient utilization of energy resources.
Future-proof your business: There is unprecedented demand for access to data
anywhere, any time and on any device. Dont let your business fall behind. By
embracing the cloud, you can handle emerging mobile, BYOD and wearable
technology trends
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
There is no doubt that businesses can reap huge benefits from cloud computing. However,
with the many advantages, come some drawbacks as well. Take time to understand the
advantages and disadvantages of cloud computing, so that you can get the most out of your
business technology, whichever cloud provider you choose.
15CS53B: Cloud Computing Unit 1: Introduction to Cloud Computing Page 10
Cloud Computing
Advantages of Cloud Computing
Cost Savings
Perhaps, the most significant cloud computing benefit is in terms of IT cost savings.
Businesses, no matter what their type or size, exist to earn money while keeping capital
and operational expenses to a minimum. With cloud computing, you can save substantial
capital costs with zero in-house server storage and application requirements. The lack of
on-premises infrastructure also removes their associated operational costs in the form of
power, air conditioning and administration costs. You pay for what is used and disengage
whenever you like - there is no invested IT capital to worry about. Its a common
misconception that only large businesses can afford to use the cloud, when in fact, cloud
services are extremely affordable for smaller businesses.
Reliability
With a managed service platform, cloud computing is much more reliable and consistent
than in-house IT infrastructure. Most providers offer a Service Level Agreement which
guarantees 24/7/365 and 99.99% availability. Your organization can benefit from a
massive pool of redundant IT resources, as well as quick failover mechanism - if a server
fails, hosted applications and services can easily be transited to any of the available
servers.
Manageability
Cloud computing provides enhanced and simplified IT management and maintenance
capabilities through central administration of resources, vendor managed infrastructure and
SLA backed agreements. IT infrastructure updates and maintenance are eliminated, as all
resources are maintained by the service provider. You enjoy a simple web-based user
interface for accessing software, applications and services without the need for
installation - and an SLA ensures the timely and guaranteed delivery, management and
maintenance of your IT services.
Strategic Edge
Ever-increasing computing resources give you a competitive edge over competitors, as the
time you require for IT procurement is virtually nil. Your company can deploy mission
critical applications that deliver significant business benefits, without any upfront costs and
minimal provisioning time. Cloud computing allows you to forget about technology and
focus on your key business activities and objectives. It can also help you to reduce the time
needed to market newer applications and services.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
Downtime
As cloud service providers take care of a number of clients each day, they can become
overwhelmed and may even come up against technical outages. This can lead to your
business processes being temporarily suspended. Additionally, if your internet connection
is offline, you will not be able to access any of your applications, server or data from the
cloud.
Security
Although cloud service providers implement the best security standards and industry
certifications, storing data and important files on external service providers always opens
15CS53B: Cloud Computing Unit 1: Introduction to Cloud Computing Page 11
Cloud Computing
up risks. Using cloud-powered technologies means you need to provide your service
provider with access to important business data. Meanwhile, being a public service opens
up cloud service providers to security challenges on a routine basis. The ease in procuring
and accessing cloud services can also give nefarious users the ability to scan, identify and
exploit loopholes and vulnerabilities within a system. For instance, in a multi-tenant cloud
architecture where multiple users are hosted on the same server, a hacker might try to
break into the data of other users hosted and stored on the same server. However, such
exploits and loopholes are not likely to surface, and the likelihood of a compromise is not
great.
Vendor Lock-In
Although cloud service providers promise that the cloud will be flexible to use and
integrate, switching cloud services is something that hasnt yet completely evolved.
Organizations may find it difficult to migrate their services from one vendor to another.
Hosting and integrating current cloud applications on another platform may throw up
interoperability and support issues. For instance, applications developed on Microsoft
Development Framework (.Net) might not work properly on the Linux platform.
Limited Control
Since the cloud infrastructure is entirely owned, managed and monitored by the service
provider, it transfers minimal control over to the customer. The customer can only control
and manage the applications, data and services operated on top of that, not the backend
infrastructure itself. Key administrative tasks such as server shell access, updating and
firmware management may not be passed to the customer or end user.
It is easy to see how the advantages of cloud computing easily outweigh the drawbacks.
Decreased costs, reduced downtime, and less management effort are benefits that speak for
themselves
Limitations of Cloud Computing
Cascading effect
If there is a problem in data center, all virtual machines are affected. There might or might
not be a backup of the data if an enterprise relies only on the cloud for its data management
needs.
Network connection
The concept assumes that the client has reliable network connection. If there are problems
of network connectivity, accessing the cloud also becomes a problem. Performance of the
15CS53B: Cloud Computing Unit 1: Introduction to Cloud Computing Page 12
Cloud Computing
cloud applications also depend on the performance of network at clients side. Upload and
download speeds are slower as compared to that of a local server.
Control of data security
In a public cloud, the client does not have the control over security of his/ her own data.
The clients data can be susceptible to hacking or phishing attacks. Since the servers on
cloud are interconnected it is easy for malware to spread.
Additional costs
Although cloud computing offers cost benefits, it has some hidden or additional costs as
well. Clients are charged extra for data transfer or other services. Initial offerings are
priced higher, till economies of scale work out for the service provider.
Peripherals
Peripheral devices like printers or scanners might not work with cloud. Many of them
require software to be installed locally. Networked peripherals have lesser problems.
Integration
Integrating internal applications with those on cloud can be complex and in some cases not
viable.
Generic
Public cloud offerings are very generic and offer multi-tenancy service which all
organizations might not be comfortable with. Implementing an in-house cloud is more
complex to implement and are burdensome on internal resources if the organization is not
large enough.
Cloud service providers are continuously evolving solutions to overcome the above
mentioned hurdles. Some enterprises are seeing clear benefits in shifting to the cloud and
are adopting it unconditionally while some enterprises are moving non-critical applications
to test the waters. Some others want to wait and watch how the technology evolves before
deciding
1.8.1 Green Washing
QUESTION BANK (5 Marks)
1. Explain the evolution of cloud computing.
15CS53B: Cloud Computing Unit 1: Introduction to Cloud Computing Page 13
Cloud Computing
2. Why cloud computing?
3. Describe the essentials of cloud computing.
4. Illustrate the development of cloud to an organization.
5. Explain the benefits and strategies of cloud.
6. Discuss the limitations of cloud computing.
7. Explain the business models around the cloud
8. Explain the characteristics of cloud computing
QUESTION BANK (10 Marks)
1. Explain the business and it perspectives of cloud.
2. Describe in detail cloud computing.
3. List and explain the usage scenarios and applications of cloud
4. Write advantages and disadvantages of cloud computing
5. Illustrate the cloud adoption
15CS53B: Cloud Computing Unit 1: Introduction to Cloud Computing Page 14
You might also like
- Cloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingFrom EverandCloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing and Virtualization: Streamlining Your IT InfrastructureFrom EverandCloud Computing and Virtualization: Streamlining Your IT InfrastructureNo ratings yet
- R20 3-1 Cce Unit - 1Document14 pagesR20 3-1 Cce Unit - 1vishnucharanbondalapatiNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing JUNE 2022Document12 pagesCloud Computing JUNE 2022Rajni KumariNo ratings yet
- cloud computing AUDocument11 pagescloud computing AUTHANGA DURAINo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 New Trends in MISDocument31 pagesLecture 4 New Trends in MISmaryallaine02No ratings yet
- Part B ETIDocument10 pagesPart B ETISoNo ratings yet
- Basic PPT On Cloud ComputingDocument32 pagesBasic PPT On Cloud ComputingSavyasachi Vats54% (13)
- Cloud ComputingDocument16 pagesCloud ComputingKranthi kumarNo ratings yet
- Detailed Overview of Cloud ComputingDocument18 pagesDetailed Overview of Cloud ComputingAravind Kumar CSNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Unit1to4Document66 pagesCloud Computing Unit1to4luffymonkeyd0123No ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument15 pagesCloud ComputingRanjith RamarNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing IEEE PaperDocument4 pagesCloud Computing IEEE PaperAsrar Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Triumph in The sky-WPS OfficeDocument24 pagesTriumph in The sky-WPS OfficeDharmrajNo ratings yet
- CS8791-CC Unit-IDocument32 pagesCS8791-CC Unit-Iparth_iarjunNo ratings yet
- nisha report3.....Document19 pagesnisha report3.....abdulqaiyum710636No ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument15 pagesCloud ComputingAtharvaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Mini Project Work Entiled OnDocument24 pagesCloud Computing: Mini Project Work Entiled OnZeanav KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document19 pagesUnit 1Mag CreationNo ratings yet
- Generic Cloud ArchitectureDocument12 pagesGeneric Cloud ArchitectureNitesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Types, Benefits, Risks & ReadinessDocument24 pagesCloud Computing: Types, Benefits, Risks & ReadinessPat LanugonNo ratings yet
- WQD180087 Assignment 4Document3 pagesWQD180087 Assignment 4Chen ChaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Cloud ComputingDocument5 pagesBasics of Cloud ComputingAtharvaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Unit-1 - Introduction To Cloud TechnologiesDocument78 pagesCloud Computing: Unit-1 - Introduction To Cloud TechnologiesSarika80% (5)
- Shri Ramswaroop Memorial University: Submitted To Mr. Anand RaiDocument19 pagesShri Ramswaroop Memorial University: Submitted To Mr. Anand RaiAaqib KhanNo ratings yet
- 8 - Intro To Cloud ComputingDocument26 pages8 - Intro To Cloud ComputingMahamed HusseinNo ratings yet
- DOM205 - Individual Project - Cloud Computing ABHARIKA MOHANTYDocument18 pagesDOM205 - Individual Project - Cloud Computing ABHARIKA MOHANTYAbharika MohantyNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Overview: Key Concepts and ApplicationsDocument6 pagesCloud Computing Overview: Key Concepts and ApplicationsArun KumarNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing ConceptsDocument10 pagesCloud Computing ConceptsNitish RanaNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument34 pagesArtificial IntelligenceHimanshu DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Abstract-: Keywords: Applications, Architecture, Business Component of CloudDocument15 pagesAbstract-: Keywords: Applications, Architecture, Business Component of CloudKrishna BoreddyNo ratings yet
- Cloud Migration Process and Benefits of Hybrid Deployment ModelDocument9 pagesCloud Migration Process and Benefits of Hybrid Deployment ModelBhumi ShresthaNo ratings yet
- CC Intro HKADocument60 pagesCC Intro HKAramakantaswain1302No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing & TypeDocument13 pagesCloud Computing & TypePooja kNo ratings yet
- Anurag CC LAB File CompleteDocument27 pagesAnurag CC LAB File CompleteBaby SauravNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument19 pagesCloud ComputingDikshith RoshanNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Cloud Computing: Submitted By: Shivansh Khatri 19BCON403Document17 pagesSeminar On Cloud Computing: Submitted By: Shivansh Khatri 19BCON403Dank BoiiNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Question Bank Modules 1-4Document9 pagesCloud Computing Question Bank Modules 1-4Rahul HarwalNo ratings yet
- Af2 U1 Francisco LizanaDocument10 pagesAf2 U1 Francisco LizanaFrancisco Javier Lizana AndradeNo ratings yet
- CLOUD COMPUTING CHALLENGES AND STACKDocument9 pagesCLOUD COMPUTING CHALLENGES AND STACKN Latha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument20 pagesCloud ComputingAthavanRamachandran100% (1)
- Cloud Computing Section-1: Prepared by Manish Kumar Aery. IET Bhaddal Technical Campus, RoparDocument16 pagesCloud Computing Section-1: Prepared by Manish Kumar Aery. IET Bhaddal Technical Campus, Roparjuanestudia12No ratings yet
- CC Evolution Od CloudDocument51 pagesCC Evolution Od CloudTushar MircheNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document13 pagesUnit 1Bnod MsraNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocument14 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To Cloud Computingjaysukhv234No ratings yet
- Deloitte Cloud - Task 1 - Understanding Cloud Computing - TemplateDocument3 pagesDeloitte Cloud - Task 1 - Understanding Cloud Computing - TemplateApurbh Singh KashyapNo ratings yet
- What Is Cloud Computing?Document4 pagesWhat Is Cloud Computing?Y Bhavani pushpa 17-222No ratings yet
- Definition of Cloud Computing - Characteristics of Cloud - Cloud Deployment ModelsDocument11 pagesDefinition of Cloud Computing - Characteristics of Cloud - Cloud Deployment Modelsvigneshg463No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing IntroductionDocument16 pagesCloud Computing IntroductionVicNo ratings yet
- Demystifying The CloudDocument16 pagesDemystifying The CloudAaron MangalNo ratings yet
- Cloud by Jagadish SirDocument71 pagesCloud by Jagadish SirBishnu BashyalNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing All Units PDFDocument110 pagesCloud Computing All Units PDFRahul Gudla100% (1)
- Cloud Infrastructure DocumentationDocument59 pagesCloud Infrastructure DocumentationGDSC Assuit UniversityNo ratings yet
- Questions & Answers in Cloud ComputihgDocument7 pagesQuestions & Answers in Cloud ComputihgMostafaElBazNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Important Questions & AnswersDocument14 pagesCloud Computing Important Questions & AnswersEr Saroj Chaudhary100% (7)
- Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Cloud ComputingManisha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Cloud ComputingDocument8 pagesEvolution of Cloud Computinghiteshsharma01abuNo ratings yet
- A Study of Cloud Computing MethodologyDocument5 pagesA Study of Cloud Computing MethodologyR Dharshini SreeNo ratings yet
- CloudDocument11 pagesCloudcherry grootNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Harnessing the Power of the Digital Skies: The IT CollectionFrom EverandCloud Computing: Harnessing the Power of the Digital Skies: The IT CollectionNo ratings yet
- Week 12 ActivityDocument10 pagesWeek 12 Activitykashinath.kbNo ratings yet
- Placement Details of Government Women'S Polytechnic, ShiralakoppaDocument1 pagePlacement Details of Government Women'S Polytechnic, Shiralakoppakashinath.kbNo ratings yet
- Week 13 Activity PDFDocument13 pagesWeek 13 Activity PDFkashinath.kbNo ratings yet
- Week 11 ActivityDocument6 pagesWeek 11 Activitykashinath.kbNo ratings yet
- A Basic Overview: The Academic Support Center at Daytona State College (Science 130 Page 1 of 21)Document21 pagesA Basic Overview: The Academic Support Center at Daytona State College (Science 130 Page 1 of 21)kashinath.kbNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Aim of The ProjectDocument29 pages1.1 Aim of The Projectkashinath.kbNo ratings yet
- Week 9 ActivityDocument3 pagesWeek 9 Activitykashinath.kbNo ratings yet
- Week 10 ActivityDocument3 pagesWeek 10 Activitykashinath.kbNo ratings yet
- Online Grievance ManagementDocument32 pagesOnline Grievance Managementkashinath.kbNo ratings yet
- MSIT-102 Programming Concepts and CDocument218 pagesMSIT-102 Programming Concepts and CSaid kiranNo ratings yet
- Digestion and AbsorptionDocument12 pagesDigestion and AbsorptionminaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Bash Scripting GuideDocument646 pagesAdvanced Bash Scripting GuideercbeaudoinNo ratings yet
- Operating System MCQsDocument49 pagesOperating System MCQsShuseel Baral100% (6)
- Syllabus Cloud ComputingDocument9 pagesSyllabus Cloud Computingkashinath.kbNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument1 pageNew Microsoft Word Documentkashinath.kbNo ratings yet
- SeleniumDocument31 pagesSeleniumArnab GhoshNo ratings yet
- PatnaDocument21 pagesPatnaRohit kumarNo ratings yet
- B.Tech IT 5 6 Semester Session 2021-22 Scheme Syllabus FinalDocument42 pagesB.Tech IT 5 6 Semester Session 2021-22 Scheme Syllabus Finaladityaa20467No ratings yet
- Fitness Center 1 Cs Practical For Class 12Document13 pagesFitness Center 1 Cs Practical For Class 12aeeeelvishbhaiiNo ratings yet
- COGNOS Guidelines and Best PracticesDocument21 pagesCOGNOS Guidelines and Best PracticessamuthiNo ratings yet
- Organisational Factors and E-Accounting Adoption in Nigerian SMEsDocument247 pagesOrganisational Factors and E-Accounting Adoption in Nigerian SMEsSanae AjtimNo ratings yet
- NVision Manual 2019Document593 pagesNVision Manual 2019Alpha MNo ratings yet
- Q 8HGJKSWKvlbOKLdTtkg Google-Cybersecurity-Certificate-glossaryDocument28 pagesQ 8HGJKSWKvlbOKLdTtkg Google-Cybersecurity-Certificate-glossaryWalid AliNo ratings yet
- Se Mini ProjectDocument12 pagesSe Mini ProjectAbhijeet MalabadeNo ratings yet
- System Analyst ResumeDocument7 pagesSystem Analyst Resumec2s6kh72100% (1)
- Constitution and by LawsDocument10 pagesConstitution and by LawsDarwinNo ratings yet
- Software Development Techniques (Eie326)Document42 pagesSoftware Development Techniques (Eie326)Opeyemi OrugunNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving Chatbot For DatastructureDocument15 pagesProblem Solving Chatbot For Datastructurekhedlekar shrutiNo ratings yet
- WAHA User GuideDocument30 pagesWAHA User GuidewahacmsNo ratings yet
- NB-IOT Part-1: Madhan Mohan.PDocument10 pagesNB-IOT Part-1: Madhan Mohan.PBorqs TestNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.3 - Configuring Floating Static Routes InstructionsDocument3 pagesChapter 2.3 - Configuring Floating Static Routes InstructionsPao Renz OngNo ratings yet
- Class 7 - Who Is Instructing WhatDocument5 pagesClass 7 - Who Is Instructing WhatNurhanNo ratings yet
- Tata HPC AmanDocument34 pagesTata HPC Amantemp mailNo ratings yet
- Graphic Era Hill University, Dehradun: TCS101 Assignment No. 1 Based On The Course Objective-1Document1 pageGraphic Era Hill University, Dehradun: TCS101 Assignment No. 1 Based On The Course Objective-1Anshika UniyalNo ratings yet
- How To Customize The OBIEE User Interface PDFDocument68 pagesHow To Customize The OBIEE User Interface PDFhuyhnNo ratings yet
- Question Bank of SOOADMDocument2 pagesQuestion Bank of SOOADMDivyakant MevaNo ratings yet
- AVEVA Communication Drivers 2020Document5 pagesAVEVA Communication Drivers 2020Issao WatanabeNo ratings yet
- PI Web API 2016 R2 Release NotesDocument11 pagesPI Web API 2016 R2 Release NotesSri KNo ratings yet
- Tyit - Old Sem - V - Adv Java MCQDocument11 pagesTyit - Old Sem - V - Adv Java MCQsandy candyNo ratings yet
- SAFE Poster PDFDocument1 pageSAFE Poster PDFEdison HaiNo ratings yet
- LightningDocument505 pagesLightningwawanknNo ratings yet
- Computer Science & Engineering: Laboratory Note BookDocument23 pagesComputer Science & Engineering: Laboratory Note BookKaustav LahiriNo ratings yet
- Fast Track 6 2 ILT Datasheet 1Document1 pageFast Track 6 2 ILT Datasheet 1Swapnil BankarNo ratings yet
- Networker 9.x - NMDA Installation GuideDocument60 pagesNetworker 9.x - NMDA Installation GuideZuhaib ShafiNo ratings yet
- Oracle CRM OnDem - WebSvcs ExamplesDocument226 pagesOracle CRM OnDem - WebSvcs ExamplesshivasvjNo ratings yet
- Ethernet Op, DSL and 4G BadDocument8 pagesEthernet Op, DSL and 4G BadTrần Quang Huy TạNo ratings yet