Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SA Flowcharts 2
Uploaded by
partymongerOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SA Flowcharts 2
Uploaded by
partymongerCopyright:
Available Formats
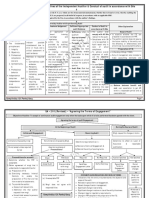
SA 200 (Revised) Overall Objectives of the Independent Auditor & Conduct of audit in accordance with SAs
(a) To obtain reasonable assurance about whether the F. S. as a whole are free from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error, thereby enabling the
auditor to express an opinion on whether the F.S. are prepared, in all material respects, in accordance with an applicable FRF.
(b) To report on the F.S. and communicate as required by the SAs, in accordance with the auditors findings.
Aspects to be considered by Auditor while performing Audit
Ethical Professional Professional Judgement Sufficient Appropriate Conduct of Audit in Other Explanation
Requirements Skepticism audit Evidence accordance with SAs
Comprise Code of Attitude that includes a The application of Sufficiency refers to The auditor shall Scope of Audit
Ethics issued by questioning mind, relevant training, quantum and comply with All SAs to examine whether the F.S. are
being alert to knowledge and Appropriateness relevant to the audit. prepared in accordance with FRF.
ICAI including
conditions which may experience, Compliance with SA The auditors opinion does not assure,
independence. refers to quality.
within the context is to be specified in the future viability of the entity nor
indicate possible Purpose: to reduce
The fundamental provided by auditing, Audit report only in the efficiency or effectiveness with
misstatement due to audit risk to an which mngt. has conducted the affairs.
principles are: accounting and ethical case of actual
error or fraud, and a acceptably low level
1. Integrity standards, compliance. Preparation of F.S.
critical assessment of
2. Objectivity in making informed and thereby enable To achieve overall is the duty of Mngt./TCWG.
audit evidence.
3. Professional decisions about the the auditor to draw objectives of audit, Duty of management also includes to
Alertness is required courses of action reasonable use the objective
competence & make accounting estimates and
w.r.t. that are appropriate in conclusions on which stated in Individual
due care selection and application of
1. Contradictory audit the circumstances of the SAs.
to base the auditors appropriate accounting policies.
4. Confidentiality, evidence. audit engagement. In case Entire SA is
opinion.
& 2. Reliability of It is required w.r.t.: not relevant due to Inherent Limitations for an audit
documents. Audit Risk: Risk that
5. Professional Materiality & audit risk. non existence of (a) Nature of Financial reporting:
3. Conditions the auditor expresses prescribed
behavior NTE of audit procedures. involves judgment by Mngt. based
indicating possible Evaluating sufficiency & an inappropriate audit conditions, comply
Independence on facts and circumstances.
frauds. appropriateness of audit opinion when the F.S. with relevant
comprises both (b) Nature of audit Procedures:
4. Circumstances procedures. are materially requirements.
directed towards obtaining
independence of requiring audit In case of failure to
Evaluating mngt misstated. reasonable assurance.
mind and procedures in judgment in applying achieve an objective
Audit Risk is a (c) Balance between benefit and
independence of addition to those applicable FRF. determine the need
function of the RMM cost: user expectation to get AR
suggested in SAs. Drawing conclusions of modified opinion
appearance. and detection risk. within a reasonable period and at
based on audit evidence. or withdrawal.
reasonable cost.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 1
SA 210 (Revised) Agreeing the Terms of Engagement
Objective of Auditor: To accept or continue an audit engagement only when the basis upon which it is to be performed has been agreed with the client.
Agreeing the terms of audit Engagement
At the Beginning of Audit During the Course of Audit
Initial audit Engagement Recurring Audit Mngt. request for changes in terms
Limitations Imposed by mngt. No Limitations Imposed by Mngt. Determine its effect on Level of
Determine requirements w.r.t.:
Assurance & reasonable
(a) Revision of terms of Engagement; &
Do not accept unless required Ascertain existence of Justification
by law Preconditions* (b) Remind the entity of existing terms
Preconditions for an audit Exist Not Exist Required Not Required Auditor Satisfied Not Satisfied
1. Determine whether the FRF is
acceptable.
Accept Audit Discuss matter Send New No Further Duty Record New Do not
2. Obtain agreement of mngt that it Terms in
with mngt. Engagement Letter accept the
understands its responsibilities for: Engagement changes
(a) Preparation of F.S. Letter
(b) Exercising necessary Internal
Do not accept audit in case of: CIRCUMSTANCES REQUIRING REVISION IN TERMS Mngt. not
Controls to enable the
(a) Unacceptable FRF Indications that the entity misunderstands the objective and permit the
preparation of F.S. that are free
scope of the audit. auditor to
from material misstatements. or continue
Revised or special terms of engagement.
(c) To provide the auditor: (b) Mngt. does not agree with Recent change of senior management.
Access to all relevant info. responsibilities Significant change in ownership.
Additional info that auditor Withdraw &
Significant change in nature or size of the entitys business.
requests from mngt. Report to
Change in legal or regulatory requirements.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg appropriate
Unrestricted access to persons Change in FRF adopted in the preparation of the F.S.
authority
within the entity. A change in other reporting requirements.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 2
SA 220 (revised) Quality Control for an audit of F.S.
Objective: Implement QC Policies that provide Reasonable Assurance that audit complies with professional standards and audit report issued is appropriate
Leadership Ethical Independence Acceptance / Continuance Assignment of Engagement Performance Monitoring
Responsibilities
Requirements of Client relationship Engagement
Team
EP should EP to remain alert Be satisfied that EP to be satisfied 1. Direction, Supervision and Obtain reasonable
performance:
emphasize the for evidence of Form a conclusion on appropriate procedures that ET & assurance that
compliance with Auditors Expert EP shall take the responsibility for
ET the following: non-compliance regarding client acceptance directions, supervision & performance firms policies /
applicable independence not part of ET
Compliance with relevant ethical requirements
/ continuance have been of audit engagement in compliance with procedures relating
have appropriate standards & regulatory requirements, &.
with requirements by ET followed. to QC are relevant,
Obtain relevant competence & to make an appropriate AR.
professional through: Determine whether capabilities to: 2. Reviews: adequate, and
information from Firm
Standards and Inquiry. conclusions reached are Perform audit EP shall take the following responsibilities: operating
appropriate. engagement in a. Reviews are being performed in
legal Observation. Identify & Evaluate effectively.
accordance with policies / procedures.
requirements. circumstances & accordance
b. Be Satisfied that SAAE has been obtained
If there is an with Consider:
Compliance
Relationship that threatens If EP obtains information to support the conclusions reached and
indications of non- independence that would have caused firm professional AR to be issued through Results of firms
with firms
compliance with to withdraw the engagement, standards and Review of Audit Documentation. monitoring
Quality Evaluate information on communicate information regulatory or Discussion with ET
relevant ethical process.
Control identified breaches. promptly to firm legal 3. Consultation:
requirements, EP EP shall undertake consultation Whether
Policies. requirements,
should: wherever required. deficiencies
Issuance of Determine if these Examples of Information and Ensure its implementation
Consult others in threaten independence Enable an AR noted may affect
appropriate 4. Engagement Quality Control Review:
the firm. 1. Integrity of Principal that is required in case of listed entities. the audit
audit report. Take appropriate action Owners, Mngt & TCWG
Determine appropriate in Matters to be evaluated by EQCR engagement.
Ability to raise to eliminate such threats 2. Competency of ET to
appropriate the
concerns perform engagement. Discussion of significant matters with ET.
or circumstances.
action. 3. Availability of necessary
without fear. Review of FS & proposed audit report.
Promptly report capabilities, including time &
Quality is
inability to take resources. Review of selected audit documentation
essential & appropriate action to 4. Compliance with relevant
indispensable ethical requirements. 5. Differences of Opinion: follow the firms
in engagement Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg 5. Significant matters that policies & procedures for dealing with and
arises during the current or resolving differences of opinion.
performance.
previous audit engagement.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 3
SA 230 (Revised) Audit Documentation
General concepts Form, Content & Extent of Specific Documentation Retention Ownership
Documentation Period
Documentation is the
Meaning: Record of: Auditor shall prepare audit documentation
property of the Auditor.
Audit procedures performed that is sufficient to enable an experienced 7 Years from May at his discretion
Relevant audit evidence
auditor to understand: date of Audit make portions of or
obtained, &
(a) NTE of the audit procedures; Report extracts from
Conclusions reached Compiled by: CA.
(b) Results of audit procedures performed, documentation available
Pankaj Garg
Purpose: includes the following: & audit evidence obtained; to client.
Assist in Planning and
(c) Significant matters arising during the
performance of Audit.
audit and the conclusions reached Documentation of Documentation of Documentation of
Direction, supervision &
Review of work. thereon, significant professional Discussion Departure from a matters arising after the
To fix accountability. judgments made in the reaching those relevant requirement Date of Auditors Report
Record for future reference. conclusions.
Quality control review and Factors affecting form, content & extent Significant Reasons for the Circumstance
inspections Matters departure. encountered.
1. The size and complexity of the entity.
Conduct of external Discussed with Alternative New or additional
inspections. 2. The nature of the audit procedures to be
Mngt. And procedures procedures
performed. TCWG. performed. performed, audit
Nature documentation must 3. Identified RMM. When and with evidence obtained,
provide for: 4. Significance of audit evidence obtained. whom the conclusions reached,
Sufficient and appropriate 5. Nature & extent of exceptions identified. discussion took and their effect on the
record of the basis for place. auditors report.
6. Need to document a conclusion or the
auditors report. How the auditor When and by whom
basis for a conclusion not readily
Evidence that the audit was address the the changes to audit
determinable from the documentation of
planned and performed in inconsistency (if documentation were
the work performed or audit evidence any detected made and reviewed.
accordance with SAs & other
obtained. during
regulatory requirements.
7. The audit methodology and tools used. discussion)
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 4
SA 240 (Revised) The Auditors Responsibilities Relating to Fraud in an Audit of Financial Statements
Fraud Risk Factors / Management Duties Auditors Responsibilities
Meaning and Nature of Fraud
Characteristics of Fraud
Meaning: Intentional Act involving use of deception to Incentive or pressure to Commit Fraud: Primary responsibility To obtain reasonable assurance
obtain an unjust or illegal advantage. Arises when mngt is under pressure to for prevention & that F.S. as a whole are free from
achieve an unrealistic target. detection of fraud rests material Misstatements.
Auditor is concerned with Fraud that causes Perceived opportunity to do so: with Mngt and TCWG
Arises when an individual believes that Maintain an attitude of
Material Misstatement.
internal control can be overridden. To ensure prevention of Professional Skepticism
Misstatement may result from: Rationalization to do so: fraud Mngt. must have an
A Fraudulent Financial Reporting Arises when an individual possess an commitment to create an Circumstances indicate existence of
1. Recording fictitious journal entries to attitude or character that allows them material Misstatement
culture of honesty and
manipulate operating results. knowingly and intentionally to commit a
Ethical behavior.
2. Inappropriate assumptions. dishonest act.
3. Changing judgements to estimate account Consider whether such a
balances. Risk associated for non detection of material misstatements misstatement is an indication of
4. Omitting, advancing or delaying recognition of Fraud. If Fraud identified
Due to Inherent limitations there is always an unavoidable risk of material
events and transactions occurred during the misstatement in F.S. due to Fraud.
year. Risk of non detecting a material misstatement resulting from fraud is Communicate to Mngt.
5. Concealing facts that affect the amount higher than the risk of non detecting one resulting from error. &TCWG (also to Regulatory &
recorded in F.S.
Risk of Material Misstatements due to Management Fraud is higher than Enforcement authorities, if
6. Engaging in Complex Transactions that are
due to Employee Fraud. required by Law
structured to misrepresent the financial
position or financial performance.
Conditions or events which increases risk of fraud or error Auditor unable to complete the
7. Altering records relating to significant
1. Discrepancies in Accounting Records: arises due to improper recording, engagement.
transactions.
unauthorised transactions, last minute adjustments.
B Misappropriation of Assets
2. Conflicting or missing evidences: missing documents, altered Consider the Possibility of
1. Embezzling receipts. withdrawing.
documents, non availability of original documents, unexplained items etc.
2. Stealing physical assets.
3. Unusual relationship between auditor & mngt: undue time pressure,
3. Causing an entity to pay for goods and services
unusual delay in providing info, unwillingness to address weaknesses in IC. If withdraw:
not received.
4. Others: Mngt not allowing auditor to meet with TCWG, varied accounting Discuss with Mngt & TCWG, &
4. Using entity assets for personal use. Report to appropriate persons
policies, frequent changes in accounting estimates.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 5
SA 250 (Revised) Consideration of Laws and Regulations in an Audit of F.S.
Management Responsibilities Auditors Responsibilities
Basic Responsibilities Specific Auditor Reporting responsibilities Indicators considered by
Responsibilities w.r.t. Auditor
Procedure in
Obtain general
case any Non-
understanding of L& R having Other L& R that do not To TCWG Auditor Report Regularity &
direct effect on affect amount and Compliance is Enforcement Authorities
Legal & Regulatory
Framework applicable determination disclosures in F.S. but identified /
Compliance by Entity of material compliance with which Suspected Material Unable to If required by Law
with that Framework. amount and may be fundamental to Effect on Conclude
due to Investigations by regulatory
disclosures in operating aspects. F.S.
Limitation bodies.
Compliance of L & R is duty of F.S.
Mngt & TCWG and may be imposed by Payment of fines or penalties.
performed through: Payments for unspecified
Q/A
1. Monitoring legal requirements Obtain services to consultants, related
& ensuring that operating parties etc.
obtain SAAE Perform limited understanding of
procedures are designed to Mngt. Circumstances Excessive Sales commissions or
procedures: the Act.
meet these requirements. agents fees.
2. Instituting & operating
Inquiring of Mngt; &
Circumstances in Purchasing at prices
appropriate systems of IC. Inspecting Q/D Consider the significantly above or below
which it is
3. Developing, publicising and Correspondence with Effect market price.
to ensure occurred.
following a code of conduct. relevant Licensing / Unusual payments in cash.
4. Ensuring employees are compliance Regulatory authority Evaluate possible
Unusual payments towards legal
properly trained & understand effects on F.S. and retainership fees.
the code of conduct. Matters involving non-
Discuss with Payments without proper
5. Monitoring compliance with to identify instances of compliance.
Mngt. & TCWG exchange control
code of conduct & take actions non compliance. If TCWG is involved, documentation.
to discipline employees who Obtain legal communicate to Higher Level, Existence of an information
fail to comply with it. advice wherever if any system which fails, to provide
6. Engaging legal advisors to
required Otherwise, obtain Legal Advice an adequate audit trail or
assist in monitoring legal
Obtain Written Representation that all sufficient evidence.
requirements.
instances of non-compliance or Unauthorised transactions or
7. Maintaining a register of Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg
suspected non-compliance have been improperly recorded
significant L & R with which the
transactions.
entity has to comply. disclosed to auditor.
Adverse media comment.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 6
SA 260 (Revised) Communication with TCWG
Meaning of Auditors Responsibilities Communication Process Factors affecting Mode of
Management & Communication
TCWG
TCWG: Persons with Determine the Matters to be communicated Communication may be Size, operating structure,
responsibility for appropriate Oral /written control environment, & legal
overseeing the (a) Auditors responsibility in relate to F.S. Audit. Detail/Summarised structure of entity.
person to whom
(b) Planned scope & timing of audit Structured /Unstructured In the case of an audit of special
strategic directions & communication
(c) Significant findings from audit w.r.t. Should be in writing purpose F.S., whether the
obligations related to is to be made.
Accounting Policies auditor also audits the entitys
Accountability. when oral
Accounting Estimates general purpose F. S.
Management : Person communication is not
F. S. Disclosures Requirements of respective law
with executive adequate. specifying written
Significant difficulties encountered
responsibility for during the audit. Communication should communication with TCWG in a
conduct of entitys Examples of Significant difficulties be on timely basis prescribed form.
1. Significant delay in providing info Expectations of TCWG,
operation
2. Unnecessarily brief time to complete including arrangements made
Evaluate adequacy of for periodic meetings or
the audit.
3. Extensive unexpected effort to obtain communication for the communications with the
SAAE. purpose of the audit. auditor.
Determine the need to communicate with 4. Unavailability of Expected The amount of ongoing contact
Governing body, if communicates with information. and dialogue the auditor has
If not adequate, evaluate
5. Restriction imposed by management. with TCWG.
subgroup. its effect, on the auditors
6. Scope limitation imposed by
If all of TCWG are involved in managing the Significant changes in the
management assessment of the risks of
membership of a governing
entity, and the matter has been material misstatement.
Material weakness in I.C. body.
communicated with persons having
Matters discuss with Mngt.
managerial responsibility, the matters need
Other significant Matters.
not be communicated again to the same Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg
(d) Statement w.r.t. compliance of ethical
persons in their governing role. requirements regarding independence.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 7
SA-265 Communicating Deficiencies in Internal Control to TCWG & Management
Meaning of Auditors Responsibilities
deficiency in internal
control
(a) Inability of I.C to prevent Identification of deficiencies in Communication of deficiencies in Internal Control
detect & correct misstatement ; Internal Control
or
Mode of communication Content of communication
(b) Absence of control necessary
Determine whether on the basis of
to prevent, detect & correct
work done any deficiency in In writing
misstatements internal control is identified
Determine whether individually or To TCWG To Mngt. (a) Description of deficiencies
in combination they constitute (b) Explanation of their potential
significant deficiencies effect
(c) Sufficient information to explain
Indicators of Significant Deficiencies Significant Significant that purpose of the audit is to
deficiencies deficiencies express an opinion
1. Evidence of ineffective aspects of control environment.
and other I. C. is evaluated to design
2. Entitys Risk assessment process Absent/ineffective. deficiencies further audit procedures
3. Ineffective response to identified significant Risks.
4. Correction of prior period misstatements arising due to fraud/error.
5. Management inability to oversee F.S. Preparation.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg
6. Misstatements detected by the auditors procedures were not
prevented, or detected and corrected by the entity I.C.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 8
SA 299 Responsibility of Joint Auditors
Division of work Co-ordination Responsibilities of Joint Auditors Reporting
By Mutual discussion If one auditor comes Generally a Single Report
Separate Joint & several
to know a matter
If joint auditors disagree -
relevant for other, he
On basis of identifiable units should communicate Separate Report
or specified areas it immediately in No one is bound by Majority.
writing to other joint For work for work not divided
auditor before allocated for joint decision w.r.t. N,
If not possible with submission of report. T, E of audit procedure.
respect to followings: for matters brought to
Assets/Liabilities; or knowledge of all by any
Income/Expense; or one of them and on which
Period they all agree.
Disclosure requirements
in F.S.
Work should not be
divided for Imp. areas Compliance of audit
report with statutory
requirement
Work so divided should be
documented and
communicated to the
entity.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 9
SA 300 (Revised) Planning in an audit of Financial Statements
Importance of Planning Preliminary Engagement Activities Planning Activities
1. To devote appropriate attention to (a) Procedures required by SA -220 w.r.t. Establishment of Audit Strategy Development of
important areas. continuous of Client relationship. Audit Plan.
2. Identify and Resolve potential (b) Evaluate compliance with Ethical so as to set the scope, timing &
problems on timely basis. direction of the audit
Requirements (SA-220) NTE of RAP (SA-
3. Properly organized & managed Audit. Factors to be considered
(c) Understanding of terms of 315)
4. Assists selection of ET members with Characteristics of Engagement.
Engagement (SA-210) NTE of furthers
requisite capabilities and competence. Reporting Objectives.
5. Co-ordination of work done by Significant factors to direct ET Audit Procedures
auditors of components and experts. Planning A Continuous Process efforts. (SA-330)
6. Facilitating direction and supervision Result of Preliminary Other Planned
of Engagement team. Engagement Activities.
Audit Procedure.
NTE of Procedures to be
performed.
Planning is not a discrete phase of an audit but rather a continuous process. It begins shortly
CHANGES TO PLANNING DECISIONS
after completion of previous audit & continues until completion of current audit engagement.
Auditor shall update & change overall audit strategy and audit plan
It includes consideration of timing of certain activities & audit procedures that need to be
as necessary during the course of the audit.
completed prior to performance of further audit procedures. E.g., planning includes the need to Audit Strategy and Audit Plan may need to be modified as a result
consider, prior to the auditors identification and assessment of the RMM, such matters as: of unexpected events, changes in conditions, or the audit evidence
1. The analytical procedures to be applied as risk assessment procedures. obtained from the results of audit procedures.
Based on the revised consideration of assessed risks, auditor need
2. Obtaining a general understanding of the legal and regulatory framework.
to modify the NTE of further audit procedures. This may be the case
3. The determination of materiality.
Compiled by: when information comes to the auditors attention that differs
4. The involvement of experts. significantly from the information available when the auditor
CA. Pankaj Garg
5. The performance of other risk assessment procedures. planned the audit procedures.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 1
SA 315 (Revised) Identifying and Assessing the Risk of Material Misstatements through understanding the Entity and Its Environment .
Risk Assessment Understanding of Entity & its Environment Risk in CIS Environment
Procedures
Risk imposed by IT/CIS Areas to be examined
Auditor shall obtain understanding of:
Program Development &
Procedures to obtain an 1. Relevant Industry, Regulatory & other External Reliance on programs that process
Maintenance.
understanding of entity Factors including FRF. inaccurate data or do inaccurate
System Software Support.
& its environment 2. Nature of Entity including. processing. Operations Including processing
including I.C. Its Operations
Unauthorized access to data that of data.
To Identify and assess Ownership & Governance structure
may result in destruction of data. Physical CIS security.
Types of investments
the RMM at F.S. and Control over access to
The way Entity is structured & how it is financed Unauthorized changes to data in
Assertion Level. specialized CIS utility programs.
3. Selection & Application of Accounting Policies & Master files.
reasons for changes thereto.
It Includes Unauthorized changes to systems. Components of Internal Control
4. Entity objectives & Strategies & those business
a. Inquiry of mngt.& others risks that may result in increase RMM. Failure to make necessary changes.
1. Control Environment
b. Analytical Procedures 5. Measurement & review of Financial Performance. Potential loss of data Communication of Ethical values.
c. Observation & Inspection 6. Internal control relevant to audit. 2. Risk Assessment Process
Inability to access data as required.
Identify Business Risk
Estimating significant Risks
Identification and Assessment of RMM Assessing Likelihood of occurrence.
Deciding response
a) F.S. Level: RMM that Assertions evaluated Steps in Risk Risk require special 3. Information System relevant to FR:
relate pervasively to Transaction Occurrence consideration Classes of transactions
Assessment
the F.S. as a whole and occurred Completeness 1. Risk of fraud Accounting procedures
Process:
potentially affect many during the Accuracy 2. Risk related to recent Accounting records
assertions. year Cut-Off Identify risks significant Economic,
Classification Financial Reporting Process.
b) Assertion level for Assess & Evaluate Accounting & other
Account Existence Controls over journal entries
classes of the identified risks. Developments.
balances at Rights & Obligations 4. Control Activities relevant to Audit
Transaction, Account 3. Complexity of Transactions.
period end Completeness Relate identified Information processes
Balances &
Valuation &
4. Transactions with Related
risk to what go Segregation of duties.
disclosures: It helps Disclosure Parties
in determining the NTE wrong at assertion 5. Significant Unusual Physical controls
Presentation Occurrence
of further audit & Completeness level. Transaction Performance Reviews
procedures necessary Disclosures Classification Likelihood of 5. Monitoring of Controls
to obtain SAAE. Accuracy & Valuation misstatement. Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Assess effectiveness of I.C. Performance.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 2
SA 320 (Revised) Materiality in Planning and Performing an Audit
Concept of Materiality Performance Materiality Auditors Duties
Materiality is a subject of The amount set by auditor at (a) Upon establishing the overall audit strategy, the auditor shall
professional judgment and less than materiality for F.S as a whole determine the materiality for the F. S. as a whole.
discussion presented in FRF (b) Determine the materiality level for specific transactions for
to reduce to an appropriately low level
which misstatements of lower amount be expected to influence
provides a reference to the auditor in the probability that the aggregate of the
the economic decisions of users.
determining materiality. uncorrected & undetected misstatement (c) Determine the performance materiality for purpose of assessing
If FRF does not include a discussion, exceeds materiality for F. S. as a whole the RMM and determining the NTE of further audit procedures.
following can be referred:
(a) Misstatements including
omissions expected to influence Revision of Materiality Use of benchmark in determining Materiality
the economic decision of users.
(b) Size or nature of misstatement & In event of becoming aware of information A %age is often applied to a chosen benchmark as a starting
the surrounding circumstances. that would have caused auditor to have point in determining materiality for the F.S. as a whole.
(c) Common financial information determined a different amount initially, Factors affecting identification of appropriate benchmark
needs of the users as a group. auditor shall revise materiality for the F.S. as a 1. The elements of the financial statements;
whole & if required, for particular classes of 2. Items on which the attention of the users of the particular
transactions, account balances or disclosures. entitys financial statements tends to be focused;
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg
If the auditor concludes that a lower 3. The nature of the entity, where the entity is at in its life
materiality than that initially determined is cycle, and the industry and economic environment in
Judgment of materiality provides a
appropriate, the auditor shall determine which the entity operates;
basis for:
whether it is necessary to revise performance 4. The entitys ownership structure and the way it is
(a) Determination of NTE of RAP
materiality, and whether the NTE of the financed; and
(b) Identifying and assessing RMM.
further audit procedures remain appropriate. 5. The relative volatility of the benchmark.
(c) NTE of further audit procedures.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 3
SA 330 Responses to Assessed Risks
Objective: To obtain Sufficient and Appropriate Audit Evidence about Assessed Risk of Material Misstatement through design and implementing Appropriate Responses
Tests of Controls Substantive Procedures
Procedures designed to evaluate the operating effectiveness of controls in preventing, Procedures designed to detect material misstatements at assertion level.
detecting or correcting material misstatements at assertion level. It comprises of:
a) Test of details (of classes of transactions, Account Balances and
Obtain audit evidences w.r.t. (a) Application of controls (b) Consistency of application Disclosures); &
(c) By whom & by what means they applied Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg
b) Substantive Analytical Procedures
Evaluate the audit evidences
External Auditor shall consider whether EC procedures are to be
Material weaknesses identified Confirmation performed as substantive audit procedures.
(EC) Factors that may assist the auditor are:
Communicate to Mngt. & TCWG on timely basis
procedures 1. Confirming party knowledge of Subject Matter.
Special Considerations Factors warranting re-test of as 2. Ability or Willingness of intended confirming part to
Using Audit Evidence obtained in Interim Period: controls substantive respond.
Obtain audit Evidence for significant changes 1. Deficient control environment. procedures 3. Objectivity of Intending Party.
subsequent to Interim Period. 2. Deficient monitoring of
Closing Reconciling F.S. with underlying A/cing Records
controls.
Determine the additional Evidence to be obtain for Process
3. Significant manual element to Examine Material Journal Entries & other adjustments
remaning period.
relevant controls. made during the course of preparing the F.S.
Using Audit Evidence obtained during previous
4. Personnel changes that Significant Procedures that are specifically responsive to that risk
audits: Establish Continuing relevance of that evidence significantly affect the
by determining significant changes subsequent to Risks needs to be applied
application of control.
previous audit 5. Changing circumstances that
Changes occurs: Test the controls in current audit indicate the need for changes
No Change Occurs: Test the controls once in three in the control. Timing: When Substantive procedures are applied for interim period, the
audits 6. Deficient general IT-controls. auditor shall cover remaining period by appropriate procedures
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 4
SA 402 (Revised) Audit Considerations relating to an Entity Using a Service Organisation
Auditors Objective Obtaining understanding of services Auditors considerations
provided by service Organisation (S.O.)
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg
Obtain an The user auditor shall obtain an User auditor shall evaluate the design and implementation of relevant controls of
understanding of understanding of how user entity uses the user entity that relate to the services provided by service organization.
nature & significance User auditor shall determine whether a sufficient understanding of nature and
services of a service organization in the user
of service provided by significance of services provided by service organization and their effect on the
entity operation, including:
the S.O. and their user entity internal control relevant to the audit has been obtained.
(a) Nature of service provided by the S.O. and If user auditor is unable to obtain a sufficient understanding from the user entity,
effect on the users
entity internal control significance of services to user entity. user auditor shall obtain that understanding from the following procedures:
relevant to the audit, (b) Nature and materiality of the transactions (a) Obtaining a Type 1 or Type 2 Report, if available.
(b) Contacting the service organization, through the user entity.
sufficient to identify processed or financial reporting processes
(c) Visiting the service organization.
and assess the RMM. affected by service organizations.
(d) Using another auditor to perform procedures that will provide the
To design and (c) Degree of interaction between activities of necessary information about the relevant controls at the S.O.
perform audit
S.O. and those of the user entity. If a S.O. uses subservice organisation, the service auditors report may either
procedures
(d) The nature of relationship between user include or exclude the subservice organisations relevant control objectives
responsive to those
& related controls in the service organisations description of its system & in
risks. entity and the service organization.
the scope of service auditors engagement. These two methods of reporting
are known as the inclusive method and the carve-out method, respectively.
User Auditor: An auditor who audits and Reports on the financial If Type 1 or Type 2 report excludes the controls at a subservice
statements of a user entity. organisation, and the services provided by the subservice organisation are
relevant to the audit of the user entitys financial statements, the user
User Entity: An Entity that uses a service organization and whose financial
auditor is required to apply the requirements of this SA in respect of the
statements are being audited. subservice organisation.
Type 1 Report: Report on the description and design of internal controls at Nature and extent of work to be performed by the user auditor regarding
a service organization for a specified date. the services provided by a subservice organisation depend on the nature
and significance of those services to the user entity and the relevance of
Type 2 Report: Report on the description, design and operating
those services to the audit.
effectiveness of controls at a service organsation for a specified period.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 5
SA 450 Evaluation of Misstatements Identified during the Audit
Meaning and Causes of Auditors Procedures if Misstatements identified
Misstatements
Difference between Accumulate the misstatements other than those that clearly trivial
amounts, classification, presentation
or disclosure of a reported financial
Communicate to management & request them to correct. Determine whether any
statement item,
revision required in Audit
and
Strategy/Plan.
amount, classification, presentation or Management corrects Management refuses
disclosure that is required for the item
to be in accordance of FRF. Perform Additional Understand the reason for not making Audit Strategy and Audit
Causes of Misstatement Procedures to Plan require revision if
(a) Inaccuracy in gathering or determine whether
Re-assess the materiality
processing data from which the misstatements Nature of identified
F.S. are prepared; remain. misstatements and the
If material, communicate uncorrected
(b) Omission of an amount or circumstances of their
misstatement and their effect on his opinion to
disclosure; occurrence indicate that
TCWG with a request that uncorrected
(c) Incorrect accounting estimate other misstatements may
misstatements be corrected.
arising from overlooking, or clear exist that, could be material;
Compiled by:
misinterpretation of, facts; and or
Not corrected
(d) Unreasonable judgments of CA. PANKAJ GARG Aggregate of misstatements
management concerning accumulated during the
Obtain a written representation from
accounting estimates. audit approaches materiality
management/TCWG w.r.t their believing that
(e) Inappropriate selection & determined in accordance
effect of uncorrected misstatements are
application of accounting policies with SA 320 (Revised).
immaterial.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 6
SA 500 Audit Evidence
Meaning and Nature of Auditors duties when an information to be used as audit evidence Audit Procedures & Methods
Audit Evidence (A.E.) for obtaining audit evidence
Meaning of A.E. Information prepared using Information Procedures to obtain A.E. Methods to obtain A.E.
Information used by auditor work of Management Expert Produced by entity (a) RAP 1. Inspection
(b) FAP (Responses): 2. Observation.
In arriving at the conclusion Tests of Control (ToC), 3. External Confirmations
1 Evaluate Competence, Capability and Obtain A.E. about the
Objectivity of the Expert Substantive 4. Recalculation
On which auditors opinion is Source of Information for evaluation: 1. Tests of Details (ToD) 5. Re-performance
Accuracy and
based. Personal Experience with previous work. 2. Substantive Analytical 6. Analytical procedures
Completeness of info.
Discussion with that expert.
Nature of A.E. Procedures (SAP) 7. Inquiry (Oral/Written)
Discussion with others. Evaluate whether info
A.E. needs to be Knowledge of experts qualification, is
memberships, other forms of recognitions.
Published books or papers. Reliability of Audit Evidence
Sufficient Appropriate sufficiently precise
Auditors expert.
Measure of Measure of and detailed for
2 Obtain an understating of expert work
quantity quality auditors purposes.
Area of Specialty
Affected by Relevance & Applicable professional standards.
RMM & reliability in Legal & Regulatory Requirements. (a) External Evidences are considered more reliable than internal evidences.
Quality of providing Assumptions and Methods used.
(b) The reliability of internal evidence is increased when the related controls, imposed
Nature of Source Data used.
Audit support for by entity are effective.
3 Evaluate the appropriateness of Expert work
evidences conclusion. (c) Audit evidence obtained directly by the auditor is more reliable than audit
Finding & Conclusion Relevance,
Reasonableness & Consistency with other evidence obtained indirectly.
A.E. (d) Audit evidence in documentary form, is more reliable than evidence obtained
Compiled by: Assumptions and Methods Relevance
orally.
and Reasonableness.
CA. PANKAJ GARG (e) Audit evidence provided by original documents is more reliable than audit
Source Data Relevance, Completeness
and accuracy. evidence provided by photocopies.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 1
SA 501 Audit Evidence Specific Considerations for Selected Items
Inventory Litigation & Claims Completeness
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg
Existence & Condition
Auditor is required to identify litigation and claims
by following procedures:
Inquiry: of Mngt. & others within entity,
General Procedures Special Procedures including in house legal counsel.
Review minutes of meetings of TCWG,
When inventory is material to the F.S. 1 Inventory counting conducted at date other than communication between entity & external legal
B/S date counsel.
the auditor shall obtain SAAE Perform audit procedures to obtain audit evidence Review legal expenses account.
If management refuses to permit auditor to
about whether changes in inventory between the count
regarding existence & condition by communicate with legal counsel / external legal
date and the date of the F.S. are properly recorded. counsel refuses / auditor unable to collect SAAE
2 Auditor unable to attend Inventory Count by performing alternate procedures
(a) Attendance at physical inventory
Make or observe some physical counts on an alternative
counting, unless impracticable, to: Modify Opinion in accordance with SA 705
date,
Evaluate mngt. instructions &
procedures for recording & and perform audit procedures on intervening Segment Reporting
controlling the results of the entitys transactions Presentation & Disclosures
physical inventory counting; 3 Attendance at inventory count is impracticable
Observe the performance of Perform alternative audit procedures to obtain S.A.A.E. Obtain SAAE regarding presentation & disclosure of segment
regarding existence and condition of inventory. information in accordance with the applicable FRF by:
managements count procedures;
(a) Obtaining an understanding of the methods used by
Inspect the inventory; management in determining segment information, and
If it is not possible to do so, modify the opinion in the
Perform test counts; auditors report in accordance with SA 705. Evaluate whether such methods are likely to result in
(b) Performing audit procedures over the disclosure in accordance with the applicable FRF; and
4 Inventory under custody and control of Third Party
Where appropriate, testing the application of such
entitys final inventory records to Obtain S.A.A.E by performing the following: methods; and
determine whether they accurately (a) Request confirmation from third party. (b) Performing analytical procedures or other audit
reflect actual inventory count results. (b) Perform Inspection/other audit procedure. procedures appropriate in the circumstances.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 2
SA 505 External Confirmation
The objective of the auditor, when using external confirmation procedures, is to design and perform such procedures to obtain relevant and reliable audit
evidence.
Meaning & Type of E.C. External Confirmation Audit Procedures in Special Circumstances Limited use of ve
Procedures Request
Mngt. refuses to allow the auditor to send request
Audit Evidence obtained as a direct written As it provides less
Determining the information to
response to auditor from 3rd Party in Inquire the reasons persuasive evidence
be confirmed.
Paper/Electronic/Other form. Evaluate the implications on RMM than the positive
Selecting the Appropriate Third Perform Alternative Audit procedure. Confirmation request.
2 Types Party. Refusal appears to Communicate to
be unreasonable TCWG.
+ ve Request - ve request Designing the confirmation
Circumstances in
request. Unable to collect Determine its affect
Request that 3rd Party Request that 3rd Party
which negative
respond directly to respond directly to audit evidence on Opinion
Sending the request including request may be used
auditor auditor
follow up. Responses to E.C. request as sole substantive
indicating whether it only if it disagrees
agrees or disagrees Creates Doubt Obtain Further procedure:
With the info in request with the information in Factors to be considered while Evidences
Low RMM.
or the request designing E.C. request: Not Reliable Consider its affect on
providing requested Population consists
Assertions being addressed. NTE of other procedures
info. of large no. of small,
Specific identified RMM. No Response Perform Alternative
homogenous
Areas where External Confirmation may be obtained: Layout and presentation of procedure
(a) Bank balance & Other confirmation from account balances.
request.
Unable to collect Determine its affect on
bankers Expectation of low
Prior Experience of audit.
(b) Account Receivable/Account Payable Balances evidence Opinion
Method of Communication. exception rate.
(c) Stock Lying with Third Parties Exception occurs Investigate to determine
Management Authorization. Auditor not aware
(d) Property Title Deed held by third parties
misstatement of circumstances
(e) Investments Purchased but delivery not taken. Ability of confirming party to
(f) Loan from Lenders provide the requested that 3rd party
(g) Terms of agreement or Transaction with Third information Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg disregard request.
Parties
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 3
SA 510 Initial Audit Engagements Opening Balances
Meaning of Initial Audit Engagement: An Engagement in which financial statements for prior period are not audited or were audited by predecessor auditor.
Meaning of Opening balance A/c balance that exist at beginning of period & also includes disclosures exists at beginning of period.
Audit Procedures Audit Conclusion & Reporting
Opening Balance Consistency of Modification in Opening Balance Consistency of Modification in
Accounting Predecessor Accounting Predecessor Auditors
Auditors Report
Policies Policies
Report
Balance
Read most recent F.S. and auditor Obtain SAAE Evaluate the Unable to Contain material Inconsistency Modification remains
report thereon. effect of obtain SAAE misstatements not exists relevant & material for
Obtain S.A. audit evidence w.r.t. modification properly or Current Period F.S.
existence of any material accounted / Changes not
misstatement by disclosed in properly
Determining correct b/f of prior current year F. S. accounted or
period closing balance. disclosed
Determining application of
appropriate accounting policies. w.r.t.
Modify Current Year
If any misstatement detected consistent
Qualified / Audit Report
perform additional procedures to application
Disclaimer Qualified / Adverse Report accordingly
determine their effect on current or
Period financial statements. Proper
If misstatement exists in Current accounting & in assessing Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg
Period F.S. communicate to Mngt & disclosure for RMM in Current
TCWG. changes. period F.S.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 4
SA 520 Analytical Procedures
Meaning and Nature of Analytical Procedures Auditors Procedures
Evaluation of financial information 1 Determine the suitability of particular substantive analytical procedures (SAP)
Following factors requires consideration:
through analysis of relationships
1. SAPs more suitable to large volumes of transactions tending to be predictable over time.
2. But suitability of AP influenced by:
among both financial and non-financial data.
AND Nature of assertion.
also encompass such investigation as is necessary of Auditors assessment of APs effectiveness to identify material misstatement.
identified fluctuations or relationships that are 3. In some cases unsophisticated predictive models may be useful.
inconsistent with other relevant information or that 4. Different types of APs provide different levels of assurance.
differ from expected values by a significant amount. 5. Particular SAP may be considered suitable when ToD are performed on same assertion.
Analytical Procedures
2 Evaluate the reliability of data
Following factors affects the reliability:
Consideration of Consideration of
Source of the information available.
Comparisons of relationships among
Financial Information Comparability of the information available. Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg
with comparable Elements of financial Nature and relevance of the information available, and
information for prior information Controls over the preparation of the information
periods. or 3 Develop an expectation of recorded amounts or ratios and evaluate whether the expectation is
or Financial information sufficiently precise to identify material misstatement.
with anticipated results and relevant non-
4 Determine the amount of any difference of recorded amounts from expected values that is
of the entity financial information.
acceptable without further investigation.
or
Auditors expectations 5 Investigating Results of Analytical Procedures
or If auditor identified fluctuations or relationships that are inconsistent with other relevant information
Similar industry or differ from expected values by a significant amount, the auditor shall investigate such differences by:
information. (a) Inquiring of management; and
(b) Performing other audit procedures as necessary in the circumstances.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 5
SA 530 (Revised) AUDIT SAMPLING
Meaning & Types of Audit Sampling Sampling risk Auditors Duties
Application of audit procedures to < Risk that auditors conclusion based on a sample may be different from 1 Sample design, size and selection of items
100 % of items within a population. the conclusion if the entire population were subjected to same audit (i) While designing, consider the purpose of
procedure. the audit procedure and the
Types of Sampling
characteristics of the population.
(a) Statistical Sampling: An
(ii) Sample size should be sufficient to
approach to sampling that has the
reduce sampling risk to an acceptably
following characteristics: Test of Tests of details Compiled by: low level.
Random selection of the controls CA. Pankaj Garg (iii) Selection should be in such a way that
sample items; and each sampling unit in the population has
a chance of selection.
The use of probability
Controls are Material Affects audit 2 Perform audit procedures
theory to evaluate sample
more effective misstatements does effectiveness and is (i) Perform audit procedures, appropriate
results, including
to the purpose, on each item selected.
than they not exist when in more likely to lead to
measurement of sampling (ii) If the audit procedure is not applicable
actually are fact it does. an inappropriate
risk. to selected item, perform the procedure
audit opinion. on a replacement item.
(b) Non Statistical Sampling: A
sampling approach that does not (iii) If the auditor is unable to apply designed
audit procedures/alternative procedure
have characteristics of random Controls are Material Affects audit to a selected item, consider that item as
selection and use of probability
less effective misstatement exists efficiency as it would a deviation.
theory is considered non-
than they when in fact it does lead to additional 3 Evaluation of results of audit sampling
statistical sampling. To determine whether the use of audit
actually are not work to establish
that initial sampling has provided a reasonable basis
for conclusions about the population that
conclusions were
has been tested.
incorrect.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 6
SA 540 (Revised) Auditing Accounting Estimates(AE), including Fair Value Accounting Estimates and Related Disclosures
Objective of Auditor: To obtain SAAE whether (a) AE including Fair Value AE are reasonable; and (b) related disclosures in the F.S. are adequate.
Meaning & Nature of Auditors Duties
Accounting Estimates Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg
Accounting estimate: Risk Assessment Procedures & Responses to Assessed Risks
An approximation of a monetary Related Activities
amount in the absence of a Based on assessed RMM, auditor shall determine:
precise means of measurement. Whether management has appropriately applied the applicable FRF.
This term is used for an amount Whether the methods are appropriate and have been applied consistently.
1. Obtain an understating of:
measured at fair value where
Requirements of applicable FRF
there is estimation uncertainty.
How management identifies
Estimation Uncertainty: General Responses to Specific Responses to Significant Estimation
transactions, events and
The susceptibility of an Assessed RMM Uncertainties
conditions that give rise to need
accounting estimate & related 1. Determine whether events 1. Evaluate the following:
for accounting estimates.
disclosures to an inherent risk of occurring upto date of How management has considered
Estimation making process
precision in its measurement. auditors report provide alternative assumptions or outcomes,
adopted by mngt. and data on
Examples of Accounting Estimates
which they are based. audit evidence regarding How management has addressed
Provision for Bad Debt,
Estimation making process AE. estimation uncertainty in making the
Inventory loss,
Methods/Model used in making 2. Test how management accounting estimate.
Warranty Obligations,
Accounting estimates. made the accounting Whether the significant assumptions
Depreciation,
Relevant Controls estimate and the data on used by management are reasonable.
Provision against carrying
Use of Management Expert. which it is based. Managements intent to carry out
amount of investments, etc.
Changes in the methods from 3. Test the operating specific courses of action and its ability
Examples of Fair Value A.E.
the prior period along with effectiveness of the to do so.
Share Based Payments,
reasons. controls. 2. If in auditors judgement, management has
Assets held for disposal,
Assessment of effect of 4. Develop a point estimate not adequately addressed the effects of
Financial Instruments,
estimation uncertainties. or a range to evaluate estimation uncertainty, the auditor shall
Assets acquired in business develop a range with which to evaluate the
2. Review of outcome of accounting managements point
combinations
estimates of prior period. estimate. reasonableness of the accounting estimates.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 7
SA 550 Related Parties Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg
Meaning of Related Party Auditors Duties
EITHER Risk Assessment procedures Responses to Assessed Risks
Related party as defined in applicable FRF (AS
18).
OR 1 Understanding the Entitys RP relationship and Transactions 1 Identification of unidentified /
Where applicable FRF establishes minimal or undisclosed RP or RP transaction.
a. Auditor to inquire management regarding:
no RP requirements:
Identity of entitys RP, changes from prior period. Communicate to other members of ET.
a. A person/entity having control/ significant
influence, over reporting entity; Nature of relationships between entity and RP. Request Mngt to identify the transactions
b. Entity over which reporting entity has Type & purpose of transactions with RP. with the newly identified RP.
control / significant influence, and b. Obtain understanding whether mngt has established controls to: Inquire reasons for mngt failure to
c. Entity under common control with Identify, account for & disclose RP relationships & transactions. identify RP or disclose RP relationship
reporting entity, through: and transactions.
Authorise & approve significant transactions with RP.
Common controlling ownership Reconsider the risk that other
Owners who are close family members Authorise & approve significant transactions outside normal course of business.
unidentified RP or undisclosed RP
Common key Mngt. 2 Maintaining Alertness for RP Information when Reviewing
transactions may exist.
Records/Documents
If non disclosure appears intentional,
Auditor to remain alert when inspecting records w.r.t. info indicating existence of RP
Auditors responsibilities in relation to RP relationships or transactions not previously identified or disclosed.
evaluate implications for audit.
If auditor identifies significant transactions outside entitys normal course of 2 Identified significant RP Transactions
Obtain an understanding of RP outside Entitys Normal course of
business, inquire of mngt about (a) Nature of these transactions, and (b)
Relation and Transactions: Business.
a. To recognize Fraud Risk factors Whether RP could be involved.
Inspect underlying contracts to evaluate
General
b. To conclude whether F.S. in so far Possible Sources for identification of RP Information:
business rationale.
as they are affected by those 1 Income Tax Returns 7 Shareholders Register
Examine the terms on which transactions
relations and transactions achieve 2 Internal Audit Report 8 Life insurance Polcies
takes place.
true and fair presentation and 3 Contracts with Mngt 9 Statement of conflict of interest
Collect evidences w.r.t. approval and
not misleading. 4 Contracts outside normal 10 Information supplied to authorisation of transaction.
Perform audit procedures to course of business regulatory authorities Collect evidences for appropriate
Identify, Assess & Respond to RMM. 5 Contracts re-negotiated 11 Specific Invoices from advisors accounting & disclosure in compliance of
Specific (FRF established
Evaluate whether Identified RP
accounting & Disclosure
6 Register of Investments 12 FRF.
relationships & Transactions have 3 Assertions that RP Transactions were
3 Identifying Fraud risk factors
requirements)
been appropriately accounted for & conducted on arm Length price.
disclosed as per FRF. Domination of mgmt by a single person or small group without compensating
Collect SAAE w.r.t. mngt assertion of
Obtain WR from Mngt./TCWG w.r.t. controls is a fraud risk factor.
Arms length transaction.
Disclosure to auditor the Indicators of dominant influence:
Compare transaction prices with the
identity of RP of which they are RP has vetoed significant business decisions taken by mgmt or TCWG.
prices for identical transactions
aware; and Significant transactions are referred to RP for final approval. prevailing in ordinary course of business.
Appropriate accounting & No/ little debate among mgmt or TCWG regarding business proposal initiated by RP.
Engage expert to determine market value.
disclosure as per FRF. Transactions involving the RP are rarely independently reviewed / approved.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 8
SA 560 Subsequent Events
Meaning Events occurring between the date of F.S. and the date of Auditors Report AND Facts that become known to auditor after the date of Auditors report.
Auditors Duties Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg
Events occurring between the date of F.S. and the date of Auditors report Facts that become known to Auditor after date of Auditors report
(i) Perform procedures to obtain SAAE that all events which require adjustment / Before issue of F.S. After issue of F.S.
disclosure have been identified. 1. In general Auditor has no obligation. 1. In general Auditor has no obligation.
2. However, in case of significant 2. However, in case of significant
(ii) For the purpose of determining nature and timing of procedures, auditor may:
matter matter
(a) Obtain the understanding of procedures applied by mngt for identification of
Discuss with Management Discuss with Management
significant events. Determine need to amend F.S.
Determine need to amend F.S.
(b) Inquire the Management as to Occurrence of subsequent events which may Inquire how mngt intends to
Inquire how mngt intends to
affect the F.S. address the matter in F.S.
address the matter in F.S.
(c) Read the Minutes of Meetings that held after the B/S date. 3. If Mngt. amend the F.S. audior shall
3. If Mngt. amend the F.S. auditor shall
Carry out procedures on
(d) Study the Interim Financial Statements, if any. Extent procedures to date of new amended F.S.
(iii) If auditor identifies any event which require any adjustment/disclosure, he should report, and Review the steps taken by mngt
ensure its appropriate treatment in F.S. provide a new auditor report on to ensure that recipient of F.S.
(iv) Obtain a WR from the Mngt. that all known events have been appropriately amended F.S. are informed of the situation.
adjusted/disclosed, as the case may be. or provide a new auditor report on
Amend the audit report to amended F.S.
Specific Inquiries to be made from management include an additional date or
1. Whether new commitments, borrowings or guarantees have been entered into. restricted to that amendment Amend the audit report to
and include an EOM/OMP. include an additional date
2. Whether sales or acquisitions of assets have occurred or are planned.
4. If mngt refuses to amend the F.S. restricted to that amendment
3. Whether there have been increases in capital or issuance of debt instruments.
Modify the report if not yet and include an EOM/OMP.
4. Whether any assets have been appropriated by government or destroyed. 4. If mngt refuses to amend the F.S.
5. Whether there have been any developments regarding contingencies. provided to entity.
Notify to mngt and TCWG, that
6. Whether any unusual accounting adjustments have been made. If report already issued, notify to
the auditor will seek to prevent
7. Whether any events have occurred that will bring into question the appropriateness mngt and TCWG not to issue F.S. reliance on Auditors Report.
of accounting policies used in the F.S.. to third parties. If mngt/TCWG does not take
8. Whether any events have occurred that are relevant to the measurement of If mngt still issues F.S., take necessary steps, take appropriate
estimates or provisions made in the F.S. appropriate action to prevent action to prevent reliance on
9. Whether any events have occurred that are relevant to the recoverability of assets. reliance on auditors report. auditors report.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 9
SA 570 (Revised) Going Concern
Mngt. Responsibilities Auditors Duties. Conditions that may case doubt
about G.C. Assumption
Responsibilities
Asses the entitys ability To obtain SAAE about the For this purpose auditor is required to A Financial Conditions
to continue as a going appropriateness of mngt use of a) Cover the same period as that used by mngt. 1. Net Liability position.
concern. going concern assumption 2. Non renewal of borrowings.
b) Consider whether mngt has considered all
General purpose F.S. are 3. Withdrawal of Financial
relevant information of which auditor is aware. Support.
prepared on a going Determine whether mngt has
4. Adverse Financial Ratios.
concern basis unless already performed a preliminary Request mngt to make its assessment of entitys 5. Inability to pay creditors.
management intends to assessment of entity ability to ability to continue as going concern. 6. Substantial Losses.
liquidate the entity or to continue as going concern.
Evaluate management plans for future. 7. Inability to arrange finances.
cease operation. 8. Negative Operating cash flow.
Consider the reliability of cash flow forecast.
In case F.S. are not Auditor identifies events that cast 9. Deterioration in value of assets.
prepared on going significant doubt on entity ability Considering availability of additional facts or
10. Discontinuation of dividend.
concern basis, the fact to continue as going concern. information since the date of mngt assessment. B Operating Conditions
would need to be Requesting WR from Mngt. regarding their plans 1. Management intention to
appropriately disclosed. Perform additional procedures for future action and the feasibility of these plans liquidate the entity.
2. Loss of KMP.
3. Loss of a major market, key
Going concern Mngt. unwilling to make its assessment customer, franchise etc.
Assumption Appropriate Going Concern Assumption 4. Labour Difficulties.
but Material Uncertainty Inappropriate 5. Shortage of Important Supplies.
exists 6. Emergence of successful
competitor.
C Others
Determine whether F.S. Adverse Opinion Consider the implications on Auditors Report
1. Non compliance of Statutory
makes relevant disclosure Requirements.
2. Pending legal proceedings
Yes No against the entity.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg 3. Uninsured or underinsured
EOM Q/A assets.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 10
SA 580 Written Representation
Meaning and Nature of WR Requirements of SA 580
A written statement by Matters for which WR may be obtained Auditor Responses in different Situations
Management
Management refuses to Reliability of WR is doubtful
provided to auditor
provide WR
(a) Preparation and
presentation of Financial
to confirm certain matters
Statements: Discuss the matter with In case of having concerns
Management responsibilities
or
In accordance with applicable management about competence and
to support other audit evidence. FRF. Re-evaluate the reliability integrity of mngt, determine
WR recognized as audit evidence (b) Information provided to and integrity of management. their effect in reliability of
as a response to inquiries. 1 Auditor: Determine possible effect on WR and other audit
WR do not provide SAAE as agreed in terms of the opinion. evidence in general.
WR should be in the form of a engagement Issue disclaimer of opinion. IF WR inconsistent with
representation letter addressed (c) Description of management other evidences, perform
to Auditor. Responsibilities: additional procedures.
WR shall be obtained for all In the manner as described in If conclude that WR is not
Compiled by:
financial statements and terms of engagement reliable, determine possible
period(s) referred in Auditors As required by other SA CA. Pankaj Garg
effect on audit opinion.
Report. Or In case of sufficient doubt
Others
Date of WR shall be as near as 2 Where auditor determines that it over integrity of
practicable to the date of the is necessary to obtain one or more management, issue a
Auditors report. WR. disclaimer of opinion.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 11
SA 600 Using the Work of Another Auditor
Applicability: In situation where an auditor (principal auditor - PA), reporting on the financial information of an entity, uses the work of another auditor (other auditor - OA) w.r.t.
to the financial information of one/more components (Division, Branch subsidiary, J. V. etc.), included in the financial information of the entity.
Non applicability: (a) Joint auditors (b) Auditors relationship with a predecessor auditor.
Principal Auditors Procedures Documentation Coordination Reporting
1. Consider the professional competence of Other 1. Components whose FS are 1. Sufficient liaison/co- 1. Express a qualified /
Auditor, if Other Auditor is not a member of ICAI. audited by Other Auditor ordination between Principal disclaimer of opinion
2. Visit component and examine books of account, if and Other auditor. because of scope
and their significance to
limitation:
essential. the financial information
2. Principal auditor may require
If Principal Auditor
3. Obtain sufficient appropriate evidence, that work of Other Auditor to answer a
of the entity as a whole. concludes that he
Other Auditor is adequate for Principal Auditor's detailed questionnaire.
2. Names of the other cannot use the work of
purposes. 3. Other Auditor should
auditors. Other Auditor;
4. Discuss audit procedures applied by Other Auditor. coordinate with Principal
3. Any conclusions reached PA unable to perform
5. Review a written summary of Other Auditors Auditor:
sufficient additional
that individual Adhering to time-table.
procedures and findings through
procedures regarding
questionnaires/checklist. components are not Bringing to the attention of
FI of the component
6. Consider significant findings of Other Auditor: material. PA any significant finding.
audited by OA.
Discuss audit findings with OA and Mgt. of 4. Procedures performed Compliance with relevant
2. Report should state
component. regarding components. statutory requirements.
clearly division of
Perform supplemental tests if necessary. 5. Conclusions reached. Respond to detailed
responsibility
questionnaire.
7. In case Other Auditor is not a professionally qualified 6. Manner of dealing with between PA and OA.
auditor - for instance, where a component is situated in Modified Report of Other
foreign country: Auditor while finalising
Procedures mentioned above assume added Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg
Principal Auditors Report.
importance.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 1
SA 610 (Revised) Using the Work of Internal Auditors
Meaning & scope of Relationship External Auditors Procedures w.r.t. Evaluation of Internal Audit Documentatio
Internal Audit Function between Internal
Audit Function & Conclusions regarding the
Meaning Determine evaluation & adequacy of
External Auditor
An appraisal activity. work.
Established/ provided. Audit procedures performed
Adequacy of Internal Audit If Adequate, consider
Role & objectives of on internal auditor work.
As a service to entity. Work for External Auditors its effect on N, T, E of
internal audit function
Also include Purpose External auditors Using Specific Work
determined by Mngt/
examining, Procedures.
TCWG. of Internal auditor
evaluating & By evaluating the following
Notwithstanding
monitoring
Degree of autonomy / Objec ti vi ty of the Evaluate the following:
adequacy / effectiveness of
objectivity, internal i nter na l a udi t f u nc ti on; Specific work was performed by
Internal Control.
audit function is not Tec hni c a l c ompete nc y Internal Auditors having adequate
independent of entity. of i nte rna l a udi t ors; Nature of specific technical training & proficiency.
External auditor has Prof essi ona l c a re w i th work performed by Work was properly supervised,
Scope of Internal Audit:
sole responsibility for w hi c h the i nte rna l Internal Auditor. reviewed & documented.
Monitoring of I. C.
audit opinion, and a udi tors w orks; a nd Assessed RMM. Adequate audit evidence obtained
Examination of financial
that responsibility not C ommuni c a ti on Degree of subjectivity by Internal auditor.
& operating information.
reduced by use of betw ee n i nte rna l in evaluation of audit Conclusions reached are
Review of operating
work of internal a udi tors & e xte rna l evidence by internal appropriate & reports prepared by
activities.
auditors. a udi tor. auditor. internal auditors are consistent
Review of compliance
with the results of work performed.
with laws & regulations.
Exceptions / unusual matters
Risk management. Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg disclosed by Internal Auditor are
Governance.
properly resolved.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 2
SA 620 Using the Work of Auditors Expert
Meaning of Auditors Expert Procedures to be followed while using the work of auditors expert
An individual or organisation 1 Determining need for an Auditors Expert 4 Agreement with Auditors Expert
possessing expertise in field An auditors expert may be needed to assist the auditor for the Need to be in writing and cover the followings:
followings: Nature, scope and Objectives of Auditors Expert
other than accounting/auditing,
Obtaining an understanding of entity & its environment, including IC. work.
whose work is used by the Identifying and assessing the risks of material misstatement. Respective Role and Responsibilities of Auditor
auditor Determining & implementing overall responses to assessed risks. and auditors Expert.
to assist the auditor in obtaining Designing and performing further audit procedures to respond to NTE of Communication including form of report.
SAAE. assessed risks. Confidentiality requirements to be observed by
Evaluating the sufficiency and appropriateness of audit evidence
Auditors Expert.
obtained.
Areas where work of AE can be
2 Evaluate Competence, Capability and Objectivity of the Expert 5 Evaluate appropriateness of Expert work
used
Source of Information for evaluation: Finding & Conclusion Relevance,
Personal Experience with previous work.
Reasonableness & Consistency with other A.E.
Valuation of complex financial Discussion with that expert.
Discussion with other Auditors.
Assumptions and Methods Relevance and
instruments, L & B, P & M, jewelry,
Knowledge of experts qualification, memberships, other forms of Reasonableness.
works of art, antiques, intangible
recognitions. Source Data Relevance, Completeness and
assets, assets acquired and Published books or papers.
accuracy.
liabilities assumed in business Auditors firm Q. C. Policies and Procedures.
combinations and assets that may 3 Obtain an understating of expert work 6 Expert work not adequate for audit purposes
have been impaired. To enable the auditor to determine the nature, scope and If Auditor concludes that work of auditors expert is
objectives of that experts work for auditors purposes. not adequate for the auditors purposes and
Actuarial calculation of liabilities
Evaluate the adequacy of that work for the auditors auditor cannot resolve the matter through the
associated with insurance contracts
additional audit procedures,
or employee benefit plans. purposes.
it may be necessary to express a modified opinion.
Estimation of oil and gas reserves.
Valuation of environmental
liabilities, and site clean-up costs. Reference to the Auditors Expert in the Auditors Report
Interpretation of contracts, laws Compiled by: No reference required in case of unmodified Audit Report unless required by L & R.
and regulations. In case of modified reports, it may be appropriate to refer to the auditors expert, to
Analysis of complex or unusual tax CA. PANKAJ GARG
explain the nature of the modification. In such case, auditor may need the permission of
compliance issues.
the auditors expert before making such a reference..
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 3
SA 800 Special Considerations Audit of F.S. prepared in accordance with SPF
Scope of SA 800: SA 800 deals with Special considerations in application of SAs in audit of F.S. (Complete set) prepared in accordance with SPF.
Objective of Auditor: to address appropriately special considerations w.r.t. (a) Engagement Acceptance (b) Planning & performance (c) Opinion & Reporting.
Meaning & Nature of Compiled by: Auditors Considerations
Special Purpose CA. Pankaj Garg
Framework (SPF)
Engagement Acceptance Planning & Performing an Audit Engagement Forming an Opinion &
Reporting
Acceptance
Meaning of SPF 1. Determine acceptability of FRF as per SA 210. 1. Determine whether application of SAs requires special
FRF designed to meet 2. Obtain understanding of: consideration in the circumstances of engagement. For example, in
Apply requirements of
financial information Purpose for which FS are prepared. SA 320, judgments about matters that are material need to be based
SA 700 (Revised).
need of specific users. Intended users on a consideration of financial information needs of intended users.
Auditors Report to
Nature of SPF Steps taken by Mngt. to determine 2. Auditor is required to consider the following:
include:
acceptability of applicable FRF. Requirement of SA 200 on applicability of SAs and absence of
It may be Fair
(a) Purpose for which
3. Consider financial information needs of users in conditions requiring applicability of an SA.
presentation or
F.S. are prepared &
determining acceptability of FRF. Requirement of SA 315 regarding understanding of selection &
Compliance.
Intended users.
4. Applicable FRF may encompass financial application of accounting policies. In case accounts are prepared
Examples of SPF
on the basis of provisions of a contract, auditor is required to (b) Mngt.
reporting standards established by an
Cash receipts and responsibility
organization that is authorized to promulgate obtain understanding of significant interpretations of contract.
disbursements basis w.r.t. F.S. and
standards for SPFS. 3. In the case of SPFS prepared in accordance with the requirements of
of accounting selection of FRF.
5. In case any conflict exists in between financial a contract, mngt. may agree with the intended users on a threshold
Financial reporting below which misstatements identified during the audit will not be (c) EOM Para to alert
reporting standards and legislative
provisions established requirements, auditor need to take action as corrected. The existence of such a threshold does not relieve the users w.r.t.
by a regulator to meet prescribed in SA 210. auditor from the requirement to determine materiality in allocation of
the requirements of 6. In case FRF encompass financial reporting accordance with SA 320. Special purpose
that regulator. provisions of a contract, acceptability of FRF is 4. In the case of SPFS, TCWG may not have a responsibility of F.S. and as such
Financial reporting determined by considering whether framework overseeing the preparation of F.S. prepared as per requirements of F.S. may not be
provisions of a exhibits attributes normally exhibited by SPF. In such cases, requirements of SA 260 may not be relevant to suitable for
contract. acceptable FRF as described in SA 210. the audit of the SPFS. another purpose.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 1
SA 805 Special Considerations Audits of Single F.S. and Specific Elements, Accounts or Items of a F.S.
Scope of SA 805: SA 805 deals with Special considerations in application of SAs in audit of Single F.S. or Single Element/Account or Item of F.S.
Objective of Auditor: to address appropriately special considerations w.r.t. (a) Engagement Acceptance (b) Planning & performance (c) Opinion & Reporting.
Compiled by: Auditors Considerations
Single Financial
Statement/ Element of CA. Pankaj Garg
Audited F.S.
Engagement Acceptance Planning & Performing an Audit Engagement Forming an Opinion & Reporting
Meaning of Element Acceptance
Element means an element,
Application of SA (a) Adapt all SAs as necessary in the audit of SFS: Apply SA 700, as necessary.
account or item of a F.S.
SA 200 requires compliance with all SAs relevant (b) Careful consideration of relevance of each SA is If also engaged to report on full FS,
Single financial statement necessary. SAs such as SA 240, SA 550 and SA 570 are, issue separate reports.
to audit.
(for example, a CFS) or a in principle, relevant. This is because the element could If audited SFS published with audited
This applies to audit of Single F.S. even if the
specific element of a F.S. (for auditor also audits the complete F.S. be misstated as a result of fraud, the effect of related full FS, presentation of SFS should be
example, cash and bank differentiated from full FS.
If auditor not also engaged to audit the complete party transactions, or the incorrect application of the
Do not issue audit report on SFS
balances) includes the FS, consider the practicability of audit of Single going concern assumption under the applicable FRF.
until satisfied with differentiation.
related notes. F.S./Specific Element in accordance with SAs. (c) SAs are written in the context of an audit of F.S.; they
Acceptability of FRF are to be adapted as necessary in the circumstances Modified Opinion/EMP/OMP Para
Examples of Elements
when applied to the audit of a single F.S. or a specific on Full FS
1. Determine the acceptability of the FRF applied in
Accounts receivable, (a) Determine effect on Single F.S.
the preparation of Single F.S. element. For example, WR from mngt. about the
Allowance for doubtful (b) If appropriate, modify opinion on
2. Determine whether application of FRF will result complete set of F.S. would be replaced by WR about
accounts receivable, SFS/include EMP, OMP.
in presentation that provides adequate single F.S. or element in accordance with the applicable
Inventory, (c) If necessary to issue adverse/
disclosures to enable users to understand FRF.
disclaimer opinion on full FS,
Schedule of externally information conveyed in Single FS or element. (d) When auditing Single F.S. in conjunction with Full F.S.,
unmodified opinion on SFS cannot
managed assets Form of Opinion audit evidence obtained as part of audit of full F.S. may
be expressed.
Schedule of net tangible Expected form of opinion depends upon be useful but auditor needs to plan & perform audit of
(d) However for separate audit of
assets applicable FRF & applicable L&R. Single F.S. to obtain SAAE.
specific element, an unmodified
SA 210 requires that agreed terms of engagement (e) Some items from Complete FS may be interrelated with
Schedule of disbursement opinion can be expressed if:
include the expected form of report to be issued. element of F.S., auditor need to perform procedures on
in relation to a lease Not prohibited by L& R;
Consider whether expected form of opinion is interrelated items.
property, AR on element is not published
appropriate in the circumstances. (f) Materialities determined for a Single F.S. or for a
Schedule of profit together with AR on full FS; &
Auditors decision as to the expected form of specific element may be lower that materiality for full
Element does not constitute a
participation or employee opinion is a matter of professional judgment. F.S., this will affects NTE of audit procedures and the
major portion of full F.S.
bonuses. evaluation of uncorrected misstatements.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 2
SA 810 Engagements to Report on Summary Financial Statements (SFS)
Scope of SA 810: deals with auditors responsibilities, when engaged to report, on SFS, derived from FS audited in accordance with SA, by that same auditor.
Objective of Auditor: to determine appropriateness of accepting the engagement & form opinion based on evaluation of Conclusions drawn from evidence obtained.
Meaning of Summary Financial Statements (SFS): Historical financial info that is derived from FS, but contains less detail than FS, while still providing a structured
representation consistent with that provided by entitys F.S.
Engagement Acceptance Nature of Procedures Form of Opinion
(a) Accept engagement only when also 1 EVALUATE Unmodified opinion shall be expressed on Summary F.S. if
engaged to audit, those F.S., from which SFS (a) Whether SFS adequately disclose
have been derived. their summarised nature & identify SFS are consistent, in all material respects, with audited FS, in accordance
(b) Before accepting Engagement, auditor audited FS. with applied criteria.
shall: (b) If SFS are not accompanied by
1. Determine acceptability of applied Special Considerations
audited FS, whether they clearly
criteria. Qualified 1. State that audit report on FS contains qualified
describe from whom or where
2. Obtain agreement of mngt that Opinion/EO opinion/EOM/OM para AND
audited FS are available;
acknowledges & understands its M/OM Para 2. Describe:
(c) Whether SFS adequately disclose
responsibilities: in Report on Basis for qualified opinion on audited FS, and that
the applied criteria.
For preparation of SFS in accordance Audited FS qualified opinion; or EOM/OM para; and
(d) Whether SFS are prepared in
with applied criteria; Effect thereof on SFS, if any.
accordance with applied criteria.
To make audited FS available to Adverse Report on SFS is required to include the following:
(e) Whether SFS contain necessary
intended users of SFS without undue Opinion/ 1. Statement that audit report contains
info & are appropriately
difficulty; and Disclaimer of adverse/disclaimer of opinion;
aggregated.
To include auditors report on SFS in Opinion on 2. Description of basis of such opinion; and
(f) Whether audited F.S. are available
any document that contains SFS and Audited FS 3. Statement that as a result of adverse/disclaimer of
to intended users without undue
that indicates that auditor has opinion it is inappropriate to express an opinion on
difficulty.
reported on them.
2 COMPARE SFS.
(c) Agree with the management the form of
SFS with related information in Modified Express adverse opinion
opinion to be expressed on the SFS.
audited F.S. to determine whether SFS Opinion on
(d) Do not accept engagement if:
agree with or can be re-calculated SFS if SFS are not consistent in all material respects with or
Criteria are not acceptable; or
from related information in audited are not a fair summary of audited FS in accordance with
unable to obtain management
F.S. applied criteria.
agreement.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 3
CARO 2016
Applicability of CARO 2016 Matters to be reported under CARO 2016 (Para 3)
CARO 2016 apply to all companies including foreign Para Reporting Area Reporting Requirements
companies except the following No.
3(i) Fixed Assets Whether proper records maintained.
(a) Banking Company Whether physical verification has been conducted at reasonable intervals by mngt.
(b) Insurance Company Whether material discrepancies noticed and if so, whether dealt properly in books.
(c) Company licensed to operate u/s 8 Title deeds of immovable properties are held in name of Co., if not provide details.
3(ii) Inventories Whether physical verification has been conducted at reasonable intervals by mngt.
(d) One Person Company
Whether material discrepancies noticed and if so, whether dealt properly in books.
(e) Small Company
3(iii) Loans and Advances Whether loans have been granted to companies, firms, LLP covered u/s 189. If so,
(f) Private limited Company (not being a subsidiary or (a) T & C are not prejudicial to the companys interest;
holding of public co) (b) Schedule of repayment of principal & payment of interest has been stipulated;
Paid up capital + Reserves & Surplus < 1Cr. (c) State the total amount overdue for > 90 days.
(as on Balance Sheet Date) 3(iv) Compliance of Provisions In respect of loans, investments, guarantees, and security
+ of Sec. 185 & 186 If not, provide the details thereof.
Total borrowings from Bank & F.I. < 1Cr. 3(v) Public Deposits Directives by RBI and Sec. 73 to 76 complied with. If not - nature of contravention.
(at any point of time during the FY) Order passed by CLB/RBI/Court/TribunalWhether complied with or not.
+ 3(vi) Cost Records Whether Specified u/s 148(1); whether accounts and records made and maintained.
Total revenue as disclosed in Schedule III < 10 Cr. 3(vii) Statutory Dues Whether undisputed PF, ESI, IT, ST, ST, Custom, Excise, VAT, cess & Other paid
(for the FY) regularly. If Not outstanding >6 months as on Balance Sheet Date.
W.r.t. disputed IT, ST, ST, Custom, Excise, VAT State Amount involved & forum
Important Notes 3(viii) Repayment of Dues Whether co. default in repayment of dues F.I., Bank, Govt., Debenture holders.
1. CARO not apply over audit report on Consolidated If Yes Nature and Amount of Default.
F.S. 3(ix) Money raised by public Whether money Raised by IPO/FPO/term Loans applied for stated purpose.
2. Provisions of CARO are equally applicable in case issue & term loans If Not details along with delay and subsequent ratification be reported.
of branches. 3(x) Fraud Whether any fraud by company or on company by its officers/employeesnoticed or reported.
3. Paid up capital includes equity as well as If Yes Nature and amount to be stated.
Preference. 3(xi) Managerial remuneration Whether managerial remuneration has been paid with requisite approvals u/s 197.
4. Reserves include all types of reserves & P & L If Not, amount involved and steps taken for securing refund to be reported.
Balance. 3(xii) Nidhi Companies Whether the net owned funds to deposits ratio 1:20.
5. All Loans (secured/unsecured, long term/short Whether 10% unencumbered term deposits maintained..
term, etc.) are to be considered and in aggregate. 3(xiii) Transaction with Whether transactions with related parties are in compliance with Sec. 177 & 188.
6. F.I. includes NBFC. Related Parties Whether details disclosed in F.S. as required by applicable AS.
7. Total Revenue comprises of Revenue from 3(xiv) Preferential Allotment Whether any preferential allotment of shares/FCD/PCD has been made.
Operations and Other Income. If so, whether Sec. 42 complied with and amount raised used for stated purpose.
If Not provide details of amount involved and nature of non compliance.
3(xv) Non cash transactions Whether co. has entered into non cash transactions with directors.
with Directors If so. Whether Sec. 192 has been complied with.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg
3(xvi) Registration with RBI Whether regn. required u/s 45IA of RBI Act, 1934. If So- whether regn. obtained.
Compiled by: CA. Pankaj Garg Page 1
You might also like
- Summary Notes IPCC Auditing 2Document11 pagesSummary Notes IPCC Auditing 2Nishant Singh78% (9)
- !P7 Audit and Assurance Summary - 1 - 20 PagesDocument20 pages!P7 Audit and Assurance Summary - 1 - 20 Pagesckomaromi776No ratings yet
- Notes CA+Inter+Audit+May+24Document280 pagesNotes CA+Inter+Audit+May+24carlsen magNo ratings yet
- QnA ISA 200 & ISA 210Document5 pagesQnA ISA 200 & ISA 210auditNo ratings yet
- Audit SA Chart by CA Sarishti SethiDocument98 pagesAudit SA Chart by CA Sarishti SethiMemory Crafterz100% (2)
- Email CampaignDocument1,252 pagesEmail Campaignvenkatesh_182980% (5)
- Audit Standards Summary Compiled With Q & ADocument86 pagesAudit Standards Summary Compiled With Q & Asantosh pandeyNo ratings yet
- Audit Charts FullDocument80 pagesAudit Charts FullsummaiyaNo ratings yet
- Types of Audits: Audit - An OverviewDocument31 pagesTypes of Audits: Audit - An OverviewRanel Clark D. TabiosNo ratings yet
- CA Final Super 25 Sas NotesDocument263 pagesCA Final Super 25 Sas NotesAnjana Ramesh0% (1)
- FM - EcoDocument352 pagesFM - EcoKinjal Jain100% (1)
- Cpa Sample QuestionsDocument43 pagesCpa Sample QuestionsFaraheen JunismanNo ratings yet
- CPA Auditing 2 - Notes FR HomeworkDocument10 pagesCPA Auditing 2 - Notes FR Homeworkpambia200050% (2)
- Auditing and Attestation Content Specification OutlineDocument5 pagesAuditing and Attestation Content Specification OutlineLisa GoldmanNo ratings yet
- Review NotesDocument146 pagesReview NotesMaria Rizza OguisNo ratings yet
- Ca Final Audit Quick Revision PDFDocument28 pagesCa Final Audit Quick Revision PDFharshNo ratings yet
- Auditing (1) Master MindsDocument18 pagesAuditing (1) Master Mindstsg_ramaraoNo ratings yet
- Auditing Notes.Document55 pagesAuditing Notes.Viraja Guru50% (2)
- Chapter 4 - Controls: External Audit EngagementDocument9 pagesChapter 4 - Controls: External Audit EngagementSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- CA Inter Audit - Integrated Case StudiesDocument22 pagesCA Inter Audit - Integrated Case StudiesGANESH KUNJAPPA POOJARINo ratings yet
- Romney Ais13 PPT 13Document11 pagesRomney Ais13 PPT 13Aj PotXzs ÜNo ratings yet
- Audit of CompaniesDocument28 pagesAudit of CompaniesKNOWLEDGE CREATORSNo ratings yet
- Rights, Duties and Liabilities of An AuditorDocument8 pagesRights, Duties and Liabilities of An AuditorShailee ShahNo ratings yet
- Full Download:: Suggested Answers To Discussion QuestionsDocument8 pagesFull Download:: Suggested Answers To Discussion QuestionsIrawatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document22 pagesChapter 7Jasmin AkterNo ratings yet
- Guidance On Tax Audit Under Section 44ABDocument5 pagesGuidance On Tax Audit Under Section 44ABSukumar BasuNo ratings yet
- Vouching Meaning: Vouching Means The Examination of Documentary Evidence in Support of Entries ToDocument4 pagesVouching Meaning: Vouching Means The Examination of Documentary Evidence in Support of Entries ToShubhangi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Standards On AuditingDocument69 pagesStandards On AuditingSaba Kazi100% (1)
- Chapter 19 - Test of ControlDocument22 pagesChapter 19 - Test of ControlJhenna ValdecanasNo ratings yet
- The Demand For Audit and Other Assurance ServicesDocument41 pagesThe Demand For Audit and Other Assurance ServicesMamatz Fth-winter100% (1)
- CA Inter Cost Blast From The Past PDFDocument83 pagesCA Inter Cost Blast From The Past PDFAashish TiwariNo ratings yet
- Copy of Different Types of Audit ReportDocument8 pagesCopy of Different Types of Audit ReportRonak SinghNo ratings yet
- The Audit Process - Final ReviewDocument5 pagesThe Audit Process - Final ReviewFazlan Muallif ResnuliusNo ratings yet
- CA Final Direct Tax Flow Charts May 2017 2SDMBZA2Document92 pagesCA Final Direct Tax Flow Charts May 2017 2SDMBZA2Meet Mehta100% (1)
- Auditing Notes KEY NOTESDocument13 pagesAuditing Notes KEY NOTESkonyatanNo ratings yet
- AuditingDocument626 pagesAuditingAbdulrehman567No ratings yet
- Audit of Different Types of Entity Summary Notes by CA Kapil GoyalDocument24 pagesAudit of Different Types of Entity Summary Notes by CA Kapil GoyalDrake DDNo ratings yet
- Audits of Financial StatementsDocument7 pagesAudits of Financial StatementsJeremy Lorenzo Teodoro VirataNo ratings yet
- Audit ReviewDocument12 pagesAudit ReviewAmanda ClaroNo ratings yet
- Special Audit of Sugar MillsDocument2 pagesSpecial Audit of Sugar MillsZoyaNo ratings yet
- CA IPCC Audit ScannerDocument10 pagesCA IPCC Audit Scannercheranjit0% (1)
- Nature and Scope of AuditingDocument23 pagesNature and Scope of AuditingPrachi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Auditing OverviewDocument1 pageChapter 2 - Auditing OverviewJean GarciaNo ratings yet
- Internal Auditing As An Aid To ManagementDocument119 pagesInternal Auditing As An Aid To ManagementJohn Bates Blankson100% (3)
- 1st Chapter AssuranceDocument5 pages1st Chapter AssuranceRashed AliNo ratings yet
- Types of Audit Reports (Opinion)Document8 pagesTypes of Audit Reports (Opinion)Anonymous HBzUFPliGsNo ratings yet
- Verification of AssetsDocument4 pagesVerification of AssetsMohammed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Assurance Ch-1-7Document14 pagesAssurance Ch-1-7tusher pepolNo ratings yet
- Arens Auditing C13e PPT Ch01Document17 pagesArens Auditing C13e PPT Ch01MeowNo ratings yet
- Verification and Valuation of Assets and Liabilities - Chapter-8Document8 pagesVerification and Valuation of Assets and Liabilities - Chapter-8Tareq90% (10)
- L3 Audit PlanningDocument7 pagesL3 Audit PlanningJun Guerzon PaneloNo ratings yet
- LambersCPAReviewAUDIT PDFDocument589 pagesLambersCPAReviewAUDIT PDFjulie anne mae mendozaNo ratings yet
- Ca Final Auditing Revision ChartsDocument151 pagesCa Final Auditing Revision ChartsKumar SwamyNo ratings yet
- Business AssuranceDocument38 pagesBusiness AssuranceRAQIB 2025No ratings yet
- Indian Accounting Standards (One Pager)Document29 pagesIndian Accounting Standards (One Pager)sridhartks100% (1)
- International Auditing Overview: Principles of Auditing: An Introduction To International Standards On Auditing - Ch. 1Document42 pagesInternational Auditing Overview: Principles of Auditing: An Introduction To International Standards On Auditing - Ch. 1Rica Mae Recososa100% (2)
- Cost AuditDocument10 pagesCost AuditHasan AhmmedNo ratings yet
- Sample For Auditing Mantras For CA IPCCDocument110 pagesSample For Auditing Mantras For CA IPCCAnurag Singal75% (4)
- Audit and AssuranceDocument16 pagesAudit and AssuranceAmolaNo ratings yet
- AUD Notes Chapter 2Document20 pagesAUD Notes Chapter 2janell184100% (1)
- Sa 200 "Overall Objectives of The Independent Auditor AND Conduct OF THE Audit IN Accordance With SasDocument1 pageSa 200 "Overall Objectives of The Independent Auditor AND Conduct OF THE Audit IN Accordance With SasKisi Ka Dar NahiNo ratings yet
- GST Rate Schedule For Certain Goods 3 June 17Document26 pagesGST Rate Schedule For Certain Goods 3 June 17CharteredAdda.comNo ratings yet
- Changelog 3 4-140Document2 pagesChangelog 3 4-140partymongerNo ratings yet
- Lokpal Bill: ... Understanding The Drafts of and Civil SocietyDocument28 pagesLokpal Bill: ... Understanding The Drafts of and Civil SocietyAbhishek GourNo ratings yet
- IOT Architecture IIDocument29 pagesIOT Architecture IIfaisul faryNo ratings yet
- LEMBAR JAWABAN CH.10 (Capital Budgeting Techniques)Document4 pagesLEMBAR JAWABAN CH.10 (Capital Budgeting Techniques)Cindy PNo ratings yet
- Sermon Manuscript Galatians 5:16-26Document9 pagesSermon Manuscript Galatians 5:16-26Nathaniel ParkerNo ratings yet
- Project Chalk CorrectionDocument85 pagesProject Chalk CorrectionEmeka Nicholas Ibekwe100% (6)
- Ismb ItpDocument3 pagesIsmb ItpKumar AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Raksha Mantralaya Ministry of DefenceDocument16 pagesRaksha Mantralaya Ministry of Defencesubhasmita sahuNo ratings yet
- First - Second and Third Class Levers in The Body - Movement Analysis in Sport - Eduqas - Gcse Physical Education Revision - Eduqas - BBC BitesizeDocument2 pagesFirst - Second and Third Class Levers in The Body - Movement Analysis in Sport - Eduqas - Gcse Physical Education Revision - Eduqas - BBC BitesizeyoyoyoNo ratings yet
- Ahmad Syihabudin: BiodataDocument2 pagesAhmad Syihabudin: BiodatabhjjqrgrwmNo ratings yet
- European Construction Sector Observatory: Country Profile MaltaDocument40 pagesEuropean Construction Sector Observatory: Country Profile MaltaRainbootNo ratings yet
- 32 Hyderabad HITEC City BisleriDocument23 pages32 Hyderabad HITEC City BisleriSridhar ViswanathanNo ratings yet
- Riqas Ri RQ9142 11aDocument6 pagesRiqas Ri RQ9142 11aGrescia Ramos VegaNo ratings yet
- Fire Prevention Plan Template - FINAL 5-30-08Document5 pagesFire Prevention Plan Template - FINAL 5-30-08Peter GeorgeNo ratings yet
- The Reason: B. FlowsDocument4 pagesThe Reason: B. FlowsAryanti UrsullahNo ratings yet
- Seizure Control Status and Associated Factors Among Patients With Epilepsy. North-West Ethiopia'Document14 pagesSeizure Control Status and Associated Factors Among Patients With Epilepsy. North-West Ethiopia'Sulaman AbdelaNo ratings yet
- IQAc 04-05Document10 pagesIQAc 04-05ymcacollegewebsiteNo ratings yet
- Motivation Theories Description and CriticismDocument14 pagesMotivation Theories Description and CriticismAhmed Elgazzar89% (18)
- LFF MGDocument260 pagesLFF MGRivo RoberalimananaNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence Practical 1Document5 pagesArtificial Intelligence Practical 1sadani1989No ratings yet
- Galman V PamaranDocument7 pagesGalman V PamaranChow Momville EstimoNo ratings yet
- Literature Review of Service Quality in RestaurantsDocument7 pagesLiterature Review of Service Quality in RestaurantsuifjzvrifNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.3.3 History of Visual Arts Modernism Post ModernismDocument17 pagesChapter 2.3.3 History of Visual Arts Modernism Post ModernismKim Ashley SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Marine Cargo InsuranceDocument72 pagesMarine Cargo InsuranceKhanh Duyen Nguyen HuynhNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Urja Vikas Nigam LTD., Vadodara: Request For ProposalDocument18 pagesGujarat Urja Vikas Nigam LTD., Vadodara: Request For ProposalABCDNo ratings yet
- GLOBE2Document7 pagesGLOBE2mba departmentNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log Quarter 1 Week 1Document5 pagesDaily Lesson Log Quarter 1 Week 1John Patrick Famadulan100% (1)
- PreviewpdfDocument29 pagesPreviewpdfSoemarlan ErlanNo ratings yet
- March For Our LivesDocument22 pagesMarch For Our LivesLucy HanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Industrial Engineering & Ergonomics - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument15 pagesUnit 2 - Industrial Engineering & Ergonomics - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inSACHIN HANAGALNo ratings yet
- Procter and Gamble - MarketingDocument10 pagesProcter and Gamble - MarketingIvana Panovska100% (5)
- William Hallett - BiographyDocument2 pagesWilliam Hallett - Biographyapi-215611511No ratings yet