Professional Documents
Culture Documents
STRRG
Uploaded by
Ahmad Rifki Mauludi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views26 pagesStruktur baja digunakan dalam berbagai konstruksi seperti stadion olahraga di Shanghai dan Bird Nest Stadium di Beijing. Baja telah digunakan dalam konstruksi sejak jembatan besi pertama pada tahun 1779. Baja terdiri terutama dari besi dengan kandungan karbon antara 0,2-2,04% dan unsur lain seperti mangan, krom, vanadium, dan tungsten. Ada berbagai jenis baja seperti baja karbon, baja tahan karat, dan baja
Original Description:
sdfegegr
Original Title
132512227-Strrg
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentStruktur baja digunakan dalam berbagai konstruksi seperti stadion olahraga di Shanghai dan Bird Nest Stadium di Beijing. Baja telah digunakan dalam konstruksi sejak jembatan besi pertama pada tahun 1779. Baja terdiri terutama dari besi dengan kandungan karbon antara 0,2-2,04% dan unsur lain seperti mangan, krom, vanadium, dan tungsten. Ada berbagai jenis baja seperti baja karbon, baja tahan karat, dan baja
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views26 pagesSTRRG
Uploaded by
Ahmad Rifki MauludiStruktur baja digunakan dalam berbagai konstruksi seperti stadion olahraga di Shanghai dan Bird Nest Stadium di Beijing. Baja telah digunakan dalam konstruksi sejak jembatan besi pertama pada tahun 1779. Baja terdiri terutama dari besi dengan kandungan karbon antara 0,2-2,04% dan unsur lain seperti mangan, krom, vanadium, dan tungsten. Ada berbagai jenis baja seperti baja karbon, baja tahan karat, dan baja
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 26
Struktur Baja
Dimana saja struktur baja dipakai ?
Shanghai Sports Stadium
has a gross area of 170,000 m (plan area
61,700 m)
More than 4,000 tonnes of hollow sections and
1,000 tonnes of steel plate were supplied to build
the Shanghai Sports Stadium
Bird Nest Stadium
Sejarah Bangunan Baja
Iron Bridge, Firth of Forth Bridge,
England, 1779 Scotland, 1881
Eifel Tower, Empire State
France , 1882 Building, USA, 1931
Akashi Kaikyo Bridge,
Japan , 1998
Proses Pembuatan Baja
Definisi Baja
Steel is an alloy consisting mostly of iron,
with a carbon content between 0.2 and
2.04% by weight, depending on grade.
Carbon is the most cost-effective alloying
material for iron, but various other alloying
elements are used such as manganese,
chromium, vanadium, and tungsten
(wikipedia.org)
Jenis-jenis baja dikenal
Carbon steel, also called plain carbon steel, is steel where the
main alloying constituent is carbon; the other elements present are
in quantities too small to affect the properties. The only other
elements allowed in carbon steel are: manganese (1.65% max),
silicon (0.60% max), and copper (0.60% max).
Stainless steel is defined as a steel alloy with a minimum of 11.5%
chromium content by mass. Stainless steel differs from carbon steel
by amount of chromium present. Carbon steel rusts when exposed
to air and moisture. This iron oxide film is active and accelerates
corrosion by forming more iron oxide. Stainless steels have
sufficient amount of chromium present so that a passive film of
chromium oxide forms which prevents further corrosion.
HSLA steel (high strength low alloy steel) is a type of steel alloy
that provides many benefits over regular steel alloys. In general,
HSLA alloys are much stronger and tougher than ordinary plain-
carbon steels. They are used in cars, trucks, cranes, bridges, and
other structures that are designed to handle large amounts of stress,
often at very low temperatures.
Tujuan Kuliah Baja 1
Mahasiswa dapat
merencanakan
kekuatan penampang
elemen struktur baja
terhadap gaya aksial,
lentur, geser dan
kombinasinya.
Isi Kuliah Baja 1
Kuliah ini mempelajari
perencanaan elemen-
elemen struktur baja,
yaitu batang tarik,
batang tekan, balok,
dan balok kolom
dengan menggunakan
metoda load and
resistance factor design
(LRFD)
Beban pada Struktur (Loads)
Secara garis besar dibagi :
1. Dead Load permanent loads (gravity loads)
the weight of structure self weight
nonstructural component floor covering, partition, and
suspended ceilings
2. Live Load not permanent load
Static Load and dynamic loads
3. Wind Load
4. Earthquake Loads
Building Codes, Design
Specification
Tata Cara Perencanaan Struktur baja
untuk Bangunan Gedung (SNI 03-1729-
2000)
American Institute of Steel Construction
(AISC, 1999)
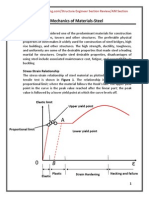
Steel Characteristics
Tensile Test
The stress and strain can
be computed as follows:
P
f Where:
A f = axial tensile stress
A = cross sectional area
L = axial strain
L = length of specimen
L L = change in length
Ductility can be measured by the elongation,
defined as:
Where:
L f Lo e = elongation (%)
e x100 Lf = length of the specimen at fracture
Lo L0 = original length
Indealization of stress strain curve
Fy = yield stress
Fu = the ultimate tensile strength
The ratio of stress to strain within the elastic range,
denoted E and called Youngs modulus or modulus of
elasticity (modulus elastisitas)
f
E
E baja = 200000 MPa High
Strength
Steel
0.002
You might also like
- Structural Concrete: The Commonwealth and International Library: Structures and Solid Body Mechanics DivisionFrom EverandStructural Concrete: The Commonwealth and International Library: Structures and Solid Body Mechanics DivisionNo ratings yet
- Struktur Baja: Yayat Hendrayana, ST.,MTDocument27 pagesStruktur Baja: Yayat Hendrayana, ST.,MTFikri FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Structural Steel OverviewDocument55 pagesStructural Steel OverviewIrish TambisNo ratings yet
- Struktur Baja 1Document33 pagesStruktur Baja 1Agung S NurcahyanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Structural Steel DesignDocument44 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Structural Steel DesignKhaled Khafagy100% (1)
- Chapter 1Document6 pagesChapter 1Haftom GebreegziabiherNo ratings yet
- Design of Steel and Timber StructuresDocument101 pagesDesign of Steel and Timber Structuresyenebeb tariku89% (18)
- Steel DesignDocument140 pagesSteel DesignGlenn PaaNo ratings yet
- Design of Steel and Timber Structures Examples PDFDocument78 pagesDesign of Steel and Timber Structures Examples PDFsamson100% (3)
- Lecture 1 - Introduction Steel FamiliarizationDocument15 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction Steel FamiliarizationDubu DubuNo ratings yet
- S Announcement 13251 PDFDocument3 pagesS Announcement 13251 PDFDada CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Steel Structures - (Introduction) - 2Document13 pagesSteel Structures - (Introduction) - 2Ceren ŞirinNo ratings yet
- Introd-Steel Struc.Document4 pagesIntrod-Steel Struc.Fuad AhmedinNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Mohamed El-SayedDocument17 pagesPrepared By: Mohamed El-SayedMoaz MoazNo ratings yet
- Mechanical PropertiesDocument9 pagesMechanical PropertiesAustin Okoth OmondiNo ratings yet
- Design of Steel Structures: Fourth Stage Civil Engineering Department Mustansiriyah UniversityDocument19 pagesDesign of Steel Structures: Fourth Stage Civil Engineering Department Mustansiriyah UniversityAlex CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SteelDocument15 pagesIntroduction To SteelgingeersboyNo ratings yet
- CE 388 Fundamentals of Steel Design ChapterDocument27 pagesCE 388 Fundamentals of Steel Design ChapterpubaccNo ratings yet
- 4 Steel Design 2Document20 pages4 Steel Design 2Joshua GonzalesNo ratings yet
- RCC Notes III II Strctral-EngineeringDocument84 pagesRCC Notes III II Strctral-Engineeringvenu madhavNo ratings yet
- Stress Analysis: M. Firdaus, MTDocument23 pagesStress Analysis: M. Firdaus, MTdaus_parisiNo ratings yet
- Material Properties in Mechanical and Machine ElementsDocument17 pagesMaterial Properties in Mechanical and Machine Elementsahmadhamada0511No ratings yet
- Chapter One ConcreteDocument28 pagesChapter One ConcreteSarfraz MunirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document43 pagesChapter 1Suleiman AldbeisNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Beam DesignDocument10 pagesFundamentals of Beam DesignVenu GopalNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Structural Steel StructuresDocument13 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Structural Steel StructuresMangoTangoNo ratings yet
- Mechanicslecture NotesDocument18 pagesMechanicslecture NotesleasterNo ratings yet
- Elemen Struktur Baja-III. COMPRESSION STRUCTUREDocument27 pagesElemen Struktur Baja-III. COMPRESSION STRUCTUREirfananda hutomoNo ratings yet
- Design of Structure-III: Unit 1Document14 pagesDesign of Structure-III: Unit 1Rohit TiwariNo ratings yet
- Steel QB With SolutionDocument64 pagesSteel QB With SolutionShazNo ratings yet
- Design of Steel Structures: Preliminary NotesDocument23 pagesDesign of Steel Structures: Preliminary NotesIrish サルタン タムビスNo ratings yet
- Steel Structure Chapter 1Document10 pagesSteel Structure Chapter 1Saly SerhalNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials-Steel: Structural Steel Properties and Stress-Strain CurvesDocument8 pagesMechanics of Materials-Steel: Structural Steel Properties and Stress-Strain CurvesNguyen SonNo ratings yet
- Tensile strength of Steel: Yield, Ultimate & types in <40 charsDocument10 pagesTensile strength of Steel: Yield, Ultimate & types in <40 charsEr. Prakash kalathokiNo ratings yet
- LECTURE NOTES ON REINFORCED CONCRETE BEAMSDocument84 pagesLECTURE NOTES ON REINFORCED CONCRETE BEAMSshambel asfawNo ratings yet
- Izod Muhammad Alhajri CompleteDocument5 pagesIzod Muhammad Alhajri Completenomi1234No ratings yet
- Nonlinear Material Properties of StructuralDocument9 pagesNonlinear Material Properties of Structuralkhawaja AliNo ratings yet
- Steel Research Es 4BDocument18 pagesSteel Research Es 4BGUTIERREZ, VIANCA MARIE R.No ratings yet
- Steel DesignDocument5 pagesSteel DesignKutty MansoorNo ratings yet
- Tensile StrengthDocument4 pagesTensile StrengthDayanski B-mNo ratings yet
- Review On Comparative Study of Steel and Aluminiumalloy Roof TrussDocument4 pagesReview On Comparative Study of Steel and Aluminiumalloy Roof TrussManikanta SharmaNo ratings yet
- Design of Steel StructuresDocument16 pagesDesign of Steel StructureszenitsuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Struc 1Document34 pagesIntroduction To Struc 1fadhlanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Introduction To Steel DesignDocument11 pagesLesson 1 Introduction To Steel DesignEJ Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Influence of Axial Load On Behavior of Belled Pile Reinforced With High-Strength Steel BarsDocument10 pagesInfluence of Axial Load On Behavior of Belled Pile Reinforced With High-Strength Steel BarscdestudosNo ratings yet
- Lec1 Steel Design 2nd Sem 2011 12Document6 pagesLec1 Steel Design 2nd Sem 2011 12Mohan ManickamNo ratings yet
- Structural Steel Design GuideDocument49 pagesStructural Steel Design GuideshalukaNo ratings yet
- Brief History and Design of Steel StructuresDocument6 pagesBrief History and Design of Steel StructuresMylfie DultraNo ratings yet
- Steel Design LMDocument16 pagesSteel Design LMJoeven DinawanaoNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials (15CV 32) : Module 1: Simple Stresses and StrainsDocument34 pagesStrength of Materials (15CV 32) : Module 1: Simple Stresses and StrainsAnonymous Qm0zbNkNo ratings yet
- Flexural Analysis of Reinforced Concrete Beams Behavior of Simply Supported Reinforced Concrete Beam Loaded To FailureDocument55 pagesFlexural Analysis of Reinforced Concrete Beams Behavior of Simply Supported Reinforced Concrete Beam Loaded To FailureheminNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Steel DesignDocument49 pagesIntroduction To Steel DesignkumuthaNo ratings yet
- Structural Design of Steel StructuresDocument43 pagesStructural Design of Steel Structureskiran sreekumarNo ratings yet
- Design of Composite ColumnDocument17 pagesDesign of Composite Columnpragati singhNo ratings yet
- Analytical Investigation of The Cyclic Behavior and Plastic Hinge Formation in Deep Wide-Flange Steel Beam-ColumnsDocument22 pagesAnalytical Investigation of The Cyclic Behavior and Plastic Hinge Formation in Deep Wide-Flange Steel Beam-ColumnsJuan BravoNo ratings yet
- Structural Response of A Material / Structure: Review On Structural MechanicsDocument4 pagesStructural Response of A Material / Structure: Review On Structural MechanicsWillisLaiNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Basic Concepts and History of Prestressed ConcreteDocument9 pagesIntroduction to Basic Concepts and History of Prestressed ConcreteAtul ManchalwarNo ratings yet
- Steel Structure IIIDocument27 pagesSteel Structure IIIUnwanus Sa'adahNo ratings yet
- Instructions on Modern American Bridge BuildingFrom EverandInstructions on Modern American Bridge BuildingNo ratings yet
- Lab Bahan Perkerasan Jalan UTY YogyakartaDocument1 pageLab Bahan Perkerasan Jalan UTY YogyakartaAhmad Rifki MauludiNo ratings yet
- Local Readiness Towards REDD+ UNFCCC Scheme (Study in Province of West Sumatera Indonesia)Document8 pagesLocal Readiness Towards REDD+ UNFCCC Scheme (Study in Province of West Sumatera Indonesia)Ahmad Rifki MauludiNo ratings yet
- Bab 10 NewDocument1 pageBab 10 NewAhmad Rifki MauludiNo ratings yet
- Aoyama H and Uemura T 1988. Structural Analysis by Matrix Method. Baifukan Inc., Tokyo.Document13 pagesAoyama H and Uemura T 1988. Structural Analysis by Matrix Method. Baifukan Inc., Tokyo.rifky07No ratings yet
- Rifki ModelDocument1 pageRifki ModelAhmad Rifki MauludiNo ratings yet
- Beam CalculationDocument43 pagesBeam CalculationjonlosNo ratings yet
- Study & Analysis of Transportation SkidDocument10 pagesStudy & Analysis of Transportation SkidJay PNo ratings yet
- 2-Plasticiy Theory and Application - A. MENDELSON - 3Document368 pages2-Plasticiy Theory and Application - A. MENDELSON - 3Ardeshir GholamiNo ratings yet
- Material Testing of M12 BoltsDocument72 pagesMaterial Testing of M12 BoltsdhaktodesatyajitNo ratings yet
- Computer Modeling and Optimization of Swage Autofrettage Process of A Thick-Walled Cylinder Incorporating Bauschinger EffectDocument33 pagesComputer Modeling and Optimization of Swage Autofrettage Process of A Thick-Walled Cylinder Incorporating Bauschinger EffectBoonsap WitchayangkoonNo ratings yet
- Design of Reinforced Concrete ColumnsDocument25 pagesDesign of Reinforced Concrete Columnsmedodo100% (1)
- CM Heavy-Duty Crane Hooks BrochureDocument12 pagesCM Heavy-Duty Crane Hooks Brochuretvmehta01No ratings yet
- 03 Design Methodology-1Document9 pages03 Design Methodology-1Abdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of An Epicyclic Gearbox For An Electric DrivetrainDocument9 pagesDesign and Analysis of An Epicyclic Gearbox For An Electric DrivetrainNajrul IslamNo ratings yet
- Plastic Product Design RaghuDocument24 pagesPlastic Product Design RaghuDeejay ShivNo ratings yet
- Weld Strength and Design PDFDocument47 pagesWeld Strength and Design PDFkhairulNo ratings yet
- How To Strengthen Dental Ceramics: KeywordsDocument4 pagesHow To Strengthen Dental Ceramics: KeywordsSajida RakhmahNo ratings yet
- Master'S ThesisDocument107 pagesMaster'S ThesisAhmed GharbiNo ratings yet
- Alu Flex System-CatalogueDocument8 pagesAlu Flex System-Cataloguemike murdocNo ratings yet
- Structural Strength Assessment of Steel Stacks Using FEADocument8 pagesStructural Strength Assessment of Steel Stacks Using FEASrinivasa Rao VenkumahanthiNo ratings yet
- Criterios de FallaDocument6 pagesCriterios de FallaJonatan Pozo PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Al Majidi2017 PDFDocument22 pagesAl Majidi2017 PDFRambabu VenkataNo ratings yet
- Steel Structures SyllabusDocument30 pagesSteel Structures Syllabusseparveenjangra100% (1)
- Micromechanics of LaminaDocument21 pagesMicromechanics of LaminamathjonNo ratings yet
- Conbextra Ep75Document4 pagesConbextra Ep75Sathiya SeelanNo ratings yet
- Plastic HingesDocument10 pagesPlastic HingesBala SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: Cobblestone Shaping MachineDocument92 pagesAcknowledgement: Cobblestone Shaping MachineFikru GebreNo ratings yet
- CH 8 Slides M PDFDocument96 pagesCH 8 Slides M PDFAnkit NayakNo ratings yet
- Particle Size Distribution (PSD) Objectives: CFB20504 Food Process Engineering Laboratory 1: Mechanical ReductionDocument5 pagesParticle Size Distribution (PSD) Objectives: CFB20504 Food Process Engineering Laboratory 1: Mechanical ReductionAziemah AulanNo ratings yet
- CompositesDocument58 pagesCompositeskasvikrajNo ratings yet
- Pricelist Midas - Okt 2017 PDFDocument10 pagesPricelist Midas - Okt 2017 PDFArhim Shorinji KempoNo ratings yet
- 6 Exercises Solutions 2010 PDFDocument88 pages6 Exercises Solutions 2010 PDFTrường TùngNo ratings yet
- Domex 355 MC: High Strength Cold Forming SteelDocument2 pagesDomex 355 MC: High Strength Cold Forming SteelKhantoNo ratings yet
- Jasa Engineering untuk Kajian Teknis Perubahan Metode CrossingDocument3 pagesJasa Engineering untuk Kajian Teknis Perubahan Metode Crossingdenstar silalahi0% (1)
- International Journal of Pressure Vessels and PipingDocument10 pagesInternational Journal of Pressure Vessels and PipingIntegridad de Equipos y Gestión de Activos NelcamNo ratings yet