Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Casting Methods Tools & Process
Uploaded by
Macel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views6 pagesfhfgjhj
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentfhfgjhj
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views6 pagesCasting Methods Tools & Process
Uploaded by
Macelfhfgjhj
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
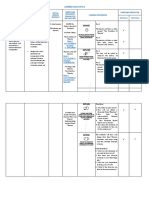
Casting
Method
Advantages Disadvantages Recommended Application
Sand Casting
Least Expensive in small quantities (less Dimensional accuracy inferior to other Use when strength/weight ratio permits
than 100) processes, requires larger tolerances
Tolerances, surface finish and low machining
Ferrous and non - ferrous metals may Castings usually exceed calculated weight cost does not warrant a more expensive
be cast process
Surface finish of ferrous castings usually
Possible to cast very large parts. exceeds 125 RMS
Least expensive tooling
Permanent and Semi-permanent Mold Casting
Less expensive than Investment or Die Only non-ferrous metals may be cast by Use when process recommended for parts
Castings this process subjected to hydrostatic pressure
Dimensional Tolerances closer than Less competitive with Sand Cast process Ideal for parts having low profile, no cores and
Sand Castings when three or more sand cores are quantities in excess of 300
required
Castings are dense and pressure tight
Higher tooling cost than Sand Cast
Plaster Cast
Smooth "As Cast" finish (25 RMS) More costly than Sand or Permanent Use when parts require smooth "As Cast"
Mold-Casting surface finish and closer tolerances than
Closer dimensional tolerance than Sand possible with Sand or Permanent Mold
Cast Limited number of sources Processes
Intricate shapes and fine details Requires minimum of 1 deg. draft
including thinner "As Cast" walls are
possible
Large parts cost less to cast than by
Investment process
Investment Cast
Close dimensional tolerance Costs are higher than Sand, Permanent Use when Complexity precludes use of Sand or
Mold or Plaster process Castings Permanent Mold Castings
Complex shape, fine detail, intricate
core sections and thin walls are possible The process cost is justified through savings in
machining or brazing
Ferrous and non-ferrous metals may be
cast Weight savings justifies increased cost
As-Cast" finish (64 - 125 RMS)
Die Casting
Good dimensional tolerances are Economical only in very large quantities Use when quantity of parts justifies the high
possible due to high tool cost tooling cost
Excellent part-part dimensional Not recommended for hydrostatic Parts are not structural and are subjected to
consistency pressure applications hydrostatic pressure
Parts require a minimal post machining For Castings where penetrant (die) or
radiographic inspection are not required.
Difficult to guarantee minimum
mechanical properties
Some of the most important foundry equipment are
1. Laboratory
1.1 Abrasive Discs
1.2 Carbon Determinators
1.3 Chemical Analysis Instruments
1.4 Core Hardness Testers
1.5 Gas Analysis Equipment
1.6 Hardness Testing Equipment
1.7 Hydrogen Porosity Tester
1.8 Laboratory Chemicals
1.9 Laboratory Furnaces
1.10 Laboratory Ovens
1.11 Pyrometers
1.12 Radiographic Equipment
1.13 Sand Testing Equipment
1.14 Spectrographic Equipment
1.15 Stress Analysis Equipment
1.16 Surface Measuring Equipment
1.17 Temperature Indicating Materials
1.18 Temperature Recording & Control Devices
1.19 Tensile Testing Machines
1.20 Thermocouple Sheaths
1.21 Analytical Equipment
1.22 Thermocouples
2. Mold, Core & Sand
2.1 Chip Dryers
2.2 Carbon Raisers
2.3 Cupola Injectors
2.4 Cupola Blowers
2.5 Cupola Chargers & Auxiliaries
2.6 Cupola Fluxes
2.7 Cables
2.8 Immersion Bells
2.9 Molding Machines
2.10 Cupola Control Equipment
2.11 Fluxes
2.12 Core Hangers
2.13 Hot Melt Aerators
2.14 Core Drawing Machines
2.15 Environmental Refractory Handling Systems
2.16 Deoxidizers
2.17 Core Binders
2.18 Sand Air Strippers
2.19 Core Extruding Machines
2.20 Molten Level Flow Control Systems
2.21 Mixers
2.22 Core Ovens
2.23 Gas Generators
2.24 Core Handling Equipment
2.25 Cupola Hot Blast Equipment
3. Cleaning & Finishing
4.1 Blasting
4. Melting, Pouring & Heat Treatment Equipment
6.1 Coke
6.2 Ductile Iron Converters
6.3 Furnaces
6.4 Chargers
6.5 Induction Heating Systems
6.6 Ingot Loaders
6.7 Ingot Pre-heaters
6.8 Inhibitors
6.9 Pouring Ladles
4.10 Pouring Equipment
5. Testing & Inspection
7.1 Radiographic Testing
7.2 Metallographic & Metallurgical Test Equipment
7.3 Nondestructive Test Equipment
7.4 Ultrasonic Test Equipment
7.5 X-Ray Diffraction Tubes
Sand Casting Process
Core Making Pattern
(if needed) Making
Preparation of
Sand Mold Making
Sand
Raw Solidification Removal of Cleaning &
Melting Pouring
Material & Cooling Sand Inspection
You might also like
- 160811143045Document53 pages160811143045Кари МедNo ratings yet
- Iso 9001Document29 pagesIso 9001Macel100% (1)
- Welders Continuity Log: Name Welder ID ProcessDocument4 pagesWelders Continuity Log: Name Welder ID ProcessMacelNo ratings yet
- BMI-WI-5711-14 Ball Valve 2in-900# Manufacturing Process Rev.0Document12 pagesBMI-WI-5711-14 Ball Valve 2in-900# Manufacturing Process Rev.0MacelNo ratings yet
- MPS.2015.07.01 Ball Valve 4in 150LbDocument11 pagesMPS.2015.07.01 Ball Valve 4in 150LbMacelNo ratings yet
- Backlight VerificationDocument1 pageBacklight VerificationMacelNo ratings yet
- Perfomance Target FormDocument1 pagePerfomance Target FormMacelNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Ball ValvesDocument12 pagesManufacturing Ball ValvesMacel100% (1)
- Written SpecificationDocument3 pagesWritten SpecificationMacelNo ratings yet
- MPS.2016.02 Ball Valve 4in 300Lb PDFDocument11 pagesMPS.2016.02 Ball Valve 4in 300Lb PDFMacelNo ratings yet
- Metallurgical Test Certificate: Doc. No. R-QC.11 Nov.12Document2 pagesMetallurgical Test Certificate: Doc. No. R-QC.11 Nov.12MacelNo ratings yet
- API 6A Conformance AssessmentDocument2 pagesAPI 6A Conformance AssessmentMacelNo ratings yet
- ISA 75.19.01 Hydrostatic Testing of Control ValveDocument34 pagesISA 75.19.01 Hydrostatic Testing of Control ValveZacLiew100% (5)
- Failure Mode Department/Area Equipment: Top Contributors ParetoDocument1 pageFailure Mode Department/Area Equipment: Top Contributors ParetoMacelNo ratings yet
- Delrin 500 Material Test Report PO50Document2 pagesDelrin 500 Material Test Report PO50Macel100% (1)
- Factory Acceptance Testing Guideline Process - NoRestrictionDocument16 pagesFactory Acceptance Testing Guideline Process - NoRestrictionhamed51060No ratings yet
- Planning Procedure Quality SystemDocument4 pagesPlanning Procedure Quality SystemMacelNo ratings yet
- BMI WI 5762 03 Crane Safety UsageDocument8 pagesBMI WI 5762 03 Crane Safety UsageMacel100% (1)
- BMI WI 5711 02 Lathe Operation Rev.1Document3 pagesBMI WI 5711 02 Lathe Operation Rev.1MacelNo ratings yet
- Ball Valve - VnumberDocument3 pagesBall Valve - VnumberMacelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Internal AuditsDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Internal AuditsMacelNo ratings yet
- NDE-Penetrant TestDocument2 pagesNDE-Penetrant TestCandy KendeeNo ratings yet
- QSP 4322-01 Personnel Competence and TrainingDocument8 pagesQSP 4322-01 Personnel Competence and TrainingMacel100% (2)
- Production PlanningDocument1 pageProduction PlanningMacelNo ratings yet
- BMI-WI-5711 - API6D Valve Marking - Rev Draft 03Document6 pagesBMI-WI-5711 - API6D Valve Marking - Rev Draft 03Macel100% (1)
- BMI WI 5711 01 Cutting ProcedureDocument3 pagesBMI WI 5711 01 Cutting ProcedureMacelNo ratings yet
- BMI WI 563 01 Raw Material AcceptanceDocument22 pagesBMI WI 563 01 Raw Material AcceptanceMacel100% (1)
- QSP 510 01 Contract ReviewDocument9 pagesQSP 510 01 Contract ReviewMacel100% (1)
- QSP-5762-01 Storage and AssessmentDocument27 pagesQSP-5762-01 Storage and AssessmentMacel100% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- ARTS 9 Q4 Week 1Document3 pagesARTS 9 Q4 Week 1Elaissa MaglanqueNo ratings yet
- Lect 1.2 Principles of Food Process DesignDocument43 pagesLect 1.2 Principles of Food Process Designmahmoud hassanNo ratings yet
- Sri Lanka, CBSLDocument24 pagesSri Lanka, CBSLVyasIRMANo ratings yet
- ATM ReportDocument16 pagesATM Reportsoftware8832100% (1)
- Infineum Ilsa Gf-6 API SP e JasoDocument28 pagesInfineum Ilsa Gf-6 API SP e JasoDanielNo ratings yet
- Gizmotchy 3 Element Complete Assembly InstructionsDocument5 pagesGizmotchy 3 Element Complete Assembly InstructionsEuropaNo ratings yet
- MechanismDocument17 pagesMechanismm_er100No ratings yet
- Design of Helical Antennas For 433 MHZ Radio Telemetry Ground Station and Uav (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle)Document7 pagesDesign of Helical Antennas For 433 MHZ Radio Telemetry Ground Station and Uav (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle)Tiara Nira SariNo ratings yet
- Demo TeachingDocument22 pagesDemo TeachingCrissy Alison NonNo ratings yet
- 68rfe IntroductionDocument71 pages68rfe IntroductionThePokeOne83% (6)
- Important instructions on judicial procedure from Narada SmritiDocument6 pagesImportant instructions on judicial procedure from Narada SmritirohitNo ratings yet
- Advanced Financial Accounting Chapter 2 LECTURE - NOTESDocument14 pagesAdvanced Financial Accounting Chapter 2 LECTURE - NOTESAshenafi ZelekeNo ratings yet
- Solution Proposal For SGF - BomDocument2 pagesSolution Proposal For SGF - BomABHISHEK ADHIKARYNo ratings yet
- Quality of Good TeacherDocument5 pagesQuality of Good TeacherRandyNo ratings yet
- Academic Language Use in Academic WritingDocument15 pagesAcademic Language Use in Academic WritingDir Kim FelicianoNo ratings yet
- A Strategic Management PaperDocument7 pagesA Strategic Management PaperKarll Brendon SalubreNo ratings yet
- Cult of KUDocument31 pagesCult of KUEli GiudiceNo ratings yet
- ATB Farmacología 2Document194 pagesATB Farmacología 2Ligia CappuzzelloNo ratings yet
- Atlanta Pipes and FittingsDocument2 pagesAtlanta Pipes and Fittingsotadoyreychie31No ratings yet
- Bimbo Marketing ResearchDocument27 pagesBimbo Marketing Researcheman.konsouhNo ratings yet
- The Four Principles of SustainabilityDocument4 pagesThe Four Principles of SustainabilityNeals QuennevilleNo ratings yet
- CFC KIDS FOR CHRIST 2020 FINAL EXAMDocument13 pagesCFC KIDS FOR CHRIST 2020 FINAL EXAMKaisser John Pura AcuñaNo ratings yet
- Case Study No. 11 - Hydroelectric Power Plant in The PhilippinesDocument26 pagesCase Study No. 11 - Hydroelectric Power Plant in The PhilippinespicefeatiNo ratings yet
- The Teacher and The LearnerDocument23 pagesThe Teacher and The LearnerUnique Alegarbes Labra-SajolNo ratings yet
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument28 pagesKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA Biology Investigatory Projectvishali GNo ratings yet
- V Bhebhe PDFDocument63 pagesV Bhebhe PDFVusi BhebheNo ratings yet
- Hireena Essay AnsDocument2 pagesHireena Essay AnsTasniiem ChandraaNo ratings yet
- ICO Basic SyllabusDocument11 pagesICO Basic SyllabusRaúl Plasencia Salini100% (1)
- Modul English For Study SkillsDocument9 pagesModul English For Study SkillsRazan Nuhad Dzulfaqor razannuhad.2020No ratings yet
- Srimanta Shankardev: Early LifeDocument3 pagesSrimanta Shankardev: Early LifeAnusuya BaruahNo ratings yet