Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drugs List
Uploaded by
zaynah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views4 pagesList of basic pharmacological drugs
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentList of basic pharmacological drugs
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views4 pagesDrugs List
Uploaded by
zaynahList of basic pharmacological drugs
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Drug Function
Tetrodatoxin Blocks sodium channels so no action
potential
Cocaine (LA) Not used clinically
Procaine (LA) Infiltration, peripheral nerve block, central
nerve block
Lignocaine/Lidocaine (LA) Topical, infiltration, peripheral nerve block,
central nerve block
Prilocaine (LA) Topical, infiltration, peripheral nerve block,
central nerve block
Amethocaine/tetrocaine (LA) Topical
Bupivacane (LA) Peripheral/central nerve block
Endrophonium Inhibit acetylcholine esterase
Neostigmine Inhibit acetylcholine esterase
Physostigmine Inhibit acetylcholine esterase
Hemicholinium Binds to choline uptake carrier and blocks it
so reducing acetylcholine levels
Triethylcholine (TEC) Partly up taken by choline carrier
Acetyltriethylcholine False substrate
Divalent cations e.g. cadmium Blocks calcium influx so inhibits transmitter
release
Botulinum toxin Muscle spasticity and destroys nerve
terminals so inhibits transmitter release
Beta bungarotoxin Reduces acetylcholine release
Alpha bungarotoxin Blocks acetylcholine receptor
Aminoglycoside antibiotics e.g. Kanamycin blocks influx of calcium by
streptomycin, neomycin, kanamycin blocking calcium channels so inhibits
transmitter release
4-aminopyridine and tetraethylammonium Blocks potassium channels so prolongs
action potentials
Tubocurarine Non-depolarising competitive blocker of
acetylcholine receptor
Pancuronium Non-depolarising competitive blocker of
acetylcholine receptor
Gallamine Non-depolarising competitive blocker of
acetylcholine receptor
Alcuronium Non-depolarising competitive blocker of
acetylcholine receptor
Atracurium Non-depolarising competitive blocker of
acetylcholine receptor
Vecuronium Non-depolarising competitive blocker of
acetylcholine receptor
Suxamethonium Depolarising non-competitive blockers of
acetylcholine receptors
Decamethonium Depolarising non-competitive blockers of
acetylcholine receptors
Suxethonium Depolarising non-competitive blockers of
acetylcholine receptors
Salbutamol Used in treatment of asthma
(adrenoreceptor agonist) targets GPCRs
Sumatriptan Used for headaches targets GPCRs
Cetirizine Antihistamine targets GPCRs
Erlotinib Inhibits epidermal growth factor receptors
acts on receptor tyrosine kinases in cancer
treatment
Prenalterol Partial agonist acting at beta
adrenoreceptors
Adrenaline and isoprenaline Full agonists acting at beta adrenoreceptors
Dichloroisoprenaline Partial agonist acting on beta
adrenoreceptors
Propanolol Antagonist acting on beta adrenoreceptors
Impromidine Partial agonist acting at histamine H2
receptors
Histamine Full agonist acting at histamine H2 receptors
Sulphonamides and sulphones Anti-malarial drugs target dihydropteroate
synthetase enzyme found in folate pathway
of malaria
Proguanil and pyrimethamine Anti-malarial drugs antagonist of
dihydrofolate reductase enzyme found in
malaria and host but malaria more sensitive
Chloroquine, quinine, melfoquine Target haem polymerase which catalyses the
conversion of free haem to hemozoin in
malaria
Artemisinin Anti-malarial drug believed to work via a
redox mechanism
AZT, DdC, Ddl, 3TC Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
used in treatment of HIV
Nevirapine, C1-TIBO, L697-661, efavirenz, Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase
delavirdine inhibitors used in the treatment of HIV
Indavir, ritonavir, saquinavir Protease inhibitors used in the treatment of
HIV
Salvarsan Antibiotic used in the treatment of syphilis
Cycloserine, bacitracin, beta lactams, Antibacterials targeting cell wall synthesis
glycopeptides
Trimethoprim, sulphonamides, sulphones Antibacterials targeting folate metabolism
Polymxins Antibacterials targeting cell membrane
Quinolones, nitroimidazoles Antibacterials targeting DNA replication
Rifamycins Antibacterials targeting DNA-dependent RNA
polymerase
Aminoglycosides, macrolides, linocosamides, Antibacterials targeting protein synthesis
streptogramins, amphenicols, tetracyclines,
rhupirocin
Chloramphenicol Bactericidal antibiotic that inhibits
transpeptidation
Tetracycline Bacteriostatic antibiotic that inhibits mRNA-
tRNA interaction and competes for the A site
Erythromycin (macrolide) Bacteriostatic antibiotic that prevents
translocation
Streptomycin Aminoglycoside antibiotic that causes
misreading of mRNA
Ciprofloxacin Fluoroquinolone, bactericidal antibiotic that
inhibits DNA gyrase
Isoniazid Bactericidal antibiotic used in the treatment
of TB as it inhibits the synthesis of mycolic
acid
Rifampicin Antibiotic used in the treatment of TB as it
inhibits prokaryotic DNA-dependent RNA
polymerase
Bupropion Used as an antidepressant but also used as a
smoking cessation therapy with an unknown
mechanism of action but believed to
involve effects on dopamine and
noradrenaline transmission
Varenicline Partial agonist of the alpha-4 beta-2 nAChR
causes a moderate and sustained increase in
mesolimbic dopamine levels. Also
competitive binding with nicotine during
relapses may reduce rewarding properties
Disulfiram Used in alcohol aversion therapy as it
inhibits aldehyde dehydrogenase
Phenobarbital Barbiturate used in treatment of epilepsy
as it acts on GABA receptors chloride
channels are held opn
Diazepam Benzodiazepine used in treatment of
epilepsy and anxiety enhances GABA-A
function
Carbamazepine, Phenytoin Sodium channel blockers used in treatment
of epilepsy
Gabapentin Calcium channel blockers used in the
treatment of epilepsy
Buspirone Enhances 5HT inhibitory function used in
treatment of anxiety
Chlorpromazine, clozapine Dopamine 2 receptor blockers used in the
treatment of schizophrenia
L-DOPA Dopamine precursor used in treatment of
Parkinsons as dopamine cannot cross blood-
brain barrier
Carbidopa Blocks L-DOPA breakdown outside CNS
given with L-DOPA in treatment of
Parkinsons
Selegiline Blocks dopamine breakdown in CNS used
in treatment of Parkinsons
Tacrine Blocks acetylcholine esterase used in
treatment of Alzheimers
Fluoxetine Increases 5HT activity used in treatment of
depression
Amytriptiline Increases NA and 5HT function used in
treatment of depression
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors Block of breakdown of monoamine oxidase
used in treatment of depression (but rarely)
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) Blocks uptake of serotonin at 5HT receptor
used in treatment of depression
Selective noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor Blocks uptake of noradrenaline at 5HT and
(SNRI) noradrenergic receptors used in treatment
of depression
Aspirin, Ibuprofen Analgesics block the production of pain
chemicals (prostanoids) in damaged tissues
Morphine Analgesic- Opioid acts on inhibitory mu
receptor in spinal cord and midbrain to block
transmitter release and reduce sensory
neurone activity
Naloxone Blocks the effect of opioids, used in
substitution therapy
Cannabis Analgesia, sedation, elevated mood,
amnesia, muscle relaxation
Amphetamines Awake, alert, confident
MDMA ecstasy Acts on 5HT receptors to increase dopamine
levels
Ivacaftor CFTR potentiator used in the treatment of
cystic fibrosis
Zolpidem Alpha 1 subtype selective benzodiazepine
agonist sedative/hypnotic effects
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Advanced Dairy Chemistry: DR - Ganesh Kumar MSC (Dairy Tech) PH.D (Dairy Tech)Document40 pagesAdvanced Dairy Chemistry: DR - Ganesh Kumar MSC (Dairy Tech) PH.D (Dairy Tech)Alemayehu YohanesNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- How Chemistry Related To Other ScienceDocument1 pageHow Chemistry Related To Other SciencePRINTDESK by Dan100% (2)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- 1.metab Nukleotida 1Document66 pages1.metab Nukleotida 1DifaniaNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
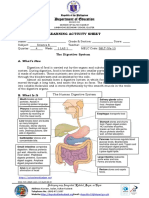
- Science Q4 W1 LAS 1 - EDONDocument4 pagesScience Q4 W1 LAS 1 - EDONKaren May UrlandaNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Successful PCR Guide: 3rd EditionDocument60 pagesSuccessful PCR Guide: 3rd Editionlpr121618100% (2)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Introduction To PharmacologyDocument50 pagesIntroduction To PharmacologyAbdishakour Hassa.100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- INBO 2023 Question-And-Answers 0Document40 pagesINBO 2023 Question-And-Answers 0vj jNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Human Genetics: From DNA to ProteinsDocument28 pagesHuman Genetics: From DNA to ProteinsjasNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Cancers 12 00037 v2Document24 pagesCancers 12 00037 v2nionNo ratings yet
- MDS Postal Coaching Synopsis Sample MaterialsDocument232 pagesMDS Postal Coaching Synopsis Sample Materialsbrihaspathiacademy100% (1)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- LDH Characterization and Kinetics AnalysisDocument23 pagesLDH Characterization and Kinetics AnalysisAngela Kc100% (3)
- Bio Inorganic ChemistryDocument49 pagesBio Inorganic ChemistryMONIRUZZAMAN MONIRNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Amino Acids: Building Blocks of ProteinsDocument45 pagesAmino Acids: Building Blocks of ProteinsOTLorzNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- PCR and Electrophoresis HandoutDocument4 pagesPCR and Electrophoresis HandoutJJJJJJJ123No ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Human Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 2014Document5 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 2014api-279830436No ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- AS LEVEL BIOLOGY Paper 1 EnzymesDocument54 pagesAS LEVEL BIOLOGY Paper 1 EnzymesADEEL AHMADNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hsslive XI Zoology CH 9 BiomoleculesDocument13 pagesHsslive XI Zoology CH 9 Biomolecules스탠 케이팝No ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- PCR OlaDocument7 pagesPCR OlaBeena KakranNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Autonomic PharmacologyDocument30 pagesIntroduction to Autonomic PharmacologyImrana AamirNo ratings yet
- Review Worksheet 1: Use The Diagram Below To Answer Questions 6-8Document2 pagesReview Worksheet 1: Use The Diagram Below To Answer Questions 6-8Natalia LisekNo ratings yet
- Lab Report CRISPR Sample 1Document9 pagesLab Report CRISPR Sample 1mayagal1707No ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsDocument10 pagesNucleic Acid - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsBauza, Stephanie Dawn T.No ratings yet
- Chemical Changes Lead to Helpful SubstancesDocument17 pagesChemical Changes Lead to Helpful SubstancesEmmnl RayNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Angew Chem Int Ed - 2019 - Imberti - New Designs For Phototherapeutic Transition Metal ComplexesDocument13 pagesAngew Chem Int Ed - 2019 - Imberti - New Designs For Phototherapeutic Transition Metal ComplexesNohemiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Genetic DiversityDocument6 pagesChapter 3: Genetic DiversityNur Bahiyah Binti Abdul Wahab IPGKTINo ratings yet
- CH 67Document14 pagesCH 67john mwangiNo ratings yet
- Karyotype 2020 V4Document33 pagesKaryotype 2020 V4Ke XuNo ratings yet
- TMOL Ch13 Qas EvensDocument3 pagesTMOL Ch13 Qas EvensHNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Disaccharides and PolysaccharidesDocument3 pagesCarbohydrates: Disaccharides and PolysaccharidesTherese Vince J. LazosNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Cell Division:mitosisDocument3 pages1.6 Cell Division:mitosisAzahra SaptoroNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)