Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Positive Form: Example: Jane Is As Tall As John
Uploaded by
Drug ElenaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Positive Form: Example: Jane Is As Tall As John
Uploaded by
Drug ElenaCopyright:
Available Formats
Positive Form
Use the positive form of the adjective if the comparison contains one of the following
expressions:
as as
Example: Jane is as tall as John.
not as as / not so as
Example: John is not as tall as Arnie.
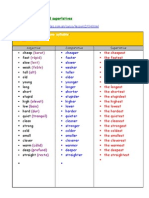
Comparative Form and Superlative Form (-er/-est)
one-syllable adjectives (clean, new, cheap)
two-syllable adjectives ending in -y or -er (easy, happy, pretty, dirty, clever)
positive comparative
superlative form
form form
clean cleaner (the) cleanest
Exceptions in spelling when adding -er / -est
silent e is dropped
Example: late-later-latest
final y after a consonant becomes i
Example: easy-easier-easiest
final consonant after short, stressed vowel is doubled
Example: hot-hotter-hottest
Comparative Form and Superlative Form (more/most)
adjectives of three or more syllables (and two-syllable adjectives not ending in -y/-er)
positive comparative
superlative form
form form
difficult more difficult most difficult
Comparative Form and Superlative Form (irregular comparisons)
positive form comparative superlative form
form
good better best
bad / ill worse worst
little (amount) less least
little (size) smaller smallest
much / many more most
far (place + time) further furthest
far (place) farther farthest
late (time) later latest
late (order) latter last
near (place) nearer nearest
near (order) - next
old (people and things) older oldest
old (people) elder eldest
Exercise on Comparison of Adjectives
ADJECTIVE OR ADVERB
THE DIFFERENCE
An adjective tells us more about a noun. Example: an
expensive car, a clever girl
An adverb tells us more about a verb. Example: He
talked nervously.
HOW TO FORM THE ADVERB
Adjective + ly
sad sadly quiet quietly
nervous nervously soft softly
Adjectives ending in -y ily
happy happily angry angrily
Adjectives ending in -le ly
terrible terribly capable capably
Adjectives ending in -ly
in a friendly way /
friendly daily daily
manner
lively in a lively way / manner early early
lonely in a lonely way / manner monthly monthly
lovely in a lovely way / manner weekly weekly
silly in a silly way / manner yearly yearly
Irregular forms
good well low low
fast fast straight straight
hard hard extra extra
long long doubtless doubtless
Double forms
hard hard hardly = kaum
near near nearly = beinahe
late late lately = in letzter
Zeit
HOW TO USE THE ADVERB
Verb + adverb
The adverb describes a verb.
Example:He drovecarefully.
verb adverb
Shesold her housequickly
verb adverb
Adjective + adverb
The adverb describes an adjective.
Example:Hernecklacewashorriblyexpensive.
adverb adjective
She wasterribly sorry.
adverb adjective
Adverb + adverb
The adverb describes an adverb.
Example:Theyplayedterribly badly.
adverb adverb
He did his
absolutelycorrectly.
homework
adverb adverb
No adverb with the following verbs
Forms of to am, is, are, was, were,
be: have been, had been,
will be
seem, get, turn, grow, sound, feel,
taste, become, smell,
look (aussehen)
It can sometimes be difficult to tell the difference between adjectives and adverbs in a sentence.
You must ask yourself what word the modifier is modifying. If the modified word is a noun, the
modifier is an adjective. If the modified word is a verb, adjective, or adverb, the modifier is an
adverb.
To complete a sentence correctly, you need to determine whether the sentence needs an adjective
or an adverb.
Cheetahs are speedy animals. (adjective modifying animal)
Cheetahs run speedily. (adverb modifying the verb run)
One area of confusion can be when an adjective is modifying a noun that is acting as an
adjective.
That is my brother. (My is an adjective modifying the noun brother.)
My brother's bike is broken. (My is still an adjective modifying the noun brother, but now
brother is a possessive noun acting as an adjective modifying bike.)
Many people unintentionally use adjectives to describe verbs. Make sure in your writing to use
adjectives to modify nouns and pronouns and adverbs to modify verbs, adjectives, and other
adverbs.
The boys walked slow toward their classroom. (incorrect)
The boys walked slowly toward their classroom. (correct)
Adjectives - word order: When there are two or more adjectives before a
noun there are some complicated "rules" for the order in which they should
appear. These are the most important:
1. opinion adjectives come before fact adjectives
2. fact adjectives appear as follows: size - age - colour - origin - material
Here are some examples:
a silly old man (an old silly man )
a beautiful blue butterfly (a blue beautiful butterfly )
an interesting historical film (a historical interesting film)
a huge metal box (a metal huge box )
a new red dress (a red new dress )
little Russian dolls (Russian little dolls )
You will need to consult a good reference grammar for full details on the
order of adjectives, and how they should be punctuated.
Do a quiz on this grammar topic.
Adjectives: -ed or -ing? English contains numerous -ed or -ingadjective
pairs derived from verbs. To avoid mixing these up, remember that the -
ed adjectives are used to describe how you feel, and the -ingadjectives are
used for what it is that makes you feel that way. Here are some examples:
I feel tired. - Working in the garden all day is very tiring.
I am bored. - This grammar lesson is boring.
She was disappointed. - Her math test score was disappointing.
I'm interested in Ancient Egypt. - I think Ancient Egypt
is interesting.
He was shocked. - He found your behaviour shocking.
I'm very confused by this film. - This film is very confusing.
Do a quiz on this grammar topic.
Adjective or adverb? In English most (but not all) adverbs have a different
form (spelling) than their corresponding adjective. It is important, therefore,
that you know whether you need an adjective or an adverb in the sentences
you want to say or write. Generally, adjectives are used to describe nouns
and adverbs are used with verbs to say howthings are done. In the following
examples, the adjectives are red and the adverbs are blue:
He's a beautiful singer. - He sings beautifully.
She's a very quick runner. - She can run very quickly.
He's a careless writer. - He writes carelessly.
She's a good worker. - She works well.
Adverbs are also used to give extra information about adjectives (or other
adverbs), as in the following examples:
I am extremely happy in my new job.
She's in hospital with a seriously injured neck.
It's incredibly easy to make a mistake when knitting.
The girl climbed dangerously high up the tree.
Because of the thick fog I drove extremely carefully.
After certain verbs (e.g. be, become, seem, look, taste, smell, etc.) the
adjective, not the adverb, is used:
She doesn't seem happy today.
Don't be stupid!
This meat tastes bad.
Those flowers smell strange.
You might also like
- Comparing Adverbs: Worse, More EasilyDocument9 pagesComparing Adverbs: Worse, More EasilyFABIAN FIENGONo ratings yet
- Adjectives and Adverbs - Adjectives and AdverbsDocument11 pagesAdjectives and Adverbs - Adjectives and AdverbsMoise Elena NatiNo ratings yet
- Adjective or AdverbDocument3 pagesAdjective or AdverbMAdriana5No ratings yet
- Adjectives ExplainedDocument12 pagesAdjectives ExplainedDeta HanifahNo ratings yet
- BingDocument16 pagesBingIntan LintangNo ratings yet
- AdverbsDocument19 pagesAdverbsFlorencia Marichal100% (1)
- The AdjectiveDocument8 pagesThe AdjectiveDelia CatrinaNo ratings yet
- Understanding AdverbsDocument22 pagesUnderstanding AdverbsHema SengodanNo ratings yet
- Comparison ExercisesDocument17 pagesComparison ExercisesnguyenngocquynhchiNo ratings yet
- Adverbs of Manner: Ruby Is A Beautiful Girl - AdjectivesDocument5 pagesAdverbs of Manner: Ruby Is A Beautiful Girl - AdjectivesnameNo ratings yet
- Comparatives SuperlativesDocument10 pagesComparatives SuperlativesmsoldugaNo ratings yet
- Adjectives and Adverbs - CAEDocument10 pagesAdjectives and Adverbs - CAEAna Maria Del Castillo-Olivares MirandaNo ratings yet
- Intermediate English GrammarDocument94 pagesIntermediate English GrammarrudbethNo ratings yet
- Adjectives and Adverbs: Here Starts The Lesson!Document23 pagesAdjectives and Adverbs: Here Starts The Lesson!Katherine Caballero RiveroNo ratings yet
- Adjectives - Degrees of ComparisonDocument6 pagesAdjectives - Degrees of ComparisonMelisaNo ratings yet
- The Rules For Forming ComparativesDocument5 pagesThe Rules For Forming ComparativesMaria RivasNo ratings yet
- Adjectives and AdverbsDocument53 pagesAdjectives and AdverbsJasper Dominic AbibasNo ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa InggrisDocument10 pagesMakalah Bahasa InggrisShelvyar INo ratings yet
- Identifying AdjectivesDocument7 pagesIdentifying AdjectivesIsildinha dos Anjo.No ratings yet
- Adjectives and AdverbsDocument9 pagesAdjectives and AdverbsEcko Dhaniez Kakak'adhekNo ratings yet
- English Grammar PDFDocument43 pagesEnglish Grammar PDFSajjad Khan100% (1)
- AdverbsDocument16 pagesAdverbsgratielageorgianastoicaNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Adjectives: Lecturer: Mr. Vinh SovannDocument16 pagesComparison of Adjectives: Lecturer: Mr. Vinh SovannStudent Sokha ChanchesdaNo ratings yet
- Comparative and Superlative Adjectives: Tú - Warm Up - KahootDocument9 pagesComparative and Superlative Adjectives: Tú - Warm Up - KahootTú Minh ChungNo ratings yet
- English Grammar - ComparativesDocument8 pagesEnglish Grammar - Comparativesblackmagic.2xNo ratings yet
- Kinds of AdverbsDocument5 pagesKinds of AdverbsANA BORONDONo ratings yet
- The Comparative and The SuperlativeDocument13 pagesThe Comparative and The SuperlativeGerardo Chahua100% (1)
- Week 6: Parts of Speech: AdverbsDocument22 pagesWeek 6: Parts of Speech: AdverbsVivian MwangiNo ratings yet
- Comparative and Superlative of AdjectivesDocument33 pagesComparative and Superlative of Adjectivesسدن آرماNo ratings yet
- Learn Essential Grammar Rules for Action Verbs, Adjectives and Adverbs (38Document8 pagesLearn Essential Grammar Rules for Action Verbs, Adjectives and Adverbs (38Tan Hui RuNo ratings yet
- Positive Form: Example: Jane Is As Tall As JohnDocument3 pagesPositive Form: Example: Jane Is As Tall As JohnAlonso ValenciaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 7 Air PollutionDocument11 pagesUNIT 7 Air Pollutionayu SariNo ratings yet
- Unlike Adjectives, Adverbs Do Not Modify NounsDocument6 pagesUnlike Adjectives, Adverbs Do Not Modify NounsVeer EnglishNo ratings yet
- How Adverbs Modify Verbs, Adjectives and Other AdverbsDocument4 pagesHow Adverbs Modify Verbs, Adjectives and Other AdverbsLeslie itzel Garcia SantiagoNo ratings yet
- AdverbsDocument7 pagesAdverbslatifa hachemiNo ratings yet
- Comparative and Superlative Adjectives and AdverbsDocument19 pagesComparative and Superlative Adjectives and AdverbsChristineNo ratings yet
- Adjectives AdverbsDocument22 pagesAdjectives AdverbsbinhNo ratings yet
- AdverbDocument15 pagesAdverbajbros1223No ratings yet
- Ingles Viii: AdverbsDocument16 pagesIngles Viii: AdverbsRonald Fernandez QuispeNo ratings yet
- Adjectives and Adverbs GuideDocument31 pagesAdjectives and Adverbs GuideAmjad KhanNo ratings yet
- Adjectives NotesDocument7 pagesAdjectives NotesLINEHELONo ratings yet
- Comparing Adjectives and Forming the SuperlativeDocument39 pagesComparing Adjectives and Forming the SuperlativescarreonmeNo ratings yet
- Selection 3Document12 pagesSelection 3api-347779657No ratings yet
- Comparative and superlative adjectivesDocument4 pagesComparative and superlative adjectivesmarina rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Adjective and AdverbDocument10 pagesAdjective and AdverbFikri HaikalNo ratings yet
- Adjectives or AdverbsDocument2 pagesAdjectives or AdverbsMiichelle ViizueteNo ratings yet
- Adjectives FormsDocument10 pagesAdjectives Formsaashish.v.s2004No ratings yet
- Errors in The Use of NounDocument20 pagesErrors in The Use of NounKaran Khatter0% (1)
- Adverb Form: Adjective Ending Do This Adjective AdverbDocument12 pagesAdverb Form: Adjective Ending Do This Adjective AdverbTram VuNo ratings yet
- Forming Adverbs From AdjectivesDocument7 pagesForming Adverbs From AdjectivesJennifer A BustoNo ratings yet
- Basic GrammarDocument10 pagesBasic GrammarLaura Pernía PerníaNo ratings yet
- Form and Comparison of AdverbsDocument4 pagesForm and Comparison of AdverbsMan EugeniaNo ratings yet
- Understanding AdverbsDocument9 pagesUnderstanding AdverbsRishut MongaNo ratings yet
- Adjectives and AdverbsDocument4 pagesAdjectives and AdverbsKhaing SuNo ratings yet
- THP Practice 2Document13 pagesTHP Practice 2Dewi Astuti Purnama SariNo ratings yet
- AdjectivesDocument22 pagesAdjectivesfran_corimNo ratings yet
- Comparatives and Superlatives 2Document7 pagesComparatives and Superlatives 2atatanriverdi14No ratings yet
- Comparing Adjectives and AdverbsDocument9 pagesComparing Adjectives and AdverbsTú Minh ChungNo ratings yet
- Comparatives and Superlatives: Unit 3Document12 pagesComparatives and Superlatives: Unit 3ANGIE LIZET RIVERA PRADONo ratings yet
- TESTE La Limba Engleza Clasa 9 Moldova 2011Document1 pageTESTE La Limba Engleza Clasa 9 Moldova 2011Drug ElenaNo ratings yet
- TESTE La Limba Engleza Clasa 9 Moldova 2011Document43 pagesTESTE La Limba Engleza Clasa 9 Moldova 2011Sestac DoruNo ratings yet
- 1irregular VerbsDocument2 pages1irregular VerbsMimi Maddy MaddyNo ratings yet
- Anexa 7-TransportDocument1 pageAnexa 7-TransportDrug ElenaNo ratings yet
- Test Initial Xi RomanaDocument4 pagesTest Initial Xi RomanaDrug ElenaNo ratings yet
- Exercitii PluralulDocument9 pagesExercitii PluralulDanieline86% (7)
- Simple Past Tense Poem WorksheetDocument1 pageSimple Past Tense Poem WorksheetPetrache Valentina RoxanaNo ratings yet
- 0fisadelucrumara I.slaviciDocument4 pages0fisadelucrumara I.slaviciDrug ElenaNo ratings yet
- 0fisadelucrumara I.slaviciDocument4 pages0fisadelucrumara I.slaviciDrug ElenaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Past Simple - Regular and Irregular VerbsDocument1 pageWorksheet Past Simple - Regular and Irregular VerbsCristina AlexandraNo ratings yet
- State Verbs ExercisesDocument3 pagesState Verbs ExercisesCrónica VerónicaNo ratings yet
- 1irregular VerbsDocument2 pages1irregular VerbsMimi Maddy MaddyNo ratings yet
- Comparative SuperlativeDocument6 pagesComparative SuperlativeMaido Membrado AndrésNo ratings yet
- Comparative SuperlativeDocument6 pagesComparative SuperlativeMaido Membrado AndrésNo ratings yet
- Positive Form: Example: Jane Is As Tall As JohnDocument6 pagesPositive Form: Example: Jane Is As Tall As JohnDrug ElenaNo ratings yet
- Comparative SuperlativeDocument6 pagesComparative SuperlativeMaido Membrado AndrésNo ratings yet
- Comparative SuperlativeDocument6 pagesComparative SuperlativeMaido Membrado AndrésNo ratings yet
- Exercitii PluralulDocument9 pagesExercitii PluralulDanieline86% (7)
- Key Words For FluencyDocument196 pagesKey Words For FluencyXì Nâu100% (1)
- Comparative SuperlativeDocument6 pagesComparative SuperlativeMaido Membrado AndrésNo ratings yet
- Postmoderntheorych1 PDFDocument24 pagesPostmoderntheorych1 PDFDrug ElenaNo ratings yet
- Comparative SuperlativeDocument6 pagesComparative SuperlativeMaido Membrado AndrésNo ratings yet
- Conditional Explanation 0123Document5 pagesConditional Explanation 0123GuadalupeGonzalezNo ratings yet
- Positive Form: Example: Jane Is As Tall As JohnDocument6 pagesPositive Form: Example: Jane Is As Tall As JohnDrug ElenaNo ratings yet
- If Clauses Conditionals Type 2 Unreal Present Exercise WorksheetDocument2 pagesIf Clauses Conditionals Type 2 Unreal Present Exercise Worksheetpepac414No ratings yet
- Conditionals Type Zero 1 PDFDocument1 pageConditionals Type Zero 1 PDFDrug ElenaNo ratings yet
- Sugestii de Teme Pentru Atestat - Limba EnglezaDocument2 pagesSugestii de Teme Pentru Atestat - Limba EnglezaGabriel Buzoianu100% (2)
- If Clauses Conditionals Type 2 Unreal Present Exercise WorksheetDocument2 pagesIf Clauses Conditionals Type 2 Unreal Present Exercise Worksheetpepac414No ratings yet
- Conditionals Zero FormDocument3 pagesConditionals Zero FormkonjustinaNo ratings yet
- Band3 12advancedDocument60 pagesBand3 12advancedLau Meng Yong100% (1)
- KenkenDocument4 pagesKenkenapi-210759763No ratings yet
- Cambuja-Bubucal Elementary School Teachers' AssignmentsDocument1 pageCambuja-Bubucal Elementary School Teachers' AssignmentsMardezz AcordaNo ratings yet
- Schools Sept 12Document36 pagesSchools Sept 12Christopher ElkinsNo ratings yet
- Reflective EssayDocument5 pagesReflective EssayBrandy MorganNo ratings yet
- Fair Use of Copyrighted MaterialsDocument2 pagesFair Use of Copyrighted Materialsapi-273168072No ratings yet
- Teachers BookletDocument55 pagesTeachers Bookletvino1978100% (3)
- Dyslexia and Thinking SkillsDocument18 pagesDyslexia and Thinking SkillsPhilip WainNo ratings yet
- Lesson Reflection 7Document2 pagesLesson Reflection 7api-340707180No ratings yet
- CY2018 Earthquake Drill ReportDocument4 pagesCY2018 Earthquake Drill ReportBENJ AMINNo ratings yet
- From Vision to Mission: Effective Supervision in EducationDocument3 pagesFrom Vision to Mission: Effective Supervision in EducationPipah KusinNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Inspectie - 6Document7 pagesLesson Plan Inspectie - 6larisa.lascau29No ratings yet
- UNT Lesson Plan Template: ListeningDocument8 pagesUNT Lesson Plan Template: Listeningapi-339889546No ratings yet
- Edfx413 Pep Unit BookletDocument25 pagesEdfx413 Pep Unit Bookletapi-265570159No ratings yet
- Aboriginal and Culturally Responsive PedagogiesDocument7 pagesAboriginal and Culturally Responsive Pedagogiesapi-379378935100% (1)
- Proposal ELT ResearchDocument16 pagesProposal ELT ResearchRiska Alfin Pramita100% (5)
- PIT Grade Point SystemDocument7 pagesPIT Grade Point SystemBhupinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Aviation English Teaching Materials and ResourcesDocument8 pagesAviation English Teaching Materials and Resourcesjimspivey75% (4)
- Branding and Brand NamesDocument2 pagesBranding and Brand NamesTony AppsNo ratings yet
- Fs 6 Ep 1Document10 pagesFs 6 Ep 1api-309997842No ratings yet
- Year 11 Yearly ExamsDocument1 pageYear 11 Yearly ExamsJeff CattNo ratings yet
- Edci301 In-Class Lesson Origami FinalDocument7 pagesEdci301 In-Class Lesson Origami Finalapi-254075066No ratings yet
- Ict Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesIct Lesson Planapi-279816119No ratings yet
- Math Lesson Plan 1Document2 pagesMath Lesson Plan 1api-267519393100% (1)
- The Princess in Black Teacher's GuideDocument6 pagesThe Princess in Black Teacher's GuideCandlewick Press100% (1)
- Mary Jane Drummond - Listening - To - Children - TalkDocument14 pagesMary Jane Drummond - Listening - To - Children - TalkVi VendemolesNo ratings yet
- REVISED 2019 Pre-Con Book Final For Web PDFDocument32 pagesREVISED 2019 Pre-Con Book Final For Web PDFwafltNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan Year 8 PhysicsDocument13 pagesUnit Plan Year 8 Physicsapi-47919087850% (2)
- UJIAN AKHIR SEKOLAH BAHASA INGGRIS SMP 2015Document14 pagesUJIAN AKHIR SEKOLAH BAHASA INGGRIS SMP 2015BaryadiNo ratings yet
- A Review of Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument18 pagesA Review of Advantages and DisadvantagesNonieto Evangelio BelotindosNo ratings yet