Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Polarity and H-bonding in Molecules
Uploaded by
Kesma HimaspalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Polarity and H-bonding in Molecules
Uploaded by
Kesma HimaspalCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry 121 (PS12)
Prof. Mines
Notes on Polarity of Molecules (and H-bond definition)
I. Molecular Polarity
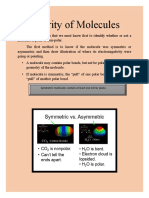
A. Meaning: A molecular substance is said to be polar if its molecules are polar
This means that each molecule has a partially positive side and a partially negative side. Such molecules are said to
have a non-zero dipole moment.
A nonpolar substance is thus a substance whose molecules are nonpolar,
This means that overall they do not have one end that is partially positive and one end that is partially negative.
These molecules have no dipole moment (or a dipole moment of zero).
Note: The terms polar or nonpolar do not apply to ionic compounds because there are no molecules!
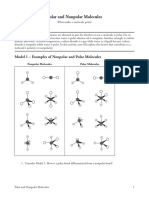
Ways to End up Nonpolar Ways to End Up Polar
no polar bonds, OR must have at least one polar
bond, AND
> 2 polar bonds, but bond dipoles the bond dipoles do NOT
completely cancel out completely cancel out
E.g., H2, Cl2, N2; CH4, CF4, E.g., H2O, SO2, NH3, H2CO,
PF5, SF6, CO2 SF4, BrF5, CCl2F2
B How to determine whether a molecule WITH ONLY ONE CENTER is polar.
1) Are there any polar bonds in the molecule?
If no, then nonpolar; if yes, continue.
2) Are all of the atoms surrounding the center the same?
If no, polar unless a special case (see footnote if interested*) If yes, continue.
3) Are there any lone pairs on the center?
If no, then nonpolar. If yes, continue.
4) Is the atom geometry square planar or linear?
If no, the molecule is polar. If yes, the molecule is nonpolar.
* If the molecule's atom geometry is octahedral, square planar, or trigonal bipyramidal, then it is possible to be nonpolar
even if not all of the outer atoms are identical. How? If the atoms DIRECTLY ACROSS from one another (i.e., at 180
degrees) are the same as one another in all cases
Most molecular compounds are polar to some degree. It is actually somewhat hard to
end up nonpolar for a large molecule (unless it is mostly hydrocarbon).
II. Miscellaneous comments regarding polarity
A. If a molecule is polar, that does NOT mean that it is charged! Molecules are, by definition, neutral. If there
is an overall charge on a species with more than one atom, it is a polyatomic ION, not a molecule.
B. Ionic compounds are neither polar nor nonpolar because there are no molecules! And remember that an
ionic compound is overall neutral as well. It is only each individual ion that has an overall charge.
C. In my opinion, it doesnt make much sense to contemplate whether or not a polyatomic ion is polar or not,
because it has an overall charge which will dominate its interactions with other species. So I would say that
ions are neither polar nor nonpolarthey are charged.
The bottom line: polarity is basically a property of either bonds or molecules (and thus of
molecular substances; see I.A. above). It is not a meaningful property of ions or ionic compounds.
III. Hydrogen Bond Definition and How to Determine if a Substance has H-bonding
A hydrogen bond is an interaction between a H atom that is covalently bound to a N, O, or F and a partially
negative N, O, or F atom to which it is not covalently bound.
To determine if a substance has H-bonding as one of its IM forces between its molecules, look for a N-H, O-H,
or F-H bond in it. If one of these is present, then it can. If not, it cannot.
NOTE: H-bonds (and IM forces in general) can be between two different molecules (I call this a self-other interaction). In this
chapter, where properties of substances are discussed, we only consider self-self interactions.
You might also like
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Molecular Polarity: Determining if a Molecule is Polar or NonpolarDocument4 pagesMolecular Polarity: Determining if a Molecule is Polar or NonpolarMims ChiiiNo ratings yet
- Polar Bonds and Polar MoleculesDocument18 pagesPolar Bonds and Polar MoleculesChe PeñalesNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Polarity and Intermolecular ForcesDocument10 pagesStudent Exploration: Polarity and Intermolecular ForcesLama Ashi83% (6)
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Polarity, Solubility and Molecular ShapeDocument38 pagesPolarity, Solubility and Molecular Shapelily smithNo ratings yet
- Intramolecular Forces and Intermolecular ForcesDocument12 pagesIntramolecular Forces and Intermolecular ForcesDuyen Nguyen100% (1)
- Polarity of MoleculesDocument45 pagesPolarity of MoleculesAliza Liban100% (1)
- Polar and Nonpolar Molecules AP PogilDocument6 pagesPolar and Nonpolar Molecules AP PogilLily Stanton67% (3)
- Polarity of MoleculesDocument14 pagesPolarity of MoleculesDenice De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- 8 - MODULE 3 - Molecular Polarity Rev 2022Document20 pages8 - MODULE 3 - Molecular Polarity Rev 2022ROGELIO RIVERA100% (1)
- Lecture05-06 Forces Acids BasesDocument59 pagesLecture05-06 Forces Acids BasesLeslieLooNo ratings yet
- Polarity and Intermolecular Forces Lab SheetDocument9 pagesPolarity and Intermolecular Forces Lab SheetLama AshiNo ratings yet
- Physical Science - M3 - Polarity of MoleculesDocument15 pagesPhysical Science - M3 - Polarity of MoleculesJodi RempilloNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Modules Week 2Document6 pagesPhysical Science Modules Week 2RODJHEN ANNE P. BARQUILLANo ratings yet
- Chemsheets GCSE 1093 (Reacting Mass Calculations 1) ANS 09351Document2 pagesChemsheets GCSE 1093 (Reacting Mass Calculations 1) ANS 09351J 6342100% (2)
- 2 A The Polarity of A MoleculeDocument41 pages2 A The Polarity of A MoleculeAdrian joseph AdrianoNo ratings yet
- Polarity of Molecule (Autosaved)Document40 pagesPolarity of Molecule (Autosaved)Yson GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Polarity of MoleculesDocument22 pagesPolarity of MoleculesEstrellita SilvioNo ratings yet
- Polarity of Molecules and Its PropertiesDocument34 pagesPolarity of Molecules and Its PropertiesNica Floresta - MendozaNo ratings yet
- Determine Polarity of Molecules from StructureDocument9 pagesDetermine Polarity of Molecules from StructureJustin BirdNo ratings yet
- LalalaDocument2 pagesLalalaKendy Livi DanawatiNo ratings yet
- Polarity of MoleculesDocument25 pagesPolarity of MoleculesEmmanuel Kenneth Contreras PotoyNo ratings yet
- Polar Molecule Properties GuideDocument7 pagesPolar Molecule Properties Guidemaxene jadeNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Day 1 Module Physical ScienceDocument4 pagesWeek 3 Day 1 Module Physical ScienceEunice AcunaNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Model of Solids and LiquidsDocument5 pagesKinetic Molecular Model of Solids and LiquidsJohn Ahron BalinoNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 2Document7 pagesPhysical Science Week 2Rona Grace MartinezNo ratings yet
- Physical Science - Module 3 (Assignment)Document1 pagePhysical Science - Module 3 (Assignment)CharlesNo ratings yet
- Worksheet: Polar Bears & Penguins - Electronegativity: NAMEDocument3 pagesWorksheet: Polar Bears & Penguins - Electronegativity: NAMERaymond LiuNo ratings yet
- Physical Science ReportDocument35 pagesPhysical Science Reportadrian lozanoNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document2 pagesModule 4Christopher Agustin Tambogon LptNo ratings yet
- Properties of Ionic and Covalent CompoundsDocument8 pagesProperties of Ionic and Covalent CompoundssandraNo ratings yet
- Notes VSEPR (CH 6)Document21 pagesNotes VSEPR (CH 6)Nestor BalboaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document25 pagesUnit 5akarshkumar115No ratings yet
- Polarity NotesDocument5 pagesPolarity NotesShailesh GhediyaNo ratings yet
- Polarity of Molecules: Symmetric Molecules Contain at Least One Mirror PlaneDocument3 pagesPolarity of Molecules: Symmetric Molecules Contain at Least One Mirror PlaneGel ButuhanNo ratings yet
- Molecular PolarityDocument25 pagesMolecular PolarityJodi AlcarazNo ratings yet
- Properties of Covalent BondingDocument9 pagesProperties of Covalent BondingMBOTAKE LawsonNo ratings yet
- POLARITYDocument23 pagesPOLARITYMelanie MirandaNo ratings yet
- Polar and Non PolarDocument22 pagesPolar and Non PolarRowena FloresNo ratings yet
- 1.-KMTDocument45 pages1.-KMTEllysa Jade VelascoNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Genchem PolarityDocument29 pagesGrade 12 Genchem PolarityJohn Milen Garvida FabiNo ratings yet
- Molecular PolarityDocument43 pagesMolecular Polaritychubbskie00No ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument15 pagesSCIENCEPaula DecenaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 2Document9 pagesPhysical Science Week 2RAINIER DE JESUSNo ratings yet
- PHY SCI DLP Q3 Week 2Document15 pagesPHY SCI DLP Q3 Week 2Radish CucumberNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Secrion 1)Document25 pagesChapter 1 (Secrion 1)Irang De OcampoNo ratings yet
- Polar and Nonpolar Compounds: (Son) Kharadar General HospitalDocument2 pagesPolar and Nonpolar Compounds: (Son) Kharadar General HospitalLOVE KUMARNo ratings yet
- Polarity of MoleculeDocument35 pagesPolarity of MoleculeAlyson Kate CastillonNo ratings yet
- Bio202 Atoms and MoleculesDocument75 pagesBio202 Atoms and MoleculesVivian PapasNo ratings yet
- Types of Intermolecular Forces of AttractionDocument9 pagesTypes of Intermolecular Forces of AttractionTrisha Mae FrialaNo ratings yet
- Flexible Learning Activity No. 1 in Physical Science 3rd GradingDocument6 pagesFlexible Learning Activity No. 1 in Physical Science 3rd GradingGeizel GuzmanNo ratings yet
- The Kinetic Molecular Model and Intermolecular Forces of Attraction in MatterDocument104 pagesThe Kinetic Molecular Model and Intermolecular Forces of Attraction in MatterMiguel TatlonghariNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Test Study Guide: Molecular Polarity and Intermolecular ForcesDocument2 pagesUnit 6 Test Study Guide: Molecular Polarity and Intermolecular ForcesDeepti SailappanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Kinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and SolidsDocument26 pagesLesson 1 Kinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and SolidsLyndy PantaoNo ratings yet
- Day 3 Handout - Electronegitivity Bond Polarity and Molecular PolarityDocument4 pagesDay 3 Handout - Electronegitivity Bond Polarity and Molecular PolarityBubblesNo ratings yet
- The Polarity of-WPS OfficeDocument7 pagesThe Polarity of-WPS OfficeJoebelle GiananNo ratings yet
- Molecular PolarityDocument26 pagesMolecular PolarityEZRA SHARIN MARATONo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Polarity and Intermolecular ForcesDocument7 pagesStudent Exploration: Polarity and Intermolecular ForcesZhaoxiaotang EstherNo ratings yet
- My Learning Episodes: The Learners Demonstrate Understanding Of..Document8 pagesMy Learning Episodes: The Learners Demonstrate Understanding Of..Radzmiya SulaymanNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces TypesDocument20 pagesIntermolecular Forces TypesYsabela MataNo ratings yet
- Maintenance and LogisticDocument4 pagesMaintenance and LogisticKesma HimaspalNo ratings yet
- NR467 - B1 - 2017-07 Rules For The Classification of Ships - Part B Hull & StabilityDocument521 pagesNR467 - B1 - 2017-07 Rules For The Classification of Ships - Part B Hull & StabilityKesma HimaspalNo ratings yet
- Listrik DinamisDocument1 pageListrik DinamisKesma HimaspalNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Lesson 12 Naming CompoundsDocument3 pagesUnit 1 Lesson 12 Naming CompoundsKesma HimaspalNo ratings yet
- Fracture Mechanics, Schreus, 2012 PDFDocument162 pagesFracture Mechanics, Schreus, 2012 PDFCarlos HernandezNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Lesson 12 Naming CompoundsDocument3 pagesUnit 1 Lesson 12 Naming CompoundsKesma HimaspalNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument5 pagesChemistryKesma HimaspalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document24 pagesChapter 12Kesma HimaspalNo ratings yet
- 216 NR - 2017 01Document262 pages216 NR - 2017 01Vanessa BorgesNo ratings yet
- 4760.5.NR500 2012-03 PDFDocument410 pages4760.5.NR500 2012-03 PDFKesma HimaspalNo ratings yet
- 4760.5.NR500 2012-03 PDFDocument410 pages4760.5.NR500 2012-03 PDFKesma HimaspalNo ratings yet
- Cost Reduction in Heat Treatment With Protective CoatingsDocument7 pagesCost Reduction in Heat Treatment With Protective CoatingsAnand KesarkarNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Chemical Formulae ExplainedDocument70 pagesAtoms and Chemical Formulae ExplainedAzie Nurul Akhtar75% (4)
- Product Catalogue: Welding ConsumablesDocument44 pagesProduct Catalogue: Welding ConsumablesSerhan AysanNo ratings yet
- RSC Advances: ReviewDocument20 pagesRSC Advances: ReviewGabrielNo ratings yet
- Dr. Fixit Flexicoat PU: Single Component, Cold Applied, Elastomeric Waterproofing Membrane CoatingDocument4 pagesDr. Fixit Flexicoat PU: Single Component, Cold Applied, Elastomeric Waterproofing Membrane Coatingkkundan52No ratings yet
- Biochemical Processes: Activity 3Document2 pagesBiochemical Processes: Activity 3Althea ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Peenya RtiDocument25 pagesPeenya Rtisatish vermaNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis - 4 (CH3COO) 2PbDocument3 pagesSalt Analysis - 4 (CH3COO) 2Pbmystical moonbeamNo ratings yet
- HF acid dangers in car wash cleanersDocument2 pagesHF acid dangers in car wash cleanersAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- Making The Keats Angle Plate From CastingsDocument15 pagesMaking The Keats Angle Plate From CastingsJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Chemical Composition of Callisia Fragrans Juice 1. Phenolic CompoundsDocument2 pagesChemical Composition of Callisia Fragrans Juice 1. Phenolic CompoundsLeTienDungNo ratings yet
- Msds Cl2Document12 pagesMsds Cl2Ganjar Tri Gita AzhariNo ratings yet
- Oreas 402Document2 pagesOreas 402flysch_ukNo ratings yet
- Ch18.pdf Aldehyde and Ketone PDFDocument43 pagesCh18.pdf Aldehyde and Ketone PDFShakesha HemmingsNo ratings yet
- Impact of Non-Uniform Fouling On Operating Temperatures in Heat Exchanger NetworksDocument7 pagesImpact of Non-Uniform Fouling On Operating Temperatures in Heat Exchanger NetworksZul FakriNo ratings yet
- Shale Oil Impacts on RefiningDocument24 pagesShale Oil Impacts on RefiningAnonymous NmOXutCKNo ratings yet
- Potential of Indonesian Palm Oil Biomass for Bioethanol ProductionDocument15 pagesPotential of Indonesian Palm Oil Biomass for Bioethanol ProductionKomanghNo ratings yet
- Standard Specification For: ScopeDocument2 pagesStandard Specification For: Scopedong ganNo ratings yet
- Flyer ChameleoBoost ConsolDocument26 pagesFlyer ChameleoBoost ConsolAnchita MitraNo ratings yet
- Sulfur Magazine Ideas For Better Clean Up Jan 09Document0 pagesSulfur Magazine Ideas For Better Clean Up Jan 09Bharat VaajNo ratings yet
- Noble Chlor Electrochlorination Systems PDFDocument2 pagesNoble Chlor Electrochlorination Systems PDFVenkatesha RaoNo ratings yet
- Ludiflash Technical InformationDocument10 pagesLudiflash Technical Information戴海No ratings yet
- Irvingia Gabonensis Seed Extract 10-1 IGSE-181011Document1 pageIrvingia Gabonensis Seed Extract 10-1 IGSE-181011Sophia XieNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Dye TechnologyDocument28 pagesEvolution of Dye TechnologyNaeem MalikNo ratings yet
- ASTM D1856 092015 Aug 2019Document4 pagesASTM D1856 092015 Aug 2019karenmerino94No ratings yet
- ConcreteDocument26 pagesConcretedreiNo ratings yet
- Iodine Based Water Disinfection A ReviewDocument6 pagesIodine Based Water Disinfection A ReviewKat MartinezNo ratings yet
- Indole and Pyrrole Synthesis PDFDocument19 pagesIndole and Pyrrole Synthesis PDFAnuar HernandezNo ratings yet