Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Think Like A Scientist Scientific Method Review 2016
Uploaded by
api-2263316590 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
113 views2 pagesOriginal Title
think like a scientist scientific method review 2016
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
113 views2 pagesThink Like A Scientist Scientific Method Review 2016
Uploaded by
api-226331659Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Think Like a Scientist/ Scientific Method Review
Observation using your senses
scientists use tools to make detailed
observations
must be factual
Qualitative Observation deal with descriptions that cannot be expressed in
numbers
Quantitative Observation Deal with a number or amount
Data The records or evidence
Inferring Explain or interpret and observation
Combine data with experience
not a fact, one of many explanations for an
observations
may be incorrect
Predicting Making an inference about a future event
based on current evidence or past
experience
May be proven false
Classifying Grouping together items that are in some way
alike
Used to organize information or objects
Making models A picture, diagram, computer image, or other
representation of a complex object or process
help people understand something that is
complex or cant be seen directly
EX: globe, model car
Scientific attitudes Way of learning about the natural world
Important to be curious, honest,
open-minded, skeptical, and creative
Communication Sharing ideas and info with other people
What are the steps of the scientific 1. Purpose/problem
method? 2. Research
3. Hypothesis
Strategy to help remember this: 4. Experiment
Purple Reindeer Have Ears An
d Can 5. Analysis
Run. 6. Conclusion
7. Repeat/communicate
Purpose first step of the scientific method
posing a question (not a question about an
opinion)
question comes from observation or
inference
must be able to be answered by making
observations and gathering evidence
Research Gather information on the problem
Hypothesis A possible explanation for a set of
observations or answer to a scientific
question
Not a fact
must be testable
Researchers must be able to carry out
investigations that will either support or
disprove the hypothesis
IF_____ then____, because______
Variable Factors being tested that can be changed or
manipulated
Controlled experiment all variables that are kept the same
Manipulated variable variable that is changed on purpose in order to
(independent variable) test the hypothesis
Responding variable what changes or what you are measuring in
(Dependent variable) response to the manipulated variable
Analysis: to record data in an organized way
Why create a data table?
Conclusion summary of what you have learned from the
experiment
Ask does the data support the hypothesis?
Repeat Repeat the work to check results
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Graff Specialtopicproject2017Document27 pagesGraff Specialtopicproject2017api-226331659No ratings yet
- Cheryl A Graff Resume 2017Document3 pagesCheryl A Graff Resume 2017api-226331659No ratings yet
- Cheryl A Graff Resume 2016Document2 pagesCheryl A Graff Resume 2016api-226331659No ratings yet
- Cheryl MusicalresumeDocument1 pageCheryl Musicalresumeapi-226331659No ratings yet
- 6 ThgradepoemsDocument10 pages6 Thgradepoemsapi-226331659No ratings yet
- LetterintroductionfallDocument1 pageLetterintroductionfallapi-226331659No ratings yet
- Name That TuneDocument23 pagesName That Tuneapi-226331659No ratings yet
- Calculator Task AnalysisDocument1 pageCalculator Task Analysisapi-226331659100% (1)
- Math CentersDocument1 pageMath Centersapi-226331659No ratings yet
- LetterintroductionspringDocument1 pageLetterintroductionspringapi-226331659No ratings yet
- CollegebingogameDocument4 pagesCollegebingogameapi-226331659No ratings yet
- Reading CentersDocument2 pagesReading Centersapi-226331659No ratings yet
- Technology Curriculum NightDocument8 pagesTechnology Curriculum Nightapi-226331659No ratings yet
- Final Camp Calendar - RookiesDocument2 pagesFinal Camp Calendar - Rookiesapi-226331659No ratings yet
- Camp Challenge Rookies 2ndDocument2 pagesCamp Challenge Rookies 2ndapi-226331659No ratings yet
- The State News Finding Their FaithDocument4 pagesThe State News Finding Their Faithapi-226331659No ratings yet
- RookieswelcomenewsletterDocument1 pageRookieswelcomenewsletterapi-226331659No ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Temp Gradient For Warping Stress in Rigid PavementDocument9 pagesTemp Gradient For Warping Stress in Rigid PavementAmul KotharkarNo ratings yet
- Phy433 Lab Report 1Document9 pagesPhy433 Lab Report 1rabbani abdul rahimNo ratings yet
- As 1463-1988 Polyethylene Pipe Extrusion CompoundsDocument6 pagesAs 1463-1988 Polyethylene Pipe Extrusion CompoundsSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- How many times do clock hands overlap in a dayDocument6 pagesHow many times do clock hands overlap in a dayabhijit2009No ratings yet
- Big Five Personality TestDocument3 pagesBig Five Personality Testchandu_jjvrpNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Chapter 50 Introduction To Ecology The Scope of EcologyDocument2 pagesWorksheet Chapter 50 Introduction To Ecology The Scope of EcologyFernando CastilloNo ratings yet
- Perfect Secrecy: Chester Rebeiro IIT MadrasDocument50 pagesPerfect Secrecy: Chester Rebeiro IIT MadrasDr. Jayanthi V.S.No ratings yet
- 2017 NEC Table of ContentsDocument124 pages2017 NEC Table of ContentsFaheem PP13No ratings yet
- Local Materials Used in Creating Art and TechniquesDocument29 pagesLocal Materials Used in Creating Art and TechniquesAnne Carmel PinoNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument5 pagesProjectMahi MalikNo ratings yet
- Modern Machine Shop 262180-MAR 2014Document228 pagesModern Machine Shop 262180-MAR 20141mmahoneyNo ratings yet
- ISO 9000 Audit Checklist for Quality Management SystemsDocument28 pagesISO 9000 Audit Checklist for Quality Management SystemsphilipalexjonesNo ratings yet
- Let's Mingle Chat Invite ExamplesDocument22 pagesLet's Mingle Chat Invite ExamplesCarmen BalbuenaNo ratings yet
- The Housekeeping Department: Learning Activity #1Document4 pagesThe Housekeeping Department: Learning Activity #1Limar Geoff G. RosalesNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About TimberDocument63 pagesEverything You Need to Know About TimberAkxzNo ratings yet
- Sample Quiz OM Chapter2Document2 pagesSample Quiz OM Chapter2Patleen Monica MicuaNo ratings yet
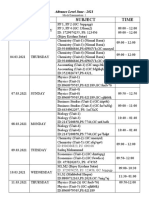
- Mock Examination Routine A 2021 NewDocument2 pagesMock Examination Routine A 2021 Newmufrad muhtasibNo ratings yet
- Porter's Five Forces: Submitted by Subham Chakraborty PGDMDocument5 pagesPorter's Five Forces: Submitted by Subham Chakraborty PGDMSubham ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- KTO12 Curriculum ExplainedDocument24 pagesKTO12 Curriculum ExplainedErnesto ViilavertNo ratings yet
- Axion DatabaseDocument25 pagesAxion Databasemacy williamsNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Practice Questions and Answers Inventory Management: EOQ ModelDocument7 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Practice Questions and Answers Inventory Management: EOQ Modelwasif ahmedNo ratings yet
- Dav Public School, Berhampur, Odisha Summer Holiday HomeworkDocument3 pagesDav Public School, Berhampur, Odisha Summer Holiday HomeworkOmNo ratings yet
- Properties of Skeletal MuscleDocument72 pagesProperties of Skeletal MuscleAakash GohilNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 2 Original TestDocument6 pagesPhysics Chapter 2 Original TestJanina OrmitaNo ratings yet
- A 18-Page Statistics & Data Science Cheat SheetsDocument18 pagesA 18-Page Statistics & Data Science Cheat SheetsAniket AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Solar Panel Cleaning System Design and DevelopmentDocument4 pagesSolar Panel Cleaning System Design and DevelopmentMohammed safarulla HNo ratings yet
- 5 Overview PsasDocument19 pages5 Overview Psasعلي صالحNo ratings yet
- VSP BrochureDocument33 pagesVSP BrochuresudhakarrrrrrNo ratings yet
- Adjustment: - Electronic Modulated Air SuspensionDocument2 pagesAdjustment: - Electronic Modulated Air SuspensionThar KyiNo ratings yet
- 5 & 6 Risk AssessmentDocument23 pages5 & 6 Risk AssessmentAzam HasanNo ratings yet