Professional Documents
Culture Documents
15eme14 PDF
Uploaded by
Ravichandran GOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
15eme14 PDF
Uploaded by
Ravichandran GCopyright:
Available Formats
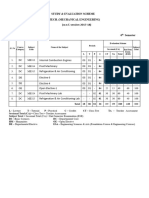
PESIT-BSC Document Title : LESSON PLAN
Department of
Science & Format No. Rev.No. Issue Date:
PES-SH 00 03.07.2015
Humanities
LESSON PLAN
15EME14/15EME24 ELEMENTS OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
Course objectives:
Students belonging to all branches of Engineering are made to learn certain fundamental
topics related to mechanical engineering so that they will have a minimum understanding
of mechanical systems, equipment and process.
(Provided by VTU)
Subject Code: 15EME14/15EME24
Total no. of Hours: 50 Number of Hours/week: 04
Name of Faculty: Mrs. SYED SHARIN Credits: 04
Course
Module / Ref.
Class No. Topic to be covered ( in detail ) % of portion covered Outcomes
Text
covered
Module 1 Chapter Cumulativ CO1
Energy wise e
Non-renewable and renewable energy
1. Resources, 20 20
resources.
Steam
Formation and
Properties Petroleum based solid, liquid fuels,
(References R1, Calorific values of
3.
TI, T4, T3) Fuels, Combustion and combustion
products of and gaseous fuels.
Solar Radiation, Solar constant
(definition only), Solar Thermal energy
4.
harvesting, ex:
Liquid flat plate collectors.
5. Solar ponds (principle of operation
only), Solar photovoltaic principle..
6. Wind Power: principle of operation of
a typical windmill. Hydro
Power :Principles of electric power
generation
PESIT BANGALORE SOUTH CAMPUS education for the real world
PESIT-BSC Document Title : LESSON PLAN
Department of
Science & Format No. Rev.No. Issue Date:
PES-SH 00 03.07.2015
Humanities
from hydropower plants.
Nuclear Power: Principles of Nuclear
7.
power plants.
Bio Fuels : introduction to bio fuels,
examples of various
biofuels used in engineering
8.
applications, Comparison of biofuels
with petroleum fuels in terms of
calorific value and emission.
Classification of boilers, Lancashire
9.
boiler, Babcock and Wilcox boiler.
Boiler mountings and accessories. Wet
10.
steam, saturated and superheated steam.
Specific volume, enthalpy andinternal
11.
energy.
Classification, Principle of operation of
12.
Impulse and reaction turbines.
Delavals turbine, Parsons turbine. (No
13.
compounding of turbines)
Classification, Working principles and
14. Operations of Open cycle and closed
cycle gas turbines
Classification, Principles and operations
15. Module 2 of Pelton wheel, Francis turbine and
Turbines and Kaplan turbine.
IC Engines and Classification, I.C. Engines parts, 2
16.
Pumps Steam Stroke and 4 stroke Petrol engines. 20 40 CO3
turbines 4 stroke diesel engines. P-V diagrams
17.
(References R1, of Otto and Diesel cycles.
18. TI, T4, T3, ) Problems on indicated power.
19. Problems on brake power
Problems on Indicated thermal
20.
efficiency, brake thermal efficiency.
Problems on mechanical efficiency, and
21. specific fuel consumption, [numericals
on IC Engines].
22. Module 3 Machine Tools Operations Turning, 20 60 CO4
Machine facing, knurling, Thread cutting, Taper
PESIT BANGALORE SOUTH CAMPUS education for the real world
PESIT-BSC Document Title : LESSON PLAN
Department of
Science & Format No. Rev.No. Issue Date:
PES-SH 00 03.07.2015
Humanities
Turning by swiveling the compound
rest.
Drilling, Boring, Reaming, Tapping,
23. Counter
Sinking, Counter Boring.
Plane milling, End milling, Slot milling.
24.
(No sketches of Machine tools,.)
Introduction, classification based on
25. Tools and
robots configuration
Automation
26. Machine Tools Polar, cylindrical, Cartesian Coordinate
Operations and spherical
(References Application Polar, cylindrical, Cartesian
27. R2,R3, T2, T4, Coordinate and spherical Advantages,
T3, ) and disadvantages
Automation, Definition, types Fixed,
28.
Programmable & Flexible Automation.
29. NC/ CNC machines
Basic elements with simple block
30.
diagrams.
31. Advantages and Disadvantages
Module 4 20 80 CO2
32. Engineering Types of Ferrous metals and alloys
materials and Applications of Ferrous metals and
33. joining alloys
processes Types and applications Nonferrous
34. (References metals and alloys
R2,R3,TI, T4, Composites :Introduction: Definition,
35. T3, ) Classification and applications (Air
craft and Automobiles).
Definitions, classification and method
36.
of soldering
Definitions, classification and method
37.
of Brazing
Definitions, classification and method
38.
of welding
39. Differences between soldering, Brazing
and Welding.
PESIT BANGALORE SOUTH CAMPUS education for the real world
PESIT-BSC Document Title : LESSON PLAN
Department of
Science & Format No. Rev.No. Issue Date:
PES-SH 00 03.07.2015
Humanities
40. Description of Electric Arc Welding
41. Description of Oxy-Acetylene Welding.
42. Properties of refrigerants.
43. List of commonly used refrigerants
Refrigeration Definitions
44.
Refrigerating effect
Ton of Refrigeration, Ice making
45.
capacity.
Module 5
COP, Relative COP, unit of
46. Refrigeration,
Refrigeration
Air-
Conditioning Principle and working of vapor 20 100 CO5
47.
( References compression refrigeration
R1, TI, Principle and working of vapour
48. T3,T4, ) absorption refrigeration.
Principles and applications of air
49.
conditioners.
Principles and applications of Room air
50.
conditioner.
51. Room air conditioner.
Book
Code Publication information
Type
V.K Manglik Elements of Mechanical Engineering PHI
Text T1
Publications 2013 (Module 1, 2, 4, 5 )
Mikell .Groover Automation production systems & CIM
Text T2
PHI ( Module -3)
PESIT BANGALORE SOUTH CAMPUS education for the real world
PESIT-BSC Document Title : LESSON PLAN
Department of
Science & Format No. Rev.No. Issue Date:
PES-SH 00 03.07.2015
Humanities
K.R Gopalkrishna A text book of elements of Mechanical
Text T3 Engineering Subhash Publishers Bangalore (Module 1-2-3-
4-5)
Kestoor Pravin , M.R Ramesh A text book of Elements of
Text T4 Mechanical Engineering. Suggi Publisher(Module 1-2-3-4-
5)
S. TrymbakaMurthy , A text book of Elements of
Reference R1 Mechanical Engineering Universities press (india) Pvt
Ltd.
Reference R2 Shop Theory By James Anderson
K.P Roy S.K Hajra And Choudhary , Nirjhar Choudhary.
Reference R3 Elements of Mechanical Engineering. Media Promoters and
Publishers Pvt Ltd.
Pravin Kumar, Basic echanical Engineering 2013 Edition ,
Reference R3
Pearson.
Literature:
Course Outcomes:
On Completion of this course, students are able to:
CO1 Gain Knowledge about Various energy sources, Energy classification and Uses of
renewable energy resources, Boilers and properties of steam.
CO2: Gain Knowledge about Prime movers such as turbines And IC Engines.
CO3: Use the knowledge gained by the study of Metal Removal process, using Lathe Drilling
Milling Robotics and Automation.
CO4: Understand basics Concepts and usage of various engineering Materials
CO5: Basic knowledge of Properties of refrigerants , System of refrigeration and air
conditioning
PESIT BANGALORE SOUTH CAMPUS education for the real world
You might also like
- Cse Eme NotesDocument65 pagesCse Eme NotesVedNo ratings yet
- 18ME25 Module-1 (WWW - Vtuloop.com)Document10 pages18ME25 Module-1 (WWW - Vtuloop.com)Robin BinoyNo ratings yet
- Cse-I-Elements of Mechanical Engg. l1Document11 pagesCse-I-Elements of Mechanical Engg. l1Hemanth Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering, SJBITDocument65 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering, SJBITMahavir DamakaleNo ratings yet
- Course Planning: Ballari Institute of Technology & Management Bellary Record Formats ISO 9001:2008Document5 pagesCourse Planning: Ballari Institute of Technology & Management Bellary Record Formats ISO 9001:2008Manjunatha EikilaNo ratings yet
- Elements of Mechanical Engineering 15me14Document65 pagesElements of Mechanical Engineering 15me14Panchami RNo ratings yet
- Cc104 - Elements of Mechanical EngineeringDocument2 pagesCc104 - Elements of Mechanical Engineeringamit2691988No ratings yet
- Power Plant Engineering Course Code: 3361906Document10 pagesPower Plant Engineering Course Code: 3361906hvmandaliaNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Semester - I/II Subject Name: Basic Mechanical EngineeringDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University: Semester - I/II Subject Name: Basic Mechanical EngineeringNirmal KushwahaNo ratings yet
- 1ET1010606 - Alternative Energy SourcesDocument2 pages1ET1010606 - Alternative Energy SourcesDivyNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityRavi Teja TNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Document2 pagesGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19AkashNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering-6 Sem NewDocument17 pagesMechanical Engineering-6 Sem Newbeastboy00077No ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument4 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityAbhishek BisoyiNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Document2 pagesGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Fa CaNo ratings yet
- ME 143 Basics of Civil & Mechanical Engg.Document4 pagesME 143 Basics of Civil & Mechanical Engg.khushbooNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering & Technology First Year Bachelor of Engineering Course Code: 102001202 Course Title: Basic Mechanical EngineeringDocument2 pagesFaculty of Engineering & Technology First Year Bachelor of Engineering Course Code: 102001202 Course Title: Basic Mechanical Engineeringharshangrana55No ratings yet
- Course Handout: Graphic Era (Deemed To Be University) Eight Semester 2018Document2 pagesCourse Handout: Graphic Era (Deemed To Be University) Eight Semester 2018Anonymous HyOfbJ6No ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering VII Sem SyllabusDocument3 pagesMechanical Engineering VII Sem Syllabussaurabh1116No ratings yet
- MTech SyllabusDocument7 pagesMTech SyllabusAyush GargNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Bachelor of Engineering Subject Code: 3130109Document3 pagesGujarat Technological University: Bachelor of Engineering Subject Code: 3130109Nisarg ShahNo ratings yet
- Mech PDFDocument2 pagesMech PDFKartik NadigerNo ratings yet
- Energy Engineering SyllabusDocument5 pagesEnergy Engineering SyllabusNikNo ratings yet
- Thermal Engineering SyllabusDocument144 pagesThermal Engineering SyllabusVpr NaturalsNo ratings yet
- 8th Sem SyllabusDocument10 pages8th Sem SyllabusSAUMYAJIT SABUINo ratings yet
- Power Plant Engineering SyllabusDocument2 pagesPower Plant Engineering SyllabusPardeep8056No ratings yet
- ME 8792 PPE Unit - 1Document142 pagesME 8792 PPE Unit - 1UdamanNo ratings yet
- Basic Mechanical EngineeringDocument2 pagesBasic Mechanical EngineeringAPOLLO Sem 4 I.T.No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Fuel Cell Technology 3-0-2 4 CHL 722: Course TemplateDocument4 pagesFundamentals of Fuel Cell Technology 3-0-2 4 CHL 722: Course TemplateSurjit DuttaNo ratings yet
- TE-I Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesTE-I Lesson PlanArunkumar MunimathanNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument4 pagesSyllabusArjun SainiNo ratings yet
- ME 8792 PPE Unit - 2Document71 pagesME 8792 PPE Unit - 2UdamanNo ratings yet
- Subject PlanDocument4 pagesSubject PlanAya HassanNo ratings yet
- Elements of Mechanical Engg Syllabus (VTU)Document4 pagesElements of Mechanical Engg Syllabus (VTU)Prabhu SwamyNo ratings yet
- TE-I-Course Handout2022Document9 pagesTE-I-Course Handout2022rambabuNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Semester - II Subject Name: Wind and Small Hydro Energy SystemDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological University: Semester - II Subject Name: Wind and Small Hydro Energy SystemfalakNo ratings yet
- Me8595 Te II Steam Turbines Unit III-2022 - 23Document175 pagesMe8595 Te II Steam Turbines Unit III-2022 - 23CAD With RaoNo ratings yet
- Institute of Engineering & Technology, Devi Ahilya University, Indore, (M.P.), India. (Scheme Effective From July 2015)Document2 pagesInstitute of Engineering & Technology, Devi Ahilya University, Indore, (M.P.), India. (Scheme Effective From July 2015)NARESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Engineering Colleges: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument126 pagesEngineering Colleges: Department of Mechanical EngineeringchandramouliNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Semester - II Subject Name: Hydrogen EnergyDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University: Semester - II Subject Name: Hydrogen EnergyfalakNo ratings yet
- Course File FormatDocument3 pagesCourse File FormatThiaga RajanNo ratings yet
- Approved by AICTE & Affiliated To Anna University, ChennaiDocument7 pagesApproved by AICTE & Affiliated To Anna University, ChennaiSAMUEL SANJAY RAJA R MECHNo ratings yet
- Thermal EngineeringDocument6 pagesThermal Engineeringtarek ali ahmedNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Page 1 of 3Document3 pagesGujarat Technological University: Page 1 of 3Tech ShutterNo ratings yet
- Revised EME Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesRevised EME Lesson PlantrishulNo ratings yet
- Course Curriculum: Course Title: Internal Combustion Engine Credit Units: 04 Course Level: UG Course Code: To Be AssignedDocument3 pagesCourse Curriculum: Course Title: Internal Combustion Engine Credit Units: 04 Course Level: UG Course Code: To Be AssignedHtat Myat AungNo ratings yet
- Aeronautical Engineering SyllabusDocument12 pagesAeronautical Engineering Syllabusashok pandiyanNo ratings yet
- PPE (2023 24) HandoutDocument15 pagesPPE (2023 24) Handoutsiva krishnaNo ratings yet
- SSM Institute of Engineering and Technology Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument11 pagesSSM Institute of Engineering and Technology Department of Mechanical Engineeringmmk.mech59No ratings yet
- Open Electives EEEDocument6 pagesOpen Electives EEEumesh kumarNo ratings yet
- EE Course File - Part 1Document8 pagesEE Course File - Part 1shreedharkoilekarNo ratings yet
- MICro Syllabus With COsDocument2 pagesMICro Syllabus With COsRajyalakshmi JammalamadakaNo ratings yet
- I. Understand The Applications of Engineering Thermodynamics in Real Life SituationsDocument18 pagesI. Understand The Applications of Engineering Thermodynamics in Real Life SituationstbnjhjlkkkkkkNo ratings yet
- Pec IiiDocument6 pagesPec Iii3111hruthvikNo ratings yet
- Approved by AICTE & Affiliated To Anna University, ChennaiDocument7 pagesApproved by AICTE & Affiliated To Anna University, ChennaiSAMUEL SANJAY RAJA R MECHNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Document3 pagesGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19AkashNo ratings yet
- NoteDocument130 pagesNoterkNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Engg Lect Notes 6th SemDocument58 pagesPower Plant Engg Lect Notes 6th SemRobin AroraNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Energy EngineeringDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University: Energy EngineeringShrikant PandeyNo ratings yet
- Machine Vision and Metrology Workshop-08.09.2018Document2 pagesMachine Vision and Metrology Workshop-08.09.2018Ravichandran GNo ratings yet
- CTP Journal PaperDocument7 pagesCTP Journal PaperRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- Workshop 09-2016 AerotrixDocument3 pagesWorkshop 09-2016 AerotrixRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- V Sem 'B' Section Ese Result Analysis FormatDocument3 pagesV Sem 'B' Section Ese Result Analysis FormatRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- Computer Literacy: Centre For Social Actions (Csa) Program ONDocument2 pagesComputer Literacy: Centre For Social Actions (Csa) Program ONRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- Elective List 7th SemDocument14 pagesElective List 7th SemRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- V SEM B LABDocument7 pagesV SEM B LABRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- Guest Lecture 08-2016 Higher Studies in USADocument5 pagesGuest Lecture 08-2016 Higher Studies in USARavichandran GNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual - FM and M LabDocument64 pagesLab Manual - FM and M LabRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- ASEE04 (Peer Review) PDFDocument11 pagesASEE04 (Peer Review) PDFRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- Natonial Conference 2016-02 (Innovative Trends in Mechanical Engineering)Document16 pagesNatonial Conference 2016-02 (Innovative Trends in Mechanical Engineering)Ravichandran GNo ratings yet
- Metal Cutting and Production LAB Manual-New (ME452)Document58 pagesMetal Cutting and Production LAB Manual-New (ME452)Ravichandran GNo ratings yet
- Mom Tcs Team 2014-06Document3 pagesMom Tcs Team 2014-06Ravichandran GNo ratings yet
- Aculty of Engineering Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument2 pagesAculty of Engineering Department of Mechanical EngineeringRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- E 410 ContentDocument29 pagesE 410 ContentRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- Guest Lecture 2015-11 MR - Gnanaseelan (How A Mechanical Engineer Shapes Him To Tailor The Needs of The Software)Document4 pagesGuest Lecture 2015-11 MR - Gnanaseelan (How A Mechanical Engineer Shapes Him To Tailor The Needs of The Software)Ravichandran GNo ratings yet
- Loading N Unloading of Tanker PDFDocument36 pagesLoading N Unloading of Tanker PDFKirtishbose ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Discover Mecosta 2011Document40 pagesDiscover Mecosta 2011Pioneer GroupNo ratings yet
- Rating SheetDocument3 pagesRating SheetShirwin OliverioNo ratings yet
- 90FF1DC58987 PDFDocument9 pages90FF1DC58987 PDFfanta tasfayeNo ratings yet
- Prachi AgarwalDocument1 pagePrachi AgarwalAnees ReddyNo ratings yet
- Micron Interview Questions Summary # Question 1 Parsing The HTML WebpagesDocument2 pagesMicron Interview Questions Summary # Question 1 Parsing The HTML WebpagesKartik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Aitt Feb 2017 TH Sem IIIDocument6 pagesAitt Feb 2017 TH Sem IIIMadhu KumarNo ratings yet
- L1 L2 Highway and Railroad EngineeringDocument7 pagesL1 L2 Highway and Railroad Engineeringeutikol69No ratings yet
- CV Ovais MushtaqDocument4 pagesCV Ovais MushtaqiftiniaziNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Presentation: Calcium Sulphate in Cement ManufactureDocument7 pagesPowerpoint Presentation: Calcium Sulphate in Cement ManufactureDhruv PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Richards Laura - The Golden WindowsDocument147 pagesRichards Laura - The Golden Windowsmars3942No ratings yet
- Reflections On Free MarketDocument394 pagesReflections On Free MarketGRK MurtyNo ratings yet
- Guide For Overseas Applicants IRELAND PDFDocument29 pagesGuide For Overseas Applicants IRELAND PDFJasonLeeNo ratings yet
- Viceversa Tarot PDF 5Document1 pageViceversa Tarot PDF 5Kimberly Hill100% (1)
- Capital Expenditure DecisionDocument10 pagesCapital Expenditure DecisionRakesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Basic DfwmacDocument6 pagesBasic DfwmacDinesh Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Form16 2018 2019Document10 pagesForm16 2018 2019LogeshwaranNo ratings yet
- The Art of Blues SolosDocument51 pagesThe Art of Blues SolosEnrique Maldonado100% (8)
- GL 186400 Case DigestDocument2 pagesGL 186400 Case DigestRuss TuazonNo ratings yet
- Phase 1: API Lifecycle (2 Days)Document3 pagesPhase 1: API Lifecycle (2 Days)DevendraNo ratings yet
- M2 Economic LandscapeDocument18 pagesM2 Economic LandscapePrincess SilenceNo ratings yet
- CNC USB English ManualDocument31 pagesCNC USB English ManualHarold Hernan MuñozNo ratings yet
- The Internal Environment: Resources, Capabilities, Competencies, and Competitive AdvantageDocument5 pagesThe Internal Environment: Resources, Capabilities, Competencies, and Competitive AdvantageHenny ZahranyNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 2: Fundamentals of Management Science For Built EnvironmentDocument23 pagesAssignment - 2: Fundamentals of Management Science For Built EnvironmentVarma LakkamrajuNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Disaster Management Notes by D. Malleswari ReddyDocument49 pagesGroup 1 Disaster Management Notes by D. Malleswari Reddyraghu ramNo ratings yet
- Laporan Praktikum Fisika - Full Wave RectifierDocument11 pagesLaporan Praktikum Fisika - Full Wave RectifierLasmaenita SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Ishares Core S&P/TSX Capped Composite Index Etf: Key FactsDocument2 pagesIshares Core S&P/TSX Capped Composite Index Etf: Key FactsChrisNo ratings yet
- BASUG School Fees For Indigene1Document3 pagesBASUG School Fees For Indigene1Ibrahim Aliyu GumelNo ratings yet
- 1.1. Evolution of Cloud ComputingDocument31 pages1.1. Evolution of Cloud Computing19epci022 Prem Kumaar RNo ratings yet
- GR L-38338Document3 pagesGR L-38338James PerezNo ratings yet