Professional Documents
Culture Documents
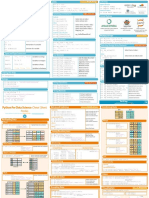
Numpy Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
Ian Flores100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
837 views1 pagenumpy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentnumpy
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
837 views1 pageNumpy Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
Ian Floresnumpy
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
LEARN DATA SCIENCE ONLINE
Start Learning For Free - www.dataquest.io
Data Science Cheat Sheet
NumPy
KEY IMPORTS
Well use shorthand in this cheat sheet Import these to start
arr - A numpy Array object import numpy as np
I M P O RT I N G/ E X P O RT I N G arr.T - Transposes arr (rows become columns and S C A L A R M AT H
np.loadtxt('file.txt') - From a text file vice versa) np.add(arr,1) - Add 1 to each array element
np.genfromtxt('file.csv',delimiter=',') arr.reshape(3,4) - Reshapes arr to 3 rows, 4 np.subtract(arr,2) - Subtract 2 from each array
- From a CSV file columns without changing data element
np.savetxt('file.txt',arr,delimiter=' ') arr.resize((5,6)) - Changes arr shape to 5x6 np.multiply(arr,3) - Multiply each array
- Writes to a text file and fills new values with 0 element by 3
np.savetxt('file.csv',arr,delimiter=',') np.divide(arr,4) - Divide each array element by
- Writes to a CSV file A D D I N G/ R E M OV I N G E L E M E N TS 4 (returns np.nan for division by zero)
np.append(arr,values) - Appends values to end np.power(arr,5) - Raise each array element to
C R E AT I N G A R R AYS of arr the 5th power
np.array([1,2,3]) - One dimensional array np.insert(arr,2,values) - Inserts values into
np.array([(1,2,3),(4,5,6)]) - Two dimensional arr before index 2 V E C TO R M AT H
array np.delete(arr,3,axis=0) - Deletes row on index np.add(arr1,arr2) - Elementwise add arr2 to
np.zeros(3) - 1D array of length 3 all values 0 3 of arr arr1
np.ones((3,4)) - 3x4 array with all values 1 np.delete(arr,4,axis=1) - Deletes column on np.subtract(arr1,arr2) - Elementwise subtract
np.eye(5) - 5x5 array of 0 with 1 on diagonal index 4 of arr arr2 from arr1
(Identity matrix) np.multiply(arr1,arr2) - Elementwise multiply
np.linspace(0,100,6) - Array of 6 evenly divided C O M B I N I N G/S P L I T T I N G arr1 by arr2
values from 0 to 100 np.concatenate((arr1,arr2),axis=0) - Adds np.divide(arr1,arr2) - Elementwise divide arr1
np.arange(0,10,3) - Array of values from 0 to less arr2 as rows to the end of arr1 by arr2
than 10 with step 3 (eg [0,3,6,9]) np.concatenate((arr1,arr2),axis=1) - Adds np.power(arr1,arr2) - Elementwise raise arr1
np.full((2,3),8) - 2x3 array with all values 8 arr2 as columns to end of arr1 raised to the power of arr2
np.random.rand(4,5) - 4x5 array of random floats np.split(arr,3) - Splits arr into 3 sub-arrays np.array_equal(arr1,arr2) - Returns True if the
between 0-1 np.hsplit(arr,5) - Splits arr horizontally on the arrays have the same elements and shape
np.random.rand(6,7)*100 - 6x7 array of random 5th index np.sqrt(arr) - Square root of each element in the
floats between 0-100 array
np.random.randint(5,size=(2,3)) - 2x3 array I N D E X I N G/S L I C I N G/S U B S E T T I N G np.sin(arr) - Sine of each element in the array
with random ints between 0-4 arr[5] - Returns the element at index 5 np.log(arr) - Natural log of each element in the
arr[2,5] - Returns the 2D array element on index array
I N S P E C T I N G P R O P E RT I E S [2][5] np.abs(arr) - Absolute value of each element in
arr.size - Returns number of elements in arr arr[1]=4 - Assigns array element on index 1 the the array
arr.shape - Returns dimensions of arr (rows, value 4 np.ceil(arr) - Rounds up to the nearest int
columns) arr[1,3]=10 - Assigns array element on index np.floor(arr) - Rounds down to the nearest int
arr.dtype - Returns type of elements in arr [1][3] the value 10 np.round(arr) - Rounds to the nearest int
arr.astype(dtype) - Convert arr elements to arr[0:3] - Returns the elements at indices 0,1,2
type dtype (On a 2D array: returns rows 0,1,2) STAT I ST I C S
arr.tolist() - Convert arr to a Python list arr[0:3,4] - Returns the elements on rows 0,1,2 np.mean(arr,axis=0) - Returns mean along
np.info(np.eye) - View documentation for at column 4 specific axis
np.eye arr[:2] - Returns the elements at indices 0,1 (On arr.sum() - Returns sum of arr
a 2D array: returns rows 0,1) arr.min() - Returns minimum value of arr
C O P Y I N G/S O RT I N G/ R E S H A P I N G arr[:,1] - Returns the elements at index 1 on all arr.max(axis=0) - Returns maximum value of
np.copy(arr) - Copies arr to new memory rows specific axis
arr.view(dtype) - Creates view of arr elements arr<5 - Returns an array with boolean values np.var(arr) - Returns the variance of array
with type dtype (arr1<3) & (arr2>5) - Returns an array with np.std(arr,axis=1) - Returns the standard
arr.sort() - Sorts arr boolean values deviation of specific axis
arr.sort(axis=0) - Sorts specific axis of arr ~arr - Inverts a boolean array arr.corrcoef() - Returns correlation coefficient
two_d_arr.flatten() - Flattens 2D array arr[arr<5] - Returns array elements smaller than 5 of array
two_d_arr to 1D
LEARN DATA SCIENCE ONLINE
Start Learning For Free - www.dataquest.io
You might also like
- Seaborn Cheat Sheet for Python Data VisualizationDocument1 pageSeaborn Cheat Sheet for Python Data VisualizationFrâncio Rodrigues100% (1)
- Pandas Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPandas Cheat SheetRoberto83% (12)
- NumPy, SciPy, Pandas, Quandl Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesNumPy, SciPy, Pandas, Quandl Cheat Sheetseanrwcrawford100% (3)
- Matplotlib Cheat SheetDocument8 pagesMatplotlib Cheat SheetTuan Ton100% (5)
- Data Analysis With PANDAS: Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesData Analysis With PANDAS: Cheat Sheetnesayu67% (3)
- Python Matplotlib Cheat SheetDocument1 pagePython Matplotlib Cheat SheetsreedharNo ratings yet
- Pandas Python For Data ScienceDocument1 pagePandas Python For Data Sciencechowdamhemalatha100% (1)
- Coffee Break NumPy PDFDocument211 pagesCoffee Break NumPy PDFKiran Kumar100% (3)
- Python 3.2 Reference CardDocument2 pagesPython 3.2 Reference CardLaurent Pointal100% (12)
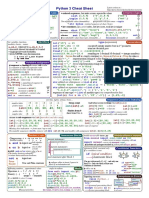
- Python 3 Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPython 3 Cheat SheetLaurent Pointal94% (48)
- Programming Languages and Kernels in Jupyter NotebookDocument1 pageProgramming Languages and Kernels in Jupyter NotebookAnurag AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Pandas Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPandas Cheat Sheetngyncloud100% (4)
- Python Cheat SheetsDocument11 pagesPython Cheat SheetsAndrew Khalatov96% (26)
- Learning The Pandas Library Python Tools For Data Munging Analysis and Visual PDFDocument208 pagesLearning The Pandas Library Python Tools For Data Munging Analysis and Visual PDFAlicia Brett100% (11)
- Python Quick Reference CardDocument17 pagesPython Quick Reference CardSérgio Luiz Araújo Silva94% (16)
- Python Data Science Cheat SheetDocument15 pagesPython Data Science Cheat SheetMuhammad Wahyu Dwimulyo100% (3)
- Python Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPython Cheat Sheetebookkarthi100% (2)
- NumPy Cookbook - Second Edition - Sample ChapterDocument32 pagesNumPy Cookbook - Second Edition - Sample ChapterPackt Publishing100% (2)
- Numpy ReferenceDocument1,183 pagesNumpy ReferenceLucian GhituNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet: The Pandas Dataframe Object: Preliminaries Get Your Data Into A DataframeDocument12 pagesCheat Sheet: The Pandas Dataframe Object: Preliminaries Get Your Data Into A Dataframetoddae100% (1)
- Numpy Python Cheat SheetDocument1 pageNumpy Python Cheat Sheetyellow_birdNo ratings yet
- Python Pandas TutorialDocument178 pagesPython Pandas TutorialDavid Charles100% (18)
- SQL Cheat Sheet PythonDocument1 pageSQL Cheat Sheet PythonAndrew KhalatovNo ratings yet
- Numpy Basics: Arithmetic OperationsDocument7 pagesNumpy Basics: Arithmetic OperationsDeepak Gupta100% (13)
- Beginners Python Cheat Sheet PCC AllDocument26 pagesBeginners Python Cheat Sheet PCC Alljohn smith96% (24)
- Robert Smallshire, Austin Bingham - The Python Master (75% Complete) - Leanpub (2019) PDFDocument187 pagesRobert Smallshire, Austin Bingham - The Python Master (75% Complete) - Leanpub (2019) PDFNasredeenAhmadNo ratings yet
- 65 Free Data Science Resources For Beginners PDFDocument19 pages65 Free Data Science Resources For Beginners PDFgirishkumarNo ratings yet
- Numpy Crash Course - Sharp SightDocument160 pagesNumpy Crash Course - Sharp SightMario Leon Gatica83% (6)
- Core Python Cheat SheetDocument9 pagesCore Python Cheat Sheetsalim100% (4)
- Ai Cheat Sheet Machine Learning With Python Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesAi Cheat Sheet Machine Learning With Python Cheat SheetA.K. Mars100% (3)
- Introductory Notes: Matplotlib: PreliminariesDocument11 pagesIntroductory Notes: Matplotlib: PreliminariesJohnyMacaroniNo ratings yet
- NumPy: Beginner's Guide - Third Edition - Sample ChapterDocument54 pagesNumPy: Beginner's Guide - Third Edition - Sample ChapterPackt Publishing75% (4)
- Intermediate PythonDocument86 pagesIntermediate Pythonsunny131987No ratings yet
- Python Reference CardDocument2 pagesPython Reference Cardmarczucker100% (4)
- Python Cheat Sheet For Data Scientists by Tomi Mester 2019 PDFDocument23 pagesPython Cheat Sheet For Data Scientists by Tomi Mester 2019 PDFDanBarbera100% (3)
- Python NumPy cheat sheet for data scienceDocument14 pagesPython NumPy cheat sheet for data scienceraghavandra ethish manickam100% (1)
- Python For Data AnalysisDocument39 pagesPython For Data Analysiswvargas92650% (2)
- Pandas DataFrame NotesDocument13 pagesPandas DataFrame Notesalainvalois67% (3)
- (Smtebooks - Eu) Coffee Break Python 1st Edition PDFDocument196 pages(Smtebooks - Eu) Coffee Break Python 1st Edition PDFsener.asli100% (7)
- Python 3 Cheat SheetDocument16 pagesPython 3 Cheat SheetFredrik Johansson71% (7)
- Python For Data Science - Cheat SheetsDocument10 pagesPython For Data Science - Cheat SheetsMustafa Ibrahim100% (4)
- Pandas 1.x Cookbook - Second Edition: Practical recipes for scientific computing, time series analysis, and exploratory data analysis using Python, 2nd EditionFrom EverandPandas 1.x Cookbook - Second Edition: Practical recipes for scientific computing, time series analysis, and exploratory data analysis using Python, 2nd EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Hands-On Data Analysis with Pandas: Efficiently perform data collection, wrangling, analysis, and visualization using PythonFrom EverandHands-On Data Analysis with Pandas: Efficiently perform data collection, wrangling, analysis, and visualization using PythonNo ratings yet
- Leaflet Cheat SheetDocument1 pageLeaflet Cheat SheetAnto Padaunan100% (1)
- Eurostat CheatsheetDocument1 pageEurostat CheatsheetAnto PadaunanNo ratings yet
- How Big Is Your Graph?: An R Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesHow Big Is Your Graph?: An R Cheat SheetIan FloresNo ratings yet
- Data Import Cheatsheet PDFDocument2 pagesData Import Cheatsheet PDFHGFERNAN100% (1)
- Reg Ex Cheat SheetDocument1 pageReg Ex Cheat SheetIan FloresNo ratings yet
- Tipping The Civil-Military BalanceDocument30 pagesTipping The Civil-Military BalanceIan FloresNo ratings yet
- Vectors and Their Representation:: Vector & Three Dimensional GeometryDocument223 pagesVectors and Their Representation:: Vector & Three Dimensional GeometryAnony PrevailsNo ratings yet
- Logarithm - DPP 03 (Of Lec 04) - (Arjuna JEE 2.0 2023)Document2 pagesLogarithm - DPP 03 (Of Lec 04) - (Arjuna JEE 2.0 2023)K C DharshanNo ratings yet
- Ship Theory - Numerical IntegrationDocument30 pagesShip Theory - Numerical IntegrationMuhammad YusufNo ratings yet
- Gender & SocietyDocument17 pagesGender & SocietyMushmallow Blue100% (1)
- Lower Secondary Mathematics Answers Stage 7Document23 pagesLower Secondary Mathematics Answers Stage 7Bharthi kp67% (18)
- Math's SBADocument14 pagesMath's SBAJahiem DurrantNo ratings yet
- TCL Assignment 1 3 QuestionDocument2 pagesTCL Assignment 1 3 QuestionNaveen SilveriNo ratings yet
- Subtracting FractionsDocument19 pagesSubtracting Fractionsarjay matanguihanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics A: Edexcel IGCSEDocument9 pagesMathematics A: Edexcel IGCSEsajeevNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Programming 2Document39 pagesDynamic Programming 2apa ajaNo ratings yet
- Introduction of PropositionDocument29 pagesIntroduction of PropositionGideon CayogNo ratings yet
- EverythingMaths Grade11 PDFDocument238 pagesEverythingMaths Grade11 PDFBou Ke Phan100% (1)
- 122 TD4Document15 pages122 TD4Sebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- Elementarytreati00lone BWDocument396 pagesElementarytreati00lone BWVamsi Krishna SogaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document8 pagesChapter 03lucashawkins464No ratings yet
- Two-Way Deterministic Finite AutomataDocument9 pagesTwo-Way Deterministic Finite AutomataDeeksha SharmaNo ratings yet
- ESO207 Theoretical Assignment 1 Semester II, 2016-17Document2 pagesESO207 Theoretical Assignment 1 Semester II, 2016-17Rohit GputaNo ratings yet
- Calculus II SyllabusDocument2 pagesCalculus II SyllabusMiliyon TilahunNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Special Products and FactoringDocument19 pages2.3 Special Products and FactoringJohn Hernan TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Fractions Comp Packet RevisedDocument20 pagesFractions Comp Packet Revisedapi-235199292No ratings yet
- Digital Logic and DesignDocument54 pagesDigital Logic and DesignANJALI PATELNo ratings yet
- Math Lesson Plan 2Document3 pagesMath Lesson Plan 2api-341731125No ratings yet
- UNIT 5 - Digital ElectronicsDocument100 pagesUNIT 5 - Digital ElectronicsThriveni GNo ratings yet
- Cross Power Spectral Density: Z T Which Is Sum of Two Real Jointly WSS Random ProcessesDocument8 pagesCross Power Spectral Density: Z T Which Is Sum of Two Real Jointly WSS Random ProcessesPramod DhaigudeNo ratings yet
- Random Variables and Stochastic Processes R13Document5 pagesRandom Variables and Stochastic Processes R13Nageswar ParasaNo ratings yet
- Accelerated Algebra 2 Unit 6 Performance Task 2 - Ferris WheelDocument2 pagesAccelerated Algebra 2 Unit 6 Performance Task 2 - Ferris WheelAnthony RelatorNo ratings yet
- Mathematics JEE Main Chapter Wise DPPDocument513 pagesMathematics JEE Main Chapter Wise DPPMurali100% (1)
- Educellence Institute: Assignment by PRANAY SRIVASTAVA Iit Ism DhanbadDocument5 pagesEducellence Institute: Assignment by PRANAY SRIVASTAVA Iit Ism DhanbadcompuerNo ratings yet
- Solve Each Equation by Factoring. Use The Zero Product PropertyDocument2 pagesSolve Each Equation by Factoring. Use The Zero Product PropertyRosa Elia AguilarNo ratings yet
- MAT2612 Solutions Review Questions Chapter 3Document4 pagesMAT2612 Solutions Review Questions Chapter 3MarkusNo ratings yet