Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nama Penyewa JUN Julai Ogos Sept OKT NOV DIS
Uploaded by
sabbysamuraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nama Penyewa JUN Julai Ogos Sept OKT NOV DIS
Uploaded by
sabbysamuraCopyright:
Available Formats
2.
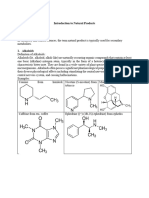
12 TEST METHOD FOR ALKALOID, FLAVONOID AND TERPENES
ALKALOID
A precise definition of the term alkaloid (alkali-like) is somewhat difficult because
there is no clear-cut boundary between alkaloids and naturally occurring complex
amines. Typical alkaloids are derived from plant sources, they are basic, they contain
one or more nitrogen atoms (usually in a heterocyclic ring) and they usually have a
marked physiological action on man or other animals. The name proto-alkaloid or
amino-alkaloid is sometimes applied to compounds such as hordenine, ephedrine
and colchicine which lack one or more of the properties of typical alkaloids.
Before that I would like to show what is the function of alkaloids in plants. The
characteristic nature of alkaloids and their often very marked pharmacological effects
when administered to animals naturally led scientists to speculate on their biological
role in the plants in which they occurred.
1 . Being of such diverse nature, alkaloids as a group could not be expected to have a
common role (if any) in the, except possibly in situations requiring a non-specific
basic compound. In this respect the increase in putrescine in barley seedlings when
grown in a medium deficient in potassium is of interest.
2 . Alkaloids often occur in plants in association with characteristic acids.For example,
the tropane alkaloids of the Solanaceae and the developing fruits. Oxidation
reduction involving N -oxides and tertiary bases is a probability. It has been
suggested that N -oxides may be involved in demethylations and their participation
in the biosynthesis of benzylisoquinoline alkaloids has also been proposed. The
solubility properties of N -oxides could influence the transport of alkaloids both
throughout the plant and also within the cell itself.
NAMA PENYEWA JUN JULAI OGOS SEPT OKT NOV DIS
FLAVONOID
Flavonoids or bioflavonoids are a class of plant secondary metabolites. Flavonoids were
referred to as Vitamin P because of the effect they had on the permeability of vascular
capillaries.According to the IUPAC nomenclature they can be classified into:
flavonoids or bioflavonoids
isoflavonoids, derived from 3-phenylchromen-4-one (3-phenyl-1,4-benzopyrone)
structure
neoflavonoids, derived from 4-phenylcoumarine (4-phenyl-1,2-benzopyrone)
structure
The three flavonoid classes are all ketone-containing compounds, and as such, are
anthoxanthins (flavones and flavonols). This class was the first to be termed bioflavonoids.
The terms flavonoid and bioflavonoid have also been more loosely used to describe non-
ketone polyhydroxy polyphenol compounds which are more specifically termed flavanoids.
The three cycle or heterocycles in the flavonoid backbone are generally called ring A, B and
C. Ring A usually shows a phloroglucinol substitution pattern.
The stock solution (1 mL) was taken in a test tube and added few drop of dilute NaOH solution. An
intense yellow colour was appeared in the test tube. It became colourless when on addition of a few
drop of dilute acid that indicated the presence of flavonoids.
You might also like
- Journal File 56c4010cf04104.95289098 PDFDocument8 pagesJournal File 56c4010cf04104.95289098 PDFana fais utamiNo ratings yet
- FlavanoidDocument9 pagesFlavanoidalvinarasoolNo ratings yet
- Lead Review Article: Polyphenols: Chemistry, Dietary Sources, Metabolism, and Nutritional SignificanceDocument17 pagesLead Review Article: Polyphenols: Chemistry, Dietary Sources, Metabolism, and Nutritional SignificancejohnheverthNo ratings yet
- By Dr. Kamran Javed Naquvi,: Unit II Pharmacognosy (DP-103)Document31 pagesBy Dr. Kamran Javed Naquvi,: Unit II Pharmacognosy (DP-103)Bashar AhmedNo ratings yet
- B Pharmacy-8 Sem-Ccp Landran Industrial PharmacognosyDocument6 pagesB Pharmacy-8 Sem-Ccp Landran Industrial PharmacognosyRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Alkaloids - Definition and DistributionDocument1 pageAlkaloids - Definition and Distributionsaihjad pramaniNo ratings yet
- STP PhytochemistryDocument16 pagesSTP Phytochemistrystar beautyNo ratings yet
- Determination of Alkaloid Structures I. Isolation Characterization and Physical MethodsDocument6 pagesDetermination of Alkaloid Structures I. Isolation Characterization and Physical Methodsgeovani2No ratings yet
- Phenolic Compounds, L-1Document46 pagesPhenolic Compounds, L-1Ammadazfar ImamNo ratings yet
- AlkaloidsDocument21 pagesAlkaloidssanjiv_m20100% (1)
- 633925018173144985Document23 pages633925018173144985Ghanshyam R. ParmarNo ratings yet
- Phenolic CompoundsDocument16 pagesPhenolic CompoundsLucíaNo ratings yet
- 2016 GCWUF 2501 Assignment 2Document15 pages2016 GCWUF 2501 Assignment 2Kaynat SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Alkaloids-: Nitrogen Terresterial Plants Spectrum Physiological Studies Synthetic DrugsDocument21 pagesAlkaloids-: Nitrogen Terresterial Plants Spectrum Physiological Studies Synthetic DrugsAnuj KaundalNo ratings yet
- FlavonoidsDocument11 pagesFlavonoidsMelva SibaraniNo ratings yet
- Alcaloides MBDocument9 pagesAlcaloides MBSule Granados DNo ratings yet
- Chem Project AlkaloidsDocument13 pagesChem Project AlkaloidsVinyas GowdaNo ratings yet
- Lec. 1 Alkaloids Introduction: DistributionDocument11 pagesLec. 1 Alkaloids Introduction: DistributionRocky KhanNo ratings yet
- Pharm 2101Document127 pagesPharm 2101Monirul Islam ShohagNo ratings yet
- Chapter-Ii Alkaloids: 2.1 IntroductioDocument14 pagesChapter-Ii Alkaloids: 2.1 IntroductioRozi KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 Chemistry of Natural ProductsDocument50 pagesChapter - 3 Chemistry of Natural ProductsAnonymous QG3UqD974No ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of Flavonoids PDFDocument15 pagesBiosynthesis of Flavonoids PDFNaouel BoudNo ratings yet
- Alkaloid 2Document6 pagesAlkaloid 2Yenni Daen MadikaNo ratings yet
- Antioxidan 1Document43 pagesAntioxidan 1pardeepbthNo ratings yet
- Waterhouse 2002Document16 pagesWaterhouse 2002Ximena CáceresNo ratings yet
- JSSC 200700261 PDFDocument28 pagesJSSC 200700261 PDFagustinalfiani100% (1)
- AlkaloidsDocument54 pagesAlkaloidshobes100% (4)
- 1982 Wollenweber Flavones and FlavonolsDocument70 pages1982 Wollenweber Flavones and FlavonolsmariangelestmNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Plaphy 2011 11 007Document7 pages10 1016@j Plaphy 2011 11 007Rusu LauraNo ratings yet
- Alkaloids SummaryDocument57 pagesAlkaloids SummaryCompletado AprilaceNo ratings yet
- Chalconas BioactivityDocument26 pagesChalconas Bioactivityjua.valverde91No ratings yet
- Biosintesis FlavonoidDocument44 pagesBiosintesis Flavonoidfriezqa ayuNo ratings yet
- ALKALOID With Some IsolationDocument24 pagesALKALOID With Some IsolationRajesh Kumar100% (1)
- Role of Microbiota in Bioavailability and Physiological Functions of Polyphenols-ReviewDocument25 pagesRole of Microbiota in Bioavailability and Physiological Functions of Polyphenols-Reviewhassan tallalNo ratings yet
- Phyto - II (CPG 604) Alkaloids' LecturesDocument61 pagesPhyto - II (CPG 604) Alkaloids' LecturesAbdelrahman WaelNo ratings yet
- Unit 10Document24 pagesUnit 10debksaha2050No ratings yet
- Bab IDocument7 pagesBab IKhaiva PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Natural Products IntroductionDocument21 pagesChapter 1 Natural Products IntroductionBakhita MaryamNo ratings yet
- Alkaline PhosphataseDocument6 pagesAlkaline PhosphataseJohn FerlasNo ratings yet
- Alkaloids Written ReportDocument12 pagesAlkaloids Written ReportRuvie Ann Alamo BallesterNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 PPIDocument17 pagesLecture 14 PPIabeehazakeeshNo ratings yet
- Alkaloid - (Chemical Compound) : Families of Flowering PlantsDocument6 pagesAlkaloid - (Chemical Compound) : Families of Flowering Plantswishintamil comNo ratings yet
- AuxinDocument18 pagesAuxinMadhusmita BalNo ratings yet
- Module 04Document60 pagesModule 04shashi vermaNo ratings yet
- Solanum Alkaloids and Their Pharmaceutical Roles - A ReviewDocument14 pagesSolanum Alkaloids and Their Pharmaceutical Roles - A ReviewHuy BakNo ratings yet
- Grafting of GraftageDocument3 pagesGrafting of GraftageAyaka PatriciaNo ratings yet
- Isolation of Alkaloids From Plants................Document28 pagesIsolation of Alkaloids From Plants................anjali singh bijyal100% (1)
- Alkaloid AlakaloidDocument21 pagesAlkaloid AlakaloidMD. Aminul IslamNo ratings yet
- Alkaloids AvnishDocument16 pagesAlkaloids AvnishDr. Avnish Upadhyay100% (22)
- Aurone & ChalconeDocument26 pagesAurone & ChalconeAulia Suci WulandariNo ratings yet
- Phytosynthesis: Pharmaceutical Botany With TaxonomyDocument2 pagesPhytosynthesis: Pharmaceutical Botany With TaxonomyVanessa RamosNo ratings yet
- Jurnal GlikosidaDocument17 pagesJurnal GlikosidarianNo ratings yet
- Bautista2015 Article EnvironmentallyInducedChangesIDocument15 pagesBautista2015 Article EnvironmentallyInducedChangesIbnechitaNo ratings yet
- Plant Bio-II 24102022Document7 pagesPlant Bio-II 24102022Aqsa RaffaqNo ratings yet
- Alkaloidal AminesDocument31 pagesAlkaloidal Aminesharishkumar kakrani100% (3)
- Review Flav On Oids 2012Document16 pagesReview Flav On Oids 2012john pierreNo ratings yet
- Extraction, Isolation and Characterization of Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids Present in Senecio Vulgaris Linn Grown in IraqDocument10 pagesExtraction, Isolation and Characterization of Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids Present in Senecio Vulgaris Linn Grown in Iraqfitrah fajrianiNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Applied to Beer Brewing - General Chemistry of the Raw Materials of Malting and BrewingFrom EverandBiochemistry Applied to Beer Brewing - General Chemistry of the Raw Materials of Malting and BrewingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology For Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsFrom EverandAnatomy and Physiology For Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsNo ratings yet
- Section A (10 Marks) (Time Suggested: 15 MinutesDocument13 pagesSection A (10 Marks) (Time Suggested: 15 MinutesMohamad Azizi YunusNo ratings yet
- Filled Application FormDocument4 pagesFilled Application FormsabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- Short Writing Task Practice 1Document1 pageShort Writing Task Practice 1sabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- Itinerary EeDocument2 pagesItinerary EesabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- BIL Name Grade Date 1 Sarbiah Binti Attan N22 6-Aug-21Document2 pagesBIL Name Grade Date 1 Sarbiah Binti Attan N22 6-Aug-21sabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- Filled Application FormDocument4 pagesFilled Application FormsabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- Filled Application FormDocument4 pagesFilled Application FormsabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- Filled Application FormDocument4 pagesFilled Application FormsabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- Filled Application FormDocument4 pagesFilled Application FormsabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- English Form 2 Units 1Document6 pagesEnglish Form 2 Units 1ClaireNo ratings yet
- Malaysia: 2016 TOTAL POPULATION: 31 187 000 2016 TOTAL DEATHS: 154 000Document1 pageMalaysia: 2016 TOTAL POPULATION: 31 187 000 2016 TOTAL DEATHS: 154 000sabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- Set 1 Set 1: Testing Date 12.09.2017 Testing Date 12.09.2017Document3 pagesSet 1 Set 1: Testing Date 12.09.2017 Testing Date 12.09.2017sabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- Unhealthy Diet Lack of Exercise Being OverweightDocument2 pagesUnhealthy Diet Lack of Exercise Being OverweightsabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- JULAI 2015: Prepare Memo + Trial Test Special X-Check Prepare Memo + Trial Test Special X-CheckDocument4 pagesJULAI 2015: Prepare Memo + Trial Test Special X-Check Prepare Memo + Trial Test Special X-ChecksabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- NBVCNNDocument1 pageNBVCNNsabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- KL Public HolidayDocument10 pagesKL Public HolidaysabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- 1 Quarterly Report 2018 Global Testing and Consultancy For Rubber (G-Tac) Centre of Excellence (Coe)Document2 pages1 Quarterly Report 2018 Global Testing and Consultancy For Rubber (G-Tac) Centre of Excellence (Coe)sabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- PT Program Performent For 129Th Series SMR Laboratories (Blended)Document3 pagesPT Program Performent For 129Th Series SMR Laboratories (Blended)sabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- MRB PT Programme MRB - PTP - 15: General Procedure of Equipment, Accommodation and EnvironmentDocument4 pagesMRB PT Programme MRB - PTP - 15: General Procedure of Equipment, Accommodation and EnvironmentsabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document3 pagesBook 1sabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- PT Program Performent For 129Th Series SMR Laboratories (Blended)Document3 pagesPT Program Performent For 129Th Series SMR Laboratories (Blended)sabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- Set 1&2Document3 pagesSet 1&2sabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- MRB PT Programme MRB - PTP - 15: General Procedure of Equipment, Accommodation and EnvironmentDocument4 pagesMRB PT Programme MRB - PTP - 15: General Procedure of Equipment, Accommodation and EnvironmentsabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- NBVCNNDocument1 pageNBVCNNsabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- Spare Sample Spare Sample Spare Sample Spare Sample: MDCT1-P2-1 MDCT1-P2-2 MDCT1-P2-3Document1 pageSpare Sample Spare Sample Spare Sample Spare Sample: MDCT1-P2-1 MDCT1-P2-2 MDCT1-P2-3sabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- UjytujytDocument6 pagesUjytujytsabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- 127th PTP Results PDFDocument9 pages127th PTP Results PDFsabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- 127th PTP Results PDFDocument9 pages127th PTP Results PDFsabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- 131St Series Proficiency Testing Program For SMR Testing: Set 1 Set 2Document354 pages131St Series Proficiency Testing Program For SMR Testing: Set 1 Set 2sabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- USSP-E1-1: 9.3.3 N-Pentane Resistance TestDocument8 pagesUSSP-E1-1: 9.3.3 N-Pentane Resistance TestsabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- Sigraflex UniversalDocument6 pagesSigraflex UniversalJan SmitNo ratings yet
- Psych Ro MetricDocument11 pagesPsych Ro MetricLucia Kara Chance100% (1)
- Rock Engineering Design of Post-Tensioned Anchors For DamsDocument13 pagesRock Engineering Design of Post-Tensioned Anchors For Damszepfer100% (1)
- IEPR Session 1 Part 2Document14 pagesIEPR Session 1 Part 2Vaidhyanathan ViswanathanNo ratings yet
- API 526 - Spring Loaded Material TableDocument1 pageAPI 526 - Spring Loaded Material TableGanda SamosirNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 3-Chapter 6 - Failure Theories-Selected ProblemsDocument22 pagesProblem Set 3-Chapter 6 - Failure Theories-Selected ProblemsIsmail DoğanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Past PaperDocument20 pagesChemistry Past PaperSaru Nadarajah0% (1)
- Hydrazine Analysis PDFDocument4 pagesHydrazine Analysis PDFShanmuga SelvanNo ratings yet
- Materials Compatibility List: Chemicals For Processing Endoscopes and Endoscopic InstrumentsDocument24 pagesMaterials Compatibility List: Chemicals For Processing Endoscopes and Endoscopic InstrumentsAlina AlinaNo ratings yet
- Guide To Method Format: (Method Shown Is Incomplete To Allow Space For Description.)Document1 pageGuide To Method Format: (Method Shown Is Incomplete To Allow Space For Description.)Douglas DíazNo ratings yet
- Reference 1Document3 pagesReference 1pathinfoNo ratings yet
- IEEE Guide For Thermal Resistivity Measurements of Soils and Backfill MaterialsDocument33 pagesIEEE Guide For Thermal Resistivity Measurements of Soils and Backfill MaterialsMarcos Serrão93% (27)
- Revision Notes On Heat TransferDocument11 pagesRevision Notes On Heat TransferAnonymous vRpzQ2BLNo ratings yet
- Determination of Titanium Dioxide in Commercial Sunscreens by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission SpectrometryDocument5 pagesDetermination of Titanium Dioxide in Commercial Sunscreens by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission SpectrometryHarySetiyawanNo ratings yet
- Fastron Gold 5w 30 API SNDocument2 pagesFastron Gold 5w 30 API SNTemanta TariganNo ratings yet
- Waters Cat17 18en SpeDocument38 pagesWaters Cat17 18en SpeG_ASantosNo ratings yet
- Northern Black Polished Ware in IndiaDocument19 pagesNorthern Black Polished Ware in IndiaMohit Sony100% (1)
- Enzyme PPT 12 PDFDocument42 pagesEnzyme PPT 12 PDFAnonymous wY9ogndU100% (1)
- Handbook of Research On Nanoscience, Nanotechnology, and Advanced Materials (2014) PDFDocument642 pagesHandbook of Research On Nanoscience, Nanotechnology, and Advanced Materials (2014) PDFJae Choi100% (1)
- DIAB Guide To Core and Sandwich P1r2 LockedDocument48 pagesDIAB Guide To Core and Sandwich P1r2 LockedM.Sreeram SanjayNo ratings yet
- ENGR 313 - Chapter 4 - DislocationsDocument48 pagesENGR 313 - Chapter 4 - DislocationsMelissa LaraNo ratings yet
- Extended SurfacesDocument13 pagesExtended SurfacesDirkMyburghNo ratings yet
- 1600060Document4 pages1600060danyNo ratings yet
- Spectrophotometric Determination of Salicylamide and ParacetamolDocument6 pagesSpectrophotometric Determination of Salicylamide and Paracetamoliabureid7460No ratings yet
- Q5 SolutionDocument18 pagesQ5 Solutionadrian_xianNo ratings yet
- Atomic and Molecular Physics - NET-JRFDocument25 pagesAtomic and Molecular Physics - NET-JRFLineesh100% (1)
- Introduction To UT Flaw DetectorDocument26 pagesIntroduction To UT Flaw DetectorNail Widya Satya100% (1)
- Allosteric EnzymeDocument22 pagesAllosteric EnzymeAhmed ImranNo ratings yet
- MetallurgyDocument2 pagesMetallurgygjabyNo ratings yet
- Who Took Jerell'S Ipod? - An Organic: Compound MysteryDocument8 pagesWho Took Jerell'S Ipod? - An Organic: Compound Mysteryakm1187No ratings yet