Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan: Nursing and Health Sciences Department
Uploaded by
JuliusSerdeñaTrapal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
442 views6 pagesNCP
Original Title
NCP.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentNCP
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
442 views6 pagesNursing Care Plan: Nursing and Health Sciences Department
Uploaded by
JuliusSerdeñaTrapalNCP
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Republic of the Philippines
Naval State University
College of Arts and Sciences
NURSING AND HEALTH SCIENCES DEPARTMENT
Naval, Biliran
NURSING CARE PLAN
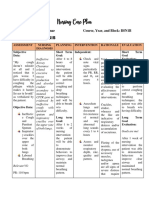
NAME: Duba, Erlinda SEX: Female AGE: 70 years old WARD: Medical DATE: 08 13 17 SHIFT: 7:00am 3:00pm
DIAGNOSIS: CAP MR, BAIAE CHIEF COMPLAINTS: Fever, cough and difficulty of breathing PHYSICIAN: Dr. Sabornido
CUES NURSING DIAGNOSIS SCIENTIFIC ANALYSIS OBJECTIVES NURSING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective: Impaired gas exchange Community- General:
maglisod kog ginhawa related to alveolar acquired pneumonia (CAP) After two days of
as verbalized by the capillary membrane is a disease in which nursing intervention,
patient. changes such as individuals who have not the client will be able
pneumoconiosis as recently been hospitalized to demonstrate
Objective: evidenced by difficulty of develop an infection of improved ventilation
- Dry cough breathing, respiratory the lungs (pneumonia). and oxygenation of
- Pale appearance rate of 25 cycles per tissues within clients
- Restless minute, pulse rate of 98 CAP is a common illness normal limits.
- Difficulty beats per minute, and can affect people of all
Sleeping restless, cough and pale ages. CAP often causes Specific: Independent:
- Difficulty of in appearance. problems like difficulty in After eight hours of 1. Evaluate the clients vital 1. To assess respiratory
breathing breathing, fever, chest nursing interventions, capacity insufficiency
- Disturbed pains, and a cough. CAP the client will be able
thoughts and occurs because the areas to show: 2. Assist the client in a 2. Facilitate easier
feelings of the lung which absorb - clear breath semi-fowlers position breathing
- Facial grimace oxygen (alveoli) from the sounds
- Oxygen via atmosphere become filled - eliminate 3. Emphasize adequate rest 3. Promotes comfort
cannula with fluid and cannot work dyspnea
- V/S: effectively - respiratory
T 35.8 rate of <20
ACTUAL NURSING DIAGNOSIS
P 98 bpm Pneumonia also is the cycles per 4.Encourage adequate oral 4. Helps liquefy secretions
R 25 cpm inflammation of the lung minute fluid intake of 2000 ml per
BP 90/70mmhg parenchyma caused by - relaxation to day
various microorganisms, condition
including bacteria, 5.Have stand by oxygen 5.For emergency use
mycobacteria, chlamydiae,
mycoplasma, fungi, Dependent:
parasites and viruses. As 6. Administer mucolytics as 6. Decreases mucus
the lung parenchyma and prescribed. viscosity
alveoli of the lungs are
inflamed it impairs gas 7. Administer antibiotics, as 7. Avoids further
exchange due to the ordered and monitor for multiplication of
alterations in the alveoli side effects microorganisms.
which is the site for actual
gas exchange. 8. Administer 8. Helps enhance passage
bronchodilator as of air to the airway.
Source: recommended.
Black, Hawks and Keene,
Medical Surgical Nursing
6th Edition, Volume 1,
page 225.
ACTUAL NURSING DIAGNOSIS
Republic of the Philippines
Naval State University
College of Arts and Sciences
NURSING AND HEALTH SCIENCES DEPARTMENT
Naval, Biliran
NURSING CARE PLAN
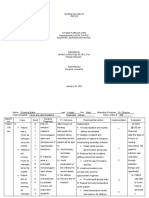
NAME: Duba, Erlinda SEX: Female AGE: 70 years old WARD: Medical DATE: 08 13 17 SHIFT: 7:00am 3:00pm
DIAGNOSIS: CAP MR, BAIAE CHIEF COMPLAINTS: Fever, cough and difficulty of breathing PHYSICIAN: Dr. Sabornido
CUES NURSING DIAGNOSIS SCIENTIFIC ANALYSIS OBJECTIVES NURSING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective: Ineffective airway When an infectious Specific: Independent:
Naa koy ubo as clearance related to particles reach the sterile After eight hours of 1. Monitor respirations and 1. Indicative of respiratory
verbalized by the patient. excessive mucous lower respiratory tract, an nursing intervention breath sounds noting rate distress/ accumulation of
production. inflammatory response the client will be able and sounds. secretion.
Objective: develop thus producing to:
- Dry cough exudates that interferes - Maintain 2. Position head 2. To maintain open airway
- Pale appearance with diffusion of oxygen patent, appropriately forage/ in at rest or compromised
- Restless and carbon dioxide areas adequate condition. individuals.
- Difficulty of of the lungs are not airway.
breathing adequately ventilated 3. Suction secretion as 3. To clear airway when
- Facial grimace because of secretions and needed. excessive secretions that
- Oxygen via mucosal edema and the are blocking the airway.
cannula client experience
- V/S: difficulty of breathing. Collaborative:
T 35.8 4. Give expectorant/ 4. To mobilize secretions to
P 98 bpm bronchodilator (Salbutamol improve respiratory
R 25 cpm neb) function and gas exchange.
BP 90/70mmhg
ACTUAL NURSING DIAGNOSIS
Source: 5. Give O2 inhalation 5. To aid in breathing.
Medical Surgical 6. Give antibiotic as 6. To treat the underlying
Nursing, 11th edition by ordered. cause of illness.
Suddarth, page 550.
7. Infuse IVF. 7. To help loosen secretion.
ACTUAL NURSING DIAGNOSIS
Republic of the Philippines
Naval State University
College of Arts and Sciences
NURSING AND HEALTH SCIENCES DEPARTMENT
Naval, Biliran
NURSING CARE PLAN
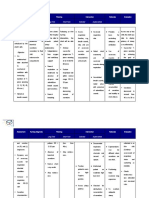
NAME: Duba, Erlinda SEX: Female AGE: 70 years old WARD: Medical DATE: 08 13 17 SHIFT: 7:00am 3:00pm
DIAGNOSIS: CAP MR, BAIAE CHIEF COMPLAINTS: Fever, cough and difficulty of breathing PHYSICIAN: Dr. Sabornido
CUES NURSING DIAGNOSIS SCIENTIFIC ANALYSIS OBJECTIVES NURSING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective: Acute pain related to Pneumonia is Specific: Independent:
masakit akong dughan localized inflammation inflammation of the After 8 hours of 1. Elevate head of the bed, 1. Lowers diaphragm,
kung muubo ko as and persistent cough terminal airways and nursing interventions, change position frequently. promoting chest expansion
verbalized by the patient. alveoli caused by acute the patient will display and expectoration of
infection by various patent airway with secretions.
Objective: agents. Pneumonia can be breath sounds clearing
- Dyspnea divided into three groups: and absence of 2. Assist patient with deep 2. Deep breathing
- Fatigue community acquired, dyspnea. breathing exercises. facilitates maximum
- Restless hospital or nursing home expansion of the lungs and
- Dry cough acquired (nosocomial), smaller airways.
- Pale appearance and pneumonia in an
- V/S taken as immunocompromised 3. Demonstrate or help 3. Coughing is a natural
follows: person. Causes include patient learn to perform self-cleaning mechanism.
T- 35.8 bacteria (Streptococcus, activity like splinting chest Splinting reduces chest
P- 98 Staphylococcus, and effective coughing discomfort, and an upright
R- 25 Haemophilus influenzae, while in upright position. position favors deeper,
BP- 90/70mmHg Klebsiella, Legionella). more forceful cough effort.
Community Acquired
Pneumonia (CAD) is a 4. Force fluids to at least 4. Fluids especially warm
disease in which 2000 ml per day and offer liquids aid in mobilization
individuals who have not
ACTUAL NURSING DIAGNOSIS
recently been hospitalized warm, rather than cold and expectoration of
develop an infection of fluids secretions.
the lungs. It is an acute
inflammatory condition
thats result from Collaborative:
aspiration of 5. Administer medications 5. Aids in reduction of
oropharyngeal secretions as prescribe: mucolytics or bronchospasm and
or stomach contents in expectorants. mobilization of secretions.
the lungs.
6. Provide supplemental 6. Fluids are required to
Source: fluids. replace losses and aid in
Medical Surgical mobilization of secretions.
Nursing, 11th edition by
Suddarth, page 600.
ACTUAL NURSING DIAGNOSIS
You might also like
- Nursing Informatics 101 PDFDocument62 pagesNursing Informatics 101 PDFhatemfaroukNo ratings yet
- Prediction TheoryDocument90 pagesPrediction TheoryJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNo ratings yet
- Music and Translation: Palgrave Studies IN Translating AND InterpretingDocument417 pagesMusic and Translation: Palgrave Studies IN Translating AND InterpretingBen Nyaman0% (1)
- NCP Fdar Fin.Document8 pagesNCP Fdar Fin.Bissette DomingoNo ratings yet
- Sample FNCPDocument90 pagesSample FNCPmuddVayne89% (19)
- FNCPDocument4 pagesFNCPJuliusSerdeñaTrapal100% (1)
- Bleeding NCPDocument13 pagesBleeding NCPBiway Regala100% (1)
- Chenrezig MeditationDocument2 pagesChenrezig MeditationMonge DorjNo ratings yet
- Explanation LetterDocument1 pageExplanation LetterJuliusSerdeñaTrapal0% (1)
- NCP Gastritis NewDocument3 pagesNCP Gastritis NewNova Triska Purnama Sari0% (1)
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument2 pagesNCP HyperthermiaMeljonesDaanNo ratings yet
- CS5 (AGE) Acute Gastroenteritis NCPDocument2 pagesCS5 (AGE) Acute Gastroenteritis NCPAudrie Allyson GabalesNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease ManagementDocument3 pagesChronic Kidney Disease ManagementAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- DNA Molecule & Central DogmaDocument43 pagesDNA Molecule & Central DogmaJoanna Ruth SeproNo ratings yet
- Statement of The Problem and HypothesisDocument6 pagesStatement of The Problem and HypothesisCharmaine Jhane BaseNo ratings yet
- English5 - q1 - Mod2 - Lesson1 - Inferring Meaning of Compound Words Using Context Clues - v3Document20 pagesEnglish5 - q1 - Mod2 - Lesson1 - Inferring Meaning of Compound Words Using Context Clues - v3Wes33% (3)
- Module 1 Guidelines in Giving Emergency CareDocument2 pagesModule 1 Guidelines in Giving Emergency CareJuliusSerdeñaTrapal100% (4)
- NCP DizzinessDocument2 pagesNCP Dizzinesschristine mercadoNo ratings yet
- Sample Statement of Purpose Computer Engineering (SOP)Document1 pageSample Statement of Purpose Computer Engineering (SOP)theonlybbb86% (7)
- Deficient Fluid Volume (Vanene)Document7 pagesDeficient Fluid Volume (Vanene)jajalerNo ratings yet
- Community Acquired Pneumonia Nursing Care Plan: Demonstrate Pursed-Lip and Diaphragmatic Breathing To The PatientDocument4 pagesCommunity Acquired Pneumonia Nursing Care Plan: Demonstrate Pursed-Lip and Diaphragmatic Breathing To The PatientKrisianne Mae Lorenzo Francisco100% (1)
- Nonaka and Takeuchi Knowledge Spiral ModelDocument18 pagesNonaka and Takeuchi Knowledge Spiral ModelkangdediNo ratings yet
- NCP - BronchopneumoniaDocument11 pagesNCP - BronchopneumoniaMaria Ivy Mendoza100% (1)
- Cap NCPDocument6 pagesCap NCPMarlo Parayno100% (2)
- Scientific Analysis Goal: Goal:: Subjective CuesDocument2 pagesScientific Analysis Goal: Goal:: Subjective CuesChloie Marie RosalejosNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- ANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationEdrianne Tui100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan: Cystic FibrosisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cystic FibrosisYael EzraNo ratings yet
- Definition of The Case + Hyperthermia NCPDocument2 pagesDefinition of The Case + Hyperthermia NCPCindy MariscotesNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing GunshotDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing GunshotMikko Enoc100% (1)
- Assessment Subjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As VerbalizedDocument2 pagesAssessment Subjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As Verbalizedmayla_jordan3666No ratings yet
- AAAAA Altered-Body-Temp-NCPDocument2 pagesAAAAA Altered-Body-Temp-NCPMoi ValdozNo ratings yet
- NafarinDocument2 pagesNafarinianecunar100% (2)
- Case Study NCP ActualDocument3 pagesCase Study NCP Actualdhamy florNo ratings yet
- LacipilDocument2 pagesLacipilianecunarNo ratings yet
- NCA2 PosttestsDocument20 pagesNCA2 PosttestsCzarena Ysabelle PayotNo ratings yet
- Iloilo Doctors' College Nursing Care Plan for Anaphylactic ShockDocument7 pagesIloilo Doctors' College Nursing Care Plan for Anaphylactic ShockAbie Jean BalbontinNo ratings yet
- NCP T2DMDocument5 pagesNCP T2DMFrancym R. BatengaNo ratings yet
- NCP H MoleDocument6 pagesNCP H MoleMina RacadioNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care Planrois romaNo ratings yet
- Tarasoff CaseDocument2 pagesTarasoff Casealyssa marie salcedo100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Tissue InjuryDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Tissue InjuryJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- BFC NCPDocument2 pagesBFC NCPMonica Melo HernandezNo ratings yet
- Medication ThalassemiaDocument3 pagesMedication ThalassemiaDivya ToppoNo ratings yet
- Learning About Pediatric Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument2 pagesLearning About Pediatric Urinary Tract InfectionsNickaela CalalangNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For InflammationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For InflammationJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- NCP 2Document3 pagesNCP 2klawdin100% (1)
- D."Parang Giniginaw Man Ako" As Verbalized, Patient CoversDocument1 pageD."Parang Giniginaw Man Ako" As Verbalized, Patient CoversSherena NicolasNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Managing HyperthermiaDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan for Managing Hyperthermiamimingdot33No ratings yet
- Assessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationimnasNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan On SepsisDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan On SepsisleoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ADocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan ACrystal WyattNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilitiesangel cenaNo ratings yet
- NCP BMDocument1 pageNCP BMSourabh MehraNo ratings yet
- Ketorolac DRUG STUDYDocument3 pagesKetorolac DRUG STUDYA.No ratings yet
- NCP For Swine FluDocument3 pagesNCP For Swine FluGiana CalloNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBMa. Elaine Carla Tating0% (1)
- Nursing Assessment Rationale and InterventionsDocument7 pagesNursing Assessment Rationale and InterventionsPJNo ratings yet
- DRUG Kalium Durule (Potasium Chloride)Document1 pageDRUG Kalium Durule (Potasium Chloride)rholiboiNo ratings yet
- Degenerative Diseases NCMB316 SEC1 AMENINDocument4 pagesDegenerative Diseases NCMB316 SEC1 AMENINHermin TorresNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesActivity IntoleranceJaney Ceniza تNo ratings yet
- NCP Raynauds Disease-Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Raynauds Disease-Acute PainEerie EraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceCaroline ChaNo ratings yet
- Elena Ocyo (Pedia - NCP)Document3 pagesElena Ocyo (Pedia - NCP)elle leliNo ratings yet
- NCP: Acute GastroenteritisDocument3 pagesNCP: Acute GastroenteritishauteanicoleNo ratings yet
- Ivf StudyDocument2 pagesIvf StudyDanePepitoNo ratings yet
- Pain NCP BillrothDocument2 pagesPain NCP BillrotharjayNo ratings yet
- Discharge PlanDocument3 pagesDischarge PlanDranlie LagdamenNo ratings yet
- Problem List Cues Problems Priority JustificationDocument3 pagesProblem List Cues Problems Priority JustificationgrazheNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SARAHDocument2 pagesDrug Study SARAHirene Joy DigaoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan & Drug Study Set #1: PneumoniaDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan & Drug Study Set #1: PneumoniaBakushidoNo ratings yet
- NCP Week 6 Nrg301 ValenzonaDocument3 pagesNCP Week 6 Nrg301 ValenzonaJoshennaNo ratings yet
- Resume of Respiratory ProblemDocument5 pagesResume of Respiratory ProblemIbi Yulia SetyaniNo ratings yet
- Windows Keyboard Shortcuts OverviewDocument10 pagesWindows Keyboard Shortcuts OverviewJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNo ratings yet
- Windows Keyboard Shortcuts OverviewDocument10 pagesWindows Keyboard Shortcuts OverviewJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper About SDG and MDGDocument1 pageReaction Paper About SDG and MDGJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document4 pagesChapter 4JuliusSerdeñaTrapalNo ratings yet
- FNCP PrioritizationDocument1 pageFNCP PrioritizationJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document2 pagesChapter 1JuliusSerdeñaTrapalNo ratings yet
- Health ProblemDocument3 pagesHealth ProblemJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNo ratings yet
- Status and Acceptability of Concrete Gravity DamDocument54 pagesStatus and Acceptability of Concrete Gravity DamJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIIDocument3 pagesChapter IIIJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNo ratings yet
- Concrete Gravity Dam Profile and AcceptabilityDocument4 pagesConcrete Gravity Dam Profile and AcceptabilityJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNo ratings yet
- Agueh Cost EstimatesDocument6 pagesAgueh Cost EstimatesJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNo ratings yet
- Enzo AppendicesDocument7 pagesEnzo AppendicesJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNo ratings yet
- Concrete Gravity Dam Profile and AcceptabilityDocument4 pagesConcrete Gravity Dam Profile and AcceptabilityJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNo ratings yet
- Enzo AppendicesDocument7 pagesEnzo AppendicesJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNo ratings yet
- PreDocument8 pagesPreJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNo ratings yet
- Summary, Conclusion and RecommendationDocument13 pagesSummary, Conclusion and RecommendationJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNo ratings yet
- Status and Acceptability of The Concrete Gravity Dam in Culaba, BiliranDocument1 pageStatus and Acceptability of The Concrete Gravity Dam in Culaba, BiliranAlex SilvanoNo ratings yet
- Status and Acceptability of Concrete Gravity Dam in Culaba, BiliranDocument1 pageStatus and Acceptability of Concrete Gravity Dam in Culaba, BiliranJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNo ratings yet
- Status and Acceptability of Concrete Gravity DamDocument54 pagesStatus and Acceptability of Concrete Gravity DamJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document3 pagesChapter 2JuliusSerdeñaTrapalNo ratings yet
- Concrete Gravity Dam Profile and AcceptabilityDocument4 pagesConcrete Gravity Dam Profile and AcceptabilityJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document9 pagesChapter 1JuliusSerdeñaTrapalNo ratings yet
- Status and Acceptability of The Concrete Gravity Dam in Culaba, BiliranDocument1 pageStatus and Acceptability of The Concrete Gravity Dam in Culaba, BiliranAlex SilvanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document9 pagesChapter 1JuliusSerdeñaTrapalNo ratings yet
- Family Breakdown PDFDocument11 pagesFamily Breakdown PDFSamantha GordonNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ SỐ 2Document3 pagesĐỀ SỐ 2Nguyễn Kiều OanhNo ratings yet
- 2013 Ecpe Class Final Test Grammar Structure Units 19 25 KeyDocument12 pages2013 Ecpe Class Final Test Grammar Structure Units 19 25 KeyLet Banis FloresNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan in Technology and Livelihood Education 9 Agricultural Crop Production Week 6 Day 1 I. ObjectivesDocument6 pagesDaily Lesson Plan in Technology and Livelihood Education 9 Agricultural Crop Production Week 6 Day 1 I. ObjectivesMike Lyster AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Experimental Research - Research DesignDocument15 pagesExperimental Research - Research Designvanilla_42kpNo ratings yet
- Pancasila Character EducationDocument6 pagesPancasila Character EducationDaniel Prayoga D100% (1)
- Summary of PBB 2019 data for Region IX elementary schoolsDocument35 pagesSummary of PBB 2019 data for Region IX elementary schoolsVIRGILIO GUZONNo ratings yet
- Tarah Viviano Revised Resume 2016Document2 pagesTarah Viviano Revised Resume 2016api-314537209No ratings yet
- 1.4 Components of Ethology: InstinctDocument7 pages1.4 Components of Ethology: InstinctAndreea BradNo ratings yet
- Dustin Resume 7 10 14Document1 pageDustin Resume 7 10 14api-270322257No ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineer ResumeDocument3 pagesMechanical Engineer ResumeHimanshu ChauhanNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument108 pagesThesisDebasis PandaNo ratings yet
- Research ProposalDocument11 pagesResearch Proposalkugan100% (2)
- Selection 6th 5 in 1 EM Term - 1Document64 pagesSelection 6th 5 in 1 EM Term - 1Jeeva BharathiNo ratings yet
- Cubeta Philosophy Managment LIBR204 081210bDocument18 pagesCubeta Philosophy Managment LIBR204 081210bjesscubesNo ratings yet
- Immersion Portfolio: Submitted By: Montebon, Maylyn R Submitted To: Remolado, Jan Michael RDocument19 pagesImmersion Portfolio: Submitted By: Montebon, Maylyn R Submitted To: Remolado, Jan Michael RBashier AmenNo ratings yet
- 9701 w13 QP 35 2 PDFDocument12 pages9701 w13 QP 35 2 PDFNeural Spark Physics CieNo ratings yet
- Ethical Issues in Multicultural PopulationsDocument19 pagesEthical Issues in Multicultural Populationsapi-162851533No ratings yet
- Spanish 2 Examen Final Presentacion Dia 1Document20 pagesSpanish 2 Examen Final Presentacion Dia 1api-263267469No ratings yet
- Sample 10762Document16 pagesSample 10762Nayanjyot SinghNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Learners' Difficulties in Writing ParagraphsDocument26 pagesGrade 8 Learners' Difficulties in Writing ParagraphsBetel Niguse100% (2)
- 2011 Thesis Guidelines Media StudiesDocument3 pages2011 Thesis Guidelines Media StudiesAshiq Jahan KhondkerNo ratings yet
- JLPT Sensei - n5 Grammar List v2Document3 pagesJLPT Sensei - n5 Grammar List v2Łukasz ZiomekNo ratings yet