Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Machine Elements Design: Screwed Fasteners, Welded Joints
Uploaded by
mukeshmystOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Machine Elements Design: Screwed Fasteners, Welded Joints
Uploaded by
mukeshmystCopyright:
Available Formats
Design of Machine Elements Part-A
1. What are the different applications of screwed fasteners?
2. What are the advantages of screwed fasteners?
3. Define pitch.
4. What are the types of welded joints?
5. Define butt and lap joint
6. Define Caulking and Fullering
7. What are the advantages of Riveted joints over the Welded Joints?
8. Explain the Knuckle joint and Cotter Joint.
9. State the two types of eccentric welded connections.
10. What stresses act on screw fastenings?
Part-B
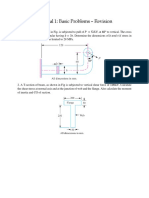
1. A rectangular cross-section bar is welded to a support by means of fillet welds as shown in
Fig. Determine the size of the welds, if the permissible shear stress in the weld is limited to 75
MPa. All dimensions in mm.
2. A rectangular steel plate is welded as a cantilever to a vertical column and supports a single
concentrated load P, as shown in Fig. Determine the weld size if shear stress in the same is not
to exceed 140 MPa. All dimensions in mm .
3. Design and draw a cotter joint to support a load varying from 30 kN in compression to 30 kN
in tension. The material used is carbon steel for which the following allowable stresses may be
used. The load is applied statically. Tensile stress = compressive stress = 50 MPa ; shear stress =
35 MPa and crushing stress= 90 MPa.
4. Design a knuckle joint to transmit 150 kN. The design stresses may be taken as75 MPa in
tension, 60 MPa in shear and 150 MPa in compression.
5. Design a double riveted butt joint with two cover plates for the longitudinal seam of a boiler
shell 1.5 m in diameter subjected to a steam pressure of 0.95 N/mm2. Assume joint efficiency as
75%, allowable tensile stress in the plate 90 MPa ; compressive stress 140 MPa ; and shear
stress in the rivet 56 MPa
You might also like
- Dme Home Assignment 2019-20Document4 pagesDme Home Assignment 2019-20VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Machine Design & Industrial Drafting SUBJECT CODE:-2141907 Tutorial - 01Document10 pagesMachine Design & Industrial Drafting SUBJECT CODE:-2141907 Tutorial - 01The AIRS CreationsNo ratings yet
- MDID Machine Design GTU PaperDocument3 pagesMDID Machine Design GTU PaperjaydeepNo ratings yet
- MDDocument4 pagesMDਲਖਵੀਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਖਾਨਾNo ratings yet
- DME Chapter 2Document5 pagesDME Chapter 2dhananjayvermaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank MD IDocument15 pagesQuestion Bank MD IvsambardekarNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument14 pagesUNIT-1: Department of Mechanical EngineeringManivannan JeevaNo ratings yet
- Dme Quest Ut-2Document9 pagesDme Quest Ut-2aadhithyarajasekaranNo ratings yet
- Kings: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument14 pagesKings: Department of Mechanical EngineeringAdam AhmadNo ratings yet
- Tension Member Design & Structural Steel ConnectionsDocument17 pagesTension Member Design & Structural Steel ConnectionsAnuj Chandiwala100% (1)
- TE - 2019 - Design of Machine Elements PDFDocument4 pagesTE - 2019 - Design of Machine Elements PDFonkar nikamNo ratings yet
- Gtustudies - FMD IMP Question BankDocument5 pagesGtustudies - FMD IMP Question BankJaideep ZalaNo ratings yet
- DME 1 Question BankDocument5 pagesDME 1 Question BankRahul YedduNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1sonawanepmsNo ratings yet
- Exercises and REVIEW QUESTIONS 2018Document12 pagesExercises and REVIEW QUESTIONS 2018Thiên LongNo ratings yet
- DMM - I Question Bank For StudentsDocument11 pagesDMM - I Question Bank For StudentsDushyanthkumar DasariNo ratings yet
- DMM - I Question Bank For StudentsDocument11 pagesDMM - I Question Bank For StudentsDushyanthkumar DasariNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine ElementsDocument10 pagesDesign of Machine ElementsMahalingam NanjappanNo ratings yet
- Common Subject Code: Shivaji University, KolhapurDocument10 pagesCommon Subject Code: Shivaji University, Kolhapursatyamchgl2010No ratings yet
- dmm1 PDFDocument9 pagesdmm1 PDFmohan_rapaka6095No ratings yet
- DMM I Assignment 3 - 2Document4 pagesDMM I Assignment 3 - 2Konduru Vinay Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Power Screws and Welded JointsDocument23 pagesIntroduction to Power Screws and Welded JointssathiaNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 3 &4 B.Tech Mechanical Engineering Third YearDocument4 pagesAssignment No. 3 &4 B.Tech Mechanical Engineering Third Yearharish_kumar201301No ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityBhavesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Assignment 02 - Machine DesignDocument2 pagesAssignment 02 - Machine DesignRatan Sadanandan O MNo ratings yet
- Assignment 02Document2 pagesAssignment 02adhnan_rasheed0% (1)
- Mechanical Engineering Design QuestionsDocument4 pagesMechanical Engineering Design QuestionsSoham MisalNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Machine Design A: Numerical Problems: Problems On Pin, Cotter and Knuckle JointsDocument25 pagesQuestion Bank Machine Design A: Numerical Problems: Problems On Pin, Cotter and Knuckle Jointsamol pogakeNo ratings yet
- DME Question Bank - 3171917Document4 pagesDME Question Bank - 3171917fgyjnsv786No ratings yet
- Question Bank - DMEDocument6 pagesQuestion Bank - DMEBdhdhshNo ratings yet
- Machine Elements Question BankDocument3 pagesMachine Elements Question BanksonawanepmsNo ratings yet
- Screws, Fasteners, and Nonpermanent Joint DesignDocument5 pagesScrews, Fasteners, and Nonpermanent Joint DesignMohamed AshrafNo ratings yet
- Me331-Design of Machine Elements Unit Iii Design of Fasteners and JointsDocument21 pagesMe331-Design of Machine Elements Unit Iii Design of Fasteners and JointsMuthuvel MNo ratings yet
- MD Tut PDFDocument6 pagesMD Tut PDFNelsan PatelNo ratings yet
- Dss - Question BankDocument10 pagesDss - Question Bankapi-306484475No ratings yet
- ME 1302 - MACHINE DESIGN (5th Mech)Document7 pagesME 1302 - MACHINE DESIGN (5th Mech)Madhu MithaNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2020-21 MEE3001 TH VL2020210101665 Reference Material I 22-Oct-2020 Module 6 Couplings New 12Document40 pagesFALLSEM2020-21 MEE3001 TH VL2020210101665 Reference Material I 22-Oct-2020 Module 6 Couplings New 12AK PRODUCTIONSNo ratings yet
- B.Tech Exam Design of Machine Members QuestionsDocument8 pagesB.Tech Exam Design of Machine Members Questionsprk74No ratings yet
- QB Unit-3,4,5Document7 pagesQB Unit-3,4,5Agranshu BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Snist Dom Previous PaperDocument9 pagesSnist Dom Previous PaperKapil Siddhant DevulapalliNo ratings yet
- 14ME-3502 Assignment –II problem sheetDocument2 pages14ME-3502 Assignment –II problem sheetVenkateshNo ratings yet
- Draw The Stress - Strain Diagram For Mild Steel. Explain.: Unit - IDocument9 pagesDraw The Stress - Strain Diagram For Mild Steel. Explain.: Unit - IKomma Hema100% (1)
- QuestionsDocument11 pagesQuestionsSundara MoorthyNo ratings yet
- DME Question BankDocument4 pagesDME Question BankILAYAPERUMAL KNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1Document8 pagesUnit - 1Dhileepan KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- ME6503-Design of Machine Elements PDFDocument15 pagesME6503-Design of Machine Elements PDFkarthikNo ratings yet
- Me 6503 Design of Machine Elements QBDocument3 pagesMe 6503 Design of Machine Elements QBDeepak SNo ratings yet
- Steel Design Tutorials and AssignmentsDocument4 pagesSteel Design Tutorials and AssignmentsChirag N PatelNo ratings yet
- Dme Question BankDocument4 pagesDme Question BankRavi Patil100% (1)
- Machine Design-AC09Document7 pagesMachine Design-AC09Ashutosh RajawatNo ratings yet
- 1 Riveted Joints PDFDocument1 page1 Riveted Joints PDFHemanth ParisaNo ratings yet
- 1 Riveted JointsDocument1 page1 Riveted JointsHemanth ParisaNo ratings yet
- Mech-V-Design of Machine Elements I (10me52) - AssignmentDocument10 pagesMech-V-Design of Machine Elements I (10me52) - AssignmentArunNo ratings yet
- QB Unit-1,2Document5 pagesQB Unit-1,2Agranshu BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine ElementDocument30 pagesDesign of Machine ElementVigneswaran K100% (1)
- CE6603-Design of Steel StructuresDocument12 pagesCE6603-Design of Steel StructuresIsrael VenkatNo ratings yet
- Composite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsFrom EverandComposite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsNo ratings yet
- United India Insurance Company LimitedDocument10 pagesUnited India Insurance Company LimitedmukeshmystNo ratings yet
- WebinarDocument23 pagesWebinarmukeshmystNo ratings yet
- Deformation Behavior of The Polycarbonate Plates SDocument9 pagesDeformation Behavior of The Polycarbonate Plates SmukeshmystNo ratings yet
- Structural Dynamic Analysis of Car Exhaust System: June 2017Document72 pagesStructural Dynamic Analysis of Car Exhaust System: June 2017mukeshmystNo ratings yet
- Lec22 PDFDocument14 pagesLec22 PDFmukeshmystNo ratings yet
- Taguchi QeDocument36 pagesTaguchi QeEmad KhanNo ratings yet
- CFD in INDIADocument10 pagesCFD in INDIAmukeshmystNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Flow SimulationDocument322 pagesTutorial Flow SimulationJuliano André Petry100% (1)
- Dynamic Finite Element MethodsDocument29 pagesDynamic Finite Element MethodsVns VnsNo ratings yet
- 24 Sample ChapterDocument14 pages24 Sample ChapterRomyMohanNo ratings yet
- Me 6604 - Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion University Questions & Answers - April/May 2015 Part - ADocument7 pagesMe 6604 - Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion University Questions & Answers - April/May 2015 Part - AmukeshmystNo ratings yet
- DOM University Question PaperDocument3 pagesDOM University Question PapermukeshmystNo ratings yet
- Loveday Design 2006 PDFDocument146 pagesLoveday Design 2006 PDFmukeshmystNo ratings yet
- ACL TECH TALK: TORQUE TO YIELD HEAD BOLTS EXPLAINEDDocument2 pagesACL TECH TALK: TORQUE TO YIELD HEAD BOLTS EXPLAINEDEric LaPointeNo ratings yet
- 20 Torque To Yield HeadboltsDocument5 pages20 Torque To Yield HeadboltsmukeshmystNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgBuc9rV2ksRQR9flbvTNz9VS4wdNauJC2gaEIqDYAocPIBRYl9WIK4cH24MrnTQ4sKf hp8C-r4xlZMLjnGw5UIEhBgZzkN19O8OIVRshnUH8NMzxZn0UISxQ8Document48 pagesACFrOgBuc9rV2ksRQR9flbvTNz9VS4wdNauJC2gaEIqDYAocPIBRYl9WIK4cH24MrnTQ4sKf hp8C-r4xlZMLjnGw5UIEhBgZzkN19O8OIVRshnUH8NMzxZn0UISxQ8mukeshmystNo ratings yet
- Final Sar Report Saatha Civil PDFDocument238 pagesFinal Sar Report Saatha Civil PDFmukeshmystNo ratings yet
- Nptel For Beam & Shell PDFDocument10 pagesNptel For Beam & Shell PDFmukeshmystNo ratings yet
- Nptel For Beam & ShellDocument10 pagesNptel For Beam & ShellmukeshmystNo ratings yet
- SFAStirling Engine TemplatesDocument4 pagesSFAStirling Engine TemplatesEl GroneNo ratings yet
- Tamilnadu Engineering Colleges FDP Workshop Invitation Sent DetailsDocument22 pagesTamilnadu Engineering Colleges FDP Workshop Invitation Sent DetailsmukeshmystNo ratings yet