Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MS PDF
Uploaded by
KareemAmenOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MS PDF
Uploaded by
KareemAmenCopyright:
Available Formats
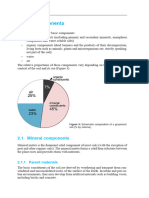
Silicate subgroups are all based on the structural arrangement of the silica tetrahedra in the crystal lattice.
The
importance of most silicate minerals is in their abundance: silicates comprise >95% of the total mass of the Earth's
crust. (Minerals in bold face are those we will study in the laboratory.)
Subgroup General structure Examples Occurrence & uses
Framework complex 3-dimensional quartz (SiO2) occurs in many rocks, very common
silicates framework many industrial uses; base for glass
manufacturing
feldspars: over 50% of entire crust !!!!
orthoclase (KAlSi3O8) plutonic and metamorphic rocks
microcline (KAlSi3O8) plutonic igneous rocks
sanidine (KAlSi3O8) silica-rich volcanic rocks
plagioclase
albite (NaAlSi3O8) silica-rich igneous & metamorphic
rocks
anorthite (CaAl2Si2O8) silica-poor igneous &
metamorphic rocks
oligoclase is sodium-rich: 70-90% albite; 10-30% anorthite
labradorite is calcium-rich: 30-50% albite; 50-70% anorthite
Sheet strong sheet structures, micas igneous and metamorphic rocks
silicates bonds between sheets muscovite (K-mica) plutonic and metamorphic rocks
weak biotite (K-Fe-Mg-mica) plutonic and metamorphic rocks;
rare in volcanics
chlorite (Fe-Mg-mica) metamorphic rocks, soils on
ultramafic intrusives
clay minerals form by weathering of other
silicates; critical in soils;
used in ceramics, paper, and
many other industrial uses
Major silicate subgroups and minerals ... Page 2 ...
Subgroup General structure Examples Occurrence & uses
Chain tetrahedra in chains
silicates single chains: pyroxenes augite (complex iron silica-poor igneous & metamorphic
silicate) rocks
double chains: amphiboles hornblende (complex silica-rich igneous and high-grade
(have water in structure) iron silicate) metamorphic rocks
actinolite (complex
Ca-Fe silicate) metamorphic rocks
Sorosilicates tetrahedra in pairs epidote (complex common alteration product in
calcium silicate) rocks, esp. igneous rocks
Ring silicates tetrahedra arranged beryl (a beryllium beryllium ore; gems (aquamarine,
in rings silicate) true emerald)
tourmaline (very minor industrial use; mostly
complex formula) gemstones (Maine state mineral)
Island silicates tetrahedra unattached to Olivine (Mg,Fe)2SiO4 silica-poor igneous rocks
each other directly; Staurolite (complex Al-rich metamorphic rocks
linked by metallic cations Ca-Al silicate)
between tetrahedra Garnet [M3M2(SiO4)3] (M=Fe,Mg,Al,Ca,Mn,Cr) variable
composition; found in
metamorphic rocks; used for
abrasives and gemstones
Zircon (ZrSiO4) usually some U replaces Zr; source
for radon gas in environment;
occurs in granitic and silica-rich
volcanic rocks; zirconium ore &
"cubic zirconia" gemstone
{ Kyanite (Al2SiO5) } {These three minerals, all with the
{ Andalusite (Al2SiO5) } same chemical formula, are found
{ Sillimanite (Al2SiO5) } in metamorphic rocks, and are
extremely useful for determining
the pressure and temperature of
recrystallization.}
You might also like
- Minerals - SilicatesDocument2 pagesMinerals - SilicatesER NurNo ratings yet
- Minerals - SilicatesDocument2 pagesMinerals - SilicateshNo ratings yet
- Sedimentary Rocks2Document254 pagesSedimentary Rocks2yovieNo ratings yet
- Aggregates in ConcreteDocument14 pagesAggregates in ConcreterajasekharNo ratings yet
- Kristal Dan Mineral - Asrim - 13 - Mineral SilikatDocument19 pagesKristal Dan Mineral - Asrim - 13 - Mineral SilikatEigerNo ratings yet
- Economic Geology: Introduction to Earth's Valuable Mineral ResourcesDocument16 pagesEconomic Geology: Introduction to Earth's Valuable Mineral ResourcesRananjay SinghNo ratings yet
- Borile Crystaline Bsam2b Soil100 Output1Document6 pagesBorile Crystaline Bsam2b Soil100 Output1Crystaline Ann B. BorileNo ratings yet
- Origins of Soils Lab ReportDocument6 pagesOrigins of Soils Lab ReportCrystaline Ann B. BorileNo ratings yet
- Materi 05 Endapan Magmatik CairDocument55 pagesMateri 05 Endapan Magmatik CairNandika Reza Faisal100% (2)
- Rock Forming MineralsDocument14 pagesRock Forming MineralsRense Jun PunsalanNo ratings yet
- Rocks and MineralsDocument38 pagesRocks and MineralsJuliah PeñalosaNo ratings yet
- Alunan, Jorbelle Dane A.Document3 pagesAlunan, Jorbelle Dane A.JORBELLE DANE ALUNANNo ratings yet
- Pràctica 9 - EnglishDocument15 pagesPràctica 9 - EnglishGhislainarrowNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Design Concentration of Talc by Emphasis On Mineralogy in The Malhamdar Index Mine in IranDocument5 pagesPreliminary Design Concentration of Talc by Emphasis On Mineralogy in The Malhamdar Index Mine in IranminingnovaNo ratings yet
- Residual Concentration Rev2016Document7 pagesResidual Concentration Rev2016Naomi Deirdre ReyesNo ratings yet
- Geol Resources Lecture 15 (Greisen SN-W and Pegmatites)Document29 pagesGeol Resources Lecture 15 (Greisen SN-W and Pegmatites)ArchieBunneyNo ratings yet
- 3-4. SST3005. Rocks and Minerals. KHMYDocument40 pages3-4. SST3005. Rocks and Minerals. KHMYFARAH HIDAYAHNo ratings yet
- EC571 Geotechs Lecture 8 - 2018 - 19 - Geoll EnviroDocument9 pagesEC571 Geotechs Lecture 8 - 2018 - 19 - Geoll EnviroPimpa MwiingaNo ratings yet
- Extrait - Essentiels of Soil SciencesDocument20 pagesExtrait - Essentiels of Soil SciencesMohamed EL BAGHDADINo ratings yet
- Ore Textures-Mid-Term Exam PDFDocument14 pagesOre Textures-Mid-Term Exam PDFkishan kumarNo ratings yet
- Atlas MineragrafiaDocument232 pagesAtlas MineragrafiaLaura RamirezNo ratings yet
- Rock Forming Minerals for Civil EngineersDocument61 pagesRock Forming Minerals for Civil EngineersInnocent RevocatusNo ratings yet
- DAY#03Document35 pagesDAY#03jeonghany727No ratings yet
- Cve 306 - 1 - Origin of SoilsDocument7 pagesCve 306 - 1 - Origin of SoilsUduebor MichealNo ratings yet
- GMBL2021 LDS OrthoMagmaticDeposits-minDocument45 pagesGMBL2021 LDS OrthoMagmaticDeposits-minPandu Deya AnankeNo ratings yet
- Eight 98%: Only Elements Make Up Over of The Earth's CrustDocument23 pagesEight 98%: Only Elements Make Up Over of The Earth's CrustD KrishanaNo ratings yet
- Non-Renewable Mineral ResourcesDocument32 pagesNon-Renewable Mineral Resourcessarah nabilaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document15 pagesAssignment 2AmyNo ratings yet
- Or To Magmatic OsDocument31 pagesOr To Magmatic Oslyo lyoNo ratings yet
- Important Building StoneDocument13 pagesImportant Building StoneGIRISHVARAN BNo ratings yet
- Igneous RocksDocument64 pagesIgneous RocksNishitaNo ratings yet
- Geology and Drilling TheoryDocument20 pagesGeology and Drilling TheoryJose Antonio Sanchez SegoviaNo ratings yet
- MineralsDocument41 pagesMineralsalbert pontusNo ratings yet
- Limestone and MarbleDocument5 pagesLimestone and MarbleWem TijNo ratings yet
- Rocks and MineralsDocument11 pagesRocks and MineralsPrincess AceroNo ratings yet
- Minerals & Rocks: Are They Important?Document33 pagesMinerals & Rocks: Are They Important?sophia gloriosoNo ratings yet
- Origin of Igneous Rocks and Associated OresDocument13 pagesOrigin of Igneous Rocks and Associated OresIgnatia ArinaNo ratings yet
- Nanzyo-Kanno2018 Chapter PrimaryMineralsDocument25 pagesNanzyo-Kanno2018 Chapter PrimaryMineralsGunasekarNo ratings yet
- Magmatic Ore-Forming Processes - Additional LectureDocument107 pagesMagmatic Ore-Forming Processes - Additional LectureRalph Carlo EvidenteNo ratings yet
- Endapan SkarnDocument40 pagesEndapan SkarnFrans AndersonNo ratings yet
- List of The Rock-Forming MineralsDocument20 pagesList of The Rock-Forming Mineralsroshan_geo07889667% (3)
- Name-Avinash Upadhyay Class - M.SC. 3RD SEM. Roll No. - 04 Sub. - Ore Geology Session - 2019-2021 Year - 2021Document10 pagesName-Avinash Upadhyay Class - M.SC. 3RD SEM. Roll No. - 04 Sub. - Ore Geology Session - 2019-2021 Year - 2021Avinash UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Earth Resources EngineeringDocument25 pagesEarth Resources EngineeringMohammed NazishNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Minerals RocksDocument8 pagesUnit 2 Minerals RocksMandora SGNo ratings yet
- Earth Materials: Rocks and MineralsDocument12 pagesEarth Materials: Rocks and MineralsCristina MaquintoNo ratings yet
- Minerals and RocksDocument24 pagesMinerals and Rocksmusic loverNo ratings yet
- GLY 206 NOTE 6 - NesosilicatesDocument5 pagesGLY 206 NOTE 6 - NesosilicatesOdebunmi PaulNo ratings yet
- Minerals and Rocks Lesson for Grade 11 StudentsDocument7 pagesMinerals and Rocks Lesson for Grade 11 StudentsSophia CabalhaoNo ratings yet
- Index Mineral of Metamorphic Rock: By:Florence Guzon and Jovan SenaresDocument29 pagesIndex Mineral of Metamorphic Rock: By:Florence Guzon and Jovan SenaresStalk Pa MoreNo ratings yet
- Processes of Sedimentary Rock FormationDocument28 pagesProcesses of Sedimentary Rock FormationPauline DejosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Clay MineralsDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Clay MineralsBijayan Pudasaini100% (1)
- Metamorphism ReviewerDocument29 pagesMetamorphism ReviewerMatthew RayNo ratings yet
- Cap 10 Interpretation of Granitc RocksDocument13 pagesCap 10 Interpretation of Granitc Rocks6m9jrdfyv9No ratings yet
- EG Unit IIDocument53 pagesEG Unit IISEKARNo ratings yet
- Shale: Devanarayanan EM I.Msc Applied GeologyDocument20 pagesShale: Devanarayanan EM I.Msc Applied GeologyDq DevanNo ratings yet
- Silica Group: Mi NeralogyDocument11 pagesSilica Group: Mi NeralogyCy RocamoraNo ratings yet
- Magmatic DepositsDocument70 pagesMagmatic Depositsdaveanthony100% (1)
- ES-Lesson 4 Rocks PDFDocument4 pagesES-Lesson 4 Rocks PDFTinetine Dizon MalqueridoNo ratings yet
- Aqaba City Census 2007 DataDocument3 pagesAqaba City Census 2007 DataKareemAmenNo ratings yet
- EIJGGS4009Document14 pagesEIJGGS4009KareemAmenNo ratings yet
- Mineral Deposit Classification GuideDocument2 pagesMineral Deposit Classification GuideKareemAmenNo ratings yet
- Oasis Montaj Best Practice Guide: VOXI Earth Modelling - Preparing Data For InversionDocument7 pagesOasis Montaj Best Practice Guide: VOXI Earth Modelling - Preparing Data For InversionKareemAmenNo ratings yet
- Kareem Muhammad Amin: ST STDocument2 pagesKareem Muhammad Amin: ST STKareemAmenNo ratings yet
- IDF ProcedureDocument5 pagesIDF ProcedurechrisNo ratings yet
- Spatial Prediction of Soil Attributes Using Terrain Analysis and Climate RegionalisationDocument16 pagesSpatial Prediction of Soil Attributes Using Terrain Analysis and Climate RegionalisationKareemAmenNo ratings yet
- Enum Instruct Jo2004 TagDocument50 pagesEnum Instruct Jo2004 TagKareemAmenNo ratings yet
- Accreditation: Acquire Practitioner (Acq2000) : What Is Involved With This Accreditation?Document2 pagesAccreditation: Acquire Practitioner (Acq2000) : What Is Involved With This Accreditation?KareemAmenNo ratings yet
- Assay Importing and QAQC (ACQ201) : Assignment OneDocument11 pagesAssay Importing and QAQC (ACQ201) : Assignment OneKareemAmenNo ratings yet
- General Background About The CensusDocument6 pagesGeneral Background About The CensusKareemAmenNo ratings yet
- Handout ImportantInformationDocument1 pageHandout ImportantInformationKareemAmenNo ratings yet
- Assay Importing and QAQC (ACQ201) : Assignment OneDocument11 pagesAssay Importing and QAQC (ACQ201) : Assignment OneKareemAmenNo ratings yet
- General Background About The CensusDocument6 pagesGeneral Background About The CensusKareemAmenNo ratings yet
- Handout - File Management Structure For AssignmentsDocument2 pagesHandout - File Management Structure For AssignmentsKareemAmenNo ratings yet
- Welcome: Instructor: Support Contact: Learning ContactDocument8 pagesWelcome: Instructor: Support Contact: Learning ContactKareemAmenNo ratings yet
- Amedjoe Adjovu 13Document14 pagesAmedjoe Adjovu 13KareemAmenNo ratings yet
- Main QVDocument1 pageMain QVKareemAmenNo ratings yet
- 10 TPH Cil Equipment-20171022Document10 pages10 TPH Cil Equipment-20171022KareemAmen100% (1)
- Geological Exploration Flowchart and SumDocument1 pageGeological Exploration Flowchart and SumKareemAmenNo ratings yet
- Facing Today'schallenges: Preparing For Tomorrow's OpportunitiesDocument2 pagesFacing Today'schallenges: Preparing For Tomorrow's OpportunitiesKareemAmenNo ratings yet
- Excutive Report CoverDocument1 pageExcutive Report CoverKareemAmenNo ratings yet
- ModellingDocument4 pagesModellingKareemAmenNo ratings yet
- Acquire Data ModelDocument1 pageAcquire Data ModelEfraim HermanNo ratings yet
- Basic Statistics of Geochemical Data AnalysisDocument3 pagesBasic Statistics of Geochemical Data AnalysisKareemAmenNo ratings yet
- Required Document For Design-20171022Document5 pagesRequired Document For Design-20171022KareemAmenNo ratings yet
- Field Guide For Preliminary Observation in An Exploration CampingDocument3 pagesField Guide For Preliminary Observation in An Exploration CampingKareemAmenNo ratings yet
- Egy SoilMapDocument1 pageEgy SoilMapKareemAmenNo ratings yet
- Metamorphic Core ComplexesDocument8 pagesMetamorphic Core ComplexesKareemAmenNo ratings yet
- Multivariate StatisticalDocument14 pagesMultivariate StatisticalKareemAmenNo ratings yet
- BPO UNIT - 5 Types of Securities Mode of Creating Charge Bank Guarantees Basel NormsDocument61 pagesBPO UNIT - 5 Types of Securities Mode of Creating Charge Bank Guarantees Basel NormsDishank JohriNo ratings yet
- Modern Indian HistoryDocument146 pagesModern Indian HistoryJohn BoscoNo ratings yet
- PC November 2012Document50 pagesPC November 2012bartekdidNo ratings yet
- For Coin & Blood (2nd Edition) - SicknessDocument16 pagesFor Coin & Blood (2nd Edition) - SicknessMyriam Poveda50% (2)
- SEMICONDUCTORS AssignmentDocument8 pagesSEMICONDUCTORS AssignmentMaryam MuneebNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Weekly Home Learning Plan Grade Ii Fourth Quarter Week 8Document8 pagesDepartment of Education: Weekly Home Learning Plan Grade Ii Fourth Quarter Week 8Evelyn DEL ROSARIONo ratings yet
- Clogging in Permeable (A Review)Document13 pagesClogging in Permeable (A Review)Chong Ting ShengNo ratings yet
- ExpDocument425 pagesExpVinay KamatNo ratings yet
- TLE8 Q4 Week 8 As Food ProcessingDocument4 pagesTLE8 Q4 Week 8 As Food ProcessingROSELLE CASELANo ratings yet
- ER DiagramDocument23 pagesER Diagramapi-2757091480% (20)
- Abinisio GDE HelpDocument221 pagesAbinisio GDE HelpvenkatesanmuraliNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument4 pagesDaftar PustakaRamli UsmanNo ratings yet
- Janome DC6030 Sewing Machine Instruction ManualDocument56 pagesJanome DC6030 Sewing Machine Instruction ManualiliiexpugnansNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument34 pagesIntroductionmarranNo ratings yet
- Irctc Tour May 2023Document6 pagesIrctc Tour May 2023Mysa ChakrapaniNo ratings yet
- Budget ControlDocument7 pagesBudget ControlArnel CopinaNo ratings yet
- 5505 SW 138th CT, Miami, FL 33175 ZillowDocument1 page5505 SW 138th CT, Miami, FL 33175 Zillowlisalinda29398378No ratings yet
- Translation EquivalenceDocument6 pagesTranslation EquivalenceJamal Anwar TahaNo ratings yet
- Driving Continuous Improvement by Developing and Leveraging Lean Key Performance IndicatorsDocument10 pagesDriving Continuous Improvement by Developing and Leveraging Lean Key Performance IndicatorskellendadNo ratings yet
- Diemberger CV 2015Document6 pagesDiemberger CV 2015TimNo ratings yet
- Corn MillingDocument4 pagesCorn Millingonetwoone s50% (1)
- Lanegan (Greg Prato)Document254 pagesLanegan (Greg Prato)Maria LuisaNo ratings yet
- BMS Technical ManualDocument266 pagesBMS Technical Manualiago manziNo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument64 pagesLaws of MotionArnel A. JulatonNo ratings yet
- (Bio) Chemistry of Bacterial Leaching-Direct vs. Indirect BioleachingDocument17 pages(Bio) Chemistry of Bacterial Leaching-Direct vs. Indirect BioleachingKatherine Natalia Pino Arredondo100% (1)
- Equipment, Preparation and TerminologyDocument4 pagesEquipment, Preparation and TerminologyHeidi SeversonNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning: Bilal KhanDocument26 pagesMachine Learning: Bilal KhanBilal KhanNo ratings yet
- 10 Slides For A Perfect Startup Pitch DeckDocument6 pages10 Slides For A Perfect Startup Pitch DeckZakky AzhariNo ratings yet
- Cisco CMTS Feature GuideDocument756 pagesCisco CMTS Feature GuideEzequiel Mariano DaoudNo ratings yet
- 5 Dec2021-AWS Command Line Interface - User GuideDocument215 pages5 Dec2021-AWS Command Line Interface - User GuideshikhaxohebkhanNo ratings yet