Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Blankenhagen-Larson-Taylor Stroke Brochure
Uploaded by
api-362395776Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Blankenhagen-Larson-Taylor Stroke Brochure
Uploaded by
api-362395776Copyright:
Available Formats
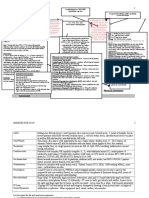
Stroke
What is a Stroke?
A stroke, also called a If the lack of blood lasts
cerebral vascular accident longer than 10 minutes,
(CVA), occurs when there is there may be brain death. Warning Signs
damage to or a block in a A stroke can leave a person of a Stroke
blood vessel that leads to the fully or partly paralyzed.
brain. This block lowers the Paralysis is when a person Trouble walking
amount of blood that gets to cannot feel or move parts Slurred speech
the brain. of their body. Feeling dizzy
Headaches
The blocked vessel
stops blood from
Numbness
getting to part of Blurry or lost
your brain. vision
Blocked blood
vessel
https://www.womenshealth.gov/publications/
our-publications/the-healthy-woman/stroke.pdf
What Puts You at Risk for Having a Stroke?
6.8 million Americans Main Risk Factors Factors that Raise Your
over the age of 20 for Stroke Risk for Stroke
have had a stroke.
Obesity Older age
Once you have had a High blood More common in women
stroke, your risk for pressure African American
having another one is Smoking background
higher. Diabetes Did not finish school
Heart disease Living in south-east parts
of the US
If you think someone is
having a stroke, call 9-1-1.
Things to do as you wait:
If they are awake:
- Put them on their side with something
under their head.
- Loosen tight clothes so they can
breathe easier.
- Do not give them food or drinks.
- Put something under weak arms or
legs to hold them up.
If they are not awake:
- Put them on their side.
- Look for breathing and feel for a
heartbeat.
- If there are no breaths or heartbeats,
put them on their back and start CPR.
http://dhhs.ne.gov/publichealth/HDSP/Pages/actfast.aspx
What Can Physical Therapy Do for You After a Stroke?
After a stroke, you might stay in a hospital or rehab center for a short time before going home. You
may see a physical therapist (PT) in the hospital and/or as an outpatient in a PT clinic based on how
much help you need to get better.
After a stroke you may have weakness and a hard time moving around on your own. The therapist
can help you get stronger and teach how to cope with any losses you may have.
What can you do by yourself? PT can work with you to reach your goals!
- Move around in bed - Stand without feeling weak
- Sit up in bed - Drive your own wheelchair
- Stand up from sitting - Change direction and speed of
- Get in/out of bed or chair walking without losing balance
- Stand without losing balance - Walk in the grocery store without
getting tired
http://www.cdc.gov/stroke/recovery.htm
Authors: Grace Blankenhagen, SPT, Stephanie Larson, SPT, Margaret Taylor, SPT; Central Michigan University
References
1. McKinley M, OLoughlin VD. Human Anatomy. 3rd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2011.
2. What to do while you wait for a stroke. Stroke Foundation Website. https://strokefoundation.com.au/About-Stroke/Stroke-symptoms/What-to-do-while-
you-wait-for-an-ambulance#sthash.uxGFRgKd.dpuf. Updated 2016. Accessed July 27, 2016.
3. Go, AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, et al; for the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease
and stroke statistics2014 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2013;129(3). doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000441139.02102.80.
4. Liao Y, Greenlund KJ, Croft JB, Keenan NL, Giles WH. Factors explaining excess stroke prevalence in the US stroke belt. Stroke. 2009;40:3336-3341.
doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.561688.
You might also like
- Chapter 36 - Inflammatory & Structural Heart DisordersDocument6 pagesChapter 36 - Inflammatory & Structural Heart Disordersjosie teehNo ratings yet
- Guide to Physical Assessment DocumentationDocument3 pagesGuide to Physical Assessment Documentationsandaman2225No ratings yet
- 1538 Exam 4 Cell Reg & GriefDocument35 pages1538 Exam 4 Cell Reg & GriefJade EdanoNo ratings yet
- Nervous System AlterationsDocument45 pagesNervous System AlterationsMajesty ParkerNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing Practice Exam X 50 ItemsDocument15 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Practice Exam X 50 ItemsclobregasNo ratings yet
- Clinical Medication WorksheetDocument1 pageClinical Medication WorksheetSrkocher100% (1)
- Bsn-Rs-Careplan 2Document9 pagesBsn-Rs-Careplan 2api-520841770No ratings yet
- Main drug therapy for ulcerative colitis is sulfa for one yearDocument4 pagesMain drug therapy for ulcerative colitis is sulfa for one yearcathyNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Et Al 11-04-15Document7 pagesConcept Map Et Al 11-04-15api-353656227No ratings yet
- Neuro Notes #3Document11 pagesNeuro Notes #3Monica JubaneNo ratings yet
- SURG - Hepatobiliary, Pancreas, SpleenDocument230 pagesSURG - Hepatobiliary, Pancreas, SpleenJoan Timbol100% (1)
- Ineffective Coping - Nursing Diagnosis & Care Plan - NurseslabsDocument13 pagesIneffective Coping - Nursing Diagnosis & Care Plan - NurseslabsLester MooreNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Assessment and Hypertension GuideDocument27 pagesCardiovascular Assessment and Hypertension GuideJasmine LiraNo ratings yet
- Completed Concept MapDocument4 pagesCompleted Concept Mapapi-607361848No ratings yet
- Presented By: Anjani.S.Kamal 1 Year MSC (N)Document23 pagesPresented By: Anjani.S.Kamal 1 Year MSC (N)shubham vermaNo ratings yet
- Head, Mouth, Nose, Throat, Neck and Regional Lymph Nodes: Kristin Clephane, MSN, RN, CPNDocument44 pagesHead, Mouth, Nose, Throat, Neck and Regional Lymph Nodes: Kristin Clephane, MSN, RN, CPNMike100% (1)
- Behavioral Health Care PlanDocument12 pagesBehavioral Health Care Planapi-520841770100% (1)
- Physical Assessment Write-UpDocument10 pagesPhysical Assessment Write-UpkathypinzonNo ratings yet
- Comfort, rest, and sleep through pain managementDocument17 pagesComfort, rest, and sleep through pain managementDyna TumbokonNo ratings yet
- Medical-Surgical Nursing Review: 315 Key ConceptsDocument15 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing Review: 315 Key ConceptsJap Avila BernasNo ratings yet
- Medication - ALT-Template - Enoxaparin SodiumDocument1 pageMedication - ALT-Template - Enoxaparin SodiumNancyAmissahNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Clients With Cardiovascular DisorderDocument16 pagesNursing Care of Clients With Cardiovascular DisorderLuna MarieNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure PDFDocument9 pagesCongestive Heart Failure PDFSheryl Ann Mae BombalesNo ratings yet
- Psoriatic ArthritisDocument12 pagesPsoriatic ArthritisSelvia RosadiNo ratings yet
- Muscular System DisordersDocument36 pagesMuscular System DisordersShawn Henry CepedaNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Nervous System2Document20 pagesDisorders of The Nervous System2Ian Rizavi Villamor AntopinaNo ratings yet
- Concept Map COPDDocument2 pagesConcept Map COPDnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Nursing Assessment For Care Plan: AllergiesDocument14 pagesComprehensive Nursing Assessment For Care Plan: AllergiesBrittany ShrewsburyNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument5 pagesConcept Mapapi-546509005No ratings yet
- Exam ReviewDocument4 pagesExam ReviewMya Thomas100% (1)
- Nursing Care of PlanDocument16 pagesNursing Care of PlanDbyNo ratings yet
- vSim CLINICAL REPLACEMENT PACKETDocument14 pagesvSim CLINICAL REPLACEMENT PACKETBhargav DaveNo ratings yet
- Shock and SIRSDocument85 pagesShock and SIRSBryan Mae H. DegorioNo ratings yet
- DRUGS AND DEFIBRILLATION IN CARDIAC ARRESTDocument20 pagesDRUGS AND DEFIBRILLATION IN CARDIAC ARRESTAfrida Sahestina100% (1)
- ATI Medication Template RanitidineDocument1 pageATI Medication Template RanitidineSharee HaywoodNo ratings yet
- Spices ToolDocument2 pagesSpices ToolTrisha Fae Loyola BalagotNo ratings yet
- ETOH Case StudyDocument5 pagesETOH Case StudyCharme Jean RaygonNo ratings yet
- Bowel Elimination: SEO-Optimized Title for Foundations I N 3305 DocumentDocument23 pagesBowel Elimination: SEO-Optimized Title for Foundations I N 3305 DocumentEli Falcon100% (1)
- Concept Map CholesectomyDocument3 pagesConcept Map CholesectomyDoreen Claire100% (1)
- Part I: Emergency Department (ED) : SKINNY ReasoningDocument6 pagesPart I: Emergency Department (ED) : SKINNY ReasoningUzumaki KNo ratings yet
- Shock Types 141009102815 Conversion Gate01Document41 pagesShock Types 141009102815 Conversion Gate01Samjaisheel SamsonNo ratings yet
- Medication List and InformationDocument9 pagesMedication List and InformationHealthAndFitnessGuyNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal disorders in childrenDocument73 pagesMusculoskeletal disorders in childrenMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11: Parenteral Administration: Intradermal, Subcutaneous, and Intramuscular Routes Test BankDocument7 pagesChapter 11: Parenteral Administration: Intradermal, Subcutaneous, and Intramuscular Routes Test BankLuna TunaNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes Lab ValuesDocument3 pagesElectrolytes Lab Valuessublee75100% (1)
- HemiplegiaDocument17 pagesHemiplegiaStefany CelineNo ratings yet
- Novolin RDocument2 pagesNovolin RAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Medsurg 2007Document15 pagesMedsurg 2007WisdomIsMisery100% (1)
- Spinal Cord Injuries-KyienDocument25 pagesSpinal Cord Injuries-KyienjohnnyienNo ratings yet
- Patient SafetyDocument102 pagesPatient SafetyAlain CheryNo ratings yet
- Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI) Signs, Diagnosis, TreatmentDocument10 pagesAcute Myocardial Infarction (AMI) Signs, Diagnosis, TreatmentBianca Watanabe - RatillaNo ratings yet
- RN review nuggets: Essential fundamentals of nursingDocument32 pagesRN review nuggets: Essential fundamentals of nursingr.a.g.No ratings yet
- SimulationDocument5 pagesSimulationJessFriend100% (1)
- Safe and Effective Care EnvironmentDocument8 pagesSafe and Effective Care Environmentgretch_carreonNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Nursing BulletsDocument7 pagesPsychiatric Nursing BulletsLouie John AbilaNo ratings yet
- Peds Charts Book NotesDocument37 pagesPeds Charts Book NotesVin Lorenzo CampbellNo ratings yet
- Academichistory 1Document3 pagesAcademichistory 1api-362395776No ratings yet
- Gmail - The Academy of Neurologic PT Newsletter 4Document13 pagesGmail - The Academy of Neurologic PT Newsletter 4api-362395776No ratings yet
- Blankenhagen ResumeDocument1 pageBlankenhagen Resumeapi-362395776No ratings yet
- Gmail - Thank You For Renewing Your Apta MembershipDocument2 pagesGmail - Thank You For Renewing Your Apta Membershipapi-362395776No ratings yet
- 5 e 5 BDDFD 2 C 46 e 7847 DC 9Document4 pages5 e 5 BDDFD 2 C 46 e 7847 DC 9api-362395776No ratings yet
- GoalsDocument1 pageGoalsapi-362395776No ratings yet
- Gmail - Orthopaedic Section News For April 2018Document2 pagesGmail - Orthopaedic Section News For April 2018api-362395776No ratings yet
- Finalized Balance HepDocument1 pageFinalized Balance Hepapi-362395776No ratings yet
- Transcript EditedDocument2 pagesTranscript Editedapi-362395776No ratings yet
- Grace Blankenhagen, SPT: Medical Grand Rounds LectureDocument1 pageGrace Blankenhagen, SPT: Medical Grand Rounds Lectureapi-362395776No ratings yet
- Spasticity After Stroke 1Document1 pageSpasticity After Stroke 1api-362395776100% (1)
- Pd-Ms In-ServiceDocument16 pagesPd-Ms In-Serviceapi-362395776No ratings yet
- Grace Blankenhagen, SPT: Medical Grand Rounds LectureDocument1 pageGrace Blankenhagen, SPT: Medical Grand Rounds Lectureapi-362395776No ratings yet
- Grace Blankenhagen, SPT: Infectious Disease UpdateDocument1 pageGrace Blankenhagen, SPT: Infectious Disease Updateapi-362395776No ratings yet
- Grace Blankenhgen, SPTDocument1 pageGrace Blankenhgen, SPTapi-362395776No ratings yet
- Blankenhagen Lit ReviewDocument4 pagesBlankenhagen Lit Reviewapi-362395776No ratings yet
- Hints Exam PresentationDocument12 pagesHints Exam Presentationapi-362395776No ratings yet
- DC Note Blankenhagen Bruns Schirer SHDocument6 pagesDC Note Blankenhagen Bruns Schirer SHapi-362395776No ratings yet
- Blankenhagen Lit Review-1Document5 pagesBlankenhagen Lit Review-1api-362395776No ratings yet
- GoalsDocument1 pageGoalsapi-362395776No ratings yet
- Blankenhagen Unofficial TranscriptsDocument2 pagesBlankenhagen Unofficial Transcriptsapi-362395776No ratings yet
- Comparison of 2 Manual Therapy and Exercise Protocols For Cervical RadiculopathyDocument2 pagesComparison of 2 Manual Therapy and Exercise Protocols For Cervical Radiculopathyapi-362395776No ratings yet
- Volunteer Sheet Spring 17Document2 pagesVolunteer Sheet Spring 17api-362395776No ratings yet
- Cva Case ArticlesDocument55 pagesCva Case Articlesapi-362395776No ratings yet
- PTH 765 - Healthcare Reform PresentationDocument34 pagesPTH 765 - Healthcare Reform Presentationapi-362395776No ratings yet
- Therapy Dogs InserviceDocument21 pagesTherapy Dogs Inserviceapi-362395776No ratings yet
- Volunteer Sheet Fall 16Document1 pageVolunteer Sheet Fall 16api-362395776No ratings yet
- SWD Lit ReviewDocument6 pagesSWD Lit Reviewapi-362395776No ratings yet
- Blankenhagen Portfolio Self AssessmentDocument3 pagesBlankenhagen Portfolio Self Assessmentapi-362395776No ratings yet
- Shakuntala and Other Works, by KåalidåasaDocument255 pagesShakuntala and Other Works, by KåalidåasaMohamed Sayed AbdelrehimNo ratings yet
- Material For Werable AntennaDocument4 pagesMaterial For Werable AntennaMujeeb AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Galway Music Officer RoleDocument20 pagesGalway Music Officer RoleJohanna KennyNo ratings yet
- INDIAMART 25012022003631 Investor Presentation Q3FY2021-22Document84 pagesINDIAMART 25012022003631 Investor Presentation Q3FY2021-22geethvazNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchangers: Thermal Activity and Fluid MotionDocument14 pagesHeat Exchangers: Thermal Activity and Fluid Motionishu vohraNo ratings yet
- Corporate Social Responsibility International PerspectivesDocument14 pagesCorporate Social Responsibility International PerspectivesR16094101李宜樺No ratings yet
- Principles of The Doctrine of ChristDocument17 pagesPrinciples of The Doctrine of ChristNovus Blackstar100% (2)
- Alchemical Psychology Uniform Edition o - HillmanDocument207 pagesAlchemical Psychology Uniform Edition o - HillmanElsy Arana95% (22)
- Forest Ecosystems and EnvironmentsDocument152 pagesForest Ecosystems and EnvironmentsSufyan MaharNo ratings yet
- WHIRLPOOL AWE 2214 User ManualDocument19 pagesWHIRLPOOL AWE 2214 User ManualSilvestru NemorovNo ratings yet
- Educational PlanningDocument20 pagesEducational PlanningedelynNo ratings yet
- Glycerol Mono StreateDocument6 pagesGlycerol Mono StreateJaleel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 2012 Singing 20190122Document91 pagesSyllabus 2012 Singing 20190122suzypienaarNo ratings yet
- How to Form Good Habits and Break Bad OnesDocument9 pagesHow to Form Good Habits and Break Bad OnesJason DavidNo ratings yet
- Business Analytics ModuleDocument22 pagesBusiness Analytics ModuleMarjon DimafilisNo ratings yet
- Climate Change ReactionDocument2 pagesClimate Change ReactionAngelika CotejoNo ratings yet
- SYKES Home Equipment Agreement UpdatedDocument3 pagesSYKES Home Equipment Agreement UpdatedFritz PrejeanNo ratings yet
- ICT Backup Procedure PolicyDocument8 pagesICT Backup Procedure PolicySultan BatoorNo ratings yet
- ADJECTIVES ENDING IN Ing and EdDocument1 pageADJECTIVES ENDING IN Ing and EdRafael FloresNo ratings yet
- EC604(A) Microcontrollers and Embedded Systems Unit 2 SummaryDocument38 pagesEC604(A) Microcontrollers and Embedded Systems Unit 2 SummaryAbhay AmbuleNo ratings yet
- Checking battery control unitDocument3 pagesChecking battery control unitjuanNo ratings yet
- MirazDocument1 pageMirazTatat PatrianiNo ratings yet
- Essay #01 (First Draft)Document2 pagesEssay #01 (First Draft)thanhtam3819No ratings yet
- Bangladesh Red Crescent Society First Aid Kit SpecificationDocument1 pageBangladesh Red Crescent Society First Aid Kit SpecificationWORLDWIDE TRANSLATIONNo ratings yet
- OE & HS Subjects 2018-19Document94 pagesOE & HS Subjects 2018-19bharath hsNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Moments and Shear: Input DataDocument3 pagesCalculation of Moments and Shear: Input DataARSENo ratings yet
- Microsoft PowerPoint Presentation IFRSDocument27 pagesMicrosoft PowerPoint Presentation IFRSSwati SharmaNo ratings yet
- LNG Bunker QraDocument58 pagesLNG Bunker QraEngineer165298No ratings yet
- English NotesDocument39 pagesEnglish NotesNorAini MohamadNo ratings yet
- ST Biology Nervous System IEP TestDocument3 pagesST Biology Nervous System IEP TestDanielle WilsonNo ratings yet