Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DHH Assessment
Uploaded by
api-361724066Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DHH Assessment
Uploaded by
api-361724066Copyright:
Available Formats
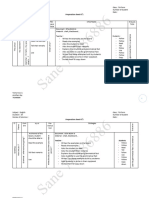
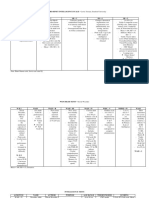
Challenge when groups
Norm- Group administration EXAMPLES
are heterogeneous in Least effective for reading Poor test taking skills
Referenced results in incorrect - SAT-HI
language, exceptionality instruction influence performance
Tests information - TERA-D/HH
and/or culture
READING EXAMPLES
- Cloze Procedure
Interpretation of test ALTERATION - Early Reading Checklist
Most not designed for
Criterion results must be done EXAMPLES - Reading Checklist
students who are deaf or
Referenced carefully and include an - Sign language READING AND WRITING EXAMPLES
hard of hearing
Tests explanation of alterations communication - Stages of Literacy Development Checklist
- Rewording questions WRITING EXAMPLES
Literacy - Cleary Language Assessment
Students Who are Deaf - Kendall Demonstration Elementary School
or Hard of Hearing
Types of Assessment
EXAMPLES
Accuracy and
- The Idaho Special Education Manual
Curriculum- completeness dependent
Assessment may not be - Hand in Hand With Special Education: A
Based upon the skills of the
"standard" Guide for Parents
Assessment person administering the
assessment - Regulations for the Education of
Exceptional Students
EXAMPLES
- anecdotal records
- work samples
Multiple approaches for
- interviews
Performance- providing a more Supports analysis of
- surveys
Based Authentic instruction comprehensive and literacy within the context
- checklist
Measures accurate picture of student of functional information
- retelling
performance
- miscue analysis
- portfolios
- rubrics
References/Resources
Easterbrooks, S. R., & Huston, S. G. (2001). Examining reading comprehension and
fluency in students who are deaf or hard of hearing. U.S.; Georgia. ERIC
Document Reproduction Service No. ED454654
French. M. (1999). Starting with assessment: A developmental approach to deaf children's
literacy. Washington DC: Laurent Clerc National Deaf Education Center.
LaSasso, C. (1999). Test-taking skills: A missing component of deaf students' curriculum.
American Annals of the Deaf, 125, 559-563
Salvia, J., & Ysseldyke, J. E. (2004). Assessment (9th ed.). Boston: Houghton Mifflin.
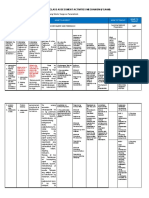
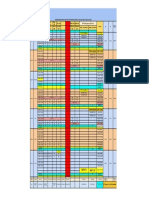
Literacy Assessment - Students who are Deaf and Hard of Hearing
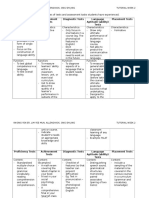
Assessment Assessment Type Assessment Areas/Notes
Stanford Achievement Norm-Referenced Measures curriculum commonly taught in grades 1 9.
Test Deaf/Hard of Group Administered Norms started as far back as 1963 and reestablished in 1996 for Deaf and hard of
Hearing (SAT-DHH) Individual Administered hearing students.
Test of Early Reading Norm-Referenced Tests meaning construction, alphabet knowledge and function, and conventions
Ability Deaf and Individual Administered of print. Designed for students age 3.0 13.11 with moderate to profound
Hard of Hearing hearing loss. Norms established in 1985.
Version (TERA-D/HH)
Test of Written Norm-Referenced Measures conceptual, linguistic, and cognitive aspects of writing in spontaneous
Language-3 (TOWL - and contrived formats. Should be used with caution when interpreting the scores
3) of DHH students.
Cloze Procedure Criterion-Referenced Reading assessment not designed for students who are D/HH. Deletion of every
fifth word within a passage. Degree of hearing loss and age of onset are two
factors shown to affect test performance. Use caution with effectiveness and
reliability.
Early Reading Criterion-Referenced Reading assessment designed for students who are D/HH looking at conventions
Checklist and Reading of print, alphabet knowledge, visual or listening comprehension, sight word
Checklist vocabulary, use of cue systems, story retelling, reading comprehension
strategies, and word analysis strategies. Completed checklist allows teachers to
see student strengths and needs at a glace, thus helping to guide instruction.
Cleary Language Criterion-Referenced Measures written and signed communication in six areas of writing using four
Assessment levels (emerging, beginning, developing and maturing). Measures students
ability to (a) develop a topic in an interesting and imaginative way, (b) produce a
product that is organized in a logical manner, (c) support ideas using relevant
information, (d) produce grammatically correct sentences, (e) use voice that is
specific and vivid in language, and (f) have few to no mechanical errors.
Kendall Demonstration Criterion-Referenced Measures meaning, linguistic features, and conventions of writing and story
Elementary School using four levels. Scale breaks down the development of writing into
manageable and teachable stages. It should not be used as catch-all as it
doesnt assess other areas of writing (e.g., voice aspects of narrative writing,
expository writing, or development of paragraphs).
Stages of Literacy Criterion-Referenced Measures reading and writing communicative competence, motivation, strategies
Development Checklist of text knowledge, reading comprehension, application of background
knowledge, reading and writing as social interactions, and concepts/forms of
print.
Idaho Special Curriculum-Based Published curriculum designed for students who are deaf and hard of hearing.
Education Manual
Hand in Hand with Curriculum-Based Published curriculum designed for students who are deaf and hard of hearing.
Special Education: A
Guide for Parents
Regulations for the Curriculum-Based Published curriculum designed for students who are deaf and hard of hearing.
Education of
Exceptional Students
Alternative Assessment Performance-Based Examples encourage students who are deaf and hard of hearing to communicate
their understanding of
- narrative text using drama
- expository text using semantic mapping
- story grammar using drawings, dialogue journals, charts, and free writing
Reading Fluency Performance-Based Screening tool supporting the use of signed communication within literacy.
Screening for Signing Assesses visual components of reading specific to text and evaluates students
Students use of semantic, morphologic, and cheremic (phonics of sign) skills related to
the text. Sign language skills analyzed include fingerspelling, signing speed,
signing space, use of eye contact and eye gaze, facial expression, and body
movement.
Teaching Test- Taking Performance-Based Assesses how students approach multiple-choice and free-response (e.g., essay)
Strategies tests, in addition to look back conditions to improve their test taking strategies.
You might also like
- Preschool ABC’s, Grade Preschool: Assessment, Behavior & Classroom ManagementFrom EverandPreschool ABC’s, Grade Preschool: Assessment, Behavior & Classroom ManagementNo ratings yet
- Melc-Based Enhanced Budget of Lessons: KindergartenDocument19 pagesMelc-Based Enhanced Budget of Lessons: KindergartenELENOR RIPALDANo ratings yet
- Aip 2013Document20 pagesAip 2013Dahlia VillarNo ratings yet
- ACE LanguageConventions Yr5Document83 pagesACE LanguageConventions Yr5Bernard Chan100% (1)
- 2023-2024 Yearly Plan - GET INVOLVED A2Document7 pages2023-2024 Yearly Plan - GET INVOLVED A2emrah gencerNo ratings yet
- Melc-Based Enhanced Budget of Lessons: KindergartenDocument19 pagesMelc-Based Enhanced Budget of Lessons: KindergartenLeahNNa vetorico100% (5)
- Assessment: Dual Language Education. Clevedon, UK: MultiDocument16 pagesAssessment: Dual Language Education. Clevedon, UK: Multinickelt23No ratings yet
- Lesson Language Language Strategies College & Career ReadinessDocument4 pagesLesson Language Language Strategies College & Career ReadinessThanh ThuyNo ratings yet
- Commission On Diocesan Schools of La Union Curriculum Map in Science 5 SCHOOL YEAR: 2020-2021Document6 pagesCommission On Diocesan Schools of La Union Curriculum Map in Science 5 SCHOOL YEAR: 2020-2021Racquel SupsupNo ratings yet
- Informal & Formal Assesment Formative & Summative Assesment Norm-Referenced & Criterion-Referenced TextsDocument1 pageInformal & Formal Assesment Formative & Summative Assesment Norm-Referenced & Criterion-Referenced TextsMIGUEL ALEJANDRO SALMON FRANCONo ratings yet
- Aims New Language Technique S Resources Evaluati On Teacher's Comments Vocabulary StructureDocument5 pagesAims New Language Technique S Resources Evaluati On Teacher's Comments Vocabulary Structureahmad adnanNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Test ScoreDocument7 pagesInterpreting Test ScoreupaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Language Language Strategies College & Career ReadinessDocument4 pagesLesson Language Language Strategies College & Career ReadinessThanh ThuyNo ratings yet
- 2 7 Artifact Datainventory JvaughnDocument8 pages2 7 Artifact Datainventory Jvaughnapi-324234986No ratings yet
- Assessment Accommodations and Modifications EDUU 512Document2 pagesAssessment Accommodations and Modifications EDUU 512Mayra Ochoa PazNo ratings yet
- Rayyan - Van Weelden 2001Document6 pagesRayyan - Van Weelden 2001Clara de LannaNo ratings yet
- Copia de Copia de Lesson Plan TemplateDocument2 pagesCopia de Copia de Lesson Plan TemplatejavoNo ratings yet
- Graphic DesignerDocument1 pageGraphic DesignerPavithraPillayRavindharanNo ratings yet
- Annex 8 Root Cause (Autosaved)Document1 pageAnnex 8 Root Cause (Autosaved)Shy Barnedo NanaNo ratings yet
- Learning Episode 13: A. ObserveDocument2 pagesLearning Episode 13: A. ObserveBon Ivan FirmezaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Language Language Strategies College & Career ReadinessDocument4 pagesLesson Language Language Strategies College & Career ReadinessThanh ThuyNo ratings yet
- Lesson Language Language Strategies College & Career ReadinessDocument4 pagesLesson Language Language Strategies College & Career ReadinessThanh ThuyNo ratings yet
- 2023-2024 Yearly Plan-GET INVOLVED B1+Document7 pages2023-2024 Yearly Plan-GET INVOLVED B1+emrah gencerNo ratings yet
- Analysis of LearnersDocument3 pagesAnalysis of LearnersAlangilan HighNo ratings yet
- Division of City Schools Caloocan City Action Plan in Edukasyon Sa Pagpapahalaga (Esp) For Sy 2015-2016Document1 pageDivision of City Schools Caloocan City Action Plan in Edukasyon Sa Pagpapahalaga (Esp) For Sy 2015-2016Christened Arbee Cristobal Pasion100% (1)
- Diagnosis and Leveling Planning Tercero BguDocument1 pageDiagnosis and Leveling Planning Tercero BguyukNo ratings yet
- Tos Sample For FS StudentsDocument31 pagesTos Sample For FS Studentsreyjanfranada932No ratings yet
- High School Data Inventory Rama BalachandranDocument4 pagesHigh School Data Inventory Rama Balachandranapi-405567093No ratings yet
- Grammar 7thDocument17 pagesGrammar 7thkirladjoNo ratings yet
- ACETDocument11 pagesACETCosella Ambil100% (1)
- T2 Types and Purposes of AssessmentDocument4 pagesT2 Types and Purposes of AssessmentAbeeramee SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Leveling Planning Segundo BguDocument1 pageDiagnosis and Leveling Planning Segundo BguyukNo ratings yet
- English PSLE Revision GuideDocument13 pagesEnglish PSLE Revision GuideRalph WNo ratings yet
- Listening E11.1.L1. Students Will Be AbleDocument22 pagesListening E11.1.L1. Students Will Be AbleSsNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan: Consumerism and Financial AwarenessDocument3 pagesDaily Lesson Plan: Consumerism and Financial AwarenessKawaiiee MelNo ratings yet
- CAT2021 Proficiency-Adult 25130Document2 pagesCAT2021 Proficiency-Adult 25130Eraldo CuniNo ratings yet
- Flexible Classroom Assessment Activities Mechanism: Oral Communication in ContextDocument3 pagesFlexible Classroom Assessment Activities Mechanism: Oral Communication in ContextJunjoy CalimzonNo ratings yet
- Examples of Artifacts: AR Teacher Excellence Support SystemDocument4 pagesExamples of Artifacts: AR Teacher Excellence Support SystemRadhika Rathore100% (1)
- CAT2020 Proficiency 23576Document2 pagesCAT2020 Proficiency 23576BânNo ratings yet
- WHLP - Week 3Document4 pagesWHLP - Week 3Emerson CalpitoNo ratings yet
- Pages: 6 Practice Tests For The Cambridge English First (Fce) For SchoolsDocument21 pagesPages: 6 Practice Tests For The Cambridge English First (Fce) For SchoolsPAULA SÁNCHEZ MASCARAQUENo ratings yet
- Autism in A NutshellDocument2 pagesAutism in A Nutshellalabanzasalthea100% (1)
- Catch Up PlanDocument4 pagesCatch Up PlanDarwin Jay GabadanNo ratings yet
- Highest Enabling Strategy To Use in Developing The Highest Thinking Skill To Assess Enabling General Strategy Flexible Learning Strategies (FLS)Document10 pagesHighest Enabling Strategy To Use in Developing The Highest Thinking Skill To Assess Enabling General Strategy Flexible Learning Strategies (FLS)Mikkaella RimandoNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Rpms-Based Teachers' Evaluation Rubrics (Special Teachers)Document8 pagesDepartment of Education: Rpms-Based Teachers' Evaluation Rubrics (Special Teachers)Jennefer Gudao AranillaNo ratings yet
- ABES Instructional Support PlanDocument3 pagesABES Instructional Support PlanMYRA ASEGURADONo ratings yet
- Gpoa - SPGDocument3 pagesGpoa - SPGReymart Villapeña100% (4)
- Sek. Men. Keb. Bugaya, Semporna English Language Lesson Plan Form 1Document1 pageSek. Men. Keb. Bugaya, Semporna English Language Lesson Plan Form 1sal811110No ratings yet
- Annotated IepformDocument10 pagesAnnotated Iepformapi-585639434No ratings yet
- FCAAMFINALDocument4 pagesFCAAMFINALGladys LiggayuNo ratings yet
- Norm and Criterion Referenced AssessmentDocument8 pagesNorm and Criterion Referenced AssessmentGenerose Querin AnchoNo ratings yet
- BRRRRRRDocument23 pagesBRRRRRRZaira Mae BantilanNo ratings yet
- SMEA Form 1Document3 pagesSMEA Form 1Johnny Reglos94% (16)
- Silabus KTSPDocument6 pagesSilabus KTSPAmy SarwindaNo ratings yet
- FIDP Personal DevelopmentDocument11 pagesFIDP Personal DevelopmentFAITH JOANGELICA EVANGELISTANo ratings yet
- Technical Assistance Problems Challenges Opportunities Epss: Schools Division of BulacanDocument18 pagesTechnical Assistance Problems Challenges Opportunities Epss: Schools Division of BulacanclynereadsNo ratings yet
- Literacy Assessment ProtocolDocument1 pageLiteracy Assessment Protocoltonia.johnsonNo ratings yet
- Week DAY Date Class Time Subject Topic Learning Outcomes Attendance Learning ObjectiveDocument4 pagesWeek DAY Date Class Time Subject Topic Learning Outcomes Attendance Learning ObjectiveMichelle DuncanNo ratings yet
- Q1 HS 2023 24 LEAST LEARNED SKILLS First QuarterDocument13 pagesQ1 HS 2023 24 LEAST LEARNED SKILLS First QuarterCorazon R. LabasanoNo ratings yet
- Transition From Asl To English WritingDocument8 pagesTransition From Asl To English Writingapi-361724066No ratings yet
- Spelling Without PhonologyDocument22 pagesSpelling Without Phonologyapi-361724066No ratings yet
- Out 1Document27 pagesOut 1api-361724066No ratings yet
- Pitcher Et Al-2007-Journal of Adolescent Adult LiteracyDocument19 pagesPitcher Et Al-2007-Journal of Adolescent Adult Literacyapi-361724066No ratings yet
- Project Muse 384753Document10 pagesProject Muse 384753api-361724066No ratings yet
- DHH AssessmenttoolsDocument8 pagesDHH Assessmenttoolsapi-361724066No ratings yet
- Asl and Acad Eng Factors Influencing The Reading of Bilingual Secondary School Deaf and Hoh StudentsDocument13 pagesAsl and Acad Eng Factors Influencing The Reading of Bilingual Secondary School Deaf and Hoh Studentsapi-361724066No ratings yet
- Gill Comprehension MatrixDocument8 pagesGill Comprehension Matrixapi-361724066No ratings yet
- Vocab Use by Low Moderate and High Asl-Proficient Writers Compared To Hearing Esl and Monolingual SpeakersDocument18 pagesVocab Use by Low Moderate and High Asl-Proficient Writers Compared To Hearing Esl and Monolingual Speakersapi-361724066No ratings yet
- Budget of Work 2nd QuarterDocument8 pagesBudget of Work 2nd QuarterChristine diane VasquezNo ratings yet
- Illiteracy Thesis StatementDocument4 pagesIlliteracy Thesis Statementsusantullisnorman100% (2)
- Piet Zwart - Typotekt!Document11 pagesPiet Zwart - Typotekt!Sibusi MatimbaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Clasa A 3-ADocument3 pagesLesson Plan - Clasa A 3-AMihaela Constantina VatavuNo ratings yet
- Pi 10 Exam ReviewerDocument5 pagesPi 10 Exam ReviewerJanna TanNo ratings yet
- 4.HS6251 - Technical English IIDocument159 pages4.HS6251 - Technical English IINeel JhaNo ratings yet
- School ViolenceDocument10 pagesSchool ViolenceCường Nguyễn QuốcNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in First Quarter Math 10Document6 pagesSummative Test in First Quarter Math 10Generoso SiaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Guide For Critical Approaches in Teaching Philippine LiteratureDocument7 pagesTeaching Guide For Critical Approaches in Teaching Philippine LiteratureMaria Zarah MenesesNo ratings yet
- Reading File 8Document2 pagesReading File 8Luciano Augusto Silveira FernandesNo ratings yet
- ISE I Sample Paper 1 (With Notes)Document12 pagesISE I Sample Paper 1 (With Notes)The Guardian100% (2)
- Planning CommentaryDocument9 pagesPlanning Commentaryapi-443510939No ratings yet
- Class 4 National Genius Search Examination: Advanced: Check The Correctness of The Roll No. With The Answer SheetDocument3 pagesClass 4 National Genius Search Examination: Advanced: Check The Correctness of The Roll No. With The Answer SheetPPNo ratings yet
- ProfEd June 16 2023Document83 pagesProfEd June 16 2023Richmond Bautista VillasisNo ratings yet
- DR B C Shah CVDocument2 pagesDR B C Shah CVbimal2011No ratings yet
- Subodh Public School: Learners 4Document9 pagesSubodh Public School: Learners 4Shresth GourNo ratings yet
- English 31Document5 pagesEnglish 31Sybil ZiaNo ratings yet
- Nurs 479 Professional Development PowerpointDocument10 pagesNurs 479 Professional Development Powerpointapi-666410761No ratings yet
- Lac Table of SpecificationsDocument7 pagesLac Table of SpecificationsMarites EstepaNo ratings yet
- TIME Table Medical 2022-23 From 24 Apr To 30 AprDocument1 pageTIME Table Medical 2022-23 From 24 Apr To 30 AprAyush KamraNo ratings yet
- Arnold's Views On Poetry in Study of Poetry: Stress On Action: He Begins His Preface To Poems' 1853, by Saying That HeDocument2 pagesArnold's Views On Poetry in Study of Poetry: Stress On Action: He Begins His Preface To Poems' 1853, by Saying That HeTANBIR RAHAMANNo ratings yet
- Science Week 678Document2 pagesScience Week 678Creative ImpressionsNo ratings yet
- Mariasole Bianco CV 0914 WebsiteDocument3 pagesMariasole Bianco CV 0914 Websiteapi-246873479No ratings yet
- Language AquisitionDocument7 pagesLanguage AquisitionJheris MartinNo ratings yet
- To Be or Not To BeDocument10 pagesTo Be or Not To BeJethro EncarnadoNo ratings yet
- Practice 2: Vocabulary I. Complete The Sentences With The Correct Form of The Words in CapitalsDocument4 pagesPractice 2: Vocabulary I. Complete The Sentences With The Correct Form of The Words in CapitalsLighthouseNo ratings yet
- IB Econ IA GuidanceDocument11 pagesIB Econ IA GuidanceKavin RukNo ratings yet
- Amit CVDocument3 pagesAmit CVchandramallikachakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Hairdressing and Beauty Therapy - Course ProspectusDocument24 pagesHairdressing and Beauty Therapy - Course ProspectusNHCollege0% (1)
- Behaviour ManADocument179 pagesBehaviour ManAlyndon_baker_1No ratings yet