Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A325n X SC
Uploaded by
Anonymous ARMtmNKLOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A325n X SC
Uploaded by
Anonymous ARMtmNKLCopyright:
Available Formats
http://www.portlandbolt.
com/technical/faqs/astm-a325-structural-bolt-connection-types/
My company is looking to purchase A325SC, A325N, and
A325X heavy hex structural bolts. What is the difference
between these three?
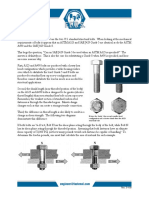
There is no difference between these bolts. The X, SC, and N simply identify the type of
connection the bolts are used in. X and N are bearing type connections, where the bolts are being
used in shear.
X means these particular A325 heavy hex structural bolts will be used in a bearing type connection
where the threads will be excluded from the shear plane, whereas N means the threads are included
in the shear plane. SC signifies a slip critical connection where the bolts are not being used in shear,
but instead the tension from the connection resists the shearing force. You simply require the same
standard A325 heavy hex structural bolt, but will be using them in three different connection types.
SC Slip critical connection.
N Bearing type connection with threads included in the shear plane.
X Bearing-type connection with threads excluded from the shear plane.
SC, N, and X specify solely the type of connections to use the A325 bolt in. There are other
types of A325 bolts that do affect the type of bolt that needs to be purchased. For these, see the
following chart.
TYPE 1 Medium carbon, carbon boron, or medium carbon alloy steel.
TYPE 2 Withdrawn November 1991.
TYPE 3 Weathering steel.
T Fully threaded A325. (Restricted to 4 times the diameter in length)
M Metric A325.
S Modified thread length or head dimensions.
The majority of A325 bolts being made in the market are A325 Type 1 and are available both plain
and hot-dipped galvanized. Type 2 was withdrawn in 1991 and no longer is in use. Type 3 is a
naturally corrosion-resistant weathering steel that typically is used in a plain finish (no finish).
Availability for the steel can be limited and standard, mass-produced bolts start at 5/8 diameter.
Below 5/8 diameter, heat-treatable weathering steel is not commonly available.
A325T bolts (covered under supplementary requirement (S1) of the A325 specification signifies that
the A325 bolt must be completely threaded, but is limited to 4 times the diameter in length. Fully
threaded A325 bolts longer than 4 times the diameter do not comply with the specification, will not be
available in the marketplace, and technically cannot be manufactured. ASTM A449 should be
considered in lieu of A325 bolts with extended threads that dont meet the requirements of A325T.
However, ASTM 3125, the new combined high strength structural bolting specification, added a new
type S that allows for an A325 bolt to have altered thread length and head dimensions. Previously,
altered thread lengths meant switching grades or accepting a bolt that didnt technically conform to
the A325 specification, but now marking the bolt head with an S allows for extended threads or using
different head dimensions.
You might also like
- BS-5950-3 - Composite Beam - Example PDFDocument7 pagesBS-5950-3 - Composite Beam - Example PDFAnonymous ARMtmNKL100% (4)
- John Deere 772d 6wd GraderDocument6 pagesJohn Deere 772d 6wd GraderyaserattiaNo ratings yet
- Aircraft RivetsDocument50 pagesAircraft RivetsPranjal DograNo ratings yet
- Astm Bolt & NutsDocument24 pagesAstm Bolt & NutsDinesh Radhakrishnan100% (3)
- ASTM A325 SpecificationDocument2 pagesASTM A325 SpecificationRay CoelloNo ratings yet
- PEB Specification and Standards With DetailsDocument15 pagesPEB Specification and Standards With DetailsMujjo SahbNo ratings yet
- A325 and A490 BoltsDocument9 pagesA325 and A490 BoltsCHECcorp100% (1)
- Dimensions, Weights and Properties of Special and Standard Structural Steel Shapes Manufactured by Bethlehem Steel CompanyFrom EverandDimensions, Weights and Properties of Special and Standard Structural Steel Shapes Manufactured by Bethlehem Steel CompanyNo ratings yet
- Weld Like a Pro: Beginning to Advanced TechniquesFrom EverandWeld Like a Pro: Beginning to Advanced TechniquesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Off-Road Welding: Advanced Techniques on How to Become a True Off-Road WelderFrom EverandOff-Road Welding: Advanced Techniques on How to Become a True Off-Road WelderRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- TDS Between A325 & GR.5Document1 pageTDS Between A325 & GR.5ASTRID AMNo ratings yet
- Article - Structural BoltsDocument6 pagesArticle - Structural Boltsing_weroNo ratings yet
- ASTM BoltsDocument3 pagesASTM BoltsAnonymous IwqK1NlNo ratings yet
- Aalco Datasheet ST ST Butt Weld FittingsDocument3 pagesAalco Datasheet ST ST Butt Weld FittingsZoran DanilovNo ratings yet
- Headed Anchor Bolts SpecsDocument3 pagesHeaded Anchor Bolts SpecsLaureano BecerraNo ratings yet
- Anchor Rods: ManufacturingDocument22 pagesAnchor Rods: Manufacturingjacopap100% (1)
- Structural Steel Materials GuideDocument3 pagesStructural Steel Materials GuideinsidereaderNo ratings yet
- Find specifications for ASTM A325 and A490 structural boltsDocument6 pagesFind specifications for ASTM A325 and A490 structural boltsalexortiz83No ratings yet
- Are You Properly Specifying Materials - Part 3 PDFDocument3 pagesAre You Properly Specifying Materials - Part 3 PDFasmasm123No ratings yet
- You Cannot Tension All Bolts PDFDocument2 pagesYou Cannot Tension All Bolts PDFAndreas Galih PamungkasNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Installation, Inspection, MaintenanceDocument23 pagesGuidelines For The Installation, Inspection, MaintenanceantiacidoNo ratings yet
- ASTM F436 Beveled Washers SpecificationDocument1 pageASTM F436 Beveled Washers Specificationgechaves1No ratings yet
- Grade 8 vs ASTM A325 Bolts Strength DifferencesDocument9 pagesGrade 8 vs ASTM A325 Bolts Strength Differencessham suzzamanNo ratings yet
- Reinforcing Bar CouplersDocument9 pagesReinforcing Bar CouplersAWAKSEORANGNo ratings yet
- Welding and bolting requirements for structural steelDocument10 pagesWelding and bolting requirements for structural steelIndra SidikNo ratings yet
- BURNDY Conectores MecanicosDocument58 pagesBURNDY Conectores MecanicosRafael RuizNo ratings yet
- FastenersDocument46 pagesFastenerser_lalitgargNo ratings yet
- Maryland Metrics - Metric ASTM Structural FastenersDocument5 pagesMaryland Metrics - Metric ASTM Structural Fastenerslimulsa78No ratings yet
- Latest structural steel materials updateDocument3 pagesLatest structural steel materials updatejworder100% (1)
- Lecture-4-Bolted ConnectionsDocument139 pagesLecture-4-Bolted ConnectionsMuhammad Jawad Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- ASTM A153 Guide for Galvanized Hardware & FastenersDocument5 pagesASTM A153 Guide for Galvanized Hardware & FastenersMekhmanNo ratings yet
- Astm A992Document2 pagesAstm A992Harley Ilave IlaveNo ratings yet
- Arcfix Arc StudDocument21 pagesArcfix Arc StudKiran Kumar KondapalliNo ratings yet
- Aluminum Design Manual Frequently Asked Questions: Structures Section 4.7.7, What Inside Radius RDocument3 pagesAluminum Design Manual Frequently Asked Questions: Structures Section 4.7.7, What Inside Radius RMeet SatheyNo ratings yet
- IFC Series Y125 and Y150 Fabricated Y-Strainers: Design FeaturesDocument2 pagesIFC Series Y125 and Y150 Fabricated Y-Strainers: Design FeaturesPrasanta Kumar Behera100% (1)
- Nut Compatibility Chart for Bolting MaterialsDocument11 pagesNut Compatibility Chart for Bolting MaterialsBHARATHNo ratings yet
- IS 1862 - Designation For StudsDocument1 pageIS 1862 - Designation For StudsKaushik ShahNo ratings yet
- Joint Design 2 (2001) - Nails, Staples & ScrewsDocument16 pagesJoint Design 2 (2001) - Nails, Staples & Screwssteveh49100% (1)
- P 1554452Document4 pagesP 1554452GusmoNo ratings yet
- A FEDS Structural BoltsDocument6 pagesA FEDS Structural BoltsCrimsonPoshNo ratings yet
- Exothermic Welding Systems: The Furseweld ConnectionDocument5 pagesExothermic Welding Systems: The Furseweld ConnectionMohd RashidNo ratings yet
- Technical DataDocument17 pagesTechnical Datat_syamprasadNo ratings yet
- Ring Joint HandbookDocument7 pagesRing Joint HandbookchiliskyNo ratings yet
- Flux Cored Wires (Elga) PDFDocument15 pagesFlux Cored Wires (Elga) PDFVladan TimotijevicNo ratings yet
- Steel SpecificationsDocument6 pagesSteel SpecificationsinsidereaderNo ratings yet
- Anclajes en MamposteriaDocument27 pagesAnclajes en MamposteriaMauricio MuñozNo ratings yet
- HARDWARE AsdfeDocument8 pagesHARDWARE AsdfeJuly TadeNo ratings yet
- CE 671 High Strength BoltsDocument25 pagesCE 671 High Strength BoltsbwahahahaNo ratings yet
- Technical Update Maintenance Welding of AluminumDocument22 pagesTechnical Update Maintenance Welding of Aluminumaxisd47No ratings yet
- Storz fittings FAQDocument2 pagesStorz fittings FAQsechooNo ratings yet
- Bolt Grip Length PDFDocument1 pageBolt Grip Length PDFmatthewwalls4386100% (2)
- Bolts: Types, Parts, Grades & UsesDocument27 pagesBolts: Types, Parts, Grades & UsesReshma MKNo ratings yet
- WWW Siddhgiritubes Com Blog Difference Between High TensileDocument4 pagesWWW Siddhgiritubes Com Blog Difference Between High TensilewonosarijayasurabayaNo ratings yet
- Tube clamps catalogue guideDocument42 pagesTube clamps catalogue guideharlyganNo ratings yet
- ACA Clamps&ConnectorsDocument4 pagesACA Clamps&ConnectorsvenkyeeeNo ratings yet
- Misc FastenersDocument30 pagesMisc FastenersFrancisco Abrigo MezaNo ratings yet
- SSINA - Designer's Handbook - Stainless Steel FastenersDocument23 pagesSSINA - Designer's Handbook - Stainless Steel FastenersSerguei DobrinNo ratings yet
- Classic Handplanes and Joinery: Essential Tips and Techniques for WoodworkersFrom EverandClassic Handplanes and Joinery: Essential Tips and Techniques for WoodworkersRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Column Splices - Code of Practice - IHBDocument13 pagesColumn Splices - Code of Practice - IHBAnonymous ARMtmNKLNo ratings yet
- 3.6 - Errors and Uncertainty, Verification and ValidationDocument26 pages3.6 - Errors and Uncertainty, Verification and ValidationAnonymous ARMtmNKLNo ratings yet
- Dlubal - Wind LoadDocument6 pagesDlubal - Wind LoadAnonymous ARMtmNKLNo ratings yet
- Strut-And-Tie Model Design Provisions: Robin G. Tuchscherer, David B. Birrcher, and Oguzhan BayrakDocument16 pagesStrut-And-Tie Model Design Provisions: Robin G. Tuchscherer, David B. Birrcher, and Oguzhan BayrakDavid Apaza QuispeNo ratings yet
- 4.9 - Wind Energy in The Built Environment - Part 1Document33 pages4.9 - Wind Energy in The Built Environment - Part 1Anonymous ARMtmNKLNo ratings yet
- Design of Rigid Pile Caps Through An Iterative Strut-And-Tie ModelDocument12 pagesDesign of Rigid Pile Caps Through An Iterative Strut-And-Tie ModeljjohnsoneNo ratings yet
- Wind Flow Around The Free EndsDocument3 pagesWind Flow Around The Free EndsAnonymous ARMtmNKLNo ratings yet
- 3.5 - Near-Wall ModelingDocument24 pages3.5 - Near-Wall ModelingAnonymous ARMtmNKLNo ratings yet
- Case Study For The Amsterdam ArenA StadiumDocument24 pagesCase Study For The Amsterdam ArenA StadiumAnonymous ARMtmNKLNo ratings yet
- Wind Loads On Multiple Cylinders Arranged in Tandem With EffectsDocument203 pagesWind Loads On Multiple Cylinders Arranged in Tandem With EffectsMohammad SheikholeslamiNo ratings yet
- Verification and Implementation of Strut-And-Tie Model inDocument281 pagesVerification and Implementation of Strut-And-Tie Model inrpatel5509No ratings yet
- 2013 WindTunnelGuide Preview PDFDocument14 pages2013 WindTunnelGuide Preview PDFmvicenteloNo ratings yet
- Simply Supported Reinforced Concrete Beam Analysis and Design (ACI 318-14)Document33 pagesSimply Supported Reinforced Concrete Beam Analysis and Design (ACI 318-14)Anonymous ARMtmNKLNo ratings yet
- Strut and Tie CalculationDocument8 pagesStrut and Tie Calculationgmazzucco100% (4)
- Address Downtown - Structural Calculation For Floor Lamp and Wall LightDocument23 pagesAddress Downtown - Structural Calculation For Floor Lamp and Wall LightAnonymous ARMtmNKLNo ratings yet
- Candidate Handbook: Leed Ap With SpecialtyDocument40 pagesCandidate Handbook: Leed Ap With SpecialtyManishRacharlaNo ratings yet
- Steel Grade Equivalents - CarbonDocument2 pagesSteel Grade Equivalents - CarbonAnonymous ARMtmNKLNo ratings yet
- Abutment WallDocument1 pageAbutment WallAnonymous ARMtmNKLNo ratings yet
- State-Of-practice of Seismic Design and Construction in IndonesiaDocument18 pagesState-Of-practice of Seismic Design and Construction in IndonesiaSuneesh PNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Mass Participation FactorDocument7 pagesUnderstanding The Mass Participation FactorDavid RajNo ratings yet
- BS en 10264 1 2002 Steel Wire and Wire ProductsDocument5 pagesBS en 10264 1 2002 Steel Wire and Wire ProductsAnonymous ARMtmNKLNo ratings yet
- Web Geometry - How To AdoptDocument1 pageWeb Geometry - How To AdoptAnonymous ARMtmNKLNo ratings yet
- Aace98-01 HajdinDocument7 pagesAace98-01 HajdinCalvin SzetoNo ratings yet
- Pds Ram Connection LTR en HRDocument2 pagesPds Ram Connection LTR en HRAnonymous ARMtmNKLNo ratings yet
- BS en 10264 1 2002 Steel Wire and Wire Products Steel Wire For Ropes Part 1 General RequirementsDocument14 pagesBS en 10264 1 2002 Steel Wire and Wire Products Steel Wire For Ropes Part 1 General RequirementsMarko ŠimićNo ratings yet
- Friction Between CablesDocument16 pagesFriction Between CablesAnonymous ARMtmNKLNo ratings yet
- Wire Rope - 7x19Document1 pageWire Rope - 7x19Anonymous ARMtmNKLNo ratings yet
- Cable Parameters For Homogenous Cable-Beam ModelsDocument13 pagesCable Parameters For Homogenous Cable-Beam ModelsAnonymous ARMtmNKLNo ratings yet
- Through Deck Stud Welding PDFDocument1 pageThrough Deck Stud Welding PDFAnonymous ARMtmNKLNo ratings yet
- UV-Vis method for quantifying anti-cancer drug CurcuminDocument6 pagesUV-Vis method for quantifying anti-cancer drug Curcuminwhy uNo ratings yet
- Software Test MetricsDocument8 pagesSoftware Test MetricscmarrivadaNo ratings yet
- Sensitivity Analysis: Enter Base, Minimum, and Maximum Values in Input CellsDocument5 pagesSensitivity Analysis: Enter Base, Minimum, and Maximum Values in Input CellsSajid IqbalNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument32 pagesThesis783255No ratings yet
- Nptel: System Analysis and Design - Video CourseDocument2 pagesNptel: System Analysis and Design - Video CourseAnu PriyaNo ratings yet
- StudenttextDocument15 pagesStudenttextapi-195130729No ratings yet
- PDCT - Hydraulic Torque Wrench - Hangzhou Penad Machinery Co.,LtdDocument4 pagesPDCT - Hydraulic Torque Wrench - Hangzhou Penad Machinery Co.,LtdQS BMDSNo ratings yet
- Shape and angle detective game for kidsDocument21 pagesShape and angle detective game for kidsbemusaNo ratings yet
- Charger Energic Plus (Catalog)Document24 pagesCharger Energic Plus (Catalog)sugar44No ratings yet
- Discoverer Installation and Integration With EBSDocument25 pagesDiscoverer Installation and Integration With EBSRajendra PrasadNo ratings yet
- Dispersing AgentsDocument6 pagesDispersing AgentsEdward MenezesNo ratings yet
- Roll Handling Data Form: Company DetailsDocument1 pageRoll Handling Data Form: Company DetailsAlfredo MinchezNo ratings yet
- Queries With TableDocument14 pagesQueries With TableAkhileshNo ratings yet
- OOPS AbapDocument188 pagesOOPS Abapraky036950% (2)
- Add Nordic Semiconductor DFU To SDK Example: Bluetooth Low EnergyDocument32 pagesAdd Nordic Semiconductor DFU To SDK Example: Bluetooth Low EnergyDaniel Ernesto EspitiaNo ratings yet
- Cognac Brandies From A Region of France, Cognac Are Called Cognac. They Are Known To Be The Best Types of Brandies in The WorldDocument3 pagesCognac Brandies From A Region of France, Cognac Are Called Cognac. They Are Known To Be The Best Types of Brandies in The Worldmanuk193No ratings yet
- Bus Network Topology GuideDocument8 pagesBus Network Topology GuideMjjames Manalo100% (1)
- CO2 Dosing and Generation SystemDocument344 pagesCO2 Dosing and Generation SystemABAID ULLAHNo ratings yet
- Aqa MM1B W QP Jun07Document8 pagesAqa MM1B W QP Jun07Annan_Faridi_517No ratings yet
- Microelectronic Circuit Design 5th Edition Jaeger Blalock Solution ManualDocument21 pagesMicroelectronic Circuit Design 5th Edition Jaeger Blalock Solution Manualruth100% (23)
- 4 UIUm 8 JHNDQ 8 Suj H4 NsoDocument8 pages4 UIUm 8 JHNDQ 8 Suj H4 NsoAkash SadoriyaNo ratings yet
- EL Bay-O-Net Current-Limiting Fuse Assembly - CA132039ENDocument4 pagesEL Bay-O-Net Current-Limiting Fuse Assembly - CA132039ENfederico4thNo ratings yet
- Faraday Rotation + Verdet Constant PosterDocument1 pageFaraday Rotation + Verdet Constant PosterAndrew PalmerNo ratings yet
- Basic Chemistry Review (Students)Document16 pagesBasic Chemistry Review (Students)AnilovRozovaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To 5g Ran2.0Document29 pagesIntroduction To 5g Ran2.0Wawan Aji95% (20)
- Dynamic Analysis of Motor Floor: Structure DataDocument6 pagesDynamic Analysis of Motor Floor: Structure Datap_ignatiusNo ratings yet
- Quarter3 Week4 ClimateDocument11 pagesQuarter3 Week4 ClimateJohn EdselNo ratings yet
- Vector Integration - GATE Study Material in PDFDocument10 pagesVector Integration - GATE Study Material in PDFTestbook BlogNo ratings yet